1Ministry of Education – Saudi Arabia
2King Abdulaziz University – Department of Information Science
Corresponding author Email: mjdabusharha@gmail.com
Article Publishing History
Received: 09/04/2019
Accepted After Revision: 28/05/2019
The present study dealt with the extraction of the implicit knowledge in the Secretariat of the Holy Makkah, which aimed to identify the experts of implicit knowledge in the Secretariat of the Holy Makkah, and the ways and methods used by the Secretariat of the Holy Makkah to draw knowledge from the knowledge experts working for them. The study relied on the use of the descriptive statistic approach to identify methods of extracting knowledge from knowledge experts located in the Secretariat of the Holy Makkah. The tool used is the interview, with the total population of the study (50) persons representing the knowledge experts working in the Secretariat of the Holy Makkah.The study sample consisted of 16 persons, 32% representing former secretaries and former leaders, as well as the second class of leaders in the Secretariat of the Holy Makkah. They were chosen by means of a intentional sample based on selective selection of the sample according to several criteria: Experience, qualification, scientific achievements, positions held. The study concluded that the Secretariat of the Holy Makkah is one of the first governmental sectors in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia to introduce knowledge management, provide the necessary IT infrastructure for the implementation of knowledge management in the Holy Makkah Municipality, knowledge management, that there is a trend from the Secretariat in the transformation towards the application of information technology in all its works, the presence of awareness of the experts in the knowledge of the importance of information technology in facilitating the municipal work, support the secretariat of the Holy Makkah for electronic archiving projects that. The study showed that 56.25% of the sample have a scientific qualification in the field of engineering in various specialties, The study produced a set of recommendations, the most important of which are: To create a working environment in the Secretariat of the Holy City to transform the implicit knowledge available to institutional knowledge through the creation of efficient and effective policies and methodologies, to empower the work environment and encourage them to create new knowledge of knowledge gained and experience accumulated by retired or departing employees, which is one of the most important sources of implicit knowledge, which must be developed in the mechanisms of extraction, preservation and participation, the establishment of a database of implicit knowledge experts in the Secretariat of the Holy Makkah.
Holy Makkah Municipality – Knowledge Management – Tacit knowledge – Knowledge extraction
AbuSharhah M. M, Ageeli U. M. Tacit Knowledge Extracting in Holy Makkah Municipality: An Empirical Study. Biosc.Biotech.Res.Comm. 2019;12(2).
AbuSharhah M. M, Ageeli U. M. Tacit Knowledge Extracting in Holy Makkah Municipality: An Empirical Study. Biosc.Biotech.Res.Comm. 2019;12(2). Available from: https://bit.ly/2K97JLV
Introduction
Access to and possession of knowledge is considered one of the most important challenges and difficulties faced by organizations that have adopted a trend towards implementing of knowledge management in their work, and there are many processes followed by organizations in obtaining knowledge that vary according to nature and environment. According to the tenth five-year plan of the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia, which was implemented in 2015-2019, the third item: “The transformation towards the knowledge-based economy and the knowledge society”, and the Supreme Order No. 546 Minister of Economy and Planning “to come up with a comprehensive national and scientific strategy, to move to the knowledge society backed by time-limited operational and time programs” and implemented the “National Strategy for the transition to a knowledge society”
( Ministry of Economy and Planning (2019) .
Recently, the number of organizations in different categories has increased, and competitiveness has become the strongest in order to maintain its survival in the labor market and gain more business. Knowledge is one of the main sources of competitive advantage of these organizations by transforming them into an added value by investing their existing knowledge Stored in the minds of individuals or what is known as human Makkah, as well as knowledge within those organizations stored in databases, research and reports. The process of knowledge extraction is one of the main activities of knowledge management, experienced and skilled workers who have acquired great knowledge in the work they have acquired during the course of their work and converted to explicit knowledge and are classified and coded to facilitate getting back to them and guide them within the organization and invest them as well, (Bawazie 2018).
Experts (the human element), or so-called intellectual Makkah, are the most important resources and knowledge assets within the organization. Knowledge organizations must give this element the greatest part of investment and development. What will be reviewed in this part of the paper falls under the concept of “implicit knowledge” Which means the set of experiences, skills and experiments lies in the minds of individuals, and are not written or encoded and difficult to move from person to person. One of the most important challenges facing organizations in implementing the concept of knowledge management is to work for the acquisition and gaining of implicit knowledge. Business organizations, economic, social, public and other organizations need implicit and explicit knowledge to gain added value in their work.The implicit knowledge is particularly important because the knowledge owned by an organization will necessarily be missing as soon as it is encoded and stored or simply distributed in directories and documents with products and services provided to beneficiaries or customers.It is necessary to define the implicit knowledge to be attracted, or to acquire and extract as well, and to establish controls that define the dimensions of the process of transforming implicit knowledge into explicit knowledge (Al-Salih, 2012).
