1 Candidate of Biological Sciences, Associate Professor of Physical Education and Sports Department at Peoples’ Friendship University of Russia. 117198, Moscow.
2Candidate of Medical Sciences, Associate Professor in Human Biology and Physiology Department, Moscow City Pedagogical University,
3Candidate of Biological Sciences, Associate Professor of the Department of physical culture for Humanities and Natural Sciences at North Caucasus Federal University, 355002, Stavropol, Pushkin street, d. 1., building 3,
4Associate Professor of Physical Education and Sports Department at Peoples’ Friendship University of Russia. 117198, Moscow, Miklukho-Maklaya str., 4. Tel. (495) 433 05 10.
5Senior lecturer of the Department of physical culture of the State University of Management, 109542, Moscow, Ryazan Avenue, d. 99,
6Teacher of the State budget educational institution of Moscow “School № 508”, 115404, Moscow, Elevator street, house 4, building 2
Corresponding author email: ea.milash@yandex.ru
Article Publishing History
Received: 13/10/2020
Accepted After Revision: 15/12/2020
According to various sources, 15–20% of the world territories, are the zones of ecological disaster, about 50% of the pop ulation live in environmentally unfriendly regions. Licorice medicinal plant with the scientific name of glycyrrhize globra is one of the medicinal plants used in cosmetics, food, health and pharmaceutical industries. The main aim of the study is to present the data on the correction of deviations concerning the adaptation system activity of 13-14-year-old adolescent bodies, exposed to chemical pollution of the environment by means of a phytoadaptogen based on licorice.According to the obtained data, they established the reduction of chemical, environmental pollution factor negative effect on the adolescent’s body: normalization of rhythm, blood pressure, heart rate, maximum oxygen consumption, and the adaptive potential of the circulatory system.The results of the study demonstrate that the use of licorice root extract as an adaptogen can help the normalization of blood pressure, heart rate, and variation range among 14-year old adolescents living in conditions of environmental chemical pollution. Besides, it can be concluded that licorice root extract is an positive natural adaptogen since it decreases the detrimental impact of chemical pollution factors on the adolescent body, and consequently results in relative normalization of blood pressure.
Adolescents, Adaptation Opportunities, Chemical Pollution Of The Environment, Phytoadaptogens, Photo Correction, Licorice.
Milashechkina E. A, Gernet I. N, Rezenkova O. V, Кunitsina E. A, Logachev N. V, Logachev A. V. Phytoadaptogen Effect Based on Licorice on Adolescent Body Adaptation Capabilities Living Under Conditions of Environment Chemical Pollution. Biosc.Biotech.Res.Comm. 2020;13(4).
Milashechkina E. A, Gernet I. N, Rezenkova O. V, Кunitsina E. A, Logachev N. V, Logachev A. V. Phytoadaptogen Effect Based on Licorice on Adolescent Body Adaptation Capabilities Living Under Conditions of Environment Chemical Pollution. Biosc.Biotech.Res.Comm. 2020;13(4). Available from: <a href=”https://bit.ly/2Ibbpxd”>https://bit.ly/2Ibbpxd</a>
Copyright © Milashechkina et al., This is an Open Access Article distributed under the Terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC-BY) https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/, which permits unrestricted use distribution and reproduction in any medium, provide the original author and source are credited.
INTRODUCTION
In recent decades, a large amount of scientific information has appeared about the influence of an unfriendly environment on the physical development and functional state of a child’s body (Agadzhanyan et al., 1993; Baevsky et al., 1987; Veltishchev and Fokeeva, 1996; Guminsky et al., 1990; Resenkova, 2003; Tolstikov et al., 1991; Ghorbanlou et al., 2020). The most acute issue is the need for effective measures aimed at body resistance increase in adverse environmental conditions. For many centuries, various medicinal substances have been used by medicine for the treatment and rehabilitation of humans. In recent years, some low-toxic biologically active herbal remedies are purposefully used in sports practice to accelerate recovery, actively replenish spent plastic and energy resources, and selectively control the most important functional systems of the body during heavy physical exercise (Brehman, 1969; Yermolova and Zimova, 2001; Kerimov and Kasumov, 1998; Resenkova, 2003; Sidorova et al., 2020).
