Department of Information Science – College of Arts and Humanities –King Abdullaziz University, Jeddah-Saudi Arabia
Article Publishing History
Received: 10/11/2020
Accepted After Revision: 25/12/2020
The present study aimed at identifying the status of previous studies related to the subject of the impact of artificial intelligence on the quality of decision-making in organizations, and providing a critical review of it. In fact, this study attempted to fill several gaps related to the recent studies in this field, which are considered few from the researchers’ point of view. Moreover, it dealt with the most important findings and recommendations reached by those studies in relation to the impact of the use of artificial intelligence on the quality of decision-making in various types of organizations, the types of decisions that can be supported by artificial intelligence techniques. in addition, it identified the most important algorithms, methods, techniques and models of artificial intelligence revealed by these studies that could help providing an accurate decision-making. In order to achieve these goals, this study used the descriptive, analytical, documentary approach. Its results showed that the use of artificial intelligence techniques positively affects the accuracy and quality of decision-making in different forms of these organizations no matter what structure of these organizations is.
The study also found that the most important popular techniques and algorithms of artificial intelligence that can be used to improve the quality of decision-making are Support Vector Machine, Artificial Neural Networks, Back-propagation neural networks, Bayesian networks, Adaptive networks, Fuzzy inference system, Random Forest, Decision Tree, Logistic Regression, and K-Nearest Neighbor. The study recommended the necessity of conducting more experimental and exploratory studies on the impact of applying artificial intelligence on the quality of decision-making within organizations. Furthermore, it recommended designing models and action plans regarding employing artificial intelligence in decision-making in order to facilitate their implementation use, understanding, and the analysis of their results.
Artificial Intelligence (AI), Information Technologies, Decision Making, Quality of Decisions, Performance of Organizations, Fourth Industrial Revolution.
El-Emary I. M. M, Al-Otaibi S, Al-Amri W. The Effect of Using Artificial Intelligence on the Quality of Decision-Making in Various Organizations: A critical Survey Study. Biosc.Biotech.Res.Comm. 2020;13(4).
El-Emary I. M. M, Al-Otaibi S, Al-Amri W. The Effect of Using Artificial Intelligence on the Quality of Decision-Making in Various Organizations: A critical Survey Study. Biosc.Biotech.Res.Comm. 2020;13(4). Available from: https://bit.ly/2J6Nsrq
Copyright © El-Emary et al., This is an Open Access Article distributed under the Terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC-BY) https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/, which permits unrestricted use distribution and reproduction in any medium, provide the original author and source are credited.
INTRODUCTION
The decision-making process in organizations is one of the most difficult stages in the administrative processes. Indeed, regardless to the leaders or to the decision-maker’s analytical capabilities, intelligence, and experiences, there is always a possibility of making wrong decisions. There is no doubt that the tremendous development in recent years in the field of AI, which in turn has brought about a qualitative leap in various fields and disciplines – especially in the areas of various organizations management – has greatly helped in facilitating and improving the quality of various administrative activities in organizations. Eletter, Yaseen, and Elrefae (2020) have clarified, through a study which they conducted on a banking organization, that the intelligent information system that relies on AI would provide organizations’ decision-makers with value-added information that helps them reduce uncertainty about the decision outcome and enhance the quality of banking services, which gives them a competitive advantage and better performance.
Recently, Bosco (2020) have showed that AI has a role in raising the efficiency of organizations ’performance in terms of employing artificial intelligence to make better and accurate decisions in order to achieve the organization’s goals. Este et al., (2020) have mentioned that the use of AI has become very popular now, and stated that it is an amalgamation of several technologies, and that it is the science and engineering of the intelligent machines manufacturing. Vedamuthu (2020) clarified what is meant by AI techniques stating that they are those techniques concerned with creating computer systems based on simulating the way humans use their senses, intelligence and abilities to accomplish the tasks that only the human mind could accomplish.In fact, artificial intelligence has begun to be introduced in healthcare for purposes such as facilitating clinical ordering systems, and identifying patients at high risk for screening tests. Besides that, artificial intelligence will have an increasing impact in healthcare and other disciplines and fields, because AI is superior in some aspects to human intelligence such as visuospatial processing speed and pattern recognition (Este et al., 2020).