There are a variety of methods and tools that organizations rely on in the process of deriving implicit knowledge, including exit interviews, best practices, post-action reviews, practice communities, social networking analysis, knowledge café, focus groups, organizational stories, etc., and there are multiple types of extraction are:
- Extraction of knowledge from individuals (experts),
- Extraction of knowledge from documents,
- Extraction of knowledge from databases.
The Secretariat of the Holy Makkah (Makkah) was one of the first Saudi government sectors to adopt the concept of knowledge management and adopted the “Knowledge Management Project Implementation Initiative”.In this study we will present the experience of the Secretariat of the Holy Makkah, The concept implementation of knowledge management and also experience in the process of deriving knowledge from its implicit knowledge experts and to document their achievements and experiences with a view to making use of them in sharing such knowledge with the rest of the Secretariat.The study includes the definition of the concept of extraction of knowledge and its characteristics, types and tools, and we will review the experience of the Secretariat of the Holy Makkah to apply the concept of knowledge management and experience in the process of extracting the knowledge from the experts of the implicit knowledge they have and documenting their achievements and experiences with a view to converting them into explicit knowledge and benefiting from them in sharing that knowledge with the rest of the Secretariat .
Next, we review the analytical aspect of the study, which is the analysis of the data collected through the interview tool with these experts and the most prominent findings. And then come up with a set of recommendations that contribute to the development of the performance of organizations and raise their productivity.
Objectives of the study:
- The present study aims to identify:
- Experts of implicit knowledge in Holy Makkah Municipality.
- Ways and methods used by Holy Makkah Municipality to extract knowledge from its knowledge experts.
The importance of studying :
The importance of the study is as follows:
- The need to activate and implement knowledge management in the Secretariat of the Holy Makkah, which includes the importance of investing in implicit knowledge and methods of extracting them.
- Apply the study to the Secretariat of the Holy Makkah to reach results that contribute to the development of performance in the knowledge management unit.
- The lack of Arabic studies that dealt with the extraction of implicit knowledge from individuals.
Methodology
The study relied on the use of the descriptive survey approach to identify methods of extracting knowledge from knowledge experts located in the Secretariat of the Holy Makkah. The method used is the interview, with the whole total of the study (50) representing the knowledge experts working in the Secretariat of the Holy Makkah. The study sample was composed of 16 people, 32% representing former secretaries and former leaders, as well as the second class of leaders in the Secretariat of the Holy City. , And were selected in a intentional sample manner, which depends on the selective selection of the sample members based on several criteria, namely: Years of Experience, Qualification, Achievements and Positions held. The subject of extracting the implicit knowledge, according to the researcher’s knowledge, is that it is one of the rare subjects that has not been studied by a small number of researchers, especially at the Arab level. This is one of the most important difficulties faced by the researcher to prepare this study, but there are some studies that dealt with the subject of implicit knowledge and its role in organizations and their relationship In making these decisions. The study (Al-Saleh, 2012), which aims to identify the role of implicit knowledge in the development of human resources in multinational companies under the concept of globalized management. The problem of the study was to try to answer the question: “does implicit knowledge have a role and an effect in the development of human resources under the concept of globalized management in the multinational company?
Pathirage et al (2007) aimed to highlight the importance of implicit knowledge in the construction industry and its impact on organizational performance., A theoretical study that showed the researchers’ view of knowledge and its organized resources and the nature of implicit knowledge strategy, and described the characteristics of the construction industry in the UK and described the factors affecting people and the role of implicit knowledge. The study concluded that implicit knowledge plays a fundamental role in the changing business environment and contributes significantly to business continuity. The implicit knowledge is based on the skills, experience, and talent that people have and have to take into account. The study shows the important role of implicit knowledge in linking organizational performance and achieve competitive advantage.
