Department of Information Systems, North Cyprus University Northern Cyprus Nicosia, Cyprus
Article Publishing History
Received: 09/04/2019
Accepted After Revision: 15/06/2019
This papers major aim is to determine the exclusivity of the concept “social business” with not just explaining the concept but also comparing it with other concepts seemingly that are similar to it such as social corporate responsibility and conventional profi t- making businesses from information technology perspective. Through this paper we have given an in-depth understanding on how social business adds superior value, addresses social problems, and may motivate the business community to dedicate their talents and energy and invest money in this business.
Social Business, Profit Making Business, Social Responsibility, Corporate Social Responsibility traditional Business, Social
Aqel M. J, Zeebaree M. A comparative Analysis Between Conventional Profit Making Business and Corporate Social Responsibility from Information Technology Perspective. Biosc.Biotech.Res.Comm. 2019;12(2).
Aqel M. J, Zeebaree M. A comparative Analysis Between Conventional Profit Making Business and Corporate Social Responsibility from Information Technology Perspective. Biosc.Biotech.Res.Comm. 2019;12(2). Available from: https://bit.ly/2Zwr2CN
Copyright © Aqel and Zeebaree, This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC-BY) https://creativecommns.org/licenses/by/4.0/, which permits unrestricted use distribution and reproduction in any medium, provide the original author and source are credited.
Introduction
Gas (2012) reported that about 81 billionaires gave to charity close to about 50 percent of their fortune, while about 128 individuals and couple billionaires signed various contracts in their death with donating their large portion of their wealth to a charitable cause. The first phases of the lives of successful business tycoons such as bill gates and Warren buffet where lived in building in a successful business structures while they are now using the second phases to generate more wealth and invest in businesses that will have a huge impact in the lives of the masses. The combination of the these two concepts which are business in generating profit for one’s satisfaction and business for the satisfaction of the masses or community is what is referred to as social business, (Irene 2015, Ghaderi 2019). Social Business can be said to be to inception of a firm whose main goal is centered in creation of benefit for a whole ecosystem which consist of the CEOs, share- holders, customers and employees by making sure that the operations and culture of the business is integrated with collaborating, engaging and information sharing tools .The concept of social business begins with analyzing the concept of deciding if to be major person making most of the profit in the market system or if you will want a business which there are equal or more opportunities to everyone involved including the poor members of the community. It is more like a selfless cause with the creation of social wealth with the aim of making sure not only the firm benefits but also the community. The introduction of Social business concept was brought about in 2007 by professor Dr. Muhammad Yunus in who is a Nobel laureate making it an area of interest for various academicians and authors. Many of companies that are interested in the developing field of social business are focuses on using business methods and practices to achieve progressive social revolution, which lead to Connecting financial to social performance, (Margolis and Walsh 2001 Hausmann 2018).
Just like every other normal business, products, employees, revenue, customers and so on are included in social business operations with the business incurring no loss or dividend but it refunds back the initial investment of the owner. A social business is completely different from a charity work in the sense that there is benefit or profit for everyone. The managers of social business also reasons and acts like the managers of normal profit making business company because it needs to recover back its capital to back the owner and also profit to sustain itself. The return of profits made back into the business makes social business have potential of growing and increasing in worth and value. Social business concept is one that combines the profit making business concept (which major aim is based on making and increasing profit) and also non-profit making organization (whose main aim is focused on charitable works). A social business the arrival of social business is one that is meant to occupy the gap created by rapid declining rate in human development and also lack of government intervention in the provision of social and basic amenities for its people, (Huda 2015).
Research Questions and Methodology
Research Questions
The introduction part of this project has given an elaboration on what social business, corporate social responsibility and also traditional or conventional profit-making business. This project will help in giving elaborate answers to the following questions:
- What is the concept behind social business?
- What are the difference and similarities between social business and CSR?
- What are the difference and similarities between social business and Conventional profit making businesses?
Research Methodology
This research was carried out based on an integrative review methodology where relevant articles based on the research scope with key words such as business, social business, corporate social responsibility and profit making organizations were used.An integrative review methodology is a unique technique that outlines relevant papers both past and present for review in other to give better understanding to the topic of discussion Souza & Silva (2010). With the use of this technique, this project was divided into four (4) stages:
- Problem Identification and Formulation Stage
- Literature Search/Data Collection
- Data Evaluation and Analysis
- Presentation.
