Department of English Language, College of Arts and Sciences, Rafha Male Campus, Northern Border University, Rafiha Kingdom of Saudi Arabia
Corresponding author email: hoppy4u@hotmail.com
Article Publishing History
Received: 18/10/2020
Accepted After Revision: 16/12/2020
Social media has definitely become an integral part of our lives especially among university students. This technology has a wide impressive effect on how people learn and communicate with each other. However, the application of social media to learning especially for English department Saudi university students, is not fully explored. Therefore, the current study aims at mapping whether social media affects students’ reading competence positively or negatively. The study also seeks to find out if there are any significant differences in the students’ competence in reading as a result of using social media with NBU students due to gender, social media, reading skills and geographical distribution. The current study used quantitative methods using a survey instrument to gather descriptive data regarding the perceptions of (n=900) randomly chosen Saudi university students. Questionnaires with Likert scale questions were used in the study. The questionnaire was divided into two main parts.
The first part began with two general questions about the number of years by which social media was used to perform general tasks and to perform specific English tasks. The second part was concerned with attitudes towards using social media, impact that social media has on reading competence. The data was analyzed using the Statistical Package for Social Sciences (SPSS) to obtain accurate results. Analysis of the collected data showed that the majority of the participants believed strongly in the pedagogical values and benefits of using social media as an ELT tool in their classrooms especially in improving reading skills. The findings also indicate that social networking websites and applications (e.g.Facebook, Youtube , Twitter, Skype) have a positive impact on learning English as a foreign language.
Social Media, English Reading Skills, University Students
Al-Mukhallafi T. R. The Influence of Social Media on Developing English Reading Skills of Saudi Universities Students. Biosc.Biotech.Res.Comm. 2020;13(4).
Al-Mukhallafi T. R. The Influence of Social Media on Developing English Reading Skills of Saudi Universities Students. Biosc.Biotech.Res.Comm. 2020;13(4). Available from: <a href=”https://bit.ly/2Wa20Jr”>https://bit.ly/2Wa20Jr</a>
Copyright © This is an Open Access Article distributed under the Terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC-BY). https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/, which permits unrestricted use distribution and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and sources are credited.
INTRODUCTION
Nowadays, the internet has become one of the most powerful avenues for disseminating information. The everyday use of the internet has played a major role in the improvement of students’ English language and has brought about significant changes in the way students find, manage and use information. The internet has been designed to meet an array of quite different purposes, some of which are certainly educational (AlQahtani,2018).
The social media include Facebook, Instagram, Twitter, Snapchat, and Whatsapp, etc. It facilitates learners easy to access at any time at any place. The rapid use of social media applications has become an order of the day for numerous purposes. The new users and apps emerge every day across the region enable one and all to express personal views, ideas, opinions, share research/educational projects, blogs writing, social networking sites, and cyber virtual space. The social media has a few well-established applications of social media. These apps are gaining a lot of interest among Saudi learners in academics alike, which exhibits interest to fetch constructive results using these apps (Sharma,2019).
Reading has been a great source of information and knowledge at all the times and in all ages. Reading is one of the oldest cultures for human progress in society. The ability to read and write is highly valued and essential for social, cultural and economic advancement. The regular and systematic reading develops the cognitive ability and improves communication skills. Reading habit is the most fundamental skill that is necessary for the success not only for academic purpose but for all walks of life . As Many studies (Junco et al., 2011; Madge et al., 2009; Olutola et al., 2016) reported that positive use of social media improved the reading habits and academic performance of students. On the other hand, Shabir et al. (2014) and Lubis et al. (2012) found that there was no significant relationship between the use of social media and academic performance (Rafiq etal.,2019). Therefore, this paper aims to investigate the ways in which social media can improve reading skills among Saudi university students.
Study questions: This paper seeks to answer the following questions:
- What is the effect of using social media on Northern Border University students’ reading proficiency?
- Does gender affect English language learning and is reading improved by the use of social media?
- Does the geographical location (distribution) of NBU among other Saudi universities make a difference in improving reading via social media?
- What are the constraints that students face when using social media to improve reading proficiency?
