Evaluation of the protective effect of vitamin C on
hepatic damage caused by formaldehyde in rats
Hasan Amiri
1
, Niloofar Ghodrati
2
, Amir Noyani
3
*, Saeed Abbasi
1
, Hamed
Basir Ghafouri
3
and Bahareh Seyyed Salehi
3
1
MD, Emergency Medicine Management Research Center, Iran University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran
2
MD, Alborz University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran
3
MD, Trauma and Injury Research Center, Iran University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran
ABSTRACT
Formaldehyde (methanol) is a chemical substance, with nasty smelling which is normally used to x cadavers and histological
process. The main use of formaldehyde is in production of synthetic resins, wood-plastic products and ber industry. Formalde-
hyde has a negative impact on performance of organ system with oxidative stress in the body .specially on the hepatic. Some stud-
ies have demonstrated that antioxidants such as vitamin C can play an important role to protect from damage caused by harmful
substance. The aim of this study was to evaluate the protective effect of vitamin C on hepatic damage caused by formaldehyde in
rats.This study included 24 adult male rats with weighing 250-300 gr. rats were randomly divided into 3 groups each comprising 8
rats. 1- Control group: exposed to normal saline (1cc/kg per day for 10 days) that injected intraperitoneally, 2 -groups E1: exposed
to formaldehyde 10mg/kg per day for 10 days, 3 - group E2: simultaneously exposed to vitamin C (200mg/kg) per day for 10 days&
formaldehyde 10 mg/kg intraperitoneally 10 days. At the end of the exposure period, the mice were placed under anesthesia and
surgery. The blood samples were taken for isolation of serum and measurement of AST and ALT in.In this study, AST and ALT
levels of 24 adult rats in the all groups were measured and the results were compared. The amount of AST in the all groups was
signi cant (P <0.05). The amount of AST in group E2 compared to controls was signi cant (P = 0<0.05) and the amount of AST in
group E2 compared to E1 was not signi cant (P = P>0.05). Also, comparison of the results showed signi cant difference in serum
ALT in third group. Serum ALT level in E1 compared to control group was signi cant (P <0.05) and ALT in group E2 compared to
control group was signi cant (P <0.05). The amount of ALT in group E2 compared to E1 was not signi cant (P = 0.847).According
to this study, intraperitoneal administration of formaldehyde at a dose of 10 mgr/kg per 10-day can increase AST and ALT and
vitamin C at a dose of 200 (mg / kg) per day for 10-days can reduce amount of AST and ALT in adult rats exposed to formaldehyde
KEY WORDS: FORMALDEHYDE, AST, ALT, LIVER
213
ARTICLE INFORMATION:
*Corresponding Author: amir_noiany@yahoo.com
Received 27
th
Dec, 2016
Accepted after revision 2
nd
March, 2017
BBRC Print ISSN: 0974-6455
Online ISSN: 2321-4007
Thomson Reuters ISI ESC and Crossref Indexed Journal
NAAS Journal Score 2017: 4.31 Cosmos IF : 4.006
© A Society of Science and Nature Publication, 2017. All rights
reserved.
Online Contents Available at: http//www.bbrc.in/
Biosci. Biotech. Res. Comm. Special Issue No 1:213-217 (2017)

214 EVALUATION OF THE PROTECTIVE EFFECT OF VITAMIN C ON HEPATIC DAMAGE BIOSCIENCE BIOTECHNOLOGY RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS
Hasan Amiri et al.
INTRODUCTION
Formaldehyde is a chemical material with a nasty smell,
which is used in xing cadavers, histological processes,
synthetic resins, wooden and plastic productions and
industrial ber production. It has a negative effect on
performance of body organs. It is metabolized to formic
acid by dehydrogenase formaldehyde and dehydrogenase
aldehyde enzymes in the liver and erythrocyte which is
exorcised through urine, excretion and breathing with
different macromolecules such as protein, acid nucleic or
interact with the light molecules like amino acid. Formal-
dehyde can cause oxidative stress in the body and has
a bad effect on respiratory system and blood circulation
and liver (Golalipour et al., 2007 Mendis et al., 2007,
Cheng et al., 2003, Collins and Lineker 2004 Kini et al.,
2004). Formaldehyde was known as a harmful factor for
liver cells in the different studies. Antioxidants are such
components that help body to destroy free radicals oxi-
dative stress is actually imbalance between oxidants and
antioxidants. When the amount of oxidants increases,
the cells are damaged. Antioxidants include Vitamin
A, E, C, Zn and selenium, which play a crucial role on
inhibition of free radicals and stability of cell membrane,
(Kini et al., 2001, Gupta et al., 2004, Woolaqrd et a;
2002).
