The comparison of ISSR and RAPD markers with
different species of
Triticum
M. Ebadi
1
* and Mahsa Eghbali
2
1
Assistant Professor, Damgan Branch, Islamic Azad University, Iran
2
Master of Genetic, Damgan Branch, Islamic Azad University, Iran
ABSTRACT
Considering genetic variety in Iran, we applied markers to determine genetic variety and phylogenic connections in
different species. On the other hand, we made an attempt to compare RADP and ISSR molecular markers on different
species of wheat considering the food consumption of Iran and easy sample to wheat. In this experimental study,
markers were applied to consider different species of wheat and they were experimented by RADP and ISSR starters.
The effect of marker was evaluated on different species of wheat by PCR test. A comparative effect of RADP and ISSR
markers via PCR method signi ed that different species of wheat based on applied starters with a clear distance from
DNA bands showed their similarities. In conclusion, the study results indicated to the effectiveness of different spe-
cies of wheat on markers. Low cost and availability to wheat species and applying their DNA can be more effective
in comparison to RADP and ISSR.
288
ARTICLE INFORMATION:
*Corresponding Author:
Received 27
th
Dec, 2016
Accepted after revision 2
nd
March, 2017
BBRC Print ISSN: 0974-6455
Online ISSN: 2321-4007
Thomson Reuters ISI ESC and Crossref Indexed Journal
NAAS Journal Score 2017: 4.31 Cosmos IF : 4.006
© A Society of Science and Nature Publication, 2017. All rights
reserved.
Online Contents Available at: http//www.bbrc.in/
Biosci. Biotech. Res. Comm. Special Issue No 1:288-292 (2017)
INTRODUCTION
Although from too many years ago human had consid-
ered drug crops of plants, the increasing production of
these crops in elds and gardens turned to a new sci-
ence since second half of the 20
th
century. Destroying
and consuming growing plants of nature were placed
by enjoying nature plants. Nowadays, the applying of
genetic engineering methods and biotechnology allow
forming DNA molecules with inheritance properties,
and a signi cant progression has created in biological
sciences. Modern biotechnology, a novel technology, is
able to increase the function of plants through changing
the genetic structure of crops and other plants.
Wheat (in science: Triticum) is a cereal grain. There
are wild and domestic types of wheat. It is belonged to
annual monocots magnoliophyta plants and Poaceae
and a member of Gramineae family.
Wheat is among the oldest crop plants used by human,
it is cultivated and harvested in a very great extent. Bot-
any, it is a member of Triticum species divided in three
different groups with determined chromosomes carrying
all genetic properties of the family (3).Two diploids are
more dif cult than other crops, as some of them belong

M. Ebadi and Mahsa Eghbali
BIOSCIENCE BIOTECHNOLOGY RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS THE COMPARISON OF ISSR AND RAPD MARKERS WITH DIFFERENT SPECIES OF
TRITICUM
289
to the wheat species of genetics with four polyploidy
chromosome chains, while other species got 6 chromo-
some chains. Diploids grow only in jungles and deserts
and cropped Einkorn wheat belong to this group.Wild
Tetraploids, and cultivated Emer and Durum belong to
this group. Hexaploids involves bread wheat 90000 hec-
tares of all 2.3 million hectares of water wheat are culti-
vated in cold regions.
PROPERTIES
Wheat contains all mineral salts. If you need to have dif-
ferent vitamins, take wheat. It is suggested to use wheat
gruel with sugar and almond to stop breast bleeding.
Wheat avoids gastric cancer.
RAPD MARKER
RADP marker starting a short oligonucleotid starter
propagates in PCR reaction with low annealing tem-
perature, a range of pieces of DNA pattern. One or more
piece of polymorph productions are created as a result of
changing in one open door in primer connection place
,and this polymorphism can be a genetic map (Kaiser
and Polatski, 1995) RADP marker is distributed in the
whole genome (Luine, Santanglo, 1994).
THE ADVANTAGES OF RAPD MARKER
It does not need the primary information on DNA orders
to design and construct starters.