Objective of the study: The present study aims at Mapping whether social media affects students’ reading competence positively or negatively,addition to find out if there are any significant differences in the students’ competence in reading as a result of using social media with Northern Border University students due to gender, social media, reading skills and geographical distribution / location.
Research design: This study used a questionnaire to collect data. The study used Likert scale statements where each statement had five Likert-type items from which participants could choose.. The questionnaire was divided into two main parts. The first part started with two general questions about the number of years in which social media had been used in general and the number of years in which social media had been used to perform some tasks in English. The second part was comprised of three main components. The first component was concerned with aattitudes towards using social media as a tool for reading in the English language. The second component addressed the specific impact that social media has on reading competence. The third component focused on the effect of social media on reading proficiency in respect to gender and location. The data was analyzed using the Statistical Package for Social Sciences (SPSS) to obtain precise results.
Participants:The sample for the study were randomly selected by using a systematic sampling method consisted of nine hundred students who studied in the English department in the first year in the first semester of the 2019 academic year at Northern Border University in Saudi Arabia.
Definition of terms: Reading is the process of looking at a series of written symbols and deducing their meaning. It is a receptive skill through which we receive information. It requires a level of skill in speaking, so that the read words can be pronounced. There are four types or skills in reading as follows:
- Intensive
- Skimming
- Scanning
- Extensive
Reading is defined as a cognitive process that involves decoding symbols to arrive at meaning. Reading is an active process of constructing the meaning of words. Reading with a purpose helps the reader to direct information towards a goal and focuses their attention. Although the reasons for reading may vary, the main purpose of reading is to understand the text. Reading is a thinking process. It allows the reader to use what he or she may already know, also called prior knowledge. During this process of acquiring information, readers use strategies to understand what they are reading, use themes to organize ideas, and use textual clues to find the meanings of new words. (https:llstudy.com).
According to Crutis and Kruidenier (2005) Reading comprehension is the process of constructing meaning from what is read. To comprehend, a reader must decode words and associate them with their meanings.
Social media:Social media consists of online communication channels dedicated to community based input, interaction, content sharing and collaboration. Websites and applications dedicated to forums, micro blogging, social networking, social curation and wikis are among the different types of social media (https:llwhatis.techtarget.com).
Importance of the study : Reading activity is the foundation of learning new knowledge and gaining new skills, and comprehension is at the heart of reading (Chen, Teng, Lee, and Kinshuck, 2011). Research on reading found that skilled readers focus on reading as a process of gaining meaning, as opposed to readers who focus on reading as a decoding process, which makes them unsuccessful or unskilled readers (Baker and Brown 1984). Decoding is turning the written word into its spoken and known equivalent while comprehension is the construction of meaning (Nation, 2008). When a reader uses too much of his/ her cognitive resources to decode, insufficient cognitive resources will be available to understand and make sense of what is read (Rasinski and Hoffman, 2003). Roberts (2011) claimed that too much time and energy spent decoding text leaves little time and energy for constructing meaning. Positively speaking, Rasinski (2012) added that with practice the lower level processes can become automatic which means a reader no longer needs to apply conscious attention to decoding and thus can become a fluent reader. In the context of reading, such technology provides a way to communicate actively, allowing students to have discussions both inside and outside the classroom. Learning is considered a social process that can be enhanced through dialogue.
Almarwany (2017) showed that in recent years social media such as Facebook, Twitter and other forms are considered useful tools for social interaction, communication and sharing information. Most scholars state that students use social media to support their emotions, to express themselves freely, and enhance their social life. Many researchers have shown the positive effects of using social media in learning English as a foreign language. When students are free to express themselves at a time and place that suits them, they can express themselves using language fluently, as a lot of students may be shy when using English as a foreign language. So with social media, they can read, write and speak without being afraid of making mistakes.