Ribeiro, (2012) reported on the implicit knowledge management, where the purpose of the study was to study the theory of knowledge as well as to describe the implicit knowledge, problems and difficulties faced by organizations and companies in the process of polarization and composition and how to overcome them. The study also dealt with some of the practices that take place in some of the companies that have identified. In which the knowledge management has been implemented and the researcher used in this study the case study. It was about a Brazilian company working in the field of mining and iron industry, which employs about 1490 people and produces 50,000 tons of nickel annually. The researcher used in this study interviews as a tool to collect information and data, and the study reached several results, including:
That all types of implicit knowledge are important in the process of iron production or mining in general smoothly and safely, during the pre-operation stage. The results of the study also indicate the importance of training and education in developing the expertise, competencies and practices of the organizational workers and linking them to their existing knowledge and the factory’s need for such knowledge, And the importance of previous experiences and their relationship to the nature of the current work and the extent of proficiency and skill in the performance of work and the measurement and identification of the existing experiences of workers and their ability to perform their work in the factory as a result of those experiences that were acquired in previous work.
Gavrilova & Andreeva (2012), emphasized the importance of deriving knowledge from the employees of the organizations (implicit – explicit) and also confirmed that part of the knowledge and experience is in the hands of the employees of the organization and belongs to them and not to the organization, Knowledge management tasks should therefore include a process of extraction from those who possess them. The study relied on a broad review of intellectual production on the subject of knowledge extraction, as well as twenty years of experience from one researcher in the application of different techniques and tools in the extraction of knowledge in many organizations. The study concluded that there is an urgent need for a specialist to obtain knowledge from Individuals (experts) ensure that these organizations benefit from existing knowledge and their participation and thus create new knowledge. The study suggested a new classification of the techniques and tools that must be relied upon in the process of knowledge extraction.
Extraction of implicit knowledge
In order to prepare this study, many studies and researches have been consulted on this concept. There are many terms used for the word extracting: Capture, Elicitation, Acquisition and Visualization. The following are the most important conclusions about the concept of knowledge extraction: The process of obtaining knowledge from its human resources (implicit knowledge of experts) and symbolic – explicit (knowledge in digital and physical media) and transfer and storage in the knowledge base or in knowledge management systems, the process by which the knowledge system development team to explore the knowledge that Used by FAO experts to accomplish the required tasks as a pilot and exploratory research process requiring interviews and protocol analysis to build knowledge management systems, (Yasin, 2006).
The process of retrieving and documenting explicit knowledge in its variousforms, or implicit in knowledge experts in organizational structures and organizations. The knowledge to be drawn outside the regulatory boundaries, including consultants, competitors, customers, suppliers and former employers of the organization, (Bisera and Rajeev 2014). A process through which knowledge is extracted from a huge number of data stored in digital repositories and databases using a set of statistical and mathematical styles and methods (Hayek, 2014).
Analysis and presentation of data
The accumulated experience of current employees, retirees or departures is one of the most important sources of knowledge that must be developed in order to extract, preserve and share mechanisms. In this regard, the current study in data analysis has been based on a number of procedures:
- The total of the knowledge experts included in the Secretariat of the Holy
Makkah of (50) persons (see Appendix 1) and the sample of the study was composed of 16 persons with 32% representing former secretaries and former leaders as well as the second row of leaders in the Makkah’s secretariat. And they were chosen in a intentional sample manner, which depends on selective selection of the sample based on several criteria: Years of experience. Qualification. Achievements and Positions held.
- Identify the appropriate study tool to extract the implicit knowledge of experts working in the Secretariat of the Holy Makkah, the interview.
- identify the axes of the interview that will be with the experts of the implicit knowledge, including:
- Curriculum vitae including ( qualification – beginning of work in the Secretariat – positions held – period spent in the Secretariat of the Holy Makkah)
- What are the main achievements or projects that took place during your tenure in the Secretariat of the Holy City?
- What elements do you think were behind the success of these projects?
- Have you encountered difficulties in implementing these projects … What are the most prominent?
- What projects have you implemented and have not been satisfied with?
- What are the causes of dissatisfaction?
- If you have the opportunity to implement the same projects again. Are you making changes to ensure success?
- What projects have you given or planned for and will not be conceived, approved or implemented?
- What are the reasons for non-implementation?
- How do you see the relationship between your administration, departments and other departments? Highlight the pros and cons or problems in this relationship?
- What are the main issues that concern you in your management?
- What important recommendations can you make to someone who may come after you in the same position?
- Are there any additions that you would like to make but not addressed?