Where, millions of information data are stored inside the computer to form a main database in analogy to the information stored inside the human mind, through learning and acquired daily experiences. Then, special programs are developed to enable computers to deal with this information in a logical manner, so these computers can solve the problems and make the decisions (Jabbari, 2016). Beside the previously mentioned about the importance of artificial intelligence, the idea of preparing this scientific study came with the aim of reviewing previous studies related to the topic to identify the extent of the impact of recent developments in AI during the past years on quality, efficiency and accuracy of decision-making in organizations. This scientific study consists of seven parts namely introduction, study problem, study methodology, previous studies, results, analysis of results, and conclusion and recommendations.
Research problem: The recent years have witnessed rapid technological developments and radical changes through the emergence of many modern technologies for information systems, most notably AI techniques. Vedomuthu (2020) indicated that AI has become a fundamental topic in the management of organizations due to its capabilities that allow cooperation between the organization staff and AI in order to improve the decision-making process. As the process of making the right decision in organizations is the basis for their success and for achieving their goals, we find that most organizations have resorted to the use of AI in decision-making processes to make use of their capabilities in analyzing data and deconstructing problems to come up with the best and most accurate decisions.
Based on the above, the researchers considered the necessity to prepare a scientific paper aiming at identifying the extent to which the use of AI in various organizations affects the quality of decision-making. Thus, the study problem can be stated through the following basic question: What is the effect of using AI on the quality of decision-making within all types of organizations? In addition, the study seeks to answer the following sub-questions, what kinds of decisions can be supported by AI techniques? what are the most important algorithms, methods, techniques and models of AI found by the study that can help in accurate decision-making?
METHODOLOGY
This study will use the descriptive analytical documentary approach, which is based on reviewing documents and literature such as scientific researches, articles, books, etc., and then studying, describing, and analyzing them in details in order to extract conclusions and indications related to answering the study questions (Al-Assaf, 2006). Therefore, this study will analyze and evaluate the published studies on the impact of AI on the quality of decision-making in the organizations. Knowing, these studies were reached via databases available through the Saudi Digital Library and the search engine Google Scholar as research tools.This section aims at looking over and critically reviewing a number of studies related to the topic of AI and its impact on the quality of decision-making in organizations, and will be arranged in descending chronological order from the most recent to the oldest. The studies fall within the period of time 2010-2020 AD. The total number of the reviewed studies is (12) which are distributed as follows:
Stone et al (2020) worked on “Artificial intelligence (AI) in Strategic Marketing Decision-Making: a Research Agenda” which described identifying the effect of AI on the efficiency of marketing decisions through a methodology based on reviewing the literature on AI applications in strategic situations. Some marketing experts has been also invited to contribute with their views to this research. The results indicate that there is very little research on the applications of AI on the strategic marketing decisions. Therefore, the importance of this study appears in it is one of the few studies that dealt with this field. This study showed that research in the field of AI linked to strategic marketing decisions seems challenging due to several restrictions and reasons namely the fact that it is a commercial field that contains sensitive data for organizations. Besides, companies that have had successful experiences in using AI in the field of decision-making do not want to spread its experience to prevent its competitors from getting benefit from it.
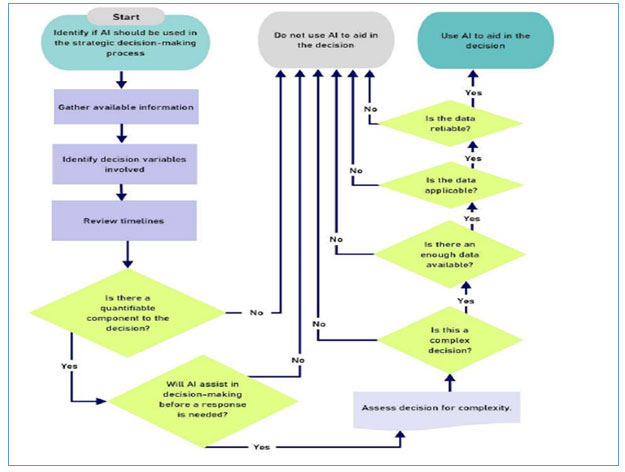
The work of Vedamuthu, (2020) entitled as “Artificial Intelligence and Human Collaboration in Project Decision-Making”, aimed at knowing the possibility of applying cooperation between humans and AI in project management to determine the current uses, and to create an applicable decision model for deciding (when and how to apply AI in project management). And the mode is designed to enhance quantitative decisions in the strategic decision-making, in order to reduce bias, human error and uncertainty in decisions. The researcher indicated that there is currently no decision model to determine how and when to cooperate with AI to make strategic project decisions. Therefore, this study came to cover this gap existing in previous studies, by developing a decision model based on flowcharts to facilitate the use of AI in strategic decisions. These charts showed how and when AI can be used in project decision-making and use this information to support the use of the decision model. The researcher reached these charts through a literary review of previous studies. Therefore, the researchers of this study believe that this model or proposal still needs more field studies to demonstrate its feasibility and effectiveness.