Looi (2011) stated that from a social constructivist point of view, reading is considered to be a social practice. The rise of web 2.0 tools such as blogs, wikis, and social networking sites, has provided a wide range of opportunities to create active interactions among learners inside and outside the school. In the past, students were merely receptive learners of knowledge, but nowadays, students are encouraged to be active members in a learning society. They are active constructors of their own learning environment and no longer learn in isolation. This study suggests that social media can be of great use. For example, Edmodo can be useful in improving reading comprehension among adult learners of English as a foreign language. This is due to learners’ positive perceptions and attitudes, the likelihood of improved performance, and opportunities for participation in the learning community. It also showed the necessity of integrating social media in teaching and learning. This can greatly enhance the learning of reading and writing in an interesting way.
Manca and Ranieri’s study (2016) aimed at identifying the uses of social media in university teaching practices. The study conducted a survey in which participants were asked to identify rate of use, motivations, teaching practices and difficulties related to the use of a number of social network sites (Twitter, Facebook), professional and academic networking services (LinkedIn, ResearchGate and Academia.edu), tools for writing and comment (blogs, wikis) and to archive and retrieve content material for lectures and group work (podcasts, YouTube and Vimeo, SlideShare). Data analysis was used to test those socio-demographic variables that most affected frequency of use, and the relationships between motivations, ways of use, obstacles to use and scientific discipline. The results showed that social media use is still rather limited and restricted in scope and that academics are not greatly motivated to integrate these devices into their practices. There are several reasons for this, such as cultural resistance, pedagogical issues and/or institutional constraints. Overall, the results stress ambivalent attitudes towards the benefits and challenges of social media in the context of higher education with obstacles prevailing over advantages.
Narayan and Sunath’s study (2016) examined the effect of media, especially print and social media, on teaching English. With the advent of computers there is more emphasis given to American English and a range of spelling is accepted. The importance of spoken style, grammar and syntax is slowly gaining credence but the convenience of auto spell check has affected the ability of students to spell correctly while some students have become totally dependent on the auto-editing mode.
The arrival of social media such as Facebook and Whatsapp has resulted in the overuse of shortened expressions. However, knowledge of these abbreviations seems to be the need of the hour and people who cannot master the art appear to be out of place. It is exactly here that English teachers can step in and help strike a balance between the younger generation and the older generation who are less proficient in social media.
Allam and Elyas’s study (2016) is based on quantitative methods using a survey instrument to gather descriptive data regarding the perceptions of 75 randomly chosen English as a Foreign Language (EFL) teachers at two Saudi tertiary institutions. The study used 14 Likert scale statements where each statement had five Likert-type items for the participants to choose from. Analysis of the collected data showed that the majority of the participants believed strongly in the pedagogical values and benefits of using social media as an ELT tool in their classrooms. However, the majority expressed reservations with regard to the extent to which social media should be freely used in the EFL classroom where they recognize it as having a dual effect. The study recommended more research studies in this area so as to closely understand how experienced EFL teachers utilize social media in their classes in order to develop best practices for implementing social media in teaching and learning in EFL in the Saudi context.
Sitthirak’s study (2013) investigated how social media has influenced teaching and learning English at present. Social media has been incorporated into an informal education system for decades; i.e. teleconferencing and distance learning before it developed into a more sophisticated system. However, there is still controversy over using new social media such as Facebook or WebChat with conflicting discussions among multiple studies. Ultimately the roles of teachers and learners must be reconsidered along with their affective and attitudinal effects on social media when used for educational purposes, since it will be or is now inescapably integrated into our daily lives.
Alsulami’s study (2016) investigated how technology affected learning English as a foreign language among female EFL students at Effatt College. Questionnaires designed with Likert scale questions were used in the study that was divided into two parts. The first part started with two general questions about age and educational level. The second part included four specific questions about technological tools that could enhance learning the English language. The sample consisted of 36 participants. The data was analyzed using the Statistical Package for Social Sciences (SPSS) to obtain precise results. The findings clearly indicated that computer software, social networking websites, online videos, audio tools (i.e., YouTube, Skype, MP3 players), and smart phone and tablet apps have a positive impact on learning English as a foreign language. Thus, technological tools can clearly be effective in improving the students’ language and communication skills.