Experts of the implicit knowledge of the Secretariat of the Holy Makkah interviewed
Table 1: showing Experts of the implicit knowledge of the Secretariat of the Holy Makkah
| M | Name | Management | qualification | Years of experience | position |
| 1 | Ibrahim Bin Sulaiman Abdullah | Information Technology | d. Assistant Information Technology | 29 | Assistant Information Technology |
| 2 | ENG. Gamal Ben Bakr Hariri | Former Undersecretary for Services (Retired) | BA – Civil Engineering | 30 | Undersecretary for Services |
| 3 | ENG. Ameen Naeb Al-Haram | General Directorate of Municipal Investments | Bachelor – Accounting | 32 | Assistant Secretary of Municipal Investments |
| 4 | Sharaf Al Abdali | Under Secretary for Studies and Projects (retired) | BA – Environmental Engineering | 40 | Undersecretary for Studies and Projects |
| 5 | Mtair Bin Menahi Al Qurashi | Personnel Management | Bachelor – General Administration | 34 | Assistant General Manager Personnel |
| 6 | ENG. Hisham Bin Abdulrahman Shali | Facilities Management and Environmental Management | Bachelor of Architecture | 28 | General Manager of Facilities and Environment |
| 7 | A. Samir Bin Mohammed Shafi | Personnel Management | BA – Administration and Economics | 40 | General Manager of Human Resources |
| 8 | ENG. Talaat Ben Salem Al Bar | General Manager | Land and Property Bachelor – Civil Engineering | 32 | General Manager Land and Property
|
| 9 | Hani Hassan Faqiha | General Services Department | Bachelor – Mechanical Engineering | 22 | General Manager General Services
|
| 10 | pm. Atef Ben Ali Mulla | Building and Engineering | Engineering Department Bachelor of Civil Engineering | 21 | Director of Buildings Affairs and Engineering Offices |
| 11 | Abdulaziz Al-Issaie
|
Office of the Secretary
|
Master – Civil Engineering
|
34 | General Supervisor of the Office of His Excellency the Secretary |
| 12
|
a. Saadi Bin Mohammed Al-Qarni | Office of the Secretary-General (Retired) | BA – General Administration | 40 | Advisor to the Secretary |
| 13 | ENG. Hassan Ben Ali Eid | Member of the Municipal Council (Retired) | Bachelor – Civil Engineering | 40 | Member of the Municipal Council |
| 14 | ENG. Gamal bin Abdullah Al – Hindi | Municipal Council | Bachelor – Computer Science and Engineering | 37 | Advisor to the Secretary of the Municipal Council |
| 15 |
Dr. Saud Mohammed Al-Hitiri | General Manager of slaughterhouses | Bachelor of Veterinary Medicine Department of Interests | Management of slaughterhouses | |
| 16 | ENG. Khalid Abdulhafid Fada | Development Authority Makkah | Bachelor – Architecture | 35 | Deputy Secretary of the development of Mecca |
It is noted from Table (2) that the experts selected to derive the implicit knowledge that they are working in different areas of the work of the Secretariat, where we find that there are 15 administrations were selected from them, as Table 2 shows the diversity of their specialties, especially in the field of engineering, (9) of the experts interviewed have a scientific qualification in engineering out of sixteen names representing 56.25% due to the nature of work in the field of the municipality as it needs the scientific qualification in most of the engineering disciplines needed by the Secretariat in the implementation of its tasks and objectives, While 43% of them hold qualifications in management , accounting and Veterinary Medicine. Table (2) shows that 100% of the selected persons have experience in the field of municipal work for at least 20 years. The selection of experts who are currently on the job is not limited to those who have been referred to but included the retirees who represent 37.5% in order to benefit from their experiences and extract their implicit knowledge and convert it into explicit knowledge.