Adaptogens are important among them. Adaptogens are the substances that have a general tonic effect on the body and increase its resistance during heavy physical exertion, under hypoxic conditions, and during drastic bioclimatic changes (Butova, 1999). Plant adaptogens can stimulate the nervous system and metabolic processes in the body moderately, which has a beneficial effect on the adaptation to physical exertion. Currently, herbal preparations based on licorice root are in the field of study by modern scientists (Brehman, 1969; Yermolova and Zimova, 2001; Resenkova, 2003; Streltsov, 2002). A number of authors indicate the presence of anti-toxic (Cekic et al., 2012; Milashechkina, 2005) and immunomodulating (Ishida and Sympos, 1983; Halberg, 1969; Singamaneni et al., 2020) properties of licorice root.
Therefore, the goal of our study is to evaluate the effect of the drug on the basis of licorice on the leading adaptation systems of the adolescent body living in conditions of chemical, environmental pollution.Belyaev(1969),Rezenkova(2002),Milashechkina (2003) studied the effect of licorice extract on the processes of the organism adaptation. The authors found that the licorice root has the obvious adaptogenic effect, which is reflected in the harmonization of the hormonal balance and, thus, the stimulation of adaptive responses to environmental factors. The confirmation is the increase of physical performance, the resistance to hypoxia and better results in the development of physical qualities – general physical endurance. Also, the licorice extract implements its adaptogenic properties by optimizing the functional state of the central nervous system, helping to balance excitatory and inhibitory processes and to improve its quantitative and qualitative characteristics (Sadek et al., 2020) These data gave rise to the use of licorice root extract as a stress-limiting agent among a group of 14-year-old teenagers, in which most of the indicators revealed the most significant negative changes.
MATERIAL AND METHODS
The influence of chemical, environmental factors on the body of adolescents was studied in natural experiment conditions. The participants of the study were 13-14-year-old adolescents, who were divided into the following groups: 1) control group (n=82; 42 boys and 40 girls ) which are living in the area without anthropogenic pressure; 2) test group (n =102; 61 boys and 41 girls) which are living in the conditions of environmental chemical pollution; 3) correctional group (n=37), with the use of licorice root extract – it consisted of 17 boys and 20 girls living in the conditions of environmental chemical pollution.
A phytoadaptogen, based on licorice extract, was given in the morning from 7.30 to 8.30 at the dose of 0.05 mg/kilogram of body weight (Resenkova, 2003). Also, to determine the adaptive capacity of the adolescent body, we used the indicators characterizing the state of regulatory mechanisms. The state of the respiratory system was determined by relative and absolute lung capacity (LC), chest excursion and maximal oxygen consumption (MOC) test, the state of the circulatory system and its regulatory mechanisms by cardiointervalography indices: HRV (heart rate variability), arterial pressure (AP), the adaptive capacity of the circulatory system and an individual minute duration.
The stress test recognized by the World Health Organization as an objective and informative indicator of the functional status of the cardiorespiratory system and the functionality of a person – the maximum oxygen consumption (MOC). According to the researchers, the indirect method for the determination of MOC was proposed by A.A. Guminsky (Dzhandarova et al., 2014). The evaluation of the test results was carried out according to the data presented in Table 1.
Table 1. Child physical performance assessment in terms of MOC/kg (A.A. Guminsky et al., 1990)
| Age, years | MOC, ml/min·kg | Evaluation | |
| Girls | Boys | ||
| 13 | 41,0
43,0 45,0 |
37,5
39,5 41,5 |
low
satisfactory high |
| 14 | 43,6
45,5 47,5 |
35,5
37,5 39,5 |
low
satisfactory high |
The adaptive potential of the circulatory system was determined by R.M. Baevsky’s method (Belyaev, 2002), adapted for the use on the child organism by P.A. Fileshy (Resenkova, 2003), the assessment was made in accordance with the data given in Table 2.