It allows a simultaneous consideration of numerous
places in sample genome.
It does not need a prober, radioactive materials, etc.
THE DISADVANTAGES OF RAPD MARKER
The location of RAPD markers is not determined on the
genetic maps.
The similarity and relationship between bands with
similar movement on electrophoresis gel are not deter-
mined.The studies accomplished by Paul et al.(1996)
show that RAPD markers show the genetic distances
between people with little distance from each other
in a less exact way in comparison to other mark-
ers. Therefore, applying markers to taxonomy studies
in species should be considered.These markers have a
dominant power and the disability of allele system in
RAPD markers results in some limitations in the marker
functions.
RANKING HARDSHIP
RAPD has a tendency to propagate repetitive parts of
genomic DNA. As an example, too many repetitive
orders of wheat genome are propagated through RAPD
reaction.
ISSR TECHNIQUE
ISSR is a PCR-based technique contained a piece of DNA
in a reproducible distance between two repetitive elds
of unique micro-satellites with opposite directs. Usually,
this technique used micro-satellites of 16-25 bp as a
primer of a mono-primary targeting poly-genomic locus
to propagate the successions between micro-satellites
with different measures. Bi-nucleotides, Tri-nucleotides,
quadra-nucleotides, or panta-nucleotides micro-satellite
repetitions can be used as primers. Although applied
markers are connected to 1-4 bases, and are enlarged
based on these connections, they are able to connect to
each point of DNA. This technique has integrated the
advantages of AFLP and micro-satellites with RAPD
comprehensiveness. The applying longer primers (16-25
mers in comparison to RAPD shorter primers (10 mers)
allow to apply high temperature of connection (45-60`C)
increasing the primer connection to determined points
of DNA with more repetitive times results in high repeti-
tion of ISSR. The studies on repetition signify that only
the weakest bands are not repetitive. Nearly 92-95% of
scored pieces can be counted in DNA samples, and can
be repeated in distinct periods of PCR when are identi-
ed by applying polyacrilamide. 25-50 nanograms of
pattern DNA in each 20 micro-liter of PCR and 10 mil-
ligram of pattern DNA can produce the same propagated
productions. The connection temperature of 45-60`C
depends on the applied primer.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
HERBAL MATERIALS
Nine varieties of wheat species (existed in Minister of
Agricultural Jihad) were applied to consider molecules.
As a whole, nine leaf samples included fresh leaves of
wheat species were collected.Starters applied 14 ISSR
and 10 RAPD starters to consider genetic relationships.
THE EXTRACTION OF GENOMIC DNA
Changed CTAB method of leaf samples was applied to
extract DNA before that samples were melted. To provide
100 milliliter buffer of 2% CTAB extraction, the compo-
nents of table 4-3 were solved in 20 milliliter of distilled
water, pH was 8 by applying chloric acid in one mullar.
Then 2 grams of hexa decyl timthyl ammonium bromide
was solved in hot distilled water, and it was added to the
previous solvent. Finally, the solvent was 100 milliliter.
The phases of DNA extraction are as following:
M. Ebadi and Mahsa Eghbali
290 THE COMPARISON OF ISSR AND RAPD MARKERS WITH DIFFERENT SPECIES OF
TRITICUM
BIOSCIENCE BIOTECHNOLOGY RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS
Before the experiment was started, CTAB buffer was
heated in water bath of 65`C.
100 milligram of fresh and clean leaves was pounded
in liquid nitrogen in a mortar. It is suggested to keep the
dish and mallet (at least in connection with leaves) cold
by adding some liquid nitrogen or putting in freezer to
make Nucleases inactive.
Put the powder in a corner of the dish, and when
buffer was melted, add 800 micro-liter of CTAB buffer
to powder and mix thoroughly. The contents of mortar
(dish) should be transferred to tube of 2 milliliter, and
was kept in 60`C for 30 minutes in water bath (In this
30 minutes, the tubes were circulated for some times
smoothly). The sample volume (800 micro-liters) of chlo-
roform/ isoamyl alcohol (24:1) was added in room tem-
perature. The tubes were turned some times in a smooth
way to have a uni ed mixture. It was centrifuged for
10 minutes and 13000 turns. The above limpid part was
removed (in 500-600 micro-liters), and was poured in
another tube.
2/3 (almost 350 micro-liters) of cold isopropanol vol-
ume (-20`C) was added to each tube. It was centrifuged
with 13000 turns for 10 minutes in 4`C. the tube con-
tents were removed smoothly and DNA string was left at
the bottom of the tube. Vacant tubes with DNA strings
were inverted on a very clean place to have dry strings.
100 micro-liters of TE buffer was added to room temper-
ature.800 micro-liters of Aminium acetate +cold ethanol
was added (2.5 molar and 1.5 liter of aminium acetate+
3.5 milliliter ethanol), the last step was accomplished on
ice, it was inverted for some times, and then tubes were
transferred to freezer. They were centrifuged with 13000
turns for 15 minutes in 4`C.
The above part was discharged. The tubes were
inverted to become dry. 150 milliliters of TE buffer was
added to each tube. The samples were kept in room tem-
perature, then some other actions to evaluate quantity
(spectro-photometry) and quality (electrophoresis on
agarose gel of 1.5% DNA) (extracted DNA) were accom-
plished. The samples were diluted in 100 nanograms to
subsequent application. Providing method of 0.8% and
1.5% agarose to determine quantity and quality and
analysis of propagated pieces
X1EDTA was diluted by water in 9:1, and then
X1EDTA was provided.
X1EDTA is put in the tube based on the electropho-
resis tank volume by the help of cylinder, it is moved
smoothly to have a good mixture. The solvent in tube
is put in the microwave so that particles will be solved
in a complete way and then a smooth solvent will be
appeared. 0.2 micro-liter of DNA safe stain was added
to gel to paint, then the gel was put in the gel dish. The
solvent in the tube is poured on the electrophoresis tray.
When 30 minutes was passed, agarose gel is stiff. The gel
was put in the electrophoresis tank by X1EDTA.
9-3 sample preparation and electrophoresis of agarose
gel
We add 5 milliliters of loaded buffer to each 5 milliliter
of sample to have a good mixture, and then the sample
is spilled into the sink. The rst sink from the lift has
been devoted to the measured marker. A 92-volt elec-
tric currency was connected to the tank. By passing 45
minutes, gel was removed from the tank, and then it was
removed from the tray. Then a picture was taken from
the gel in photography machine.
10-3 The components of polymerase chain reaction
The components presented in table 5-3 were applied to
carry out PCR reaction in 12 micro-liter.
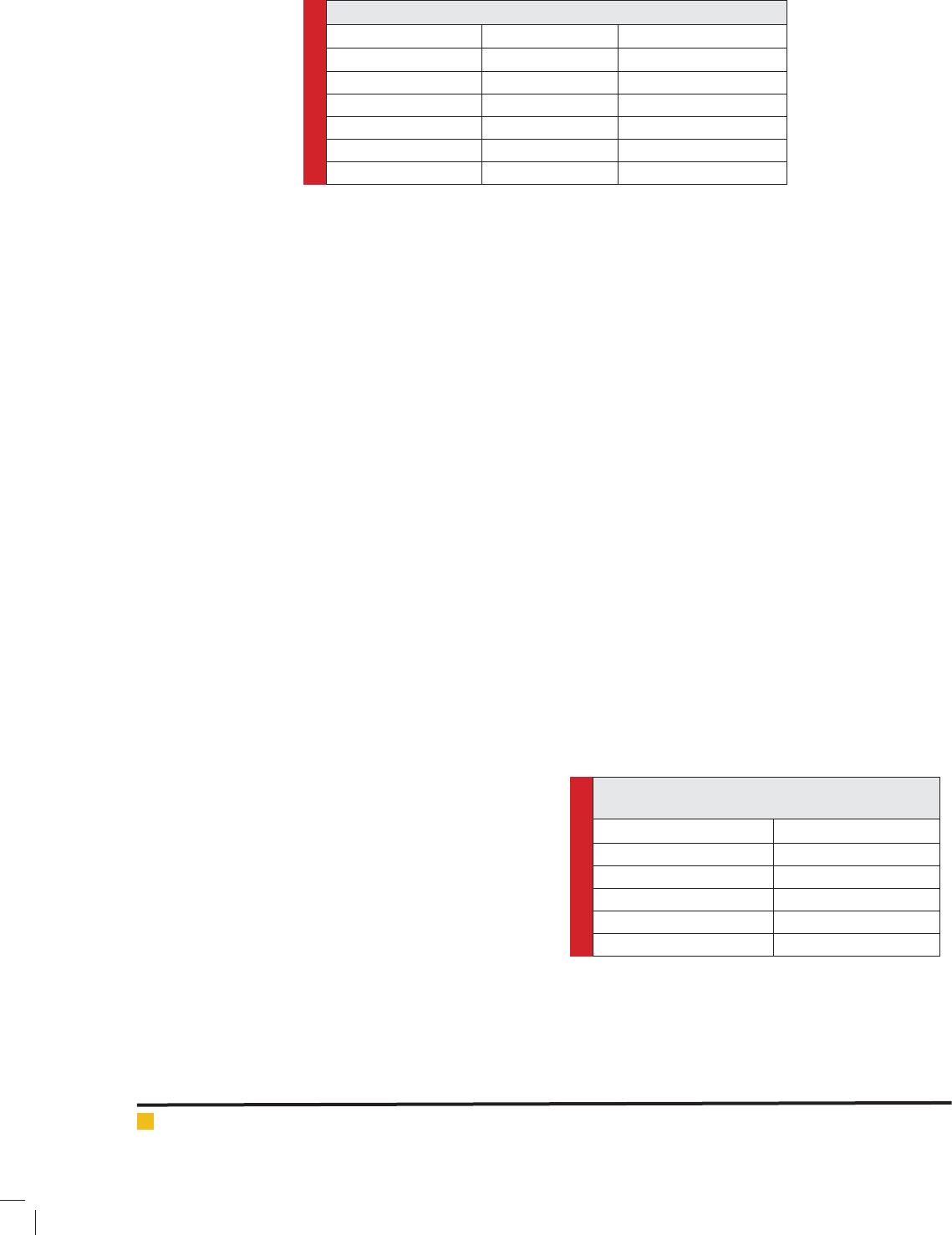
Table 4-3. The composed components of DNA extraction buffer
Final destinationAmountBuffer components
100 millimolar1.211 gTris-HCL
4 molar8.19 gNaCl
0.2% (volume-volume)0.744 gEDTA
0.2% (weight-volume)2 gCTAB
0.5 molar200 microliterMerkapto etanol
0.2% (weight-volume)2 gpvp
Table 5-3. The applied components to carry out PCR
reaction
Amount (micro liter)Component
5PCR kate (Master mix)
5Deionized water
1.1Starter
1Genomic DNA
12.1Total
11-3 Time cycle and polymerase chain reaction steps
The polymerase chain reaction was accomplished in
thermocycler (Bio Rad) in 4 minutes and initial com-
pounding in 94`C via 10 initial touching down denatura-
tion (so that the connection temperature of starter was

M. Ebadi and Mahsa Eghbali
BIOSCIENCE BIOTECHNOLOGY RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS THE COMPARISON OF ISSR AND RAPD MARKERS WITH DIFFERENT SPECIES OF
TRITICUM
291
considered to be 5`C higher than the real connection
temperature, and 0.5`C was decreased from the connec-
tion temperature to achieve the real connection temper-
ature). This action allows to decrease similar bands of
micro-satellites causing some problems in scoring the
PCR typical cycles. It is suggested to apply 30 cycles
containing 30 seconds of denaturation in 94`C to each
starter in 45 seconds (to connect starters), and 2 minutes
in 72`C to extend, and the last extension was carried out
in 72`C for 7 minutes.
DATA ANALYSIS
The applied markers in this study are of dominated
markers which are scored in interpreting gel as 1(indi-
cating to the presence) or 0 (indicating to the lack).
CLUSTERING ANALYSIS
According to raw data obtained from ISSR and RADP
molecular markers, the clustering analysis was accom-
plished by UPGMA method and applying the jaccard
similarity coef cient to determine similarity between
two individuals, Darwin 6 and Post 3 software.
THE ANALYSIS TO BASIC COMPONENTS
The analysis to basic components is another multi-vari-
ant method which is of high application in genetic vari-
ety analysis with clustering analysis. This method can
be applied to present two-dimensional distribution of
individuals in a eld of plot signifying genetic similarity
among them. PCA is a method to decrease data to con-
struct relationships between two or more variants and
to explain the changes of whole basic and primary data
by some new independent variants called basic compo-
nents.To decrease data is accomplished by linear chang-
ing of basic data to new independent variants called
basic components, so that the rst PC explains the max-
imum initial data, and the second PC explains remained
changes after the rst PC, etc. it should be noted that
each PC explains those changes not been explained by
other PCs.
As PCs are independent, each one presents differ-
ent properties of basic data, and they should be inter-
fered differently from each other. When PCA is applied
to analyze molecular data, similarity matrix should be
changed via the following formula to remove negative
inert roots:
ij=Sij-Sio-Soj+SooóS
in which, Sij represents similarity coef cient between
I,j individuals, Sio shows the average of similarity coef-
cient in n
th
individuals, Soj shows the average of simi-
larity coef cients of j
th
individual, and Soo is the total
average of similarity coef cients. This changing causes
to move similarity matrix to zero root. These similarity
properties calculated by any method will be kept.
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
A study accomplished by Aslani (2013) on the genetic
variety of molecular genotype of Mirabilis jalapa by
applying ISSR marker showed that ISSR does not need
radioactive materials and pattern DNA sequence. There-
fore, ISSR was a good marker to consider genetic vari-
ety and relationship which was coincide with our results
(Aslani,2013).
A study accomplished by Heidari Nejad on the
genetic variety of African Violets varieties by apply-
ing RAPD marker signi ed that morphologic properties
are in uence by various factors with no effect on DNA.
These factors which are similar in DNA based on the
data, are similar to or different from each other in mor-
phologic properties. Therefore, it is expected that RAPD
data may have no similarity with individual grouping
in planting and morphological properties by consider-
ing the effectiveness of environmental factors on these
properties.
This result has been reported by Martinz-Gumz et al.
(2003) on almond. Therefore, considering individuals
based on planting and morphological properties can`t
result in favorable results (Heidari Nejad, 2012).
Stephonova et al. (2014) accomplished a study on
genetic variety of 16 species of Amaranthus of Cary-
ophyllales family by applying molecular ISSR marker.
Amaranth is a most important species existing in all
around the world. In this study, ISSR method was applied
to analyze variety in and among 16 species of amaranth.
Eleven primaries were applied in this study. The den-
drogram divided 16 varieties into 3 groups in which 2
groups belong to India and one group is belonged to
Nepal. The similarity average was 0.154-1.000. This
study indicated that ISSR is of high ef ciency (Stepho-
nova et al. 2014).
In a study accomplished by Ray et al. (2007) on the
genetic relationships of Aramanthus which is belonged
to Caryophyllales by applying molecular ISSR and
RAPD markers, it was used from 18 starters and to ISSR
marker and 15 starter to RAPD. The similarity coef cient
of ISSR and RAPD markers were 0.45 and 0.47; respec-
tively. Also, Cophenetic coef cient of both markers was
0.83. These coef cients refer to a good tting between
similar matrix and dendrogram, and both dendrograms
showed a good similarity between species indicating
that ISSR and RAPD markers are of high suf ciency to
determine genetic relationships, and they are suitable
tools to cluster species (Ray et al. 2007).

292 THE COMPARISON OF ISSR AND RAPD MARKERS WITH DIFFERENT SPECIES OF
TRITICUM
BIOSCIENCE BIOTECHNOLOGY RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS
M. Ebadi and Mahsa Eghbali
CONCLUSION
In general, the study results signi ed that there is a differ-
ence on the least and most distance of bands in different
analyses. ISSR marker showed bands with less distance
and more similarity in comparison to RAPD marker.
REFERENCES
Ajmone-Marsan, P., Castiglioni, P., Fusari, F., Kuiper, M. and
Motto, M. 1998. Genetic diversity and its relationship to hybrid
performance in maize as revealed by RFLP and AFLP markers.
Theor. Appl. Genet. 96: 219-227.
Arzani, A. Mourtazavi, A. (2001), The principles of genetic
analysis, 2
nd
volume, sixth edition, The publication of Isfahan
University of Technology, page 320
Awasthil A K, Nagaraja G M, Naik G V, Kanginakudru S,
Thangavelu k, Nagaraju J,2004. Genetic diversity and relation-
ships in mulberry (genus Morus) as reveald by RAPD and ISSR
marker assays. BMC Genetics 5: 1-9.
Behnam, B. Yazdi Samadi, B, Abd-Mishani, S. Shah Nejat
Bushehri, A. (1998), Applying RAPD method as DNA marker to
diagnose multiform in different criticum species of Iran, Iran
Agricultural sciences journal, 31:20-24
Burstin, J., de Vienne, D., Dubreuil, P. and Damerval, C. 1994.
Molecular markers and protein quantities as genetic descrip-
tors in maize. I. Genetic diversity among 21 inbred lines. Theor.
Appl. Genet. 89: 943-950.
Cockerham, C. C. 1973. Analysis of gene frequencies. Genetics
74: 679-700.
Excof er, L., Smouse, P. E., and Quattro, J. M. 1992. Analy-
sis of molecular variance inferred from metric distance among
DNA haplotypes: Application to human mitochondrial DNA
restriction data. Genetics 131: 479-791.
Franco, J., Crossa, J., Villasenor, J., Taba, S., and Eberhart, S. A.
1997. Classifying Mexican maize accessions using hierarchical
and density search methods. Crop Sci. 37: 972-980.
Ghareyazi, B. (1995), The applying of DNA markers in plant
breeding, 3
rd
congress of agriculture and plant breeding of Iran
Ghareyazi, B. (1997), The applying of DNA markers in plant
breeding, The key articles of 4
th
congress of agriculture and
plant reformation of Iran
Hartl, D. L., and Clark, A. G. 1997. Principles of population
Genetics. 3rd ed. Sinauer Associates Inc. Sunderland, MA.
Johnson, A. R. and D. W. Wichern. 1992. Applied Multivariate
Statistical Analysis. 3rd ed.
Kiani Fariz, M. Zamani, Z. (2010), The genetic variety of Dam-
ask Rose by morphologic and RAPD marker: New genetic
Kiani, S. Abd-Mishani, S. Shah Nejat Boushehri, A. (2002),
Rapeseed genetic variety by applying RAPD-PCR marker, MA
thesis, The plant breeding group, The agriculture faculty of
Tehran University, page 120
Sahriyari, F. Imam Jome`, A. (2002), Polymerase chain reac-
tions (Newton, C.R and Graham, A), First edition, Imam Reza
University, page 228
Salehi Jowzani, GH. (1999), The genetic variety of some busi-
ness potato species of Iran by applying RAPD-PCR technique,
MA thesis, The plant reformation group, The agriculture of
Tehran University, page 130
Sameei, L. Naderi,R. (2012) The genetic variety of L. Rosa
canina genotypes in Iran with applying morphologic markers
and micro-satellites, 7
th
national congress of biotechnology of
Islamic Republic of Iran.