Table 2: showing Accomplishments of Knowledge Experts in the Secretariat of the Holy Makkah
| id | Name of the expert | achievements
|
| 1 | d. Ibrahim Sulaiman Abdullah | Transferring Transactions in the Secretariat to Electronic – Customer Service Systems represented by Sabeel, which provides 36 services – Geographic database SDI – Hajj Housing Services Project – Issuing shop licenses electronically – JRB project for financial purchases and monitoring of Inventory – Supervision of projects Electronic archiving in the Secretariat. |
| 2 | Mtair Bin Menahi Al Qurashi | Manual Job Description – Introducing Technology in the Work of Personnel Management – Employees ‘Electronic Employees’ Transfer Project |
| 3 | ENG. Hisham bin Abdulrahman Shali | Implementation of sports stadiums in Mecca – Increase green spaces in the streets and neighborhoods of Mecca – The allocation of the territory of the Secretariat in the neighborhoods to establish sports stadiums – Urban Park – Supervising the global competition to beautify Mecca. |
| 4 | Mr. Samir bin Mohammed Shafi | introduction of computer in the work of personnel management – recruitment of specialists in the management of personnel – archiving staff files in electronic – supervision of the installation of employees on the item of wages after the issuance of royal orders under the late King Abdullah bin Abdul Aziz – Special promotion items and competitions. |
| 5 | ENG. Talaat Ben Salem Al Bar | Supervising the improvement and beautification of the entrances to Madinah – Introducing GIS to land management in the Holy City Secretariat – Introducing the land expropriation system – Introducing the electronic archiving system in the land and property administration – Introducing the so-called land registry map (file containing all documents). |
| 6 | Hani Hassan Faqih | supervision of the return of electricity to the feelings in less than 24 hours after the fire incident Mona 1417 e – the addition of communication towers on the mountains in the feelings – privatization of equipment – the privatization of cameras – the modernization of the Secretariat’s central program – the introduction of an automated system of the positions of the Secretariat. |
| 7 | ENG. Atef Bin Ali Mullah | Organizing the work of engineering offices – Developing the system of licenses (Licenses no hassle) – Establishment of an automated system for the registration of engineering offices. |
| 8 | Abdulaziz Al-Isaii | Management of the Kadi Streets Project – Increasing the streets and roads in Bahra Municipality – Supervising the cleanliness of the holy sites during the Hajj season – Establishing the advisory bodies in the office of His Excellency the Secretary |
| 9 | a. Saadi bin Mohammed Al-Qarni (retired) | Design of the organizational structure of the municipalities in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia -Supervision of development Management in the Secretariat – Supervision of the work of Hajj. |
| 10 | pm. Hassan bin Ali Eid (retired) | Department of Municipal Investment in the Secretariat of the Holy Makkah – Supervision of the allocation of the central market (the ring) – Supervising the scheme of limited income – Development of the market Otaibia – Development of security and safety management and the introduction of uniforms uniform guards and the introduction of cars special security and safety. |
| 11 | ENG. Gamal bin Abdullah Al-Hindi | Development of the Information Technology Department in the Secretariat of the Holy Makkah – Development of municipal procedures such as shop licenses and linking the procedures of their extraction with the relevant authorities – Supervision of the new building of the Information Technology Department |
| 12 | Dr. Saud Mohammed Al-Hitiri | Launch of the Award of the Custodian of the Holy Mosques for Institutional Excellence – Establishment of control offices in the slaughterhouse – Imposition of violations of the meat shops violation – Establishment of two new slaughterhouses in Mecca – Dealing with the accumulation of sacrificial animals slaughtered during the Eid al-Adha. |
| 13 | Dr. Ashraf Al-Abdali (retired) | Improvement and development of land – Development of Al-Awali neighborhood – Development of Al-Azizia neighborhood and planning – Third ring line – Planning 60 thousand pieces of land – Establishment of sub-municipalities – Giving powers to municipalities to issue permits. |
| 14 | ENG. Ameen Naeb Al-Haram | Development of an automated system for the management of financial affairs – Establishment of a system to accelerate employee promotions – Increase the resources of the Secretariat – the collection of 100 million riyals during a short period. Investment of the new livestock market – Chairman of the Knowledge Committee of the Secretariat |
| 15 | ENG. Khalid bin Abdulhafid Fada | Supervising the implementation of 5 arterial roads in the Secretariat of the Holy Makkah Garden design – Supervision of the Fourth Ring Road – Supervision of consulting contracts – Supervision of the restoration of the historic Palace of Saqqaf |
| 16 | ENG. Jamal Hariri (retired) | Supervision of land management in the Secretariat of the Holy Makkah – Supervision of granting of limited income – Accelerate achievement in grant transactions and organization – Supervision of the expansion of the Malawi – Supervision of the allocation of the project of cleanliness – Afforestation of feelings(sites) – Offering maintenance and operation contracts for street planting. |
Table 3 shows that most of the achievements made by tacit knowledge experts are the shift towards the application of information technology in the performance of their departments. Where most agreed and this is what was concluded through the interview that 60% of them had the largest role in the development of automated systems in the work of departments and the shift to automate their work.Dr. Ibrahim Sulaiman, Assistant Secretary of Information Technology, is the most prominent in accomplishing achievements in the work of the Secretariat because of the great orientation of the former secretaries and the current Secretary of the Secretariat to move towards the application of information technology and to provide the best means and methods that serve the clients benefiting from the work of the Secretariat. As evidenced by the interviewees. It also shows that there is a tendency from most departments towards electronic archiving, especially those that have archival sections and deal with important documents such as Instruments and financial management documents such as financial derivatives of Masha Which are valuable historical and reference in the case of need to make a decision. This is an important indicator of the application of the concept of knowledge management in organizations. The most important challenges facing organizations to implement knowledge management are the readiness of the IT infrastructure.
