Estimating the prevalence of risky behaviors by using
network scale-up method in Larestan City
Bashir Hashemi
1
and Abbas Yazdanpanah
2*
and Parviz Aghaei
3
1
Department of Healthcare Management, Marvdasht Branch, Islamic Azad University, Marvdasht, Iran
2
Assistant professor, Department of Healthcare Management, Marvdasht Branch, Islamic Azad University,
Marvdasht, Iran
3
Assistant Professor, Departmentof Medical Education Management, Cellular and Molecular Research Center,
Yasuj University of Medical Sciences, Yasuj, Iran
ABSTRACT
Risky behavior is a series of behaviors that not only seriously damages the person engaged in this behavior and
important people in his life, but also causes the unintentional harm to other innocent people. This study aimed to esti-
mate the prevalence of risky behaviors by using Network Scale-Up method in Larestan in 2016. This cross-sectional
study was conducted on 800 people aged 18 to 30 in Larestan in 2014. It was used the data checklist made by the
researcher to collect data. In order to assess the demographic variables in the subjects, SPSS software (version 16)
was used. Also, to estimate the prevalence of risky behaviors, Stata version 11 was used.Chi- Square test was used
to compare the prevalence of risky behaviors in men and women. In all analyzes, the signi cance level was 0.05.
The ndings of the study showed that the most common risky behavior in the age group of 18-30 years in Larestan
in both males and females is the tobacco products consumption in the amount of 16.82 percent and 11.06 percent,
respectively. In contrast, tattoo risk behavior on both males and females respectively in the amount of 1.18 percent
and 0.46 percent has the lowest rate. Despite the low prevalence of risky behaviors in Larestan, paying more atten-
tion to sexually active individuals can play an important role in reducing this phenomenon in the society. Therefore,
developing serious planning by the agencies that are responsible for the health, especially the health centers is essen-
tial to reduce these behaviors in the community.
KEY WORDS: LARESTAN, RISKY BEHAVIOR, NETWORK SCALE-UP METHOD
133
ARTICLE INFORMATION:
*Corresponding Author: abbas_yaz@miau.ac.ir
Received 27
th
Nov, 2016
Accepted after revision 18
th
March, 2017
BBRC Print ISSN: 0974-6455
Online ISSN: 2321-4007
Thomson Reuters ISI ESC and Crossref Indexed Journal
NAAS Journal Score 2017: 4.31 Cosmos IF : 4.006
© A Society of Science and Nature Publication, 2017. All rights
reserved.
Online Contents Available at: http//www.bbrc.in/
Biosci. Biotech. Res. Comm. Special Issue No 1:133-138 (2017)

134 ESTIMATING THE PREVALENCE OF RISKY BEHAVIORS BY USING NETWORK SCALE-UP METHOD BIOSCIENCE BIOTECHNOLOGY RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS
Hashemi and Yazdanpanah and Aghaei
INTRODUCTION
Risky behavior is a series of behaviors that not only
seriously hurts the person engaged in this behavior and
important people in his life, but also causes the unin-
tentional harm to other innocent people. Nowadays, the
prevalence of risky behaviors among young people is
one of the main concerns of the human societies and
despite the measures taken in the past three decades, the
risky behaviors have the exponential growth throughout
the world (Headquarters, 2015).
According to the report of UN Of ce on Drugs and
Crime (UNODC) in 2009, about 147 to 272 million peo-
ple in 15-64 year age group have used drugs at least
once during the past 12 month.The most common health
risky behaviors include the excessive consumption of
alcohol, drug abuse, unsafe sex, reckless driving, dan-
gerous sports, gambling and illegal acts (TW, 2006).
Researches has shown that most of these behaviors
occur on the campus (MT, 2005) and the risky behaviors
such as excessive alcohol consumption, illicit drug use
and unsafe sexual behavior can lead to high levels of
morbidity and mortality among them (Wilson , 1995).
Health risky behaviors usually begin from the child-
hood and adolescence, are established at a young age
and will continue into adulthood(Yach D, 2004). Due to
the fact that half of our population is below the age of
25 years, exploring these behaviors is important to plan
for the future. Also, since the group of society is very
vulnerable, the awareness of risky behaviors among
them is very important (Momen Nasab, 2006).Risky
behaviors have causes that must be understood and we
shall strive to eliminate the favorable social contexts for
the people’s suffering. Unfortunately, in our country, the
exact statistics on the prevalence of these behaviors in
different age groups is not available (Akbar, 2013).