Table 2. Evaluation of organism functional capabilities according to the values of the circulatory system adaptive potential
| AP (in the cond. score) | Assessment of adaptation degree | Functionality level | Recommendations and activities |
| <1.60 | Satisfactory | Optimal | Therapeutic |
| 1.60-2.09 | Incomplete or partial | Sufficient | Therapeutic |
| 2.10-2.59 | Unstable | There is a risk of decline | Improving and preventive |
| 2.60-3.09 | Stress adaptation mechanisms | Reduction | Preventive and curative |
| >3.10 | Unsatisfactory, overstrain of adaptation mechanisms | A sharp decline | Medicinal |
The vital capacity of the lungs (VCL), expressed in litres, was measured using a spirograph. The subject drew the maximum inhale and then gradually exhaled the air through the mouthpiece into the spirograph. Cardio intervals were recorded and analyzed using the Varicard automated computer instrument. Statistical characteristics of the dynamic range of cardio intervals included: expectation (M), heart rate (HR) and standard deviation (s), expectation (M). The numerical characteristics of variational pulsograms along with indicators of statistical estimates were mode (Mo), variational span (Dx) and mode amplitude (АМо).
Individual minute (IM) was determined by F. Halberg’s method. According to the author method, the value of IM is a fairly informative test. The magnitude of myocardial infarction is a relatively stable indicator among healthy people. Mathematical-statistical processing of the survey results was carried out using Microsoft Excel software. The level of different significance for the studied parameters was determined using Student’s criterion. The results were considered statistically significant at p ≤ 0.05.
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
According to the data we obtained (Table 3), when you use a phytoadaptogen based on licorice VCL tends to increase among boys and girls, and SP has decreased significantly among boys (P<0,05), girls show the tendency of its decrease. This can be explained by the fact that the boys had more pronounced changes in blood pressure indicators as compared with girls, so they were also more sensitive to the effects of phytoadaptogen.
Table 3. The state of the cardiorespiratory system among 14-year-old adolescents living in a chemically contaminated area after photo correction
| Indicators | Control | Test | Р1 | Correctional group | Р2 | Р3 |
| Girls | ||||||
| VCL, l | 2,38±0,05 | 2,27±0,08 | >0,05 | 2,32±0,12 | >0,05 | >0,05 |
| SP, mm.m.col. | 99,29±1,70 | 109,70±1,70 | <0,01 | 109,29±4,90 | <0,05 | >0,05 |
| DP, mm.m.col. | 59,29±0,29 | 63,77±1,52 | <0,05 | 67,57±3,16 | <0,01 | <0,01 |
| HR,b/min | 81,77±3,01 | 92,2±3,63 | <0,05 | 85,81±4,36 | >0,05 | >0,05 |
| Boys | ||||||
| VCL, l | 3,34±0,05 | 2,29±0,15 | <0,001 | 2,32±0,16 | <0,001 | <0,001 |
| SP, mm.m.col. | 99,17±1,52 | 121,26±2,59 | <0,001 | 107,33±1,75 | <0,001 | <0,01 |
| DP, mm.m.col. | 57,92±0,52 | 76,6±1,34 | <0,001 | 66,33±5,50 | >0,05 | >0,05 |
| HR,b/min | 81,45±3,52 | 86,78±2,00 | >0,05 | 88,00±1,39 | >0,05 | >0,05 |
| Note: P1 – the reliability of differences in average values between the experimental and control groups; P2 – the reliability of differences in average values between the experimental and correction groups; P3 – the reliability of differences in average values between the control and correction groups. | ||||||
The intake of licorice root extract contributed to the normalization of the cardiovascular system functional capabilities (Table 4). The indicators of the expectation and heart rate variation decreased significantly among girls and boys, approaching the control group, as compared with the original (P>0.05).