Vitamin C (Ascorbic Acid) is a white or yellow odor-
less solid substrate with the molecular formulation of
C6H806. Ascorbic Acid is produced in the liver of plants
and animals (except some special kind and human). Vita-
min C operates as antioxidants in the body and cause
acceleration of Fe, Cu and also revives of folic acid and
collagen making. Vitamin C as a soluble antioxidant
becomes active by moving oxygen and nitrogen ele-
ments. The role of vitamin E as a protective agent on
liver damage caused by formaldehyde in the previous
studies was approved. The role of A,E,C Vitamins as
protective antioxidants on liver hepatotoxicity was also
investigated. It is possible to evaluate liver function by
checking the indicators in the blood, (Kum et al., 2011,
Kini et al., m 2011, Djeffal et al., 2011, Ememghorashy
et al., 2012).
With regard to the formaldehyde effects in making
oxidative stress, free radicals and their effect on liver
performance and in accordance with the performed
studies related to the formaldehyde on the liver tis-
sue changes as glomerular vascular congestion and
also minor decline holes in the pipe cells and stud-
ies about the protection effect of Vitamin C on pre-
vention of formaldehyde damage, in this study, we
decided to investigate the protection effect of Vita-
min C on liver performance of rats after exposing to
formaldehyde.
METHODOLOGY
In this study 24 adult rat of Wistar bread were selected
and divided into 3 equal groups. The rst group (c)
received 1cc/kg of normal saline and the second group
(E2) received 10 mg/kg formaldehyde and the third group
(E3) received both 10mg/kg formaldehyde and 200 mg/
kg Vitamin C in 10 days by injection into peritoneal.
During the study, the rats were under normal condition
of shelter with 24±2 temperature and appropriate feed-
ing. 3 weeks after nishing the injection phlebotomy,
after anesthesia by sterile syringe was performed. After
making occulation by centrifuge, samples were sepa-
rated with 1500 rpm during 10 minutes and they were
kept in -20 c till testing for evaluation of ALT and AST.
The amount of ALT and AST were measured by using
Pars Azmoon kits and auto analyzer tool (BiotecticaIn-
strument BT 1000).
Data analysis was performed after entering the data
to SPSS Ver.20program and to investigate normality of
cantinas quantitative data distribution, Shapiro-wilk
test was conducted. The explicit result of the groups was
reported as average and deviation from standard devia-
tion. The comparison between the investigated groups
was performed by using ANOVA test. If the average dif-
ferences of statistic results were meaningful the LSD test
were used to compare them. The meaningful level was
considered less than 0.05 (P<0.05).
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
In this study, 24 adult male rats of Wistar bread were
involved. Among them 8 rats (33%) considered as con-
trol group, 8 rats (33%) considered as test group 2 (E2)
and another 8 rats (33.3%) as test group 2 (E2). Descrip-
tive factors and the comparison between the weights of
rats among 3 groups of control E1, E2 was shown in the
table 1. In order to compare AST level in 3 groups of
control (c) E1,E2. Variance analysis test (ANOVA) was
conducted and in order to compare 2 group’s level of
ALT, the LSD test was came out. Descriptive speci ca-
tions and the comparison between ALT levels of three
groups include group c, E1, E2 were listed in the table 2.
According to the comparison of AST level, it was sug-
gested that there is a signi cant difference in 3 groups
of control, E1, E2 (p<0.05). Also, with regard to the 2
groups comparison, The difference between the AST
level of group c and group E1 was meaning (p<0.05)
and the difference between AST level of control (c) and
test group (E1) was also meaningful (p<0.05). However,
there is not a meaningful difference between AST level
of study group E1 and E2 (p>0.05) (plot 1). In order to
compare, ALT level in 3 study groups of control (c), E1,
BIOSCIENCE BIOTECHNOLOGY RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS EVALUATION OF THE PROTECTIVE EFFECT OF VITAMIN C ON HEPATIC DAMAGE 215
Hasan Amiri et al.