Problem Identification and Formulation Stage
There are a lot of similarities on the concept of social businesses and corporate social responsibility and also social businesses with profit making businesses. Despite the fact that all these three topics share common characteristics but there still exist mega differences between them which we will highlight and discourse in more details, (Cornelius et. al 2008).
Literature Review
Social Business
Despite the fact that that social business concept is gradually becoming a trend in the academic line, there are several opinions to what the exact concept of social business is. A lot of authors have brought out their ideas to what social business is. Yunus has made elaborations o the concepts of social business some of which was centered on social business been a social problem solving financially fit organization in which the initial investment can be removed while the remaining profit can be reinvested into the business in other to increase its impact in the society, (Yunus, 2014).
Muhammed Yunus came up with this concept due to the obvious reason of money-centric firms and also charitable acts not been able to solve the increasing issues of poverty in the world. He saw that social business could be a medium in making all parties benefit from business. He was of the view that in solving the problems of humans using a business approach is usually a very effective means. New companies should see the way their business will also be of benefit to others and not just only themselves. The profit realized from social business companies should be returned back into the business inn other to increase the company’s growth and reach thereby helping more. He also made argument-elaborating entrepreneurs should not limit their scope in business to just selfish interest but also to put the benefit of the community in mind, (Muktadir-AlMukit 2016).
It also allows for the foundation of Low-Profit Limited Liability Corporations and outlines its benefits and latent weaknesses to social entrepreneurs. Galpin and Bell (2010). Additionally, we can organize some of social business benefits in brief as enhanced customer satisfaction, improving products and services by applying their input and affects more invested and engaged part of your business. Competitive advantage often comes from
innovate usage which is a practice that is reinforced by the support from institutional environment, (Roy et al 2015).
The present needs of social enterprises are not compatible by the present delivery for such organizations since such endowment miscarries to statement the planned tension that be existent between social and business purpose. Settles with recommendation for instruction to the social enterprise sector and business support providers. By investing in social business, companies have better chance situated to grab the open doors in
present unstable, virtual business environment, (Prusak et al 2001).
Traditional Profit-Making Business
This is an organization whose sole aim for all their operation is for the purpose of making profit. The normal operations in traditional profit-making business is for the purpose of maximizing the wealth of the organization and its owners. Profits that are gained in this type of business are either used to improve the organization and its operations or shared by the owners as dividend. The structure of a traditional profit making organization can be either based on sole proprietorship, partnering, Hindu united partnership or even a joint venture.
The activities that take place in this type of business focuses on minimizing business input and maximizing the business profit which basically means been efficient and effective, (Sigurjonsson et al (2018)
Differences between social businesses traditional profit making business
Yunnus set clear differences between social business and conventional business where he stated that the evaluation between the two should be made by their objectives in which is shown in table 2.1. After Grove and Berg (2014).
As we will discussed next, another worldview for innovation is rising, an association between private endeavor and public interest that generate beneficial and feasible change for the two sides. There are several of companies or corporations moving further than corporate social responsibility to corporate social innovation to accomplish the future.
Corporate Social Responsibility
There is a strong culture of corporate social responsibilities in a lot of organizations especially in the past decade when people began to pick up interest in it because it stood for positive impact in the society. A lot of reasons such as sense of obligation, economic interest and so on have made lots of organizations partake in corporate social responsibilities. CSR can be said to be a hard on contract that involves having social responsibility or
obligation to a community. The rate and extent of the agreement is not certain when dealing with CSR and it has been in use by organizations since in the 1950 in the North. CSR have been seen in the light of various meanings and interpretations based on the ideas of several authors and companies. The several perspectives and notions to what CSR is brings about several issues especially to companies that want to invest in certain communities, (Spieth et al 2018).
An author caller Weber gave an explanation on CSR as a selfless social operation in handling the societal and environmental needs. Elaborating that CSR should be seen as a form of corporate selfless act or activity that goes beyond the law Weber, (2008).