Monica and Anamaria’s study (2014) aimed at investigating the impact of computers and social media on improving students’ knowledge of English language especially vocabulary acquisition (focusing on Facebook) with intermediate and upper intermediate first and second year ELT students in Economics at the Faculty of Economic Sciences, University of Oradea. The study was conducted with 127 students of the Faculty of Economic Sciences, University of Oradea, 1st and 2nd year students following specializations in International Business, Management, Marketing, Finances who were studying in the academic year 2013-2014. The development of each group was measured and clearly demonstrated a more significant improvement in vocabulary knowledge among the group exposed to Facebook. Such an innovative study is rare as there are few studies exploring the value Facebook can add to learning in Romania. The results of the study did not support the assumption that the experimental group would outperform the control group, as the differences between the two groups were not particularly significant. However, there was an improvement in both of the groups from pre-test to post-test scores.
Alfahadi’s (2017) study examined how social media sites can develop English language skills among Tabuk University students and to determine the most commonly used social media by the learners in order to practice English language skills. The researcher concluded that social media sites can be integrated in the EFL syllabi as teaching and learning aids because they contain a broad combination of sound, text and videos where students can express their viewpoints and receive direct remedial feedback. The study also found that You Tube is the most common social media site used by students at Tabuk University to practice English Language.
Suswati and Saleh’s study (2019) investigated social media to assess EFL students at the State University of Medan (UNIMED) in their second semester English educational program. This research concentrated on how social media influences students’ writing skills. The problems included how it influenced their ability to develop their ideas in writing; develop reading and writing materials; and change students’ opinions on social media in writing class. The questionnaire was designed to gather the students’ thoughts on social media matters, their intention to use social media for study, particularly in reading and writing topics and the influence of social media on their ability to develop an idea in writing class. The instruments used in this research were social media such as Facebook, WhatsApp and Instagram as texts in reading and writing class. The sample consisted of 80 students from two classes in the English educational program. Data was analyzed using the Research & Development Method (R&D) and the Linkert Scale to ascertain the percentage of students’ perception. The findings of this paper indicated that students enjoy and engage in writing class more when using social media for their assessments, as well as using social media to develop ideas and be more creative in writing skills.
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Data Analysis: This section presents the results of the study. To analyse data, the SPSS program was conducted as shown in the tables and diagrams below to process the data yield including chi-squared analyses.
The First Part:
Table 1. Frequency and percent of male and female respondents
| Frequency | Percent | |
| Male | 120 | 50.0 |
| Female | 120 | 50.0 |
| Total | 240 | 100.0 |
Table (1) shows that both males and females responded equally to the questionnaire. This indicates that they were both interested in sharing their experience using social media in learning.
Table 2. what is the social media most used by you
| Frequency | Percent | ||||
| You Tube | 90 | 37.5 | |||
| 20 | 8.3 | ||||
| 10 | 4.2 | ||||
| Snap chat | 120 | 50.0 | |||
| Total | 240 | 100.0 | |||
Table (2) above shows that the social media most commonly used in the study area are: Snap chat 50%, You Tube 37.5%, Instagram 8.3% and Twitter 4.2%.
Table 3. Years of using social media
| Frequency | Percent | ||
| Valid | Less than 3 years | 30 | 12.5 |
| 3-5 years | 172 | 71.7 | |
| more than 7 years | 38 | 15.8 | |
| Total | 240 | 100.0 | |
Table (3) shows that 71.7% of the students used social media for 3-5 years.
Table 4. Years of using social media to perform some tasks in English
| Frequency | Percent | ||
| Valid | Less than 3 years | 138 | 57.5 |
| 3-5 years | 52 | 21.7 | |
| more than 7 years | 50 | 20.8 | |
| Total | 240 | 100.0 | |
Table (4) shows that 57.5% of respondents used social media to perform tasks in English for less than 3 years.
