Relationship between teachers’ tolerance, self-concept
and personality type in teachers
Rozkhaton Kord
1
and Bahman Kord Tamini
2
1
M.A. Student in General Psychology, Department of Psychology, Islamic Azad University, Zahedan Branch, Iran
2
Corresponding Author, Faculty Member, Department of Psychology, University of Sistan and Baluchestan,
Zahedan, Iran
ABSTRACT
The purpose of this research was to study the relationship between teachers’ tolerance, self-concept and personality
type in teachers. The population of this study included all school teachers of Khash city in 2015 – 16. The sample con-
sisted of 316 teachers that were selected at random. To collect the data tolerance, self-concept and personality type
questionnaires were used. For analyzing the data Pearson correlation coef cient and stepwise regression was used.
Results demonstrated that there was a positive and direct relationship between teachers’ tolerance and self-concept.
There was no relationship between teachers, self-concept and personality type. There was no relationship between
teachers, self-concept and tolerance. Tolerance and self-concept variables could not predict teachers’ personality type.
KEY WORDS: TOLERANCE, SELF-CONCEPT, PERSONALITY TYPE, TEACHERS
209
ARTICLE INFORMATION:
*Corresponding Author: bahmanpsy@ped.usb.ac.ir
Received 30
th
Dec, 2016
Accepted after revision 29
th
March, 2017
BBRC Print ISSN: 0974-6455
Online ISSN: 2321-4007
Thomson Reuters ISI ESC and Crossref Indexed Journal
NAAS Journal Score 2017: 4.31 Cosmos IF : 4.006
© A Society of Science and Nature Publication, 2017. All rights
reserved.
Online Contents Available at: http//www.bbrc.in/
Biosci. Biotech. Res. Comm. Special Issue No 1:209-212 (2017)
INTRODUCTION
Teaching job has internal and external stressful resources.
Internal stressful resources of teaching job include the
nature of teacher role, readiness level, competences and
ability for doing duties. Decreasing the competence level
can be resulted from lack of training before doing services.
School environment can create stressful conditions for
teachers such as students’ destructive behaviors, insuf -
cient encouragement structure, job isolation, opposed and
multiple roles (Brook, Green, Geless & Chovarzer, 1996).
During recent 20 years, studies related to tolerance
have increased signi cantly. Thus, it is necessary to
conduct more researches in this eld faster than past
because of several reasons. Firstly, increasing the num-
bers of people who they expose problems and also the
numbers of problems. Secondly, understanding the dan-
gerous and protective factors and their performance way
can be led to suitable clinical interventions. Thirdly, it
seems this topic is important because it is close rela-
tionship with mental health (Vaiv, Feredrikson & Tailor,
2008).

Kord and Tamini
Tolerance is not resistance against dangerous situ-
ations or damages, but it means active and construc-
tive cooperation in environment. Indeed, as Rechardson
(2002) stated tolerance is positive growing and adjusting
following a period of unbalance rather than as simple
recovery from damage and disaster. According to Bona-
noo (2004) tolerance is something more than living under
stressful conditions it does not mean lack of vulnerable
against stress. Previous theories about tolerance empha-
sized on related features with positive consequences in
facing with life problems and disasters. They introduced
external factors such as ef cient school, communication
with protective adults as improving factors for toler-
ance. While, contemporary theories introduce tolerance
as multiple subject composed of natural variables such
as physical constitution and personality associated with
special skills like problem solving. It allows people resist
against life stressful events, suitably (Sha Zadeh, 2012).
Tolerance has recognized as effective subject in discus-
sions about teaching process. Tolerance level affects on
teachers ability for managing answers and reactions
which it is complex and dif cult process. It is consid-
ered as effective factor on improving quality and job
standards (Goo & Di, 2007).