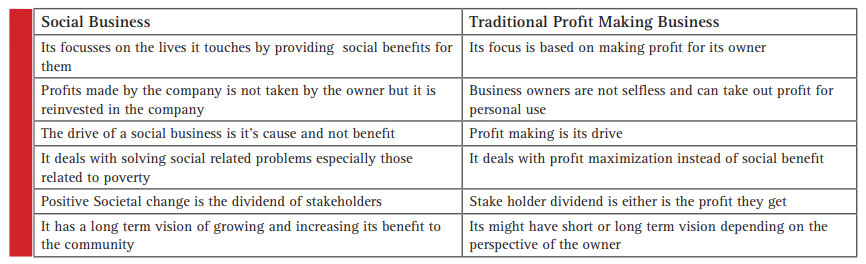 |
Table 1 |
Another author by the name Milton made his own elaboration by stating that when In business, an organizations responsibility to a society is by operating and making profit within the boundaries of the law in the country or state in which they operate in. Social responsibility should be left for people while organizations main concern should revolve around sticking to the rules and making profits, (Baden 2014).
Other ethical authors have disputed the fact that companies have no role to play in social responsibility in the sense that social responsibility is far beyond obedience to law, guidance and contracts. Everyone who is impacted by the activities of an organization (stakeholders) also has should also be seen as part of the organization. As shareholders believe that an organization is meant to go after the irgoals, which is usually maximizing profit in a short and long run, the companies’ activity is what attracts or repels investors and putting the society in mind is a aroma that paints an organization in a good light attracting more investors.
Another researcher by the name Parnell explained that recent view of CSR is intertwined with competitive advantage manages strategy.
Despite the fact that CSR is been seen as a charitable set aside donation or act by a fi rm in other to positively impact or influence the society in which she operates in.
Some of the CSR implemented by firms includes building of affordable schools for children, giving scholarship sopport unities, building hospitals that is affordable for the community and so on Xinhua (2018).
The Multinational enterprises possibly try in being not only part of the problem, but yet additionally maybe part of the solution, is progressively acknowledge and took the forward of the stage in research concentration in corporate social responsibility (CSR) activities and supportable development inferences of IB. kolk et al (2010).
Types of CSR
- There are several types of social responsibilities which are
- Corporate Philanthropy: This is seen as the most compliant form of social responsibility. It deals with giving of charities to the less privilege, helping sponsor events for the betterment of the society, assisting in handling matters bigger than the community etc. Fritscher & Pigneur (2014).
- Active Risk Management: This is a social responsibility that deals with the relationships of an organization. It deals with social activities that is of more benefit to the face of the stakeholders Abdul (2018).
- Social Investment: This deals with an organization making long term investment in the community in which they operate an example is creation of schools
Shared Value Creation: This deals with operations to help the society and also bring more profit to the organization. An example is the development of profitable business opportunity that the society will stand to benefit from, (Ghaderi 2019).
We can take a short window and mention some of CSR benefits.One, it inspires businesses to act morally and to think through the social and environmental effects of their industry. Two, it prop the outcomes value of public. Three, it empowers both expert and self-improvement,
and Four it improves associations with customers.
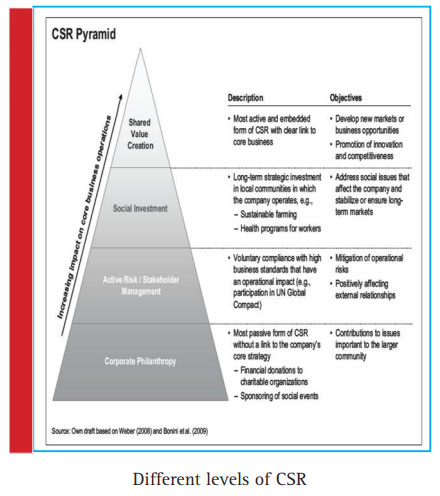 |
Figure 1 |
Corporate Social Responsibility Versus Social business
There is a lot of similarities between Social business and Corporate Social Responsibility. The two of them have the stakeholders in mind and want them to benefit from business and at the same time addressing and handling societal problems. This doesn’t dispute the fact that the both of them are still different in a lot of aspects such as aim, policies relating to profit, issues with compliance etc. table shows lighter on this differences, Renck (2014) Projects that involves sustainable CRS has a financial impact on shareholders of the company. Despie the fact that people value the concept or benefit from CSR, the cost is solely beard by the organization. Sharehold-ers always kick against corporate society responsibility when the see that the profit that will be generated from the investment will be given back to the society Chao et al (2018). In CSR the business handles all the cost in incurring the project in other to solve a problem affecting the society, this makes the business selfless which will give them the satisfaction of having to touch, impact and improve lives. The efforts of CSR are normally aimed at little aspects of the problems in a society , that is CSR basic focus in on the reduction or suppression of the problems that the society is facing whereby social business has an objective of fixing a large portion of the societies issues such as poverty, child abuse etc. The individuals that venture into social businesses are far better than large firms in identifying societal problems and the strategy in solving it. Ferrell (2019).