Table 4. Heart rate variability among 14-year-old adolescents living in a chemically contaminated area, after photo correction
| Indicators | Control group | Test group | Р1 | Correction group | Р2 | Р3 |
| Girls | ||||||
| М, ms | 743±27,90 | 673,45±17,34 | <0,05 | 715,45±46,79 | >0,05 | >0,05 |
| MSD, ms | 58,33±5,89 | 76,82±4,66 | <0,05 | 66,45±9,50 | >0,05 | >0,05 |
| ΔХ, ms | 331,33±30,23 | 649,70±61,54 | <0,001 | 372,00±47,77 | <0,001 | >0,05 |
| Мо, ms | 716,67±33,22 | 647,73±18,84 | >0,05 | 704,55±58,74 | >0,05 | >0,05 |
| АМо, % | 36,83±3,40 | 36,25±2,19 | >0,05 | 34,00±2,84 | >0,05 | >0,05 |
| Boys | ||||||
| М, ms | 747±33,19 | 707,67±20,46 | >0,05 | 683,56±10,64 | >0,05 | >0,05 |
| MSD, ms | 64,82±12,56 | 68,99±3,40 | >0,05 | 66,44±10,53 | >0,05 | >0,05 |
| ΔХ, ms | 362,91±51,36 | 563,90±31,65 | <0,01 | 421,00±64,56 | <0,01 | >0,05 |
| Мо, ms | 731,81±42,80 | 673,91±19,05 | >0,05 | 683,33±17,54 | >0,05 | >0,05 |
| АМо, % | 35,36±4,19 | 36,10±1,62 | >0,05 | 35,44±2,92 | >0,05 | >0,05 |
| Note: P1 is the reliability of differences in average values between the experimental and control groups; P2 is the reliability of differences in average values between the experimental and correction groups; P3 is the reliability of differences in average values between the control and correction groups. | ||||||
Analyzing the indicators of IN before and after licorice extract application (Fig. 1), they revealed the increase of adolescent number with a state of vegetative balance, both among boys (66.77%) and among girls (45.45%), which indicates the “smoothing” of chemical pollution negative impact after the use of phytoadaptogen based on licorice root. Moreover, 20.3% of adolescents from the correctional group, had the value of IN even lower than in the control group, which, together with the change of expectation and variation scope indicators, indicates a high sensitivity of the vegetative nervous system to this phytoadaptogen.
Figure 1: IN in st. units among 14-year-old girls and boys, living in a chemically polluted area, after photo correction with licorice root extract
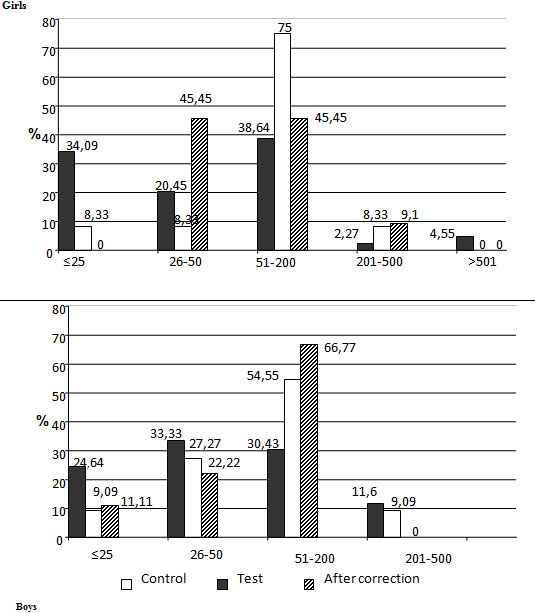
They revealed the positive effect of licorice extract on the level of adolescent body adaptive abilities (Table 5). Thus, the relative magnitude of MOC/kg improved by 1.26 times among girls, and by 1.32 times among boys and approached that in the control group. The same can be said about the indicators of the circulatory system adaptive potential and the duration of an individual minute (Table 5). After correction, the average values of AP decreased and varied within the limits of a sufficient level of organism functional capacity of the organism (AP=1.61-2.09) both among girls and boys, averaging 1.93 ± 0.26. There has been an increase in individual minute duration.