It is also shown from Table (3) that, according to the interview, there were experiments conducted in the Secretariat of the Holy Makkah and the first at the level of the departments in the governmental sector, especially the municipal work. The Secretariat is distinguished by the rest of the secretariats in Saudi Arabia for their presence in mecca, Of direct services to pilgrims in the Hajj season, as well as pilgrims for the whole year. The privatization experience in the government sector started early in the work of the Secretariat. For example, the Secretariat privatized heavy equipment and machines and delivered them to the private sector for operation and maintenance, as well as privatization of the cleaning sector, maintenance and irrigation of gardens, Safety cars, and photocopiers, They confirmed who were supervising these projects that the Secretariat of the Holy Makkah was the first in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia in the implementation of these projects and benefited from the experience and then circulated to the rest of the secretariats and other government sectors.
As shown in Table (3), some of the experts of implicit knowledge interviewed during the period of their work in the Secretariat required them to deal with them more accurately and able to deal with crises, as happened in the fire incident in 1417 e and burning a large part of the camps in addition to the power outages and the burning of cables and control panels for the delivery of electricity was in the pilgrimage season that year and specifically on the seventh day of the month of Dhu Al-Hijjah This represents a major challenge to the parties involved in providing solutions, and these incidents are rare but may occur again, It is important to document this incident To try to know the reasons and methods of prevention so as not to recur, and it was important to document the solutions reached in order to be used in the case of God forbid again.
As well as the experience of working in the slaughterhouses, especially in the Hajj season and the required preparation and processing of those abattoirs due to the large numbers of sacrifices that are slaughtered in this period and how to deal with and benefit from them to be distributed to the poor and needy of the poor Mecca and the world also instead of what was previously Leaving some to rot and become unfit for human consumption, and introducing nitrogen cooling technology as a solution to freeze the meat quickly, as well as benefit from the project to benefit from the meat of sacrifice. Through the interview with the experts of the implicit knowledge in the Secretariat of the Holy Makkah to extract their experiences and their desire not to lose the knowledge they hold and benefit from them in the current municipal work, where 30% of the 50 names proposed (see Appendix No. 1) have been referred to retirement After they reach the statutory age or have completed their period of employment in the Secretariat, and some of them prefer to leave the work in the Secretariat to practice in the private sector.
One of the most important experiences in the Secretariat of the Holy Makkah is the implementation of the job description manual and its electronic availability on the internal rules of the secretariat. It includes all the tasks required to be performed by the employee. This is one of the most important procedures practiced by organizations that have adopted the concept of knowledge management. This guide contributes to the dissemination of knowledge to be provided by the employee and he / she shall be given the means and channels of communication with the other departments and shall indicate the limits of his powers so as not to interfere with the functions of another function.
As shown in Table (3), the direction taken by the Secretariat of the Holy Makkah to develop municipal investments through the investment of land and the projects it owns. One of those who worked in this administration stated that the revenues that enter the budget of the Secretariat increased from 35 million riyals in the past 20 years to about 350 million riyals during the year and this is the largest number in the level of secretariats in Saudi Arabia because of its presence in Mecca and the high prices of real estate in them.
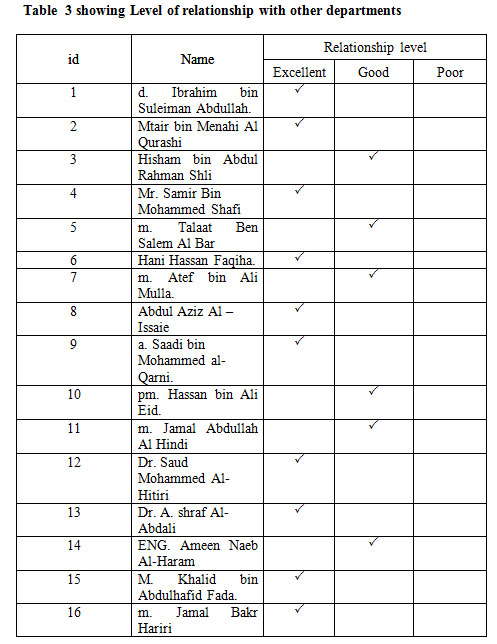 |
Table 3: showing Level of relationship with other departments |
The study aims (from the table 3) to identify the level of relationship with other departments to show the extent, integration and participation in the dissemination of knowledge among the departments operating in the Secretariat of the Holy Makkah.Table 3 shows that through the interview with the experts of implicit knowledge in the Secretariat, A constant need for coordination and partnership between competent departments in order for the process to be integrated.During the interview, it was found that 62.5% of the departments have a high level of coordination with the other departments in the Secretariat. For example, the IT Department has direct interaction with all departments and administrations in the Secretariat due to the shift in the application of IT in all the works of the Secretariat, whether it is an electronic archiving process or the introduction of automated systems in the work of these departments. The interview also revealed that the IT Department is responsible for managing the secretariat electronic portal, which includes providing all services and news of departments, as well as facilitate electronic transactions such as issuing licenses Construction, customer services, etc.