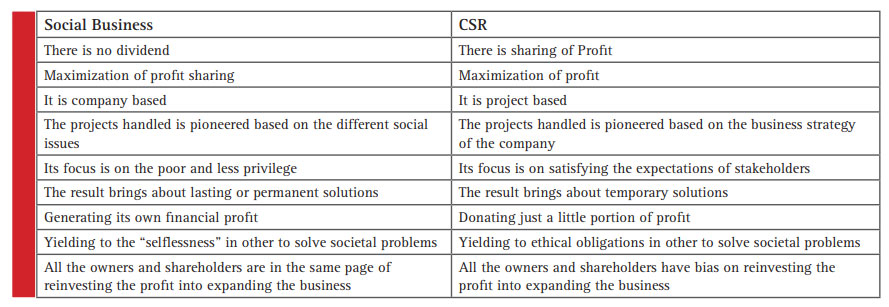 |
Table 2 |
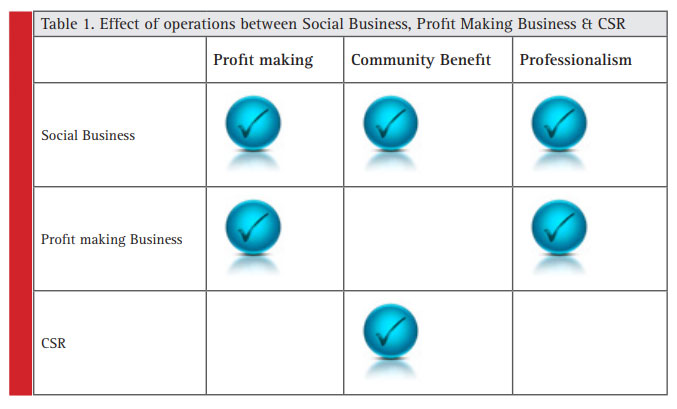 |
Table 1a |
Data Evaluation and Analysis
- From the various data gotten from the various articles it is seen that social businesses have unique features such as:
- In the Social Business social business concept, beneficiaries are not been considered as object, they are just seen as independent business partners. The owner doesn’t also see the business as a charity but he sees it as a normal business that is growing making profit and impacting the society and the poor people are seen as employees, managers and workers that can think, act make decisions and also earn salary making them confident and independent. The poor people can then get independent and get the ability to employ and empower others.
- Charities and donation does not initiate the concept of social business, the initial investment can come inform of charity or donations, but when the investment is made, the entity becomes a business that runs and generates profit which is then recycled to generate more and more profit that will be used to expand the business. The making of profit is similar or the same to that of profit making business where there is production of goods or services and then sold for profit. Muhammad Yunus, made it clear that the startup of a social business can be from charity income at first but the returns can be reinvested for as long as possible. A social business has an obligation to be competitive like any other profit making business in the aspect of their product quality, customer service, product creation etc.
- Social businesses has a fundamental aim of sorting out social problems and solving social needs. Despite the fact that social business is a business in all ramification, it cant put profit making strategy over that of the societal needs. The fact of been of major service to the community as been the vision of a social business its what makes it different from a profit making enterprise. Social business can thrive to make enormous profit, but not at the expense of ignoring the societal needs of the society it was meant to cater for.