On the other hand, today most of scientists and psychol-
ogists believe that self- concept determines the individual’s
behavior. When a person is faced with a situation and
stimulant that it is inconsistent with her/his behavior and
values, he/she shows strong resistant against it, but if it be
consistent with his/her behavior and values, he/she accepts
it. Charlz Werth (1995) believes that self – concept is com-
posed of three parts: 1. Body image that shows individual’s
view about his/her physical condition and it includes his/
her physical reactions. 2. Self – social includes self- racial,
cultural and religious. 3. Self – cognition that states indi-
viduals’ view about his/her mental talents. Damoon & Hart
(2001) in their research related to self- concept found out
that individuals’
positive and negative self- evaluations
affect on their social relations. Whatever it is important
that individuals behave in way to imagine themselves as
they like. They may behave in different social situations in
a way that others like them. While, those who think they
are not lovely may behave in a way that others do not
like (Homan & Deh Abadi, 2013). Also, personality types
determine mental talents and describe human behavior in
different life situations. These personality types must be
considered in job and educational consultations, whatever
is often forgotten. Holland as one of famous theorists in
eld of work psychology, his theory has been successful
more than other theories in this eld. Holland states his
theory based on two main principals:
1. Job selecting depends on type of individuals’ per-
sonality.
2. There is direct relationship between job selecting
and individuals’ view and attitude.
Hypotheses of Hollands’ theory on job selecting and
evolution has been stated based on 7 hypotheses:
1. Most people are classi ed in one of below 6 per-
sonality types: realist, searcher, artist, social, ad-
venturous and normative individuals.
2. Holland believes that there are 6 types of work
places consistent of 6 personality types. If each
personality type be in its suitable environment, it
can lead to most success.
3. Individuals search environments where allow them
to show and grow their abilities, skills, roles, val-
ues and attitudes that they like.
4. Individuals’ behavior forms by personality and
environmental factors. Job events such as job sat-
isfaction, job selecting, job success and job conti-
nuity can be predicted through consistent of per-
sonality models with environmental models.
5. It can be used hexagonal model to show the rela-
tionship between individual and job. For example,
realist person has more consistent with jobs related
to realist type and has less consistent with jobs
related to social type.
6. Also, it can be used hexagonal model to show the
adaptation level of individual with environment.
For example a person (R- N-S: realist, normative
and searcher) has more adaptation with this envi-
ronment more than a person (R-A-N: realist, artist