Due to the sensitive issue of risky behaviors among
sexually active population and due to legal and reli-
gious restrictions, there is not much information about
this sensitive issue. Therefore, there are very few reliable
local studies in the eld that can be cited as a prec-
edent and because of the limitation of direct methods to
estimate the risky behaviors, the need to be done simi-
lar studies as soon as possible using indirect methods
will be determined to estimate such a critical behaviors
in the country (Hamdye M, 2008).Therefore, this study
aimed to estimate the prevalence of risky behaviors by
using Network Scale-Up method in Larestan in 2016.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
This is a cross-sectional study. The study population
consisted of sexually active people who were exposed
to health risky behaviors in 2016 in the city of Lar. The
instrument used is the self-made checklist. The check
list contains 2 sections. The rst part of demographic
information includes gender, age, occupation, place of
education, place of residence and marital status, and the
second part of checklist is the questions related to the
risky behaviors (smoking, hookah, pipe, opium, trama-
dol, alcohol, ecstasy and unknown drugs, migration
history, self-mutilation, drug injection as well as the
prevalence of sexual behaviors outside of marriage). The
self-made checklists were completed by the clients after
providing the necessary explanations by the interviewer,
and in the case of illiterate persons, they answered the
questions with the help of a questioner.
Since the prevalence of risky behaviors in Network
Scale-Up method is indirectly estimated, unlike other
studies, there is no formula for determining the sam-
ple size. Thus, by classifying people across age groups,
a sample with an appropriate volume is considered to
make the accuracy of estimates desirable. According to
the number of people who are sexually active in 2016