- A lot of opportunities are created by Social business in assisting the masses that have not been giving the opportunity to put their diverse talent
and skills into good use due to financial constraints. Social businesses generates a professional platform in which investments can be made in
form of charity or donations to bring a lasting solution to societal problems. These poor masses will have the opportunity to be under successful
entrepreneurs with the opportunity of meeting and learning from their experiences in business. Investors get the opportunity of implanting a structure that will continuously sort out the need of the poor masses without losing money. - I the hierarchy need of Maslow, it was stated that self-actualization is the paramount interest of those that are at the hierarchy top. The urge of
Self-fulfillment is been achieved by those who has already sorted out their materialistic needs when they establish momentous projects that makes their legacy to live on and on in ages making them immortals. A typical example are billionaires that have donated a huge part of their wealth to the society such as Bill Gates and Warren Buffet. Self-actualization can be achieved by those who invest in social businesses because their service to humanity is one that will bring in a continuous change in the lives of people without losing his or her capital. In the words of Muhammad Yunus “to make money is happiness but making other people happy is super happiness” - An opportunity for the lower class and unprofessional people is created by social businesses by making them to have access to professional experience, steady income, empowerment and the opportunity to empower others. This opportunity brought by social business is not just one that will change the lives of the poor but it is an opportunity that will make the poor to be relevant in the industry. Social business has made the lives of a lot of people better with happiness and self-suffi-ciency and meaningful life. 2
Social business gives the opportunity for investors to be selfless. According to professor Yunus in a poverty free nation article offers a reason to investors for selflessness. Professor Muhammad Yunus has put an emphasis in his article Vision 2050: A Poverty-Free World that “the mightiest mistake in describing capitalism is the process of misunderstanding or confusing the nature of humans. People that run several business are seen as beings that are 1 dimensional with the sole purpose of maximizing their profit. There exists in this definition a wrong description of humans due to the fact that the definition doesn’t contain the area of life itself but that humans can also be seen as multi-dimensional and not as machines that exist to just make money.It can’t be denied that humans have their selfish aspect but in every human also lies a selfless part.With Social business,
humans will have the opportunity to execute their ‘selfsacrifice’ which can hardly be found in the traditional profit making business. This is achieved by surprising or eliminating the personal gain motive and applying societal benefit motive.
Conclusion
A great no return investment opportunity is seen in Social Business. Satisfaction is the generated return that can be gotten from social business making the investor having a legacy of creating an unending circle of benefit for the poor. There is a great respect by people to the individuals who do impactful selfless acts for the benefit of the. There is always a special recognition given to the by the society which one cannot measure or compare with money. The measurement of success in a traditional profit business-making venture is by the amount of profit, which they earn in a given period.
Acknowledgement
In order to prepare this research, we have relied on following up on our own work, by defining the role of social work in the development of business and educational projects under implementation. We noted that, by supporting the idea of social work, and introducing this idea within our educational institutions, which is international Brayan primary private school,of the system and institutions, all of which led to the work of the search, and compare between social work and traditional work and the impact of each one in the institutions concerned and impact within the community quickly.
References
Abdul, A., & Bass, J. M. (2018, August). Hierarchical multitenancy in business to business software services. In 2018 44th Euromicro Conference on Software Engineering and Advanced Applications (SEAA) (pp. 494-501). IEEE.
Artur Steiner, Simon Teasdale, (2016) “The playground of the rich? Growing social business in the 21st century”, Social Enterprise Journal, Vol. 12 Issue: 2, pp.201-216,
Brammer, S. J., &Pavelin, S. (2006). Corporate reputation and social performance: The importance of fi t. Journal of management studies, 43(3), 435-455.
Chao, A. C., & Hong, L. (2018). Corporate Social Responsibility Strategy, Environment and Energy Policy. Structural Change and Economic Dynamics. DeFillippi, Robert, (2014) “Co-creation in the era of social business”, Strategy & Leadership, Vol. 42 Issue: 4, https://doi. org/10.1108/SL-05-2014-0039.
Defi ning Social Business SideraWorks LLC – SideraWorks.com v.10. Retrieved from www.microsoft.windowscommunicatio nsapps_8wekyb3d8bbwe/LocalState/Files/S0/249/social business[358].pdf.
Denise Baden,& Stephen Wilkinson. (2014). Socially Responsible Enterprise in Cuba: A Positive Role Model for Corporate Social Responsibility? International Journal of Cuban Studies, 6(1), 55-86. doi:10.13169/intejcubastud.6.1.0055
Ferrell, O. C., Harrison, D. E., Ferrell, L., & Hair, J. F. (2019). Business ethics, corporate social responsibility, and brand attitudes: An exploratory study. Journal of Business Research, 95, 491-501.