The Second Part: This part consists of the questionnaire items, which are classified into three components
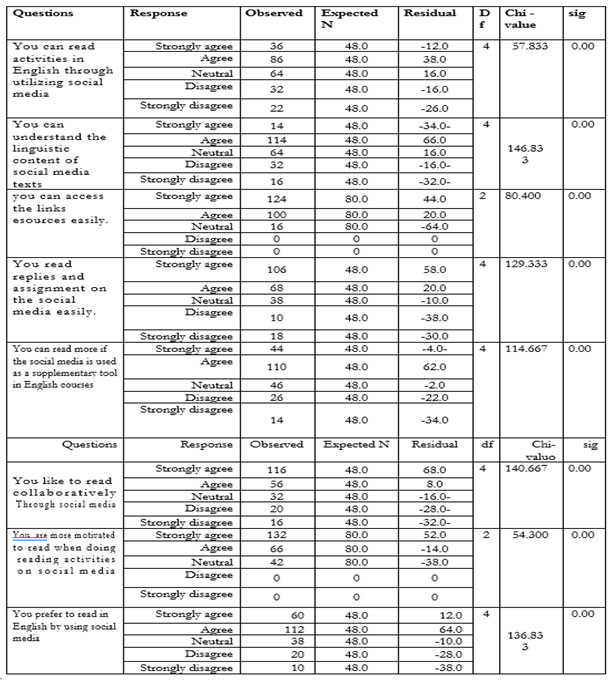
Table 6. Attitudes towards using social media as a tool for reading in the English language
Table (7) shows that most of the responses tend to agree with the items. The following information is evident: 86 of the sample agreed that they can read activities in English through utilizing social media. 114 of them agreed that they can understand the linguistic content of social media texts. In addition, 124 of the sample strongly agreed that they can access the resource links easily. Also, 106 of the respondents strongly agreed that they understood replies and assignments on social media easily. Of the respondents 110 read more if social media is used as a supplementary tool in English courses. It was agreed by 116 agreed that they liked to read collaboratively through social media while 123 respondents strongly agreed that they are more motivated to read when doing reading activities on social media and 112 agreed with a high level of statistical significance (sig less than 0.05) that they preferred to read in English by using social media.
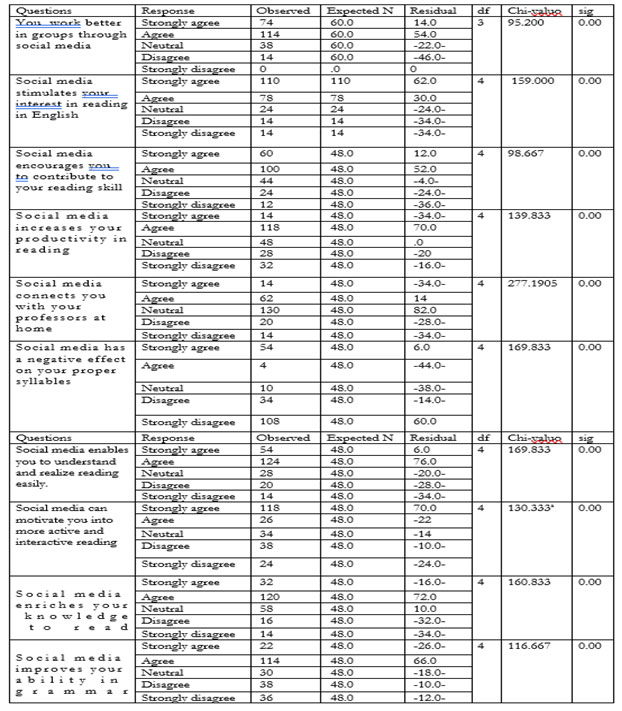
Table 7. Impact that social media has on reading competence
Table (7) shows that there is a very substantial trend towards agreement on the items, with a high level of statistical significance. Among the respondents 114 agreed that they work better in groups through social media and 110 strongly agreed that social media stimulates their interest in reading in English. One hundred of the respondents agreed that social media encouraged them to contribute to their reading skills.1 One hundred and eighteen respondents agreed that social media increased their productivity in reading. Also 130 agreed that social media connected them with their professors at home. One hundred and thirty respondents had neutral responses to social media as a means to connect with their professors at home while 108 strongly disagreed that social media had a negative effect on their proper syllables. One hundred and twenty-four agreed that social media enabled them to understand and realize reading easily. One hundred and eighteen respondents strongly agreed that social media could motivate them into more active and interactive reading, and 120 agreed that social media enriched their reading knowledge. Also social media improved their ability in grammar, with a high level of statistical significance (sig less than 0.05) which means social media had a positive impact on reading competence in the study area.
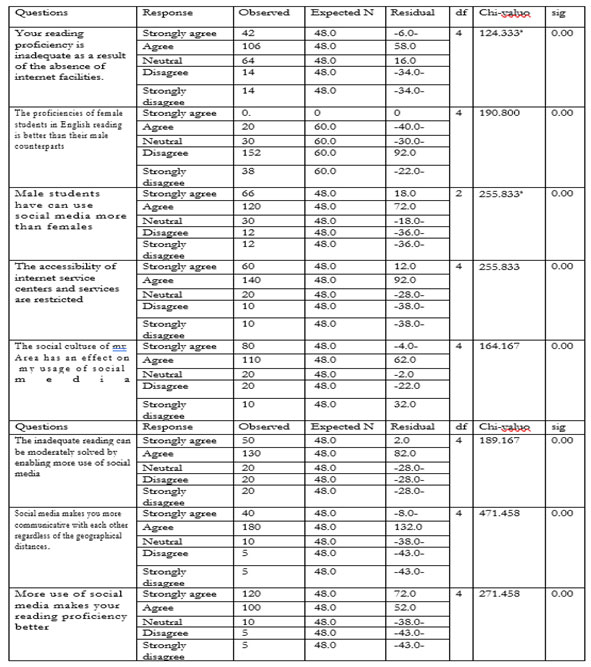
Table 8. The effect of social media on the reading proficiency
Table (8) shows the effect of social media on the reading proficiency with respect to gender and location. It seems that most of the responses tended to agree to items with the following information being evident: 106 of the sample agreed that their reading proficiency was inadequate as a result of the absence of internet facilities, but 152 disagreed that female students were more proficient in English reading than their male counterparts. In addition, 120 agreed that male students could use social media more than females. Of the sample, 140 agreed that access to Internet service centers and services was restricted. One hundred and ten of the sample agreed that the social culture of their area had an effect on their usage of social media. Within the sample 110-130 agreed that inadequate reading can be moderately solved by enabling more use of social media, while 180 of the sample agreed that social media made them more communicative with each other regardless of geographical distance. Also 120 of the sample strongly agreed that greater use of social media improved reading proficiency with a high level of statistical significance (sig less than 0.05).
From the above analysis and discussion, the results revealed that the most university students use social media in their area of study (You Tube, Snap chat, Instagram and Twitter), the most students had used social media for 3-5 years but they had used it to do some tasks using English language for less than 3 years, most of the students in the study area can read activities in English by utilizing social media. They can also understand the linguistic content of social media texts. In addition they are able to access the links resources, Most students in the study read more if social media was used as a supplementary tool in English courses, Most students in the study enjoyed reading collaboratively through social media, Respondents confirmed that they are more motivated to read when doing reading activities on social media and they preferred to use social media to read in English, Social media encouraged the students in the area of study to improve their reading skills and also increased the amount they read, social media had a positive effect on their correct use of syllables, and social media enriched the reading knowledge of the students in the area of the study knowledge and also improved their ability in grammar.
Also , the results indicated that social media had a positive impact on reading competence in the study area with a high level of statistical significance (sig less than 0.05), university students in the study area considered that their reading proficiency was inadequate as a result of the absence of Internet facilities, respondents emphasized that the proficiency of female students in reading English was not superior to their male counterparts, university students in the study area considered that male students used social media more than females, the social culture of the study area had no effect on students’ usage of social media, inadequate reading can be somewhat improved by enabling more use of social media, social media enables students to be more communicative with each other regardless of geographical distance, and greater use of social media improved reading proficiency of university students in the study area.
CONCLUSION
The study concluded that social media has a positive influence on learning reading English as a foreign language in Saudi universities. To achieve this objective, those who teach and those who learn English as a foreign language should be well trained in new technology. This will enable both to make efficient use of social media. The culture of using social media should spread throughout the learning community and environment. This will pave the way for learners of English as a foreign language to learn adequately and become self-learners.Curricula should be designed to cope with state of the art technology. It is necessary to apply this technology from primary education on, so that students will be well prepared and ready to use social media wisely in learning English as a foreign language. Ongoing training is very important to cope with state of the art technology, and exchange of experience is of utmost importance in this domain.