(28192 women and 30390 men), 800 patients were
studied.
After extracting and summarizing, the data was
encoded and then entered into SPSS version 16 and
Microsoft excel and nally was analyzed. The results
were reported as “number (percent)” for the qualita-
tive variables. Chi- Square test was used to compare the
prevalence of risky behaviors in men and women.
Moreover, Stata 11 software was used to estimate the
prevalence of risky behaviors in Wald method. The sig-
ni cance level was 0.05 in tests.
RESULTS
In total, 400 men and 400 women were studied. In table
1, it is shown the frequency distribution of demographic
variables in 18-30-year-old people who completed the
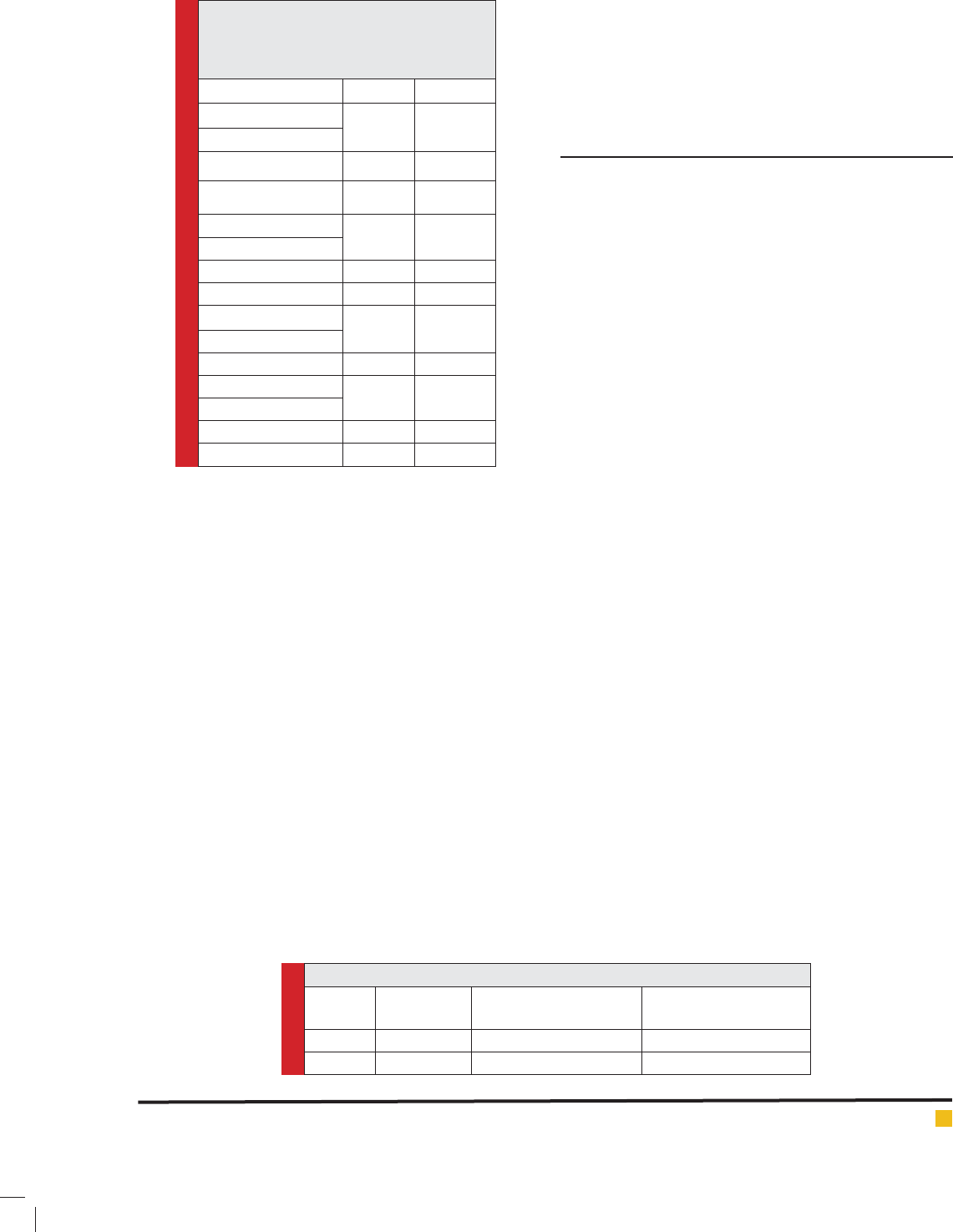
questionnaire in Larestan in 2016. As the results show
the people over 25 years old have the highest frequency
(45.42 percent). Also, most of the subjects were married
and high school graduates and were living in the city
and (Table 1).
Table 2 shows that the total of social networks in men
and women is respectively 6515 people with an average
16.29 and 5803 people with an average of 14.50 people.
In this study, the social network size (C) was found 296
people. The ndings of the study showed that the most
common risky behaviors among the age group of 18- 30
years in both males and females in Larestan is the use of
tobacco products with a frequency of 16.82 percent and
11.06 percent, respectively. In contrast, the tattoo risk
behavior on both males and females respectively with a
frequency of 1.48 percent and 0.46 percent has the low-
est rate (Table 3).
BIOSCIENCE BIOTECHNOLOGY RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS ESTIMATING THE PREVALENCE OF RISKY BEHAVIORS BY USING NETWORK SCALE-UP METHOD 135
Hashemi and Yazdanpanah and Aghaei
Table 1. The frequency distribution of
demographic variables in 18-30-year-old
people who completed the questionnaire in
Larestan in 2016.
Variable Number Percent
Age groups
8 2
11.05
Under 20 years old
20-25 years old 323 43.53
25-30 years old 337 45.42
Marital status
313 42.64
Single
Married 401 54.63
Widow 20 27.0
Address
598 78.58
City
Village 163 21.42
Education
205 27.82
Under diploma
High school Diploma 340 46.13
Collegiate 192 26.05
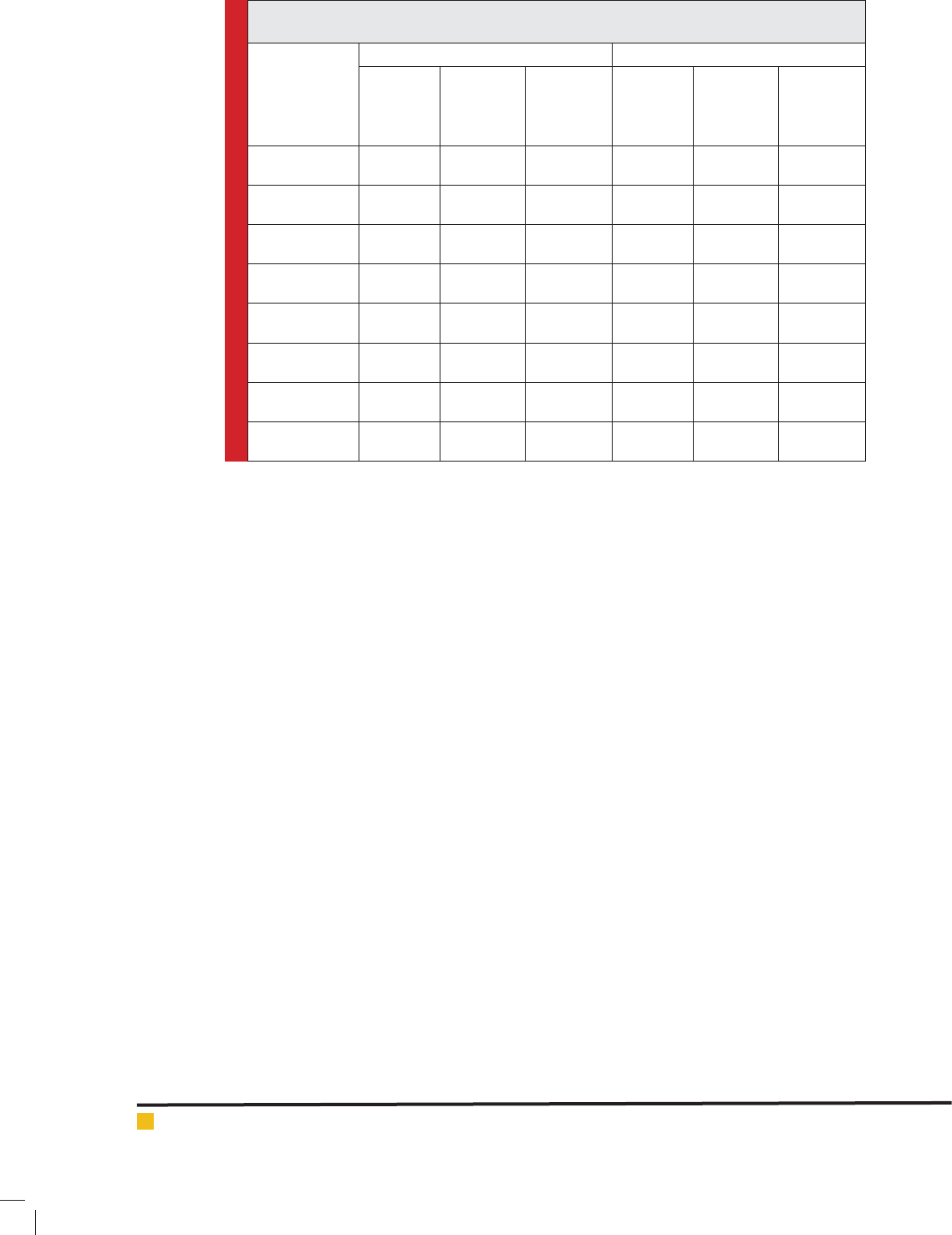
Table 3 shows the frequency of risky behaviors dif-
ferentiated by gender. The results of frequency table
estimated show the prevalence of tobacco consumption
among young people aged 18-30 years in Larestan. As
can be seen, the prevalence of tobacco consumption
among men is more than women. This difference was
statistically signi cant (P<0.001).
Also, the prevalence of drugs in men was signi -
cantly higher than women (P<0.001). The results of table
3 show the increased prevalence of psychotropic drug
use in men than in women that this difference was sta-
tistically signi cant (P=0.003). Also, in the prevalence
of dangerous actions and the estimated frequency, there
statistically was a signi cant difference between men
and women (P<0.001).
Further, the results in Table 3 show that the preva-
lence of alcohol consumption is higher in men than in
women, and this difference was statistically signi cant
in alcohol consumption (P<0.001). Moreover, the preva-
lence of unprotected sex outside the family was different
in men and women, so that the prevalence was reported
in men more than in women (P<0.001). In addition, the
prevalence of migration, particularly migration abroad
was higher among men than women (P=0.163). Finally,
the prevalence of tattooing was signi cantly higher
among men (18-30 years) than women in Larestan
(P<0.001) (Table 3).
DISCUSSION
The ndings of the study showed that the most com-
mon risky behaviors among the age group of 18- 30
years in both males and females in Larestan is the use
of tobacco products with a frequency of 16.82 percent
and 11.06 percent, respectively. In contrast, the tattoo
risk behavior on both males and females respectively
with a frequency of 1.48 percent and 0.46 percent has
the lowest rate.
The results showed that the prevalence of tobacco
products (Cigarette and hookah) has the highest fre-
quency among the other high-risk behaviors (14.05 per-
cent). According to the results of this study, it was found
that the prevalence of (cigarette) smoking is more than
hookah smoking among the subjects. In addition, the
use of tobacco products (Cigarette and hookah) in all
subjects was more common in boys than girls. Atai et
al reported the prevalence of smoking is 31.3 in Isfa-
han (Ataei B, 2011).While Ismail Zadeh in his study
showed that the hookah smoking (59.2) is more prev-
alent compared with the experience of smoking (32.7)
among students (Ismail-Zadeh, 1393).Also, in the study
of Taremian et al conducted on 2997 students in six
Tehran universities in the academic year 2005-2006, the
prevalence of smoking and hookah was estimated 15.7
and 22.1 respectively, in the past year. Contrary to the
results of this study, the prevalence of hookah smoking
was higher that this could be due to changing patterns
of tobacco use among young people and the dif culty
of hookah smoking in the student dormitories as well as
ease of smoking.
The results of this study showed that the prevalence
of drug abuse in the 18-30 year-old young people is
2.5% in Larestan. While Ismail Zadeh reported in his
study that the illicit drug abuse is 7.3%(Ismail-Zadeh,
1393). The results of another study in Kerman and Raf-
sanjan showed that the prevalence of injecting drug
use has a frequency of 61.5 percent(Torkashvand F,
2015).
Table 2. Sample size and social network total of friends of respondents
Variable Sample size Social network total of
respondents’ friends
Social network total of
respondents’ friends
Male 400 6515 16.29
Female 400 5803 14.50
136 ESTIMATING THE PREVALENCE OF RISKY BEHAVIORS BY USING NETWORK SCALE-UP METHOD BIOSCIENCE BIOTECHNOLOGY RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS
Hashemi and Yazdanpanah and Aghaei
Another study in Isfahan showed that the prevalence
of drug use among prisoners is 30.1%(Ataei 2011). Gar-
maroudi et al hjave also reported 2.7 percent of drug
use in the past month(Garmarodi, 2009). In the study
of Shokoohi et al, the estimate derived from the indi-
rect method showed that 13.1 percent of people has the
experience of drug use(B. M. Shokoohi M, Haghdoost AA
2012). The Sheikh Zadeh’s study ndings showed that
Intravenous drug use has the lowest frequency among
students(Sheikhzadeh 2016). In explaining this relation-
ship, it can be concluded that men are more exposed
to the social and economic problems and work-related
stress compared to women, which may put them at risk
for drug use.
Also, the study results showed 11.61 percent preva-
lence of alcohol and alcoholic beverages in the region.
Ismail Zadeh reported 16.7 percent of drinking alcohol
in his study(Ismail-Zadeh, 1393).The results of a study
reported an experience 17.8% in Isfahan(Ataei B, 2011).
Garmaroudi et al also reported the alcohol consumption
to 7.4 percent in the past month(Garmarodi GhR, 2009).
In the study of Shokoohi et al, the estimate derived
from the probabilistic method was higher than the fre-
quency in the direct method. According to the proba-
bilistic method, 13.7% of men had used alcohol at least
once a year( Shokoohi et al., 2012). In this study, similar
to previous studies, the prevalence of risk behaviors is
higher among boys than girls that this can be justi ed
according to boys’ more freedom in the family and soci-
ety, more courage and ease of access to drugs and alco-
hol, psychological stress caused by unemployment on
the boys and on the other hand, family’s more precise
control over the behavior of girls.
In addition, the study results showed that the preva-
lence of dangerous acts is 5.77 percent. The study of
Torkashvand et al showed that men compared with
women signi cantly had the behaviors such as self-
mutilation (p = 0/001), after the diagnosis and aware-
ness of their disease. The results of a study in Tehran
showed that most patients with self-mutilation suffer
from the borderline personality disorder and antiso-
cial personality disorder. More patients had attempted
self-mutilation in their upper limbs. Furthermore, most
patients with self-mutilation had the previous self-muti-
lation symptoms, and the average number of previous
self-mutilations was approximately 9 times and patients
with a history of 2 self-mutilations had the highest fre-
quency. In explaining the risky behavior prevalence, it
can be mentioned the people’s easy access to sharp tools
to harm themselves and attract others.
Also, the Immigration prevalence as another risky
behavior was estimated 5.75 percent in the whole sam-
ple. No studies have been conducted in this area. In
explaining the prevalence of this risky behavior (5.75%),
it can be noted that due to the city’s proximity to the
Persian Gulf states, most residents of Larestan city
migrate to the Persian Gulf states, especially Abu Dhabi,
Kuwait and Qatar.
Table 3. Risky behaviors prevalence among youths (18-30 years) differentiated by gender in
Larestan
Risky behavior
Male Female
Estimated
frequency
Prevalence 95%
con dence
interval
Estimated
frequency
Prevalence 95%
con dence
interval
Consumption of
tobacco products
5112 16.82 -17.75
15.92
3119 11.06 10.26
-11.89
drug use 1129 3.71 3.26
-4.20
364 1.29 1.01
-1.61
Psychotropic
drug use
708 2.33 1.98
-2.72
446 1.58 1.27
-1.94
Dangerous Acts 2020 6.64 6.05
-7.27
1360 4.82 4.28
-5.40
alcohol
consumption
4373 14.39 -15.27
13.55
2433 8.63 7.92
-9.38
Sex outside the
family
2631 8.65 7.98
-9.36
1756 6.23 5.62
-6.89
Emigration 1833 6.032 5.48
-6.63
1536 5.44 4.87
-6.06
Tattoo 359 1.18 0.93
-1.47
132 0.46 0.30
-0.67

BIOSCIENCE BIOTECHNOLOGY RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS ESTIMATING THE PREVALENCE OF RISKY BEHAVIORS BY USING NETWORK SCALE-UP METHOD 137
Hashemi and Yazdanpanah and Aghaei
Another high-risk behavior examined in this study
was a history of sex before marriage that it was observed
nearly 7.5 percent of 15-30 year-olds have experienced
this behavior. The results of a study in Isfahan showed
that the risky behaviors, including partner’s illicit sex is
22.1%, illicit sexual relationship and a history of tem-
porary marriage are 17.8%(Ataei B, 2011). The study
results of Torkashvand et al in the city of Kerman and
Rafsanjan indicated that the unprotected sexual behav-
ior with a frequency of 40% is a risky behavior before
HIV diagnosis(Torkashvand 2015)Kolahi et al showed in
their study that the female sex workers (prostitutes) who
have non-commercial intercourse use condom 1.8 times
less than those that have commercial intercourse(Kolahi
AA). Garmaroudi et al reported that the prevalence of
health risk behaviors such as sexual activities is 20.2%
in Tehran(Garmarodi 2009).
In the study of Shokoohi et al in the indirect method,
sex outside the family was estimated 12% over the last
year, while sex with female sex workers was reported
7%(Shokoohi et al., 2012). Moreover, in the study of
Sheikh Zadeh et al in the indirect method, the alco-
hol consumption was the most common risky behavior
among men and sex outside of marriage was the most
common behavior in women(Sheikhzadeh 2016).The
history of premarital sex among boys was more than
girls that due to the cultural and religious structure of
Iranian society is a signi cant outbreak.
The high prevalence of premarital sex can be a sign of
fading interest in religion among young people, lack of
suitable conditions for marriage and sometimes a sign of
modernity.Although tattooing is often done with care, it
is not totally risk-free, and can transmit the blood-borne
infections. Limited serologic studies on people who have
a history of tattooing have shown that tattooing could
be a way to transfer the viral infections, particularly
hepatitis B virus.
Tattoo prevalence was estimated 0.84% in the total
sample. A study in 2002 showed that people who
have been tattooed become infected with the Hepati-
tis C virus 9 times more than those who have not been
tattooed. Also, among the 454 students, 50 percent
of them pierced parts of the body such as the lip, ear
and navel, and 25 percent had a history of tattooing.
Almost 20 percent of those who had the tattoo effects
on their body were suffering from the complications
such as bacterial infection, bleeding and skin and tis-
sue damage in the area of tattooing. The results of a
study showed that the rate of positive HBsAg in the tat-
tooed women was 7.9% in Zahedan(Shari moud and
Metanat 2007). Torkashvand et al stated in their study
that a third of people with HIV had a history of tat-
tooing before the diagnosis of the disease (Torkashvand
2015).
The prevalence of psychotropic drug use was 0.84
percent in the total sample. In the study of Hamdieh
et al, the prevalence of psychotropic drugs was reported
3.8% in youth and adolescents in Tehran(Hamdieh et al.,
2008). In the study conducted by Ahmadi et al on the
students of Shiraz city, a frequency of smoking mari-
juana, heroin, morphine and cocaine was 0.8, 1, 0.8 and
0.5 percent, respectively(Ghaderi, 2015). Pourasl et al
stated in their study that 20 percent of high school stu-
dents have the experience of psychotropic drug use in
Tabriz. Perhaps, a possible justi cation for the increase
in other studies is that people in those areas have easy
access to the psychoactive drugs.
In the results of this study, social network size in
males and females was estimated 16.29 and 14.5, respec-
tively. This suggests that on average, men and women
in the age group 18-30 years are familiar with 16 males
and 14 females in this age group. This implies that on
average, each man communicates with 1.12 people more
than women. While a study in Kerman showed that the
social network size in men and women is 25.8 and 29.5,
respectively. On average, each man communicates with
3.8 people more than women(Sheikhzadeh 2016).
Moreover, in the study of Shokoohi et al in 2010, it
was suggested that the social network size estimated in
Iranian population is 303 people( Shokoohi et al., 2012).
The value has been estimated much more in this study
and a study done in Kerman. This difference may be due
to the different de nitions of social network in the stud-
ies. In a study of Kerman, it was related only to the social
network of students on campus. In this study, it also
covered the sexual age groups 18-30 years(Sheikhzadeh
2016).
According to the results, the following suggestions
are recommended:
In addition, to reduce the prevalence of risky behav-
iors among young and active population of our country,
the following are recommended:
Improving the knowledge and attitude of people, especially
sexually active people aged 18-30 years in conjunction
with risky behaviors
Improving the knowledge and attitude of mental health care
workers and psychiatrists in relation to the risky behaviors
through mandatory training sessions for all employees
Development of life skills training as a primary prevention
program of alcohol, tobacco and other drugs in the youth
in order to reduce drug use among young people by Educa-
tion’s of cials and planners
A comprehensive review and evaluation on a large scale
in the eld of implementing the program by counseling
center for the prevention of behavioral health and identify-
ing the weaknesses and providing the strategies to improve
the program
Evaluation of the knowledge and attitude of mental health
care workers in relation to the risky behaviors

138 ESTIMATING THE PREVALENCE OF RISKY BEHAVIORS BY USING NETWORK SCALE-UP METHOD BIOSCIENCE BIOTECHNOLOGY RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS
Hashemi and Yazdanpanah and Aghaei
Evaluation of the knowledge and attitude of target groups
in relation to the risky behaviors
Further studies on the causes and motivations of people for
the tendency toward the risky behaviors
CONCLUSION
Despite the low prevalence of risky behaviors in Lar-
estan, paying more attention to sexually active individ-
uals can play a critical role in reducing this phenome-
non in the community. Therefore, developing the serious
planning by the agencies that are responsible for the
health, especially the health centers is essential to reduce
these behaviors in the community.
STUDY LIMITATIONS
Entry criteria for the study includes all women and men
aged 18-30 years living in Larestan.
Exclusion criteria do not include other people outside
the age group 18-30 years are not included.
Exclusion criteria do not include other non-native
people.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The authors thank and appreciate all those who have
cooperated in implementing this plan as well as health
personnel who have cooperated and assisted in complet-
ing the checklists.
REFERENCES
Akbar, A. (2013). Past Human Development Quarterly Journal
of Social Deveopment, 7(3), 123-154.
Ataei B, K. F., Azadeh S, Nokhodian Z, Kassaian N, Anahita
Babak. (2011). The Prevalence of High Risk Behaviors among
Women Prisoners in Isfahan. Journal of Isfahan Medical School
2011, 29(150), 170-177.
Garmarodi GhR, M. J., Abasi Z. (2009). Health risky habits in
students of Tehran Monitoring 9(1), 9-13.
Ghaderi, M. A., Zeinab; Darabzadeh, Fatemeh; Nasiri, Morteza;
Fakouri, Elham. (2015). Correlation between Emotional Intel-
ligence and Risky Sexual Behaviors in Nursing Students of
Khozestan Province Universities in 2013. Journal of Clinical
Research in Paramedical Sciences, 4(1).
Hamdye M, M. N., Hasheri H, Berojerdi A. (2008). Prevalence
of stimulant drugs, alcohol and psychoactive drugs Youth and
adolescents 15-35 years in Tehran. Original Article, 32(4), 315.
Headquarters, I. D. C. (2015). Exponential Growth of Danger-
ous Behaviour Among Youngsters Etemad Newspaper, 16().
Ismail-Zadeh, H., Asadi, M., Miri, Mir Nadir, Kramtkar, Mary.
(1393). MaryThe prevalence of risky behaviors among Journal
of Epidemiology Specialist. adolescents in iran, 10, 75-82.
Kolahi AA, R. A., Abadi AR, Nabavi M, Sayyarifard A, Sohrabi
M. The knowledge and attitudes of a female at risk popula-
tion towards the prevention of AIDS and sexually transmitted
infections in Tehran. J Res Med Sci 16(11), 1452-1455.
Momen Nasab, M. N., Seyed Saeid; Kaveh, Mohammad Hos-
sein; Ahmadpour, Farnaz. (2006). Evaluation of Spreading
Amount of Risky Sanitary Behaviour Among the Students of
Higher Education in the City of Khorram Abad in 2005-06.
Hafteh, 8(2), 29-32.
Buelow MT (2005). The In uence of Cognitive, Personality and
Social Variables: Predicting Changes in Risky Behaviors over a
Two-Year Interval. College of Arts and Science.
Gestv R, B. (2013). Comparison of indicators related with
injecting drug users(IDUs) in Iran before and after the harm
reduction programme. Kerman University of Medical Sciences;.
Shari moud B. Metanat M, G. H. (2007). Prevalence Of Trans-
fusion-Transmitted Viral Infections Among Women With His-
tory Of Tattoo In The City Of Zahidan During 2004-06. Iranian
Journal of Infectious Diseases and Tropical Medicine, 12(37),
66-69.
Sheikhzadeh KH, B. M., Afshari M, Haghdoost AA (2016).
Comparing direct, network scale-up, and proxy respondent
methods in estimating risky behaviors among collegians. Jour-
nal of Substance Use, 21(1), 9-13.
Shokoohi M, B. M., Haghdoost A. (2012). Size Estimation of
Groups at High Risk of HIV/AIDS using Network Scale Up in
Kerman, Iran. International journal of preventive medicine,
3(7), 471.
Shokoohi M, B. M., Haghdoost AA (2012). Size estimation of
groups at high risk of HIV/AIDS using network scale up in Ker-
man, Iran. Int J Prev Med, 3, 471-476.
Torkashvand F, A. M., Sheikh Fathollahi M, Sheikhi E, Salehi
Shahrbabaki M.H, Hoseini OR, Bakhtar M, Bidaki R (2015).
Frequency of High Risk Behaviour in HIV Positive Patients
Referred to Centers for Behavioural Disorders of Rafsanjan
and Kerman. J RafsanjanUniv Med Sci in 2012, 14(7), 587-
598.
Boyer TW ( 2006). The development of risk-taking. multiper-
spective review. Dev Rev, 26, 291-345.
Wilson MD, J. A. (1995). Adolescent medicine. JAMA, 273(21),
1657-1659.
Yach D, H. C., Gould CL, Hoffman KJ. (2004). The Global Bur-
den of Chronic Disease: Overcoming impediments to preven-
tion and control. JAMA, 291
, 2616-2622.