Fritscher, B., &Pigneur, Y. (2014, July). Visualizing business model evolution with the business model canvas: Concept and tool. In Business Informatics (CBI), 2014 IEEE 16th Conference on (Vol. 1, pp. 151-158). IEEE.
Ghaderi, Z., Mirzapour, M., Henderson, J. C., & Richardson, S. (2019). Corporate social responsibility and hotel performance: A view from Tehran, Iran. Tourism Management Perspectives, 29, 41-47.
Grove A. and G.A. Berg (eds.) (2014), Social Business,-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg, Social Business: Defining and Situating the Concept retrieved from www. Hasan, Khalid, (2016), Social Marketing and Social Business, in Syed Saad Andaleeb , Khalid Hasan (ed.) Strategic Marketing
Management in Asia, pp.475 – 509
Hausmann, V. (2018). Social Business Documents: An Investigation of their Nature, Structure and Long-term Management (Doctoral dissertation, Universität Koblenz-Landau).
Hines, Frances, (2005) “Viable social enterprise: an evaluation of business support to social enterprises”, Social Enterprise Journal, Vol. 1 Issue: 1, pp.13-28, retrieved from https://doi. org/10.1108/17508610580000704.
Hitt, M. A., Lee, H. U., &Yucel, E. (2002). The importance of social capital to the management of multinational enterprises: Relational networks among Asian and Western fi rms. Asia Pacifi c Journal of Management, 19(2-3), 353-372.
Holsapple, C., Hsiao, S. H., &Pakath, R. (2014). Business social media analytics: defi nition, benefi ts, and challenges. Huda, M., Mulyadi, D., Hananto, A. L., Nor Muhamad, N. H., Mat Teh, K. S., & Don, A. G. (2018). Empowering corporate social responsibility (CSR): insights from service learning. Social Responsibility Journal, 14(4), 875-894.
Irene, B., Marika, A., Giovanni, A., & Mario, C. (2016). Indicators and metrics for social business: a review of current approaches. Journal of Social Entrepreneurship, 7(1), 1-24.
IT Briefcase Exclusive Interview: The Pros and Cons of Social Business with Mac McConnell, BonitaSoft, (2013). Retrieved http://www.
itbriefcase.net/it-briefcase-interview-the-pros-and-cons-ofsocial-business. John E. Tyler III, Evan Absher , Kathleen Garman , Anthony
Luppino, (2017), Purposes, Priorities, and Accountability Under Social Business Structures: Resolving Ambiguities and Enhancing Adoption, in Andrew C. Corbett , Jerome A. Katz (ed.) Hybrid Ventures (Advances in Entrepreneurship, Firm Emergence and Growth, Volume 19) Emerald Publishing Limited, pp.39 – 60
Kanter, R. M. (1999). From spare change to real change. The social sector as beta site for business innovation. Harvard business review, 77(3), 122-32.
Kolk, A., & Van Tulder, R. (2010). International business, corporate social responsibility and sustainable development. International business review, 19(2), 119-125.
Laura Michelini, Daniela Fiorentino, (2012) “New business models for creating shared value”, Social Responsibility Journal, Vol. 8 Issue: 4, pp.561-577, https://doi.org/10.1108/17471111211272129.
M Business Administration and Business Economics Marketing Accounting. (2014). Journal of Economic Literature, 52(1),
307-313. Retrieved from http://www.jstor.org/stable/24433894
Nusrate M Aziz, Osman Bin Mohamad, (2016) “Islamic social business to alleviate poverty and social inequality”, International Journal of Social Economics, Vol. 43 Issue: 6, pp.573-592, https://doi.org/10.1108/IJSE-06-2014-0129
Makuei, Gabriel, (Fab 2018). Building social business by Muhammad yunus, Journal of Contemporary Scientific Research (ISSN (Online) 2209-0142) Volume 2 Issue 2, retrieved from www.jcsronline.com.
Mawdudur Rahman, Mostaq Hussain, (2012) “Social business, accountability, and performance reporting”, Humanomics, Vol. 28 Issue: 2, pp.118-132, https://doi.org/10.1108/08288661211228889.
MdMahfuz Ashraf, Mohammed AbdurRazzaque, SiawTengLiaw, Pradeep Kumar Ray, MdRashadul Hasan, (2018) “Social business as an entrepreneurship model in emerging economy: Systematic review and case study”, Management Decision, https://doi.org/10.1108/MD-04-2017-0343 microsoft. windowscommunicationsapps_8wekyb3d8bbwe/LocalState/Files/S0/249/2[355].pdf
Muir, Samantha, (July 2015). Top 5 benefi ts of Corporate Social Responsibility, Retrieved from http://cubegroup.com.au/
top-5-benefi ts-of-corporate-social-responsibility/.
Mulgan, G. (2006). The process of social innovation. Innovations: technology, governance, globalization, 1(2), 145-162.
Necati Aydin, (2015) “Islamic social business for sustainable development and subjective wellbeing”, International Journal of Islamic and Middle Eastern Finance and Management, Vol. 8 Issue: 4, pp.491-507, https://doi.org/10.1108/IMEFM-09-2014-0097.
Peter J. Korsten, Eric Lesser, James W. Cortada, (2013) “Social business: an opportunity to transform work and create value”, Strategy & Leadership, Vol. 41 Issue: 3, pp.20-28, https://doi.org/10.1108/10878571311323181.
Prusak, L., & Cohen, D. (2001). How to invest in social capital. Harvard business review, 79(6), 86-93.
Renck, R., & Thomas, C. (2014). Recent Developments in Business Commercial Courts in the United States and Abroad. Business Law Today, 1-3. Retrieved from http://www.jstor.org/stable/businesslawtoday.2014.05.02
Roy, Kaushik, Karna, Amit, (2015) “Doing social good on a sustainable basis: competitive advantage of social businesses”, Management Decision, Vol. 53 Issue: 6, pp.1355-1374, retrieved from https://doi.org/10.1108/MD-09-2014-0561.
Sabatier, Valerie, Medah, Ignace, Augsdorfer, Peter, Maduekwe, Anthony (2017) “Social business model design and implementation in developing countries: Learning from an affordable medicine developed in Burkina Faso”, Journal of Management Development, Vol. 36 Issue: 1, pp.48-57, https://doi.org/10.1108/JMD-03-2015-0041.
Seelos, C., &Mair, J. (2005). Social entrepreneurship: Creating new business models to serve the poor. Business horizons,
48(3), 241-246.
Sigurjonsson, T. O., Vaiman, V., &Arnardottir, A. A. (2014). The role of business schools in ethics education in Iceland: The managers’ perspective. Journal of Business Ethics, 122(1), 25-38.
Singhapakdi, A., Kraft, K. L., Vitell, S. J., &Rallapalli, K. C. (1994). The perceived importance of ethics and social responsibility on organizational effectiveness: A survey of marketers. Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science, 23(1), 49-56.
Social business, (2019). Retrieved from https://www.tbd.community/en/t/social-business. Spieth, P., Schneider, S., Clauß, T., &Eichenberg, D. (2018).
Value drivers of social businesses: A business model perspective. Long Range Planning. Weber, M. (2008). The business case for corporate social responsibility: A company-level measurement approach for CSR. European Management Journal, 26(4), 247-261.
Xinhua, Z. (2018, June). Research on information disclosure of corporate social responsibility based on environmental friendliness. In 2018 Chinese Control And Decision Conference (CCDC) (pp. 5558-5563). IEEE.
Yunus, M. (2014). Interview with Nobel Laureate Prof. Muhammad Yunus. Educational Technology, 54(1), 55-57. Retrieved from http://www.jstor.org/stable/44430239
Zwilling, Martin, (Jan 2017). 8 Reasons Why Being Socially Responsible Is Good for Business, retrieved fromhttps://www. inc.com/martin-zwilling/8-reasons-why-being-sociallyresponsible-is-good-for-business.html. Muzakkeer, Huda, (July 2016). Social Business: Meaning,
Scope, And Evaluation. Global Marketing Conference at Hong Kong Proceedings: 1262-1281. retrieved from http://dx.doi.org/10.15444/GMC2016.09.06.03.