Bejger and Elster (2020) described “Artificial Intelligence in Economic Decision-Making: How to Assure a Trust” which deals with the decisions made by modern AI models, which are called “black boxes”, which are systems that use statistical algorithms and do not reveal their internal mechanisms (such as the neural Artificial network). Thus, people do not trust them in decision-making. These advanced models came after the glass-box models, which are characterized by transparency and the use of symbolic results that are understandable to humans, but are less sophisticated than black box models. The research showed that AI models need regulations and laws for work. It also need to convert these regulations and laws into action plans for decision-making practices, and at the same time, need technical and practical tools to ensure confidence and transparency in decisions.
The research has listed examples of initiatives from different organizations and countries such as Poland, Britain, U.S.A, Canada and Japan in order to make AI models more transparent and reliable. In this regard, the research suggested conducting fundamental adjustments to one of the practical tools, which is the famous standard CRISP DM process model – which is considered one of the practical tools for machine learning and data mining – in order to enhance its work transparency. The research also explained one of the official technical tools, which is the “Anchors” tool, which can support AI models to make them more accurate, reliable and transparent. The strength of the research lies in all the solutions and tools that it presented, and the multiple methodologies it used in conducting the study namely inductive and deductive inference methods, descriptive and comparative analysis, and the experimental method, (Beiger 2020).
In the study of How et al (2020) entitled “Artificial Intelligence-Enhanced Decision Support for Informing Global Sustainable Development: A Human-Centric AI-Thinking Approach” the researcher dealt with AI and its ability to inform sustainable development and its associated organizations through assisting in analyzing primary social and environmental data in order to support decision-makers to take appropriate and correct action on sustainability in development. The paper also made clear that the use of AI was not easy for those who are not trained and who are not proficient in the computer using.
The strength of this scientific paper lies in its clarification of the method of using AI through the researcher’s use of a “human-centric probabilistic reasoning approach”, which is the Bayesian Network (BN). That technology was benefited people, who did not have talent and experience in using computers, in using of the AI to analyze the environmental performance indicators (EPI) data related to sustainability. Moreover, this study is also strong in its application of the study methodology over (180) countries, which resulted in important conclusions such as the fact that the BN approach can simulate many scenarios that are not available in the real world.
This helps officials and organizations in accurate decision-making and predictive analysis, especially under the conditions of best and worst results based on EPI indicators at the global system level. The results of the study found that there are four of the EPI indicators, which are the most influential in all scenarios. These are as follows, classified from best to worst, drinking water quality, sterilization, exposure to lead, and wastewater treatment, (How et al 2020).
“A Study on Artificial Intelligence Interaction with Organizational Performance” aimed at bridging the gap related to implementing AI in organizations in order to raise performance, facilitate decision-making and raise efficiency and quality. This study used the descriptive approach based on electronic questionnaires and interviews on a sample of (100) employees in order to know the impact of AI on raising the efficiency of the performance of organizations and the possibility of employing AI in organizations to make accurate decisions, in order to achieve the organization goals. The results found that organizations are ready to employ AI in several areas within the organization in order to make decisions, raise efficiency, reduce costs, and increase profits. However, there are obstacles to applying AI techniques namely cyber security challenges, protecting customer data, and insufficient budgets, (Bosco,2020).
Lange, Konig, & Busch, (2020) worked on “Changing the Means of Managerial Work: Effects of Automated Decision Support Systems on Personnel Selection Tasks” the researcher touched on ways to enhance the quality and efficiency of decision-making through the use of automation based on AI, and to know its impact in support of administrative tasks and decisions related to employee selection. The strength of this study lies in the fact that it came in contradiction to most theoretical studies that dealt with these topics.