The level of relationship between personnel departments and all other departments in the Secretariat is excellent because it is the administrative reference for all employees of the Secretariat of the recruitment and administrative transactions and promotions and leave and save the files of staff and other services provided by the Department, while Land and Property Management has relationships with IT departments, document management and urban planning management as they need to coordinate with them on facilitating access to information on the nature of their work.
Difficulties and Challenges:The study found that, according to the axes of the interview, there are a number of difficulties and challenges faced by implicit knowledge experts in their implementation of some projects in the Secretariat: The following are the most prominent difficulties:
- Resistance of some leaders in the Secretariat of the Holy Makkah and staff to change and shift to the use of information technology in the provision of municipal services.
- Lack of awareness among intermediate administrations of the role of technology in accomplishing work.
- The inability of some employees to describe the appropriate procedures in their work to delay the issuance of the job description manual.
- The weakness of electronic archiving projects which have not been completed as required, the difficulty of retrieving information, the lack of comprehensiveness of bibliographic data of the document, and the loss of some important documents during the archiving process.
- The loss of a lot of implicit knowledge because of the departure of experts to the Secretariat.
- Lack of financial allocations for the implementation of some electronic archiving projects.
- Weak provision of qualified national cadres, especially in the field of programming and information networks.
- Lack of awareness of some of the experts and implicit knowledge in the importance of sharing knowledge and transfer to others.
- Not to benefit from the projects and consultancy studies that worked in the Secretariat.
- Lack of young leaders qualified to complete the process of the secretariat in municipal work.
Conclusions and Recommendations
First- Results: The study reached a number of results, as follows:
- The Secretariat of the Holy Makkah is one of the first government sectors in Saudi Arabia that initiated the implementation of knowledge management.
- the importance of implicit knowledge in the development and advance of work in all areas.
- Availability of the IT infrastructure required to implement knowledge management in the Holy Makkah Municipality.
- The study found that there is understanding and awareness of employees in the Secretariat of the Holy Makkah towards the concept of knowledge management.
- Support the senior management in the Secretariat of the Holy Makkah to implement the concept of knowledge management, and this is reflected in the Official correspondence that are made to all those working in cooperation and facilitate the task of the Department concerned with the application of knowledge management.
- The Secretariat is moving towards the application of information technology in all its works.
- The existence of awareness of knowledge experts about the importance of information technology in the facilitation of municipal work.
- Support the Secretariat of the Holy Makkah for electronic archiving projects that contribute to the preservation of important documents from damage and loss and also help in decision-making.
- The study found that the IT Department has played a major role in developing the performance of many departments in introducing the systems they need and supervising electronic archiving projects.
- The study found the need for the Secretariat of the Holy Makkah to extract and document knowledge from the experts of implicit knowledge before losing it due to the loss of the person.
- The study found that the Secretariat of the Holy Makkah in its Personnel Department has a job description manual for all posts in the Secretariat and is available electronically.
- The study showed that 56.25% of the sample of the study have a scientific qualification in the field of engineering in various specialties.
- Absence of encouraging incentives for sharing knowledge among individuals.
Second: Recommendations
Based on the results of the study, it is possible to come up with a set of recommendations and proposals that can be used by organizations and bodies to invest their resources and knowledge assets, through the following:
- Creating the working environment in the Secretariat of the Holy City to transform the implicit knowledge available to institutional knowledge assets through the creation of efficient and effective policies and methodologies.
- The working environment will empower staff and motivate them to create new knowledge of the acquired knowledge.
- Utilizing the accumulated knowledge and experience of retired or departing staff, which is one of the most important sources of implicit knowledge, which must work to develop mechanisms of extraction, conservation and participation.
- The establishment of a database of implicit knowledge experts in the Secretariat of the Holy Makkah represent most of the specialties needed by the Secretariat and be a reference when needed to take a decision or solve a problem.
- Attracting qualified and trained professionals to implement knowledge management requirements.
- To work on spreading and strengthening the knowledge culture among the employees of the secretariat, and embed them within the institutional culture.
- The Secretariat of the Holy Makkah has to benefit from the sources of explicit knowledge available in it, such as: the Documentation Center and the Library of knowledge that was created recently and the portal of knowledge of the Secretariat.
- Creating special programs to activate the Knowledge Café, which was established at the Secretariat’s Knowledge Management Headquarters, with the aim of extracting, transferring and sharing the knowledge of the experts to the rest of the employees.
References
Bawazir, Khalid (2018) Benefit from the knowledge bases in the extraction and transfer of knowledge of civilian pilots in the Academy of Prince Sultan Aviation Sciences in Jeddah .
Thesis PhD .- King Abdulaziz University: Jeddah.2018
Bisera, Erma, Saberwal, Rajeev (2014) Wahbi Translation, Muhammad Shehata. Knowledge Management: Systems and Processes – Riyadh: Institute of Public Administration.2014
Hegazi, Haitham . The Integrated Methodology of Knowledge Management in Organizations: An Approach to Achieving Organizational Excellence in the Third Millennium – Amman Al-Radwan Department for Publishing and Distribution .2014
Al-Saleh, Asma Rashad (2014)The implicit knowledge and its role in the development of human resources under the concept of globalized management: an applied study of multinational companies. – International scientific conference – globalization of management in the age of knowledge.- University of Hanan.- Tripoli: Lebanon.2012
Arif, Mohammed Jaafar . Knowledge Culture Workshop: Knowledge and Work Environment Oasis, (lecture), Makkah Al Mukarramah: Secretariat of the Holy Makkah, 19 April 2016.
Ifada Consulting Office . reports and outputs of the surveys carried out to determine the readiness of the knowledge management application in the Secretariat of the Holy Makkah.2016.
Najm, Aboud Najm . Management and e-Knowledge: Strategy – Jobs – Domains .- Amman: Dar Al Yazuri.2009
Hamshari, Omar . Knowledge Management The Road to Excellence and Entrepreneurship.- Amman: Dar Safaa Publishing and Distribution.2012
Ministry of Economy and Planning (2019) .10th Five-Year Development Plan for Saudi Arabia (2015-2019)
Ministry of Economy and Planning( 2015) Strategic Plan for the transformation towards the knowledge society.2015
Yasin, Saad Ghaleb . Knowledge Management: Concepts, Systems, Technologies.Amman: The Curriculum House.2006
Becerra-Fernandez, I., Del Alto, M., & Stewart, H. (2009) A Case Study of Web-Based Collaborative Decision Support at NASA. International Journal of e-Collaboration (IJeC), 3(2), 50-64.
Xia, R. Wang and S. Hu, “Social Networks Analysis of the Knowledge Diffusion among University Students,” 2009 Second International Symposium on Knowledge Acquisition and Modeling, Wuhan, 2009
Focus group: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Focus_group
Nonaka I.&Takeuchi H. (1995)The knowledge creating company how Japanese companies create the dynamics of innovation” New York ,NY university press. Oxford.1995
Parthirage,Chaminda,Dilanthi Amartunga and Richard High (2007) Tacit Knowledge and organization performance: construction industry perspective”Journal of knowledge Management,v.11,1,pp 115-126.2007
Rodrigo Ribeiro (2012) Tacit knowledge management. Phenomenology and the Cognitive Sciences. June 2013, Volume 12,Issue 2, pp 337-366 .First online: 22 January 2012.avalable at :
http://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s11097-011-9251-x/fulltext.html
C.A & Wilson L.T.(1998) The process of Knowledge Management Harvesting The knowledge management .Business Information Management: adaptive Futures 8 Annual BIT Conference.43.1998
Christian Severin (2014) Thomas Roth-Berghofer . Extracting knowledge from web communities and linked data for case-based reasoning systems. Expert Systems .vol 31.no 5.2014
Karl M (1993) Knowledge management foundations: Thinking about thinking—how people and organizations create, represent, and use knowledge.- Expert Systems with Applications. Volume 13, Issue 1, July 1993, Pages 1–14