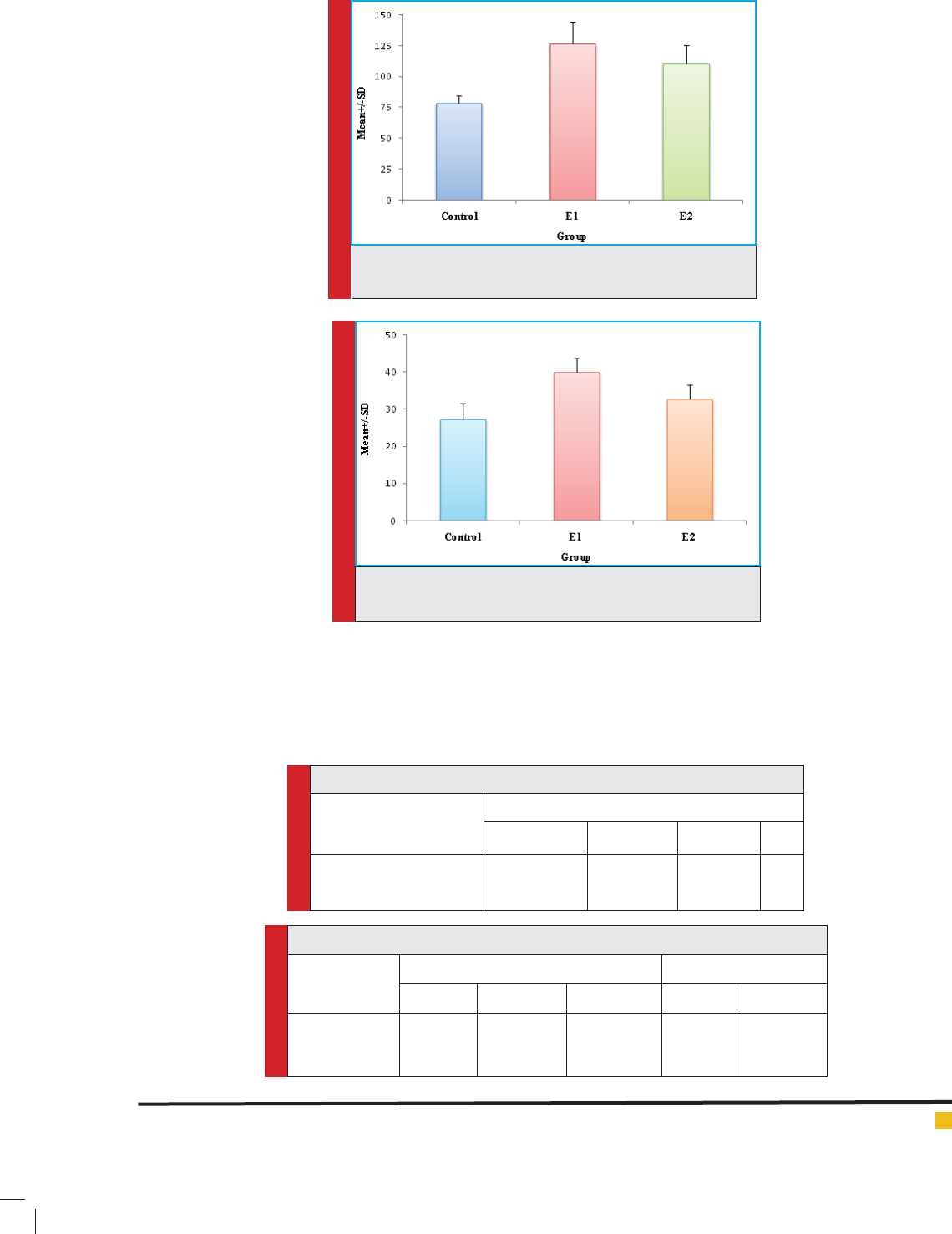
PLOT 1. AST level average plot for 3 study groups of control
(c), Test 1 (E1), Test2 (E2)
PLOT 2. ALT level average plot of 3 study groups of control
(c), Test 1 (E1), Test 2 (E2)
Table 1. Rats weight in 3 study groups of control (c), E1, E2
Speci cation
P-Value
Control Test 1 Test 2
Weight (gr)
Standard deviation ± Mean
Range
214,37 ± 11,01
202-235
212,12±2,79
208-217
215,5±3,96
211-222
0.62
Table 2. AST amount of 3 study groups of control (c), Test 1 (E1), Test 2 (E2)
speci cation Group Comparison among groups
Control E1 E2 Statistic F P-Value
AST
Mean±SD
Range
78.5±5.75
68-86
126.5±18.08
96-145
110.75±14.81
86-136
24.78 <0.001
E2. The one way variance analysis (ANOVA) was con-
ducted and in order to compare ALT level between 2
groups, the LSD test was used.