It was distinguished by the abundance of its hypotheses subject to the experimental laboratory study to ensure the accuracy of the results, which amount to six hypotheses, and applying it to a random sample of three groups of specialists in personnel affairs. The sample was subjected to five repeated rounds of personnel or employee selection processes. The results showed that satisfaction with employment decisions was higher for the participating group that received support from the automated system after the group had previously performed a human-processing process for applicants. Moreover, participants in this group showed a sharp increase in self-efficacy in employee selection compared to the other groups.
The recent work of Pourhomayoun Shakibi (2020) entitled “Predicting Mortality Risk in Patients with COVID-19 Using Artificial Intelligence to Help Medical Decision-Making in the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic” designed and developed a predictive model that relies on AI and machine learning algorithms to identify health risks and predict mortality risk among COVID-19 patients. The study used documented and laboratory-confirmed data of 117,000 patients all over the world with COVID-19. The study proposes an AI model to help hospitals and medical facilities for identifying who needs attention first, who has a higher priority for hospitalization, patients sorting and ranking when the system is very crowded, and eliminate delays in providing necessary care. The results showed an overall accuracy of 93% in predicting the death rate. Furthermore, the study used several machine-learning algorithms to predict the death rate in patients with COVID-19. The strength of this study lies in its practical methodology based on a large and reliable sample, as well as in its proposed model, which has proven its effectiveness.
Chernov et al (2019) explained “The Usage of Artificial Intelligence in Strategic Decision Making in Terms of Fourth Industrial Revolution“finding out the effect of using AI on the accuracy and quality of strategic decision-making through primary and secondary research work methods. In the first stage of secondary research, the researchers collected huge data from independent studies, technical journals, and reliable data sources. Next, the results of the first phase were the basis for the authors ’work in the second phase of the study. In the initial research, the authors used the Delphi method to collect data by interviewing several experts and influencers in the field about their use of AI to make strategic decisions.
However, we believe that one of the weaknesses of this study is that the type and number of the sample were not explained. The results of the study showed that, only, 24% of managers of organizations are willing to use AI applications in order to support the efficiency of strategic decision-making. Most of these managers were from technical or banking companies, which justified their knowledge of the capabilities of AI, while the rest of the managers were found to have insufficient background on the capabilities of AI to support decision-making, especially the strategic ones.
More (2019) worked on “Disaster Management Using Artificial Intelligence” focused on the use of AI in managing crises and disasters and making decisions in times of crises that lead to great damage to the society and economic crises. In this study, AI can be used to analyze data that can be used to predict a future event, create awareness, and then make the decision for the situation. The results of the study questionnaires showed that 95% of the participants feel that AI can be used to manage crises and 80% of them feel that the impact of AI improves their lives for the better. On the other hand, we believe that the fundamental problem of this research is that the study was applied to a sample of less than 100 people, which prevents a conclusive generalization of its results. Hence, the study needs to be re-applied to a larger sample.
The exploratory study of Schmidt (2019) titled as “The Impact of Artificial Intelligence on Decision-Making in Venture Capital Firms” examined the employment of AI in the decision-making process in venture capital. Venture investors have to make decisions under uncertainty, time pressure and suffering from self-decisions. This study examines the potential of AI to overcome these challenges and improve the process. The results are based on a qualitative analysis based on 12 interviews with venture investors, AI experts, and companies providing venture capital solutions, as well as secondary data in the form of academic articles and online journals. The results reveal things. Fist, the AI is actually implemented and the interviews show that AI can be implemented at every step of the decision-making process, especially at the beginning of the decision-making process. Second, the use of AI improves the decision-making process by reducing uncertainty and bias and increasing productivity and efficiency. Third, the results determine use cases, implementation challenges and usage implications. Last, the results also show that the venture investors were able to make more accurate and better decisions using AI, which positively affected their portfolios.
Earlier, Liao et al (2013) published a work, “Applying Artificial Intelligence Technology to Support Decision-Making In Nursing: A case study in Taiwan” which aimed at identifying the effect of using an AI system on the ability to make decisions, solve problems and diagnose patients, on a sample consisting of Nurses inside a Taiwanese hospital. After the system implementation, the results were that the accuracy and efficiency of decision-making and problem solving were of a higher degree and in a less time, compared to the conditions before the application of the artificial system. However, the compatibility rate between the nurses’ diagnosis and the system diagnosis was only 87%. It is worth mentioning, this study used an AI system based on back-propagation neural networks, data mining tools, and statistical analysis.
Similarly Eletter et al (2010) through their “Neuro-Based Artificial Intelligence Model for Loan Decisions” description, aimed at designing a tool to support decisions related to classifying loan applications submitted by clients into good or bad in Jordanian commercial banks. This study developed a proposed model that uses an artificial neural network as an enabler to evaluate loan and credit applications. The model used a multi-layered neural network containing a back-propagation learning algorithm to build the proposed model. This network, by its adaptive nature, can implement the new data without reprocessing the old data. After the experimental application of the proposed model, the results indicated that artificial neural networks are a successful technology that can be used to efficiently evaluate loan applications and make sensitive decisions related to them. It is worth noting that researchers have had difficulty identifying the variables that affect approval of the loan decision.
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
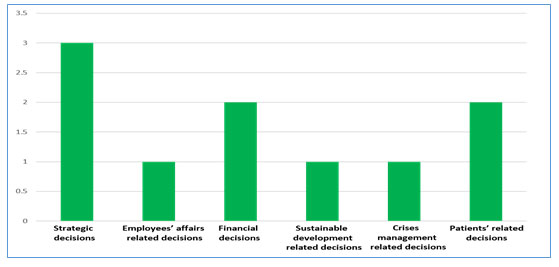
Through reviewing of previous studies, the researchers reached many aspects and results, the most important of which are: Previous studies have shown the possibility of using AI in different types of decisions. We found that some studies have used AI on strategic decisions such as the work of (Stone et al. ,2020), (Vedamuth, 2020), (Chernov, Chernova, & Komarova,2019). Other studies have benefited from it in decisions related to sustainable development like study (How, et al 2020) as well as the possibility of using it on financial decisions such as : ( Schmidt, 2019) and (Eletter et al 2020). In addition to decisions related to patients such as the work of Liao, Hsu, Chu, (2013) and (Pourhomayoun, Shakibi, 2020). Moreover, some studies have shown the possibility of using it in employees’ or personnel affairs related decisions such as study (Langer, Konigm Busch, 2020). As for the work of More, (2019) it clarified the possibility of using AI in decisions made in times of disasters and crisis as illustrated in the following figure(1):
Figure 1: Types of decisions in current study
Some previous studies have showed some difficulties that may face organizations during the applications of AI in decision-making processes. For instance, (Stone et al, 2020) found difficulty in the field of AI related to strategic marketing decisions for several reasons including the fact that it is a commercial field containing sensitive data for organizations, also companies that have had successful experiences do not want to share their experiences with others so that competitors will not benefit from them. Bejger amd Elster, (2020) found that AI models still need some regulations and laws, and then convert them into action plans for decision-making practices, and there is still a need for more technical and practical tools to ensure confidence and transparency in the decision.
While How et al, (2020) have shown the difficulty of using AI lies in the inability of untrained employees, who are unable using the computer to deal with AI techniques. Bosco, (2020) also showed that the most important difficulties and challenges facing the use of AI in decision-making processes are challenges related to cybersecurity, customer data protection, and insufficient budgets. As for the work of (Chernov et al, 2019), the obstacle is the lack of knowledge of some managers of the capacities and capabilities of AI to support taking accurate decisions. Eletter et al (2020) faced the difficulty of identifying the variables that affect strategic decisions regarding loans.
The work of Schmidt, (2019) is considered one of the important studies as it focused on the importance of employing AI in the decision-making process in venture capital. Thus, risk investors have to make decisions in light of uncertainty, time pressure and suffering from self-decisions. The study found that AI is actually used in every step of the decision-making process, especially at the beginning, and that the use of AI improves the process of decisions making by reducing productivity and efficiency. The study also showed that the risk investors were able to make more accurate and better decisions using AI, so this positively affected their portfolios. uncertainty and bias and increasing.
Some previous studies have suggested models, methods, algorithms and types of AI to aid in the decision-making process, including: Bejger and Elster, (2020) proposed fundamental modifications to the famous standard CRISP DM process model – which is considered one of the practical tools for machine learning and data mining – in order to enhance the transparency of its work, by enriching it with several regulations, laws and guidelines. As well, the study suggested technical and formal tools to enhance confidence and transparency in AI models including the “Anchors” method or tool that can support AI models to make it more accurate, reliable and transparent, especially with regard to economic decisions.
As for study of How et al (2020), it illustrated a method for using artificial intelligence. Where the researcher used a “human-centric probabilistic reasoning approach”, which is the Bayesian Network (BN). This has benefited people who do not have the talent and the experience of using computers in their harnessing of AI to analyze environmental performance indicators (EPI) data related to sustainability. Pourhomayoun and Shakibi, (2020) designed and developed a predictive model relies on AI and machine learning algorithms and techniques including Support Vector Machine, Artificial Neural Networks, Random Forest, Decision Tree, Logistic Regression, and K-Nearest Neighbor. All that, in order to develop an AI model to help hospitals and medical facilities identify who needs attention first, sort patients when the system is overcrowded, and eliminate delays in providing needed care.
Recently Eletter et al, (2020) have designed a tool to support decisions related to classifying loan applications submitted by clients into good or bad in Jordanian commercial banks by developing a proposed model that uses the artificial neural network- the MLFF network- as an enabler to evaluate loan and credit applications. A multi-layered neural network was used to build the proposed model, and this network, by its adaptive nature, can implement the new data without reprocessing the old data. Liao et al, (2013) used an AI system based on neural networks and compared the results of the pre- and post-experience of the studied system that used fuzzy inference system, which based on an adaptive network and back-propagation neural network..
Both Eletter et al (2020) and Liao et al (2013) have used machine-learning algorithms based on back-propagation neural networks and adaptive networks, whereas Vedamuthu, (2020) developed a decision model based on flowcharts with the aim of codifying the process of using AI in strategic decisions. It can be illustrated as follows in figure (2):
Figure 2: The process of using AI in strategic decisions and the flowchart (Vedamuthu, 2020)
The work of Schmidt, (2019) is considered one of the important studies as it focused on the importance of employing AI in the decision-making process in venture capital. Thus, risk investors have to make decisions in light of uncertainty, time pressure and suffering from self-decisions. The study found that AI is actually used in every step of the decision-making process, especially at the beginning, and that the use of AI improves the process of decisions making by reducing uncertainty and bias and increasing productivity and efficiency. The study also showed that the risk investors were able to make more accurate and better decisions using AI, so this positively affected their portfolios.
Langer et al (2020) depicted the effect of using AI in supporting decisions related to personnel affairs, was unique among the rest of the studies by the abundance of its hypotheses subject to the experimental laboratory study to ensure the accuracy of the results, which amount to six hypotheses. The researchers applied this study to a random sample of three Groups of personnel specialists who were subjected to five rounds of personnel selection processes. The first group received an evaluation of job applicants with the help of an automated support system before the participants processed the applicants’ information personally (pre-processing support group). The second group obtained an evaluation of the applicants with the help of an automated support system after they processed the applicant information personally (post-processing support group). The third group did not receive any automatic support in the assessment (no support group).
The results showed that satisfaction with the decision was higher for the post-treatment support group, i.e. the second group. Moreover, participants in this group showed a sharp increase in self-efficacy in employee selection compared to the other groups. However, the researchers of current study see that the weakness of this study is in the fact that this experiment was not completely real, but rather a simulation, as the participants were not managers but rather people interested in the field of personnel affairs, and that the applicants ’applications for employment and employment processes were not real.
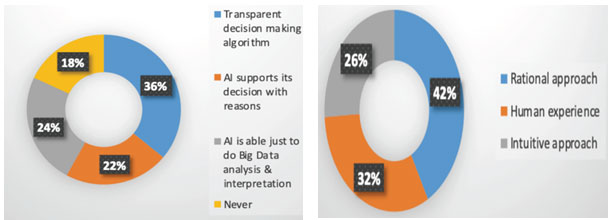
The paper of Pourhomayoun and Shakibi, (2020) is the only study that used a technical tool to verify the efficiency and effectiveness of the proposed AI model in study, the tool is the Confusion matrix. Bosco, (2020) agreed with study of Schmidt (2019) that the use of AI in the decision-making processes of organizations helps in facilitating and improving the accuracy of decision-making and reducing uncertainty, as it contributes to raising efficiency, increasing productivity and profits, and reducing costs. The study of Chernov et al, (2019) was distinguished by containing important statistics, as shown in the next figures, (figure3 and 4):
Figures ( 3 and 4), from study (Chernov et al, 2019, 24), show the statistics on the answers of the study participants
Figure 3 illustrates managers’ responses regarding the conditions under which they are willing to transfer strategic decision-making to AI. Where 22% of them refused to use AI -categorically-in all circumstances, maybe because they do not believe in AI abilities. As for the rest, which is 78%, they agreed to use artificial intelligence in only three cases, namely: If AI technology has algorithms that help in the transparency of decisions, if the AI technology able to provide reasons to the decisions or in the case of big data analysis and interpretation.