Table 5. Adaptive abilities of 14-year old schoolchild body, living in a chemically contaminated area, after photo correction
| Indicators | Control group | Test group | Р1 | Correction group | Р2 | P3 |
| Girls | ||||||
| MOC/kg, ml./min./kg. | 45,84±0,40 | 36,17±0,62 | <0,001 | 45,45±1,29 | <0,001 | >0,05 |
| AP, st.un. | 1,75±0,03 | 2,27±0,08 | <0,001 | 2,05±0,09 | >0,05 | <0,05 |
| IM, s | 45,56±0,02 | 56,91±0,99 | <0,001 | 49,55±3,52 | <0,05 | >0,05 |
| Boys | ||||||
| MOC/kg, ml./min./kg. | 47,79±0,42 | 45,17±0,51 | <0,001 | 46,83±1,09 | >0,05 | >0,1 |
| AP, st.un. | 1,76 ±0,03 | 2,22±0,05 | <0,001 | 1,99±0,07 | <0,001 | <0,05 |
| IM, s | 54,68±0,11 | 45,90±0,53 | <0,001 | 49,50±2,62 | <0,05 | >0,05 |
| Note: P1 is the reliability of differences in average values between the experimental and control groups; P2 is the reliability of differences in average values between the experimental and correction groups; P3 is the reliability of differences in average values between the control and correction groups. | ||||||
In this study, the data on the correction of deviations concerning the adaptation system activity of 13-14-year-old adolescent bodies, exposed to chemical pollution of the environment by means of a phytoadaptogen based on licorice was investigated. The outcomes revealed that the application of licorice root extract as an adaptogen contributed to the normalization of blood pressure, heart rate, and variation range among 14-year old adolescents living in conditions of environmental chemical pollution, (Sadek et al., 2020).
Moreover, more pronounced changes towards the normalization of the functional state of the cardiorespiratory system were found among boys, which is probably explained by their more pronounced changes before correction. Among the adolescents of the correctional group, the level of adaptive capacity has increased, as was indicated by AP and MOC indicators. The indicators of IM approached those of the control group, which indicates the stabilization of rhythmostasis (Sidorova et al., 2020).
CONCLUSION
The study found that licorice root extract is an effective natural adaptogen because it reduces the negative effect of chemical pollution factors on the adolescent body: it leads to a relative normalization of blood pressure, heart rate indicators, individual minute and maximum oxygen consumption. This provides a scientific basis for the development and the use of herbal remedies based on licorice as adaptogens, in order to level the negative effects of environmental chemical pollution.
REFERENCES
Agadzhanyan NA, Aleksandrov SI, Aptikaeva OI, Glavatskikh SP, Grachev VA, Dmitrieva TB, Zhalkovskii EA, Kiselev GP, Letnikov FA, Oleinik OV, Rastorguev VN (2006). Human ecology in a changing world. UB RAS, Ekaterinburg (in Russian). Amirova G.S. Licorice in Azerbaijan. – Baku, 1993. – 112 p.
Baevsky R.M., Bersenyova A.I., Paleev N.R (1987). Assessment of the adaptive capacity of the circulatory system during mass prophylactic examinations. – M.: Express information VNIIMI,. – 19 p.
Belyaev N.G (2002). The use of licorice extract as a prophylactic means of disadaptation to physical exertion // Organizational and methodological aspects of strengthening the health status of student youth in the Siberian region. The mater. of interreg. scientific and practical conf. – Irkutsk. – pp. 137–138.
Brehman I.I. (1969). Adaptogens of plant origin – pharmacological means of body efficiency and resistance increase // Pharmacology of physical activity. – M.,. – pp. 9–26.
Butova O.A. (1999). Physiological and anthropological characteristics of adolescent health: Author’s abstract from the dis. by Doctor of medicine. – M. – 38 p.
Cekic B, Muftuler FZ, Kilcar AY, Gunay N, Sakarya S, Unak P. (2012). Anti toxic effect of broccoli extract on stannous dichloride toxicity. Acta cirurgica brasileira. 27(9):606-10.
Dzhandarova T.I., Sheykina N.V., Yushkova L.N., Kozlova K.A. (2014). The effect of hawthorn fruit on the level of corticosteroids in blood // Basic research in biology and medicine. Collection of scientific papers. Stavropol, Publisher: North Caucasus Federal University. pp. 54–57.
Ghorbanlou, M., Rostamkhani, S., Shokri, S., Mahmazi, S., Fallah, R., Moradi, F., & Nejatbakhsh, R. (2020). Possible ameliorating effects of Glycyrrhiza Glabra (Licorice) on the sperm parameters in rats under high fat diet. Endocrine Regulations, 54(1), 22-30.
Guminsky A.A., Leontyeva N.N., Marinova K.V. (1990).The guide to laboratory work in general physiology. – M.: The Enlightenment,. – pp. 216-221.
Halberg F.(1969). Cit.: Moiseeva N.I., Sysuev V.N. Temporal environment and biological rhythms. – L.: Science, 1981. – 127 p.
Ishida N., Sympos R. (1983). On Liver and Glycyrrhizin Minophagen // Pharmaceutical. Co., Tokyo,. – pp. 120–124.
Kerimov S.A., Kasumov Ch.Yu. (1998). The effect of licorice extract and tetrachlorethylene vapors on the level of some mediators of brain amino acid structure among young animals // Experiment. and clinic. pharmac.,. – №3. – pp. 54–56.
Milashechkina E.A. (2005). An integrated approach to the assessment of psychosomatic health and personality-oriented methods of its correction among the adolescents living in environmentally unfriendly areas. Author’s abstract from the Diss by the Cand. of Biology. – Stavropol,. – 21 p.
Resenkova O.V. (2003). The study of licorice extract effect on the processes of body adaptation. // Author abstract from the dis by the cand. of biol. – Stavropol, – 22 p.
Sadek, E. M., Tawfik, N. R., Hussein, A. K., & Abdelhakeem, M. A. (2020). Efficacy and Safety of Liquorice Extract in Patients with Bronchial Asthma: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Indian Journal of Public Health, 11(04), 585.
Sidorova, Y. S., Petrov, N. A., Shipelin, V. A., & Mazo, V. K. (2020). Spinach and quinoa-prospective food sources of biologically active substances. Voprosy pitaniia, 89(2), 100-106.
Singamaneni, V., Sharma, U., Lone, B., & Gupta, P. (2020). Phytochemistry and Pharmacological Activities of Rhodiola imbricata Edgew., a High Value Medicinal Herb of Cold Desert Himalaya. Botanical Leads for Drug Discovery, 159-178.
Streltsov A.B. (2002). Bioindication of urban environment quality based on the analysis of the spatial distribution of pediatric ecopathologies. // The effect of environmental pollution on human health. Mater. from the 1st All-Russian conf. with international. part. – Novosibirsk, – pp. 34–35.
Tolstikov G.A., Baltina L.A., Ryzhova S.A. (1991). The development of new means to fight HIV infection based on glycyrrhizic acid // Study and use of licorice in the national economy of the USSR. – Alma-Ata,. – pp. 160-161.
Veltishchev Yu.E., Fokeeva V.V. (1996). Ecology and children health. Chemical ecopathology. – M. – 57 p.
Yermolova L.S., Zimova L.N., (2001). Study and use of adaptogenic properties of licorice. The bulletin of Stavropol State University. 31/2002. – pp. 101–104.