Descriptive speci cations and the comparison of ALT
level among 3 study groups of control (c), test 1 (E1) and
test 2 (E2) was shown in the table 3. According to the
comparison of three groups, the ALT level has a mean-
ingful difference (p<0.05). It was also suggested that
there is a signi cant difference between ALT level of
control group (c) and test 1 group (E1). (p<0.05) and ALT

Hasan Amiri et al.
216 EVALUATION OF THE PROTECTIVE EFFECT OF VITAMIN C ON HEPATIC DAMAGE BIOSCIENCE BIOTECHNOLOGY RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS
level of C and E2 group (p<0.05) and also between E1,E2
groups (p<0.05).
Formaldehyde can affect the body organs due to cre-
ating free radicals. Formaldehyde can also affect the
kidney performance such as excretion of waste sub-
stances. Antioxidant can prevent the harmful effect of
formaldehyde . Vitamins are one of the most important
antioxidants – especially Vitamin C – which play an
effective role in protection against oxidative damage
caused by free radicals . On the other hand, this Vitamin
can enhance the activity of antioxidant enzymes in the
liver tissue,( Claudia et al., 2003, HaiXia et al., 2012,
Ukmali and Armutcuf 2011, Sajadi et al., 2008, Shang
et al., 2014).
18-WILSON ET AL., 2014)
According to the above description, 24 rats of Wistar
bread were involved in this study with regard to the pre-
vious studies and the ability and facility of laboratory
and human resource present in the research center. This
study was similar to the study of Ukmali et al. (2011).
Histology of liver cells was just investigated and no
treatment was suggested to prevent formaldehyde effect.
In the study of Ukmali some evidences were shown
about in ammation in the liver cells .
On the other hand this study was similar to that of
Shang et al (2014), except that in this study, Vitamin C
was fed to the rats and histology of kidney and liver cells
was investigated. With regard to the performed studies
and the side effect of formaldehyde which was approved
by them and also concerning this fact that people and
doctors are always exposed to this substrate without
being able to perform histology investigations on human
body, the liver enzymes was measured to evaluate ALT
and AST indicators. It was shown that there were a sig-
ni cant difference between the control groups and the
groups exposed to formaldehyde which can be related to
the in ammatory response of liver cells to formaldehyde
injection. Standardization was performed according to
the weight, gender and bread. So, the meaningful differ-
ence statistically approved the harmful effect of expos-
ing to this substrate (p<0.0001). On the other hand, ALT
and AST level in the E2 group treated by vitamin C were
decreased but not to the normal level of liver enzymes
which is probably because of high toxicity effect of for-
maldehyde. More reduction may be reached by increas-
ing the time of treatment or Vitamin C dose.
CONCLUSION
According to this study, intraperitoneal administration
of formaldehyde at a dose of 10 mge/kg per 10-day can
increase AST and ALT and vitamin C at a dose of 200
(mg / kg) per day for 10-days can reduce amount of AST
and ALT in adult rats exposed to formaldehyde.
REFERENCES
Cheng G, Shi Y, Sturla SJ, Jalas JR, McIntee EJ, Villalta PW,
Wang M, Hecht SS, Reactions of formaldehyde plus acetal-
dehyde with deoxyguanosine and DNA: formation of cyclic
deoxyguanosine adducts and formaldehyde cross-links. Chem
Res Toxicol. 2003 Feb;16(2):145-52 .
Claudia P, Fabio P. Lopasso P.Protective effect of ascorbic acid
in experimental gastric cancer: reduction of oxidative stress,
Department of Gastroenterology School of Medicine, Univer-
sity of Sao Paulo.2003Dec; 22(1):57–66.
Collins JJ Lineker GA. A review and meta-analysis of for-
maldehyde exposure and leukemia .Regul Toxicol Pharmacol.
2004 Oct;40(2):81-91.
Djeffal A, Messarah M, Boumendjel A, Kadeche L, Protec-
tive effects of vitamin C and selenium supplementation on
methomyl-induced tissue oxidative stress in adult rats El Feki
A.Faculty of Sciences, Badji Mokhtar University, Annaba,
Algeria. Toxicol Ind Health.2011 May;47(55); 21–29.
Ememghorashy F, Owj I and Motamedifar M. Evaluation of
Effectiveness of Vitamin C and E on Prevention of Renal Scar
due to Pyelonephritis in Rat Department of pediatric shiraz,
shiraz nephrology research department .2012 Dec; 42(3):657-
665.
Golalipour MJ, Azarhoush R, Ghafari S, Gharravi AM, Fazeli
SA, Davarian A, Formaldehyde exposure induces histopatho-
logical and morphometric changes in the rat testis. Department
of Histology and Embryology, Gorgan University of Medical
Sciences.2007 Aug;66(3):167-71.
Gupta RS, Jisun K, Cynthia G,Effect of ascorbic acid supple-
mentation on testicular steroidogenesis and germ cell death in
cadmium-treated male rats, Molecular and Cellular Endocri-
nology .2004Nov;43(23): 57–66.
Table 3. ALT among 3 study groups of control (c), Test 1 (E1), Test 2 (E2)
speci cation Group Comparison among groups
Control E1 E2 Statistic F P-Value
ALT
Mean±SD
Range
27.25±4.3
68-86
39.87±4.01
32-44
32.62±3.96
28-38
19.14 <0.001

BIOSCIENCE BIOTECHNOLOGY RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS EVALUATION OF THE PROTECTIVE EFFECT OF VITAMIN C ON HEPATIC DAMAGE 217
Hasan Amiri et al.
HaiXia L, ShengJie LI, YongNia Y, A liver analog construct
for use as an alcoholic liver disease model, Department of
Mechanical Engineering, Tsinghua University, Beijing 100084,
China. 2012 Oct;40(31):169-173.
Kini RD , Tripathi Y , Raghuveer C, the role of vitamine C as an
antioxidant in cadmium choloride induce testicular damage.
international gournal applied biology. 2004 Oct;40(2):6-91.
Kini RD .,Tripathi Y.,CV Raghuveer .,SheilA R.,Pai Ramaswamy
C and Priya Kamath.,Role of Vitamine C as an Antioxidant in
Cadmium Chloride Induced Testicular Damage, J of Applied
Biology and Pharmaceutical Technology.2011Feb;2(3) ; 484-
488.
Kini, RD Tripathi Y, CV Raghuveer, SheilA R Pai, Ramaswamy
C., Role of vitamin C as an antioxidant cadmium chloride
induced testicular damage.2001Feb; 2(3):484-488.
Kum C, Sekkin S, Kiral F, Akar F , Effects of xylene and formal-
dehyde inhalations on renal oxidative stress and some serum
biochemical parameters in rats. Department of Pharmacology
and Toxicology, Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, Adnan Men-
deres University. 2011 JUN;140(2);177-185.
Masoomi GH, Noyani A , Investigation of protection effect
of Vitamin C on kidney performance of an adult male rat
exposed formaldehyde, Biosci. Biotech. Res. Comm. Special
Issue (2017): 1-11
Mendis-Handagama SM, Ariyaratne HB, Mrkonjich L, Ivell R
Expression of insulin-like peptide 3 in the postnatal rat Leydig
cell lineage: timing and effects of triiodothyronine-treatment.
Reproduction. 2007 Feb;133(2):479-85.
Sajadi A,Dormanesh B, Zare M, Effect of vitamin c in blood
pressure anemia and uremia , Army Journal.2008 Feb;4(5):2-10.
Shang Z. Abdulqader, Inaam A.Mustafa, The Protective Role of
Vitamin C against Formaldehyde induced hepatotoxicity and
nephrotoxicity in Male Rats, IOSR Journal of Pharmacy and Bio-
logical Sciences (IOSR-JPBS) e-ISSN: 2278-3008, p-ISSN: 2319-
7676. Volume 9, Issue 4 Ver. III (Jul -Aug. 2014), PP 21-26.
Ukmali E, Armutcuf L, The effects of formaldehyde intoxica-
tion on the inducible nitric oxidesynthase expression and nitric
oxide level in the liver tissue of rats Department of Pathology,
Sema Training and Research Center, Fatih University, I
∙
stanbul,
Turkey .2011 Jun;8(4):1–8.
Wilson, Michelle K.; Baguley, Bruce C.; Wall, Clare; Jameson,
Michael B.; Findlay, Michael P. (2014-03-01). Review of high-
dose intravenous vitamin C as an anticancer agent”. Asia-
Paci c Journal of Clinical Oncology. 10 (1): 22–37
Woollard KJ, Loryman CJ, Meredith E, Bevan R, Shaw JA,
Lunec J, Grif thsHR. Effects of oral vitamin C on monocyte:
endothelial cell adhesion in healthy subjects, Biochem Biophys
Res Commun. 2002 Jun 28;294(5):1161-8.