So, the previous study considered this approach to be the correct approach -to some extent- for many reasons, because the strategic decision-making process within artificial intelligence depends – only – on a rational approach, but skills such as abstract thinking, intuition and context analysis are not available for the smart machine. Where abstract thinking helps a person to work on different concepts basis. Context analysis helps the human to make strategic decisions when he has a lack of information or in conditions of asymmetry of this information. Intuition is the ability to make decisions without thinking logically or using logic, but using a combination of emotions, feelings and past experience.
According to Figure 4, 26% of managers use intuitive methods, 42% of them use rational methods, and 32% of them use personal experiences, in the strategic decision-making process. Thus, combining both approaches – rational and intuitive – appears to be the most effective method of strategic decision-making. Where with such a combined method, the intuitive decision is verified by a rational approach, and is adjusted if necessary. Therefore, the most effective method for the strategic decision-making process- based on the previous study- can be considered the cooperation of man and artificial intelligence, so that the person uses an intuitive approach to make a strategic decision, and then uses the rational approach that uses artificial intelligence.
The results of the study have showed the following: The previous studies have been applied to various types of organizations, such as administrative, financial, health, and environmental organizations etc. Most of the previous research has shown that the use of AI techniques positively affects the accuracy and the quality of decision-making in the various types of these organizations.
- The studies showed the possibility of using AI in different types of decisions, such as financial, strategic, personnel, patients-related, disaster management and sustainable development decisions.
- The most important and well-known mentioned techniques and algorithms of AI that can be used to improve the quality of decision-making are Support Vector Machine, artificial neural networks, back-propagation neural networks, Adaptive Network, Bayesian Network, fuzzy inference system, Random Forest, Decision Tree, Logistic Regression, and K-Nearest Neighbor.
- Based on study (Vedamuthm 2020), it is possible to use AI applications in decision-making processes when the following conditions are met:
- The presence of complex decisions, adequate reliable applicable data, quantifiable or measurable elements within decisions, and when the decision support is needed before the response is needed.
- There are technical tools to verify the efficiency and effectiveness of the proposed AI models such as the Confusion matrix.
- The researchers noticed – through a review of previous studies – several gaps. First, the related studies concerned with researching the subject of this study, which is the effect of applying AI techniques on the quality of the decision, are considered very few. Second, some previous studies were not clear in their methodology. Some of them did not adopt large and sufficient samples during the experiment, or did not explain the nature and characteristics of these samples such as (Vedamuthu,2020), (More, 2019), (Bosco, 2020), (Schmidt, 2019), (Liao et al,2013) (Eletter et al, 2020) and (Chernov et al, 2019)
All previous studies agree with the current study in that they all aim at knowing the effect of applying AI techniques on the quality of decision-making. The current study differs from previous studies in that it seeks to know the effect of applying AI on the quality of decision-making for different types and forms of organizations and decisions, and therefore it is not restricted to one type of organizations or decisions like the previous studies. The current study also differs in that it makes an inventory of the most important technologies, algorithms and models of AI that contribute in efficient and high-quality decision-making within organizations.
CONCLUSION AND RECOMMENDATIONS
Depending on the above findings, the researchers reached the following recommendations:-The necessity of designing models and action plans regarding employing AI in decision-making, in order to facilitate implementation and work on them, and to facilitate understanding and analysis of their results.- The need to conduct more experimental and exploratory studies on the impact of applying AI on the quality of decision-making within organizations, especially in the Arab countries. Because the researchers found that, these studies within the Arab geographical area are rare.- The necessity of conducting experimental studies regarding employing AI in decision-making. The same applies to other forms of institutions, organizations – and the decisions related to them – that have not been considered in these studies like agricultural, educational, and commercial organizations, customer service centers and factories … etc.- The necessity to hold local and international conferences and seminars in sufficient and periodic manner in order to introduce the novelties and developments in this field.
REFERENCES
Al-Assaf, Saleh Hamad. (2006). Introduction to research in the behavioral sciences. Riyadh: Obeikan Library.
Bosco, M. V., (2020). A Study on Artificial Intelligence Interaction with Organizational Performance. International Journal of Research in Engineering, Science and Management, 3 (2). Available at:
https://www.ijresm.com/Vol.3_2020/Vol3_Iss2_February20/IJRESM_V3_I2_130.pdf
Bejger, S., and Elster, S. (2020). Artificial Intelligence in economic decision making: how to assure a trust ?. Ekonomia i Prawo. Economics and Law, 19 (3), pp.411-434. Available at:
https://apcz.umk.pl/czasopisma/index.php/EiP/article/view/EiP.2020.028
Chernov, A. V. Chernova, V. A., and Komarova, T. V. (2019). The Usage of Artificial Intelligence in Strategic Decision Making in Terms of Fourth Industrial Revolution. In 1st International Conference on Emerging Trends and Challenges in the Management Theory and Practice, pp. 22-25.
Eletter, S. F., Yaseen, S. G., and Elrefae, G. A. (2020). Neuro-Based Artificial Intelligence Model for Loan Decisions. American Journal of Economics and Business Administration, 2 (1), pp.27-34. Available at: https://cutt.us/TnSFb
Este, D., Graham, S., Nguyen, T., Depp, C., Lee, E., and Kim, H. (2020). Beyond artificial intelligence: Exploring artificial wisdom. International Psychogeriatrics, 32(8), pp.993-1001. doi:10.1017/S1041610220000927
How, M. L., Cheah, S. M., Chan, Y. J., Khor, A. C., and Say, E. M. P. (2020). Artificial Intelligence-Enhanced Decision Support for Informing Global Sustainable Development: A human-centric AI-thinking approach. Information, 11,39. doi:10.3390/info11010039
Jabbari, Latifa., (2016). Methods of Decision Making Using Artificial Intelligence: A Comparative Study of Predicting the Electric Power of Tlemcen Province Using Artificial Neural Networks. Published PhD thesis, Faculty of Economics, Facilitation and Business Sciences, Abi Bakr Belkaid University, Algeria. Available on: http://dspace.univ-tlemcen.dz/handle/112/8806
Langer, M., Konig, C.J., and Busch, V. (2020). Changing the Means of Managerial Work: Effects of Automated Decision Support Systems on Personnel Selection Tasks. Journal of Business and Psychology, 1-19
Liao, P. H., Hsu, P. T., Chu, W., and Chu, W. C. (2013). Applying Artificial Intelligence Technology to Support Decision-Making in Nursing: A case study in Taiwan. Health informatics journal, 21 (2),pp. 137-148.
More. Y.M. (2019). Disaster Management Using Artificial Intelligence, Journal of Xi’an University of Architecture & Technology, X1 (X11), pp.1633-1637.
Pourhomayoun, M., and Shakibi, M. (2020). Predicting mortality risk in patients with COVID-19 using artificial intelligence to help medical decision-making. Available at: https://www.medrxiv.org/content/10.1101/2020.03.30.20047308v1.full.pdf+html
Schmidt, C.M. (2019). The Impact of Artificial Intelligence on Decision- Making in Venture Capital Firms. Doctoral dissertation, at the Universidade Catolica Portuguesa.
Stone, M., Aravopoulou, E., Ekinci, Y., Evans, G., Hobbs, M., Labib, A., and Machtynger, L. (2020). Artificial Intelligence (AI) in Strategic Marketing Decision-making: A research agenda.The Bottom Line.
33 (2), pp.183-200. DOI 10.1108/BL-03-2020-0022 Available at:
https://www.emerald.com/insight/content/doi/10.1108/BL-03-2020-0022/full/html
Vedamuthu, T. (2020). Artificial Intelligence and Human Collaboration in Project Decision-making. Doctoral dissertation, The College of St. Colatsica.