and normative).
7. Distinction level affects on adaptation between
individual and environment. If a person be more
similar to environment (for example, S-A-A: so-
cial, artist, adventurous) the probability of job sat-
isfaction will be more in that environment (Mon-
tazer Gaib & Keaikha Nejad, 2012).
Regarding to mentioned materials, current research has
tried to study the relationship between tolerance, self-
concept and personality type of teachers of Khash city
during 2015-16.
RESEARCH QUESTIONS AND OBJECTIVES
The main aim of this research is to study the relationship
between tolerance, self-concept and teachers
,
personality
type from Khash city. Below questions will be studied to
achieve mentioned aim:
1. There is signi cant relationship between teachers
,
tolerance and self-concept of Khash city.
2. There is signi cant relationship between teach-
ers
,
self-concept and personality type of Khash
city.
210 RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN TEACHERS’ TOLERANCE, SELF-CONCEPT AND PERSONALITY TYPE IN TEACHERS BIOSCIENCE BIOTECHNOLOGY RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS
Kord and Tamini
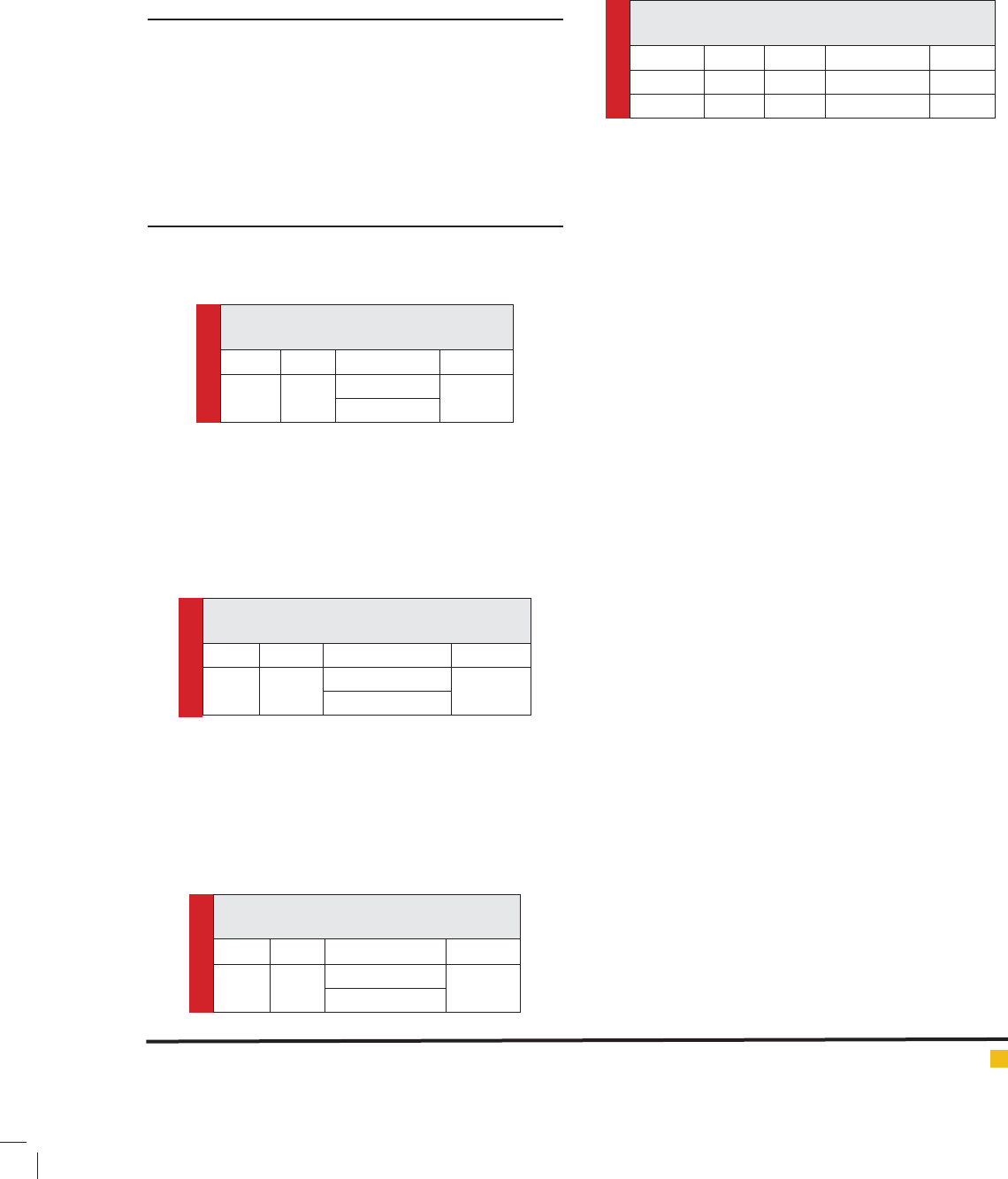
Table 1. Correlation coef cient of
teachers’ tolerance and self-concept
Group Variables rSig.
Teachers Tolerance 0.2170.01
Self-concept
Table 2. Correlation coef cient of teachers’
self-concept and personality type
Group Variables rSig.
Teachers Self-concept 0.0160.788
Personality type
Table 3. Correlation coef cient of teachers’
tolerance and personality type.
Group Variables rSig.
Teachers Tolerance 0.0950.09
Personality type
Table 4. Regression analysis of teachers’ personality
type based on tolerance and self-concept
Step Variables RR
2
Sig.
1Tolerance 0.0980.0100.090
2Self-concept0.0160.0000.788
3. There is signi cant relationship between teach-
ers
,
tolerance and personality type of Khash city.
4. Tolerance and self- concept variables predict
teachers
,
personality type.
METHODS
Current research is descriptive and correlative research.
Statistical population of this research includes 1760
teachers of Khash city during 2015-16. The sample con-
sists of 316 teachers that were selected at random and
from them were asked to ll the tolerance, self-concept
and personality type questionnaires.
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
First hypothesis: there is signi cant relationship between
teachers’
tolerance and self- concept of Khash city.
The ndings of table 3 revealed that there was no
signi cant correlation between tolerance and personal-
ity type of teachers of Khash city.
Forth hypothesis: tolerance and self-concept variables
predict teachers
,
personality type.
The ndings of table 1 revealed that there is signi -
cant and positive correlation between teachers’ toler-
ance and self – concept (r=0.217, p<0.01).
Second hypothesis: there is signi cant relationship
between teachers
,
self- concept and personality type of
Khash city.