Recommendations: In light of the results of the study the recommendations are proposed that Lecturers are encouraged to use websites as a guide to obtaining scientific material and assignments, Lecturers are encouraged to use a range of social media to develop university students’ reading skills especially academic reading skills, Lecturers are invited to use social media technology to enhance other language skills inside and outside the classroom, Social media could be used as a powerful tool to meet different students’ interests and learning profiles. Thus students of the same learning profiles could be engaged in similar reading activities. Along the same vein, students with the same interests could be engaged in reading similar topics and further related discussions, and Lecturers should be required to provide positive guidance for their students on how to benefit from the available social media tools to improve their reading skills.
Ethical Clearance Statement: The Current Research Work Was Ethically Approved by the Institutional Review Board (IRB) of Northern Border University, Rafha Kingdom of Saudi Arabia.
Conflict of Interest: Authors declares no conflicts of interests to disclose.
REFERENCES
Alfahadi, A. M. A. (2017). The Role of Social Media Sites in the Enhancement of English Language Learning at the University of Tabuk. International Journal of English and Education, 6(3), 105-113.
Allam, M., & Elyas, T. (2016). Perceptions of Using Social Media as an ELT Tool among EFL Teachers in the Saudi Context. English Language Teaching, 9(7), 1-9.
Almarwacy, Alyaa Omar (2017). (networking sites in learning English language and students self-efficacy, US china education, Using social review, vol.7. this reference doesn’t make sense
AlQahtani, N. A. (2018). The Effect of Social Networks on the Improvement of Saudi EFL Students. Journal of humanities and Social Sciences, 2(8).
Alsulami, S. (2016). The effects of technology on learning English as a foreign language among female EFL students at Effatt College: An exploratory study. Studies in Literature and Language, 12(4), 1-16.
Baker, L and Brown, A (1984). Metacognitive skills and reading, Retrieved from www.scrip.com Books, Google.
Brien, Lynne (2012). Six ways to use social media in education. Retrieved from www.learninginnovation.duke.edu
Looi, C.Y., Yusop, F.D. (2001). Potential use of social networking tool to assist reading comprehension for practice and future research. Journal Pendidican, 31(1), 189-201.
Manca, S., & Ranieri, M. (2016). Facebook and the others. Potentials and obstacles of social media for teaching in higher education. Computers & Education, 95, 216-230.
Monica-Ariana, S., & Anamaria-Mirabela, P. (2014). the impact of social media on vocabulary learning case study -facebook. Annals of the University of Oradea, Economic Science Series, 23(2).
Narayanan, D. K., & Sunath, B. (2016). Influence of print, visual and social media in teaching english. TJGAJ Vol. 11 No. 1 JAN-2016, 1.
Nation, I. S. (2008). Teaching ESL/EFL reading and writing. Routledge.
Rafiq, M., Asim, A., Khan, M. T., & Arif, M. (2019). The Effects of Social Media on Reading Habits. Pakistan Journal of Information Management and Libraries, 21, 46-65.
Rasinski, T. (2012). Why reading fluency should be hot. Reading Teacher, 65(8), 516-522.
Rasinski, T., & Hoffman, J. (2003). Oral reading in the school literacy curriculum. Reading Research Quarterly, 38(4), 510-522.
Roberts, J. A. (2012). The effect of differentiated instruction and universally designed reading curriculum on English language arts achievement scores of at-risk students (Doctoral dissertation, Capella University).
Sharma, V. (2019). Saudi Students’ Perspective on Social Media Usage to Promote EFL Learning. Online Submission, 2(1), 129-139.
Siddiqui, S., & Singh, T. (2016). Social media its impact with positive and negative aspects. International Journal of Computer Applications Technology and Research, 5(2), 71-75.
Sitthirak, C. (2013). Social media for language teaching and learning. Recuperado de http://164.115, 22.
Suswati, R., & Saleh, S. (2019). The Use of Social Media in Designing The Writing Assessment for EFL Students. Journal of ELT Research, 26-34.