The ndings of table 2 revealed that there is no sig-
ni cant correlation between self – concept and person-
ality type.
Third hypothesis: there is signi cant relationship
between teachers
,
tolerance and personality type of
Khash city.
The results of table 4 show that tolerance and self-
concept variables could not predict teachers
,
personality
type.
The results of rst hypothesis related to study the
relationship between teachers
,
tolerance and self-con-
cept showed that there was positive and positive rela-
tionship between teachers
,
tolerance and self- concept.
It means that increasing tolerances leads to increasing
self-concept at high level. Also, high self-concept leads
to increasing individuals
,
tolerance.
The results of the second hypothesis related to study
the relationship between teachers
,
self-concept and per-
sonality type showed that there was no signi cant rela-
tionship between teachers
,
self-concept and personality
type.
The results of the third hypothesis related to study the
relationship between teacher’s tolerance and personality
type showed that there was no signi cant relationship
between teachers,
tolerance and personality type.
The results of the forth hypothesis related to study
predictor variables of teachers
,
personality type showed
that tolerance and self-concept variables could not pre-
dict teachers
,
personality type.
Since, human resource is considered as the most
important and strategic resources of each organiza-
tion and regarding to importance of education system
for improving society and future of citizens, it is neces-
sary to provide suitable conditions such as agreement
off teachers
,
duties with their interests , competences
and abilities, selecting teachers according to their com-
petences and abilities, studying and recognizing needs
and expectations of human force, attempting to meet
their needs, creating and increasing job importance,
creating active and stimulus environment, recognizing
stressful elds and their consequences, providing con-
sulting services, creating and keeping desirable human
relations, organizing management training courses, pro-
viding suitable physical conditions and creating oppor-
tunities for resting, leaving from work temporary and
continually decrease teachers
,
mental stresses and help
their mental health.
BIOSCIENCE BIOTECHNOLOGY RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN TEACHERS’ TOLERANCE, SELF-CONCEPT AND PERSONALITY TYPE IN TEACHERS 211

Kord and Tamini
Teachers are main element of education system. If
a manager can meet teachers
,
needs, he has acted in
direction to provide needed conditions and opportuni-
ties for creating spirit, job satisfaction to achieve goals
of education system. Thus, communication of manager
with teachers is very important especial for managing
school better. When, all of responsible people in the
organization try to provide suitable and ef cient envi-
ronment for increasing the ability of their abilities and
competences and for others, this education system has
achieved perfect ef ciency. They try to provide suitable
conditions to rely on others and communicate correctly.
Thus, each member of the group can achieve job sat-
isfaction by team working, correct communication and
thinking alike each other and nally they increase the
ef ciency of education system.
REFERENCES
Burke, R., Greenglass, E. R., & Schwarzer, R. (1996). Predicting
teacher burnout over time: Effects of work stress,social sup-
port, and self-doubt on burnout and its consequences. Anxi-
ety, Stress and Coping: An International Journal, 9(3), 261-
275.
Gu, Q., & Day, Ch. (2007), Teachers resilience: A necessary
condition for effectiveness, Journal of Teaching and Teacher
Education, 23(8), 1302- 1316.
Homan, H. A., Deh Abadi, S. (2013). Psychological features of
self-concept and its relationship with social adaptation among
high school students, Sabzevar city. Journal of psychological
researches, 8, 69-84.
Montazer Gaib, T., Kaikha Nejad, M. (2012). Relationship
between job fatigue factors and Joan Holland
’
s personality
types among teachers and principals of primary schools. Jour-
nal of job and organizational consulting, 10, 92-104.
Sha Zadeh. R. (2012). Relationship between tolerance and
main ve factors of personality. Journal of research in applied
psychology. 13(3), 95-102.
Waugh, Ch. E., Fredrickson, B.L., & Taylor, S.F. (2008), Adapt-
ing to life’s slings and arrows: Individual differences in resil-
ience when recovering from an anticipated threat. Journal of
Research in Personality, 42, (1), 1031- 1046.
212 RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN TEACHERS’ TOLERANCE, SELF-CONCEPT AND PERSONALITY TYPE IN TEACHERS BIOSCIENCE BIOTECHNOLOGY RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS