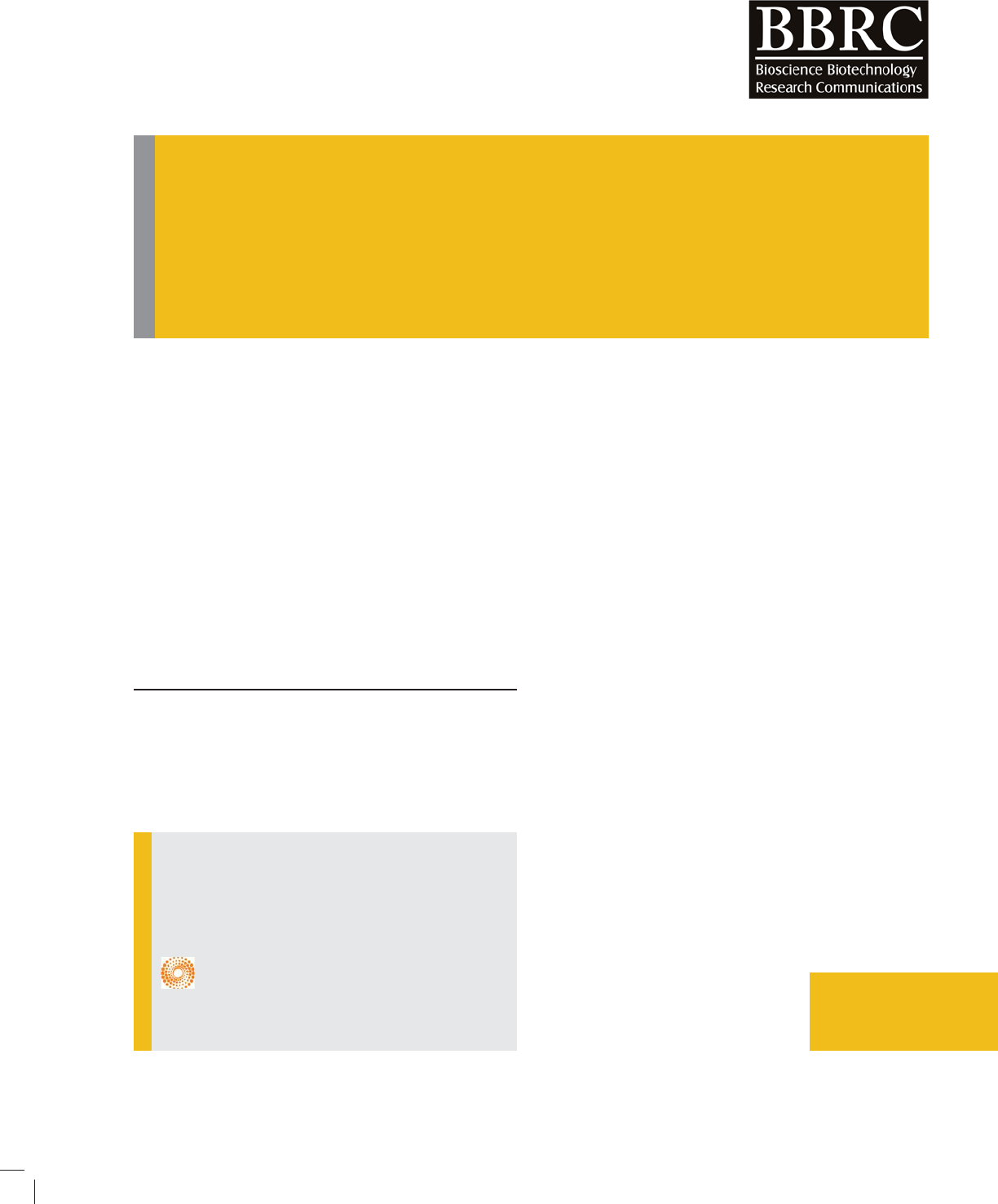
Investigating pseudo Jahn-Teller effect on inter-
molecular hydrogen bond in enolic forms of benzonium
compounds and analog containing P and As atoms
Elahe Jalali
Department of Chemistry, Damghan Branch, Islamic Azad University, Damghan, Iran
ABSTRACT
This study investigates the effect of Pseudo Jahn-Teller Effect (PJTE) on distortion of hydrogen bonds of high sym-
metry forms of 1, 3-di (pyridine-2-yl) Benzonium (1) and analog containing P (2) and As (3) atoms. The results of
B3LYP/6-311++G** method indicate that the forms having inter-molecular hydrogen bond in compounds (1)-(3)
with C2V symmetry have the highest value of ground state electron con guration energy (ECE). Applying normal
coordination, C2V high symmetry forms turn into Cs low symmetry forms. C2V high symmetry form have two vir-
tual frequencies with b2 and b1 symmetry. In Pseudo Jahn-Teller problem, compounds (1)-(3) are in in the forms of
(A1+B2) b2 and (A1+B1) b1, and the energy difference between reference combining levels (Δ) reduces from
compound (1)-(3).
KEY WORDS: PSEUDO JAHN-TELLER EFFECT, HYDROGEN BOND, INTER-MOLECULAR DISTORTION, COMPUTATIONAL CHEMISTRY, GAUSSIAN
SOFTWARE
122
ARTICLE INFORMATION:
*Corresponding Author: ala.jalali@gmail.com
Received 29
th
Dec, 2016
Accepted after revision 29
th
March, 2017
BBRC Print ISSN: 0974-6455
Online ISSN: 2321-4007
Thomson Reuters ISI ESC and Crossref Indexed Journal
NAAS Journal Score 2017: 4.31 Cosmos IF : 4.006
© A Society of Science and Nature Publication, 2017. All rights
reserved.
Online Contents Available at: http//www.bbrc.in/
INTRODUCTION
In recent years, increasing growth of quantum chemistry
and emergence of high-speed computers has led to crea-
tion of a new eld in chemistry, called computational
chemistry, in which computers are used as an empirical
device. The main objective of this newly found eld in
the chemistry science is just proving the results related
to chemistry problems, and the computational methods
used today are one of the most powerful tools to study
the mechanism of reactions and predict the characteris-
tics of stable molecules, namely their nature, formation,
bond energy, etc. (Hamilton et al. 1962).
In certain chemical compounds, hydrogen bond
has been the subject of many researches because of its
signi cant importance. The signi cant role of hydrogen
Biosci. Biotech. Res. Comm. Special Issue No 1:122-129 (2017)
Elahe Jalali
bond in chemical and bio-chemical phenomena, as well
as the nature of this bond’s structure, has scienti cally
made it remarkable and worthy of further scrutiny and
research. Phenomena affected by hydrogen bond are
extensively found in daily life. These phenomena can
go under specialist assessment by empirical techniques
(Pimcntel and Clellan, 1976).
Inter-molecular hydrogen bond (IMHB) exists in many
organic molecules and bio-molecules such as carbohy-
drates, hormones, and proteins. Furthermore, this type of
bond determines the con guration of many molecules,
and it is because of such bond that proteins have unique
con gurations. An important parameter in classifying
systems with hydrogen bond is its strength. Structur-
ally, this strength is determined by parameters such as
the distance between two electronegative atoms (A…B),
length of hydrogen bond (H…B), length of covalent bond
(A–H), and bond angle (A^H^B), as well as thermodynamic
parameters such as enthalpy of formation (ΔHf), entropy
of formation (ΔSf), and Gibbs free energy (ΔGf) (Pauling,
1960; Speakman, 1975). These empirical methods expe-
rienced cannot measure hydrogen bond strength, or at
least have limited applications. Theoretical and computa-
tional methods are more ef cient and comprehensive in
this context, in which molecules can be optimized in any
structural and electron mode in terms of energy. These
methods, which seem necessary for measuring inter-
molecular hydrogen bond energy, have also signi cantly
developed after emergence of ultra-modern computers
with high speed and performance.
Reviewing the literature revealed that no reports have
yet been published related to the objectives of this study.
Given the fact that hydrogen bond is one of the effec-
tive factors in human life, its effect has been examined in
1,3-di(pyridine-2-yl)Benzonium (1) and analog contain-
ing P (2) and As (3) atoms by pseudo Jahn-Teller analysis
using high level B3LYP/6-311++G** theoretical method.
It is expected that the pseudo Jahn-Teller effect can
describe the transformation of C2V high symmetry
structures to Cs low symmetry structures in the follow-
ing compounds (Figure 1):
(1) 1,3-di(pyridine-2-yl)Benzonium (2) and analog
containing P atoms (3) and As atoms
It was found that compounds (1)-(3) mentioned above
have C2V high symmetry con guration. By Q transfor-
mations, the rst three compounds with C2V high sym-
metry con guration turn into Cs con guration.
This study carefully investigates the important issue
of ground state electron mixing in electron exited
state in the direction of applying normal coordination
describing leaving high symmetry and transforming into
low symmetry. The major cause of deformation was the
pseudo Juan-Teller effect, which was created by com-
bining the ground state and excited states.
Since the electron ground state of these compounds
is not aligned, it is obvious that all deformations
observed from linear con guration with the highest
symmetry is due to pseudo Juan-Teller effect (Bersu-
ker, 2006). Generally, the pseudo Juan-Teller effect is
associated with non-aligned stated of any system,
Juan-Teller effect is associated with aligned stated of
non-linear molecules, and Renner-Teller effect is associ-
ated with aligned stated of linear molecules (Bersuker,
2001).
All of these effects are general and unique forms,
each describing symmetrical instability and many other
issues brie y discussed in the following.
MATERIAL AND METHODS
COMPUTATIONAL METHODOLOGY
First, the molecular form, written based on Zmatrix, will
be drawn and numbered, given the desired symmetry.
Then, the optimal molecular structure and its negative
frequency will be calculated using Gaussian 03 & 98
software. Then, DFT hybrid-based method (B3LYP) with
6-311++G** base series will be used for all desired com-
pounds.
Computational time depends on the Density Function
Theory (DFT). TD-DFT is, for sure, one of the most com-
mon tools for investigating the excited levels of molecu-
lar systems, which has been used to study the electron
con guration of Enolic structures of 1,3-di(pyridine-
2-yl)Benzonium and analog containing P and As
atoms.
Results of B3LYP/6-311++G** and TD-DFT shows that
the major reason for deformation of high symmetry con-
gurations (C2V) to low symmetry con gurations (Cs)
for these compounds is pseudo Juan-Teller effect, which
is created by combining ground state and excited stated.
The energy difference (Δ) and pseudo Juan-Teller stabil-
ity energy between reference stated and ΔEe1 in these
forms (C2V Cs) is also investigated.
FIGURE 1. Symmetrical transformation of C2V and
3-di(pyridine-2-yl)Benzonium, analog containing P
and As atoms in Cs form (C2V Cs) using calcula-
tions in B3LYP/6-311++G** theoretical level (X= N,
P, As)
BIOSCIENCE BIOTECHNOLOGY RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS INVESTIGATING PSEUDO JAHN-TELLER EFFECT ON INTER-MOLECULAR HYDROGEN BOND 123
Elahe Jalali
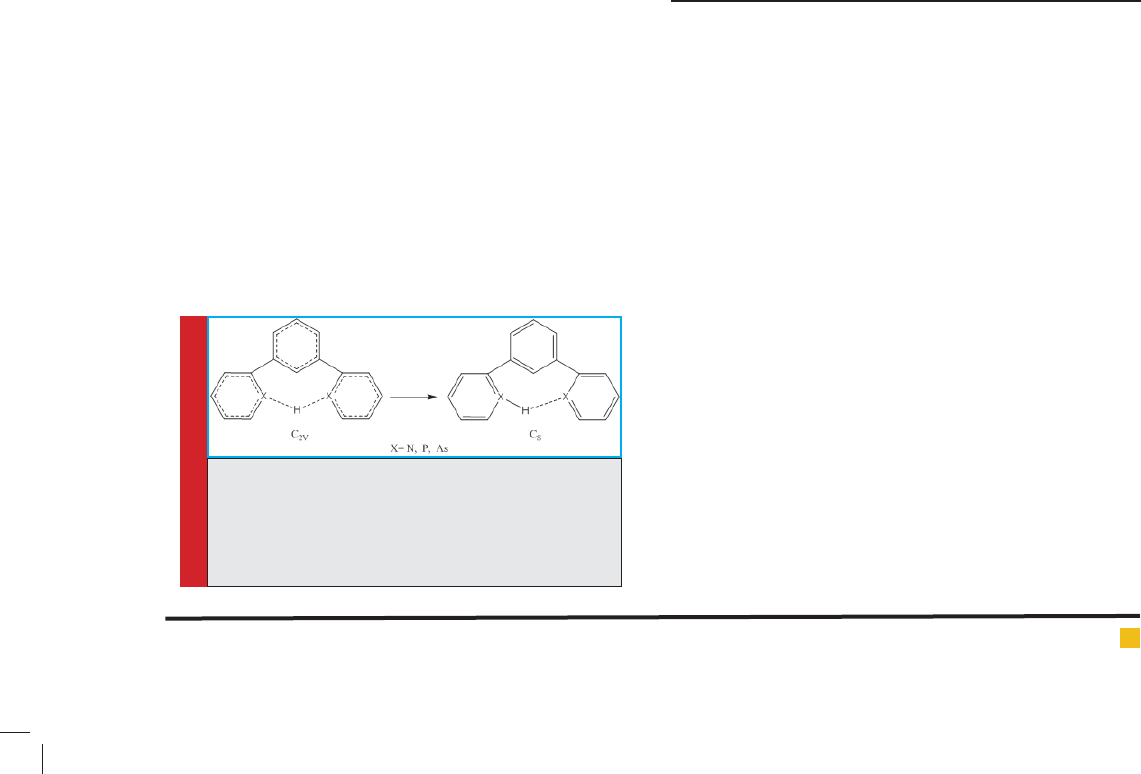
FIGURE 2. Symmetrical transformation of C2V in
1,3-di(pyridine-2-yl)Benzonium (C2V Cs) using
calculations in B3LYP/6-311++G** theoretical level
FIGURE 3. Initial energy levels calculated (ground state and excited state with
B2 symmetry) in 1,3-di(pyridine-2-yl)Benzonium molecule, and their changes
by pseudo Juan-Teller effect ( rst case)
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Quantum mechanics calculations in the B3LYP/6-
311++G** initial level was used to examine the structural
properties of molecules in compounds (1)-(3).
3-1. Investigating pseudo Juan-Teller effect on
distortion of 1,3-di(pyridine-2-yl)Benzonium molecule
(compound No. 1)
Initial quantum mechanics calculations in the B3LYP/6-
311++G** theoretical level showed that 1,3-di(pyridine-
2-yl)Benzonium structure has C2V high symmetry, while
has low symmetry in Cs point group, whose deviation
with high symmetry arrangement is due to pseudo Juan-
Teller effects, which is the only source of instability for
arrangements with high symmetry in aligned and non-
aligned states. Deviations is created by combining the
base level A1 and the excited level B2 through displace-
ment of b2, and in another case by combining base level
A1 and the excited level B2 through displacement of b1.
Pseudo Juan-Teller results in (A1+B2) b2 and (A1+B1)
b1 problems.
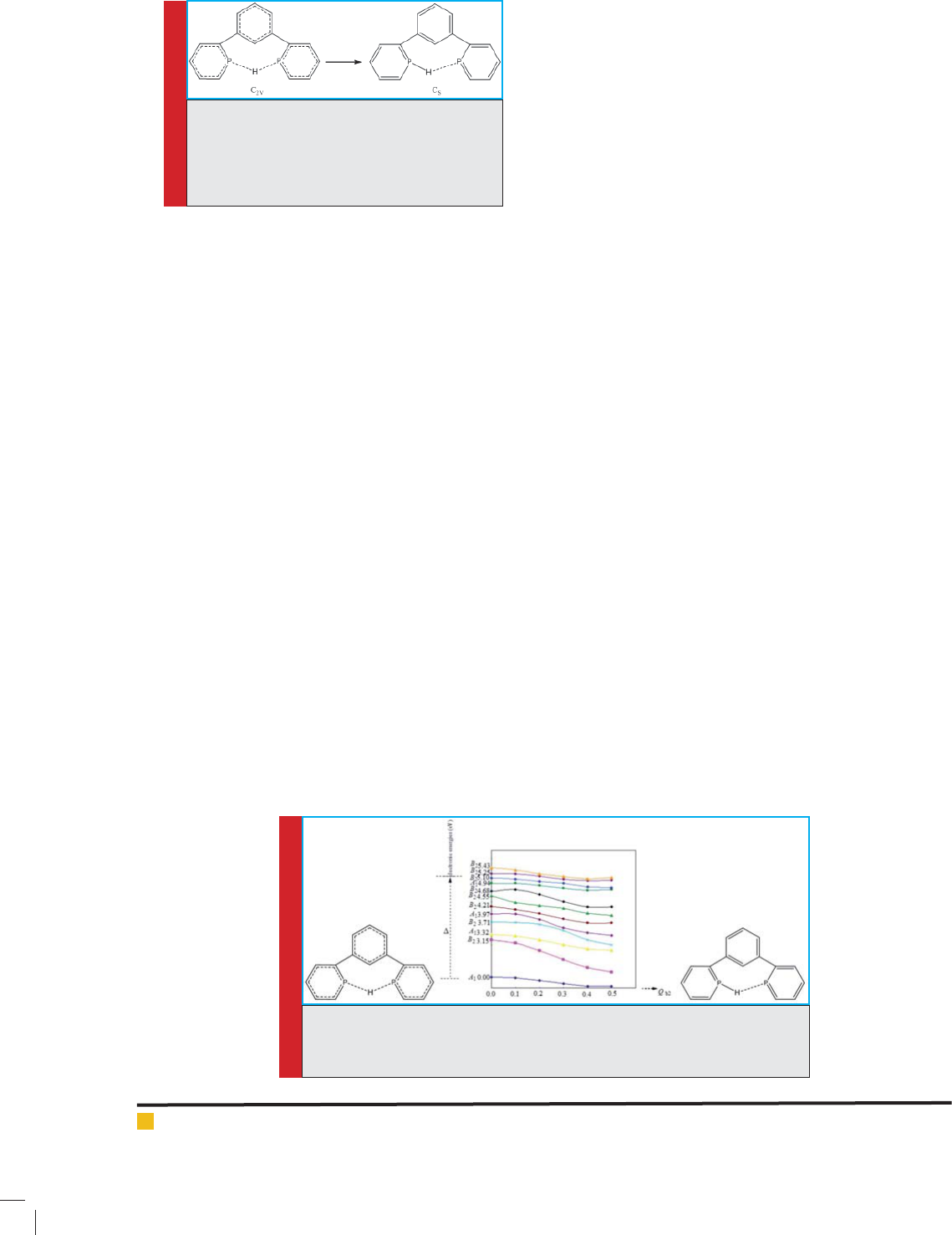
The energy difference between ground state and
excited level B2 (Figure 3) and between ground state
and excited level B1 (Figure4), along with combination
of orbitals is 5.35 eV and 5.55 eV, respectively.
1. [Homo – 3 (A2) Lumo 1(B1), Homu – 2(B1)
Lumo (A2), Homo –1 (A2) Lumo + 3 (B1)],
[Homo – 1 (A1) Lumo + 5(B1)]
2. [Homo – 7 (A1) Lumo + 1(B1), Homo – 5(B2)
Lumo (A2)]
Given the reduction of energy difference in your
desired compound in B2 symmetry compared to B1, its
pseudo Juan-Teller energy would be higher. ΔEe1 also
con rms it in this case.
The electron energy of some excited levels for
1,3-di(pyridine-2-yl)Benzonium structure, calculated
in B3LYP/6-311++G** theoretical level (eV), is given
in Table 1, which indicates that B1 excited level with
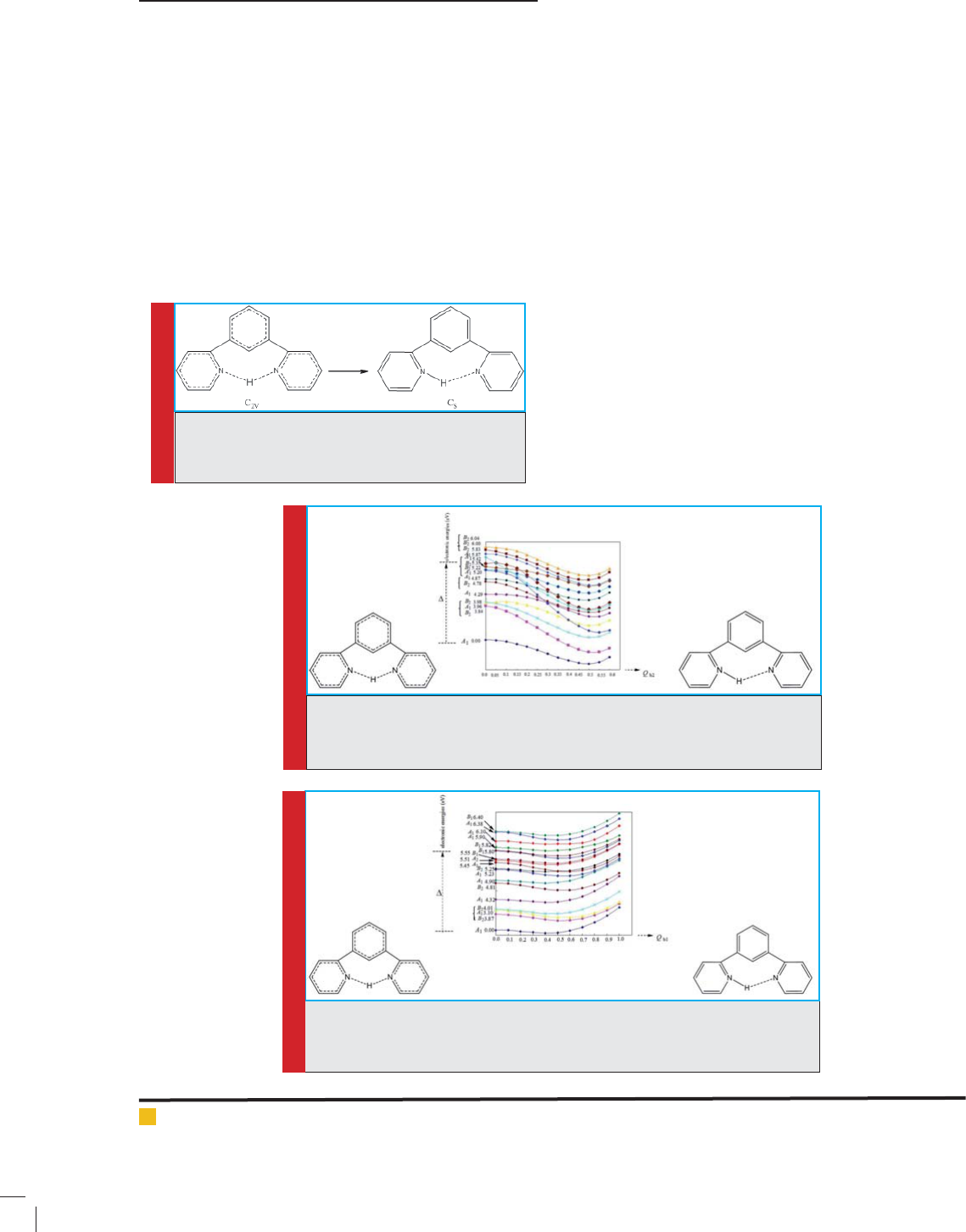
FIGURE 4. Initial energy levels calculated (ground state and excited state with
B1 symmetry) in 1,3-di(pyridine-2-yl)Benzonium molecule, and their changes
by pseudo Juan-Teller effect (second case)
124 INVESTIGATING PSEUDO JAHN-TELLER EFFECT ON INTER-MOLECULAR HYDROGEN BOND BIOSCIENCE BIOTECHNOLOGY RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS
Elahe Jalali
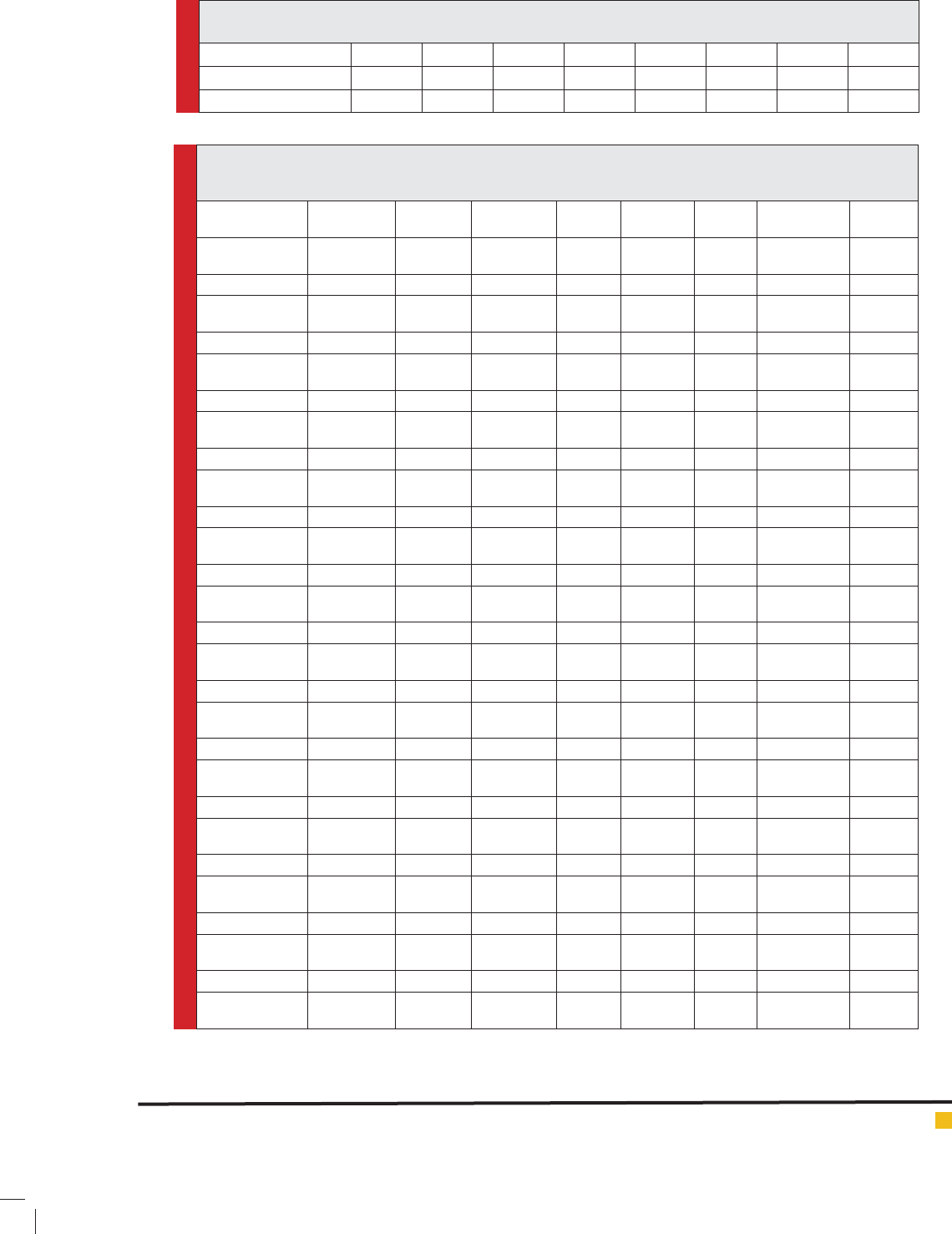
Table 1. Investigating the energy of excited levels (eV) of 1,3-di(pyridine-2-yl)Benzonium in symmetrical
transformation (C2V Cs) (two cases).
B
2
A
1
B
2
A
1
B
2
B
2
A
1
B
1
1. C
16
H
13
N
2
(+1) 3.84 3.96 3.98 4.29 5.22 5.35 5.42 –
2. C
16
H
13
N
2
(+1) 3.87 3.10 4.01 4.32 5.25 – 5.45 5.55
Table 2. The thermodynamic functions calculated (enthalpy, Gibbs free energy (Hartree), and entropy (calmil-1k-1)), ground
state energy, and their changes in 25°C and 1 atm for compounds ,3-di(pyridine-2-yl)Benzonium, analog containing P and As
atoms, using calculations in B3LYP/6-311++G** theoretical level.
Geometries H (Hartree)
S
(cal mol
1
K
-1
)
G (Hartree)
ΔHa
(Hartree)
ΔS
a
(calmol
1
K
-1
)
ΔG
a
(Hartree)
Eel ΔEel
1-C16H13N2(1+).
TD 0.0
-726.618341 109.243 -726.670246 0.120568 0.0000 0.123099 -726.8782112 0.1259201
(75.66) (77.25) (79.02)
1- C16H13N2(1+).
TD 0.5
-726.738909 114.569 -726.793345 0.0000 5.326 0.0000 -727.0041313 0.0000
(0.00) (0.00) (0.00)
2- C16H13N2(1+).
TD 0.0
-726.618341 109.243 -726.670246 0.076013 0.000 0.076965 -726.8782112 0.0765166
(47.70) (48.30) (48.01)
2- C16H13N2(1+).
TD 0.4
-726.694354 111.246 -726.747211 0.0000 2.003 0.000 -726.9547278 0.0000
(0.00) (0.00) (0.00)
3- C16H13P2(1+).
TD 0.0
-1299.850127 118.706 -1299.906528 0.045676 4.414 0.043578 -1300.0992816 0.0477544
(28.66) (27.35) (29.97)
3- C16H13P2(1+).
TD 0.4
-1299.895803 114.292 -1299.950106 0.0000 0.0000 0.0000 -1300.147036 0.0000
(0.00) (0.00) (0.00)
4- C16H13P2(1+).
TD 0.0
-1299.850127 118.706 -1299.906528 0.02395 0.0000 0.024946 -1300.0992816 0.0244918
(15.03) (15.65) (15.37)
4- C16H13P2(1+).
TD 0.4
-1299.874077 120.804 -1299.931474 0.0000 2.098 0.000 -1300.1237734 0.0000
(0.00) (0.00) (0.00)
5- C16H13As2(1+).
TD 0.0
-5088.839500 120.345 -5088.896680 0.03185 1.068 0.031342 -5089.0854207 0.0346449
(19.99) (19.67) (21.74)
5- C16H13As2(1+).
TD 0.4
-5088.871350 119.277 -5088.928022 0.0000 0.0000 0.000 -5089.1200656 0.0000
(0.00) (0.00) (0.00)
6- C16H13As2(1+).
TD 0.0
-5088.839500 120.345 -5088.896680 0.017477 0.0000 0.021056 -5089.0854207 0.0189186
(10.97) (13.21) (11.87)
6- C16H13As2(1+).
TD 0.5
-5088.856977 127.877 -5088.917736 0.0000 7.532 0.0000 -5089.1043393 0.0000
(0.00) (0.00) (0.00)
7- C16H13As2(1+).
TD 0.0
-5088.839500 120.345 -5088.896680 0.000686 0.0000 0.002027 -5089.0854207 0.001695
(0.43) (1.27) (1.06)
7- C16H13As2(1+).
TD 0.4
-5088.840186 123.167 -5088.898707 0.0000 2.822 0.0000 -5089.0871157 0.0000
BIOSCIENCE BIOTECHNOLOGY RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS INVESTIGATING PSEUDO JAHN-TELLER EFFECT ON INTER-MOLECULAR HYDROGEN BOND 125
Elahe Jalali
an energy about 5.55 eV poorly contributes in creating
pseudo Juan-Teller effect.
The value of thermodynamic parameters ΔG, ΔH, ΔS,
and ΔEe1 of the desired compound, shown in Table 2,
was calculated using B3LYP/6-311++G** method. The
results show that the value of ΔEe1 for 1,3-di(pyridine-
2-yl)Benzonium is 79.02 kCal/mol and 48.01 kCal/mol
for B2 symmetry and B1 symmetry, respectively, which
implies that the desired compound with B1 symmetry
has lower pseudo Juan-Teller stability energy. Since the
energy difference between the ground and excited states
of B2 is lower than that of B1, its ΔEe1 is higher, so
1,3-di(pyridine-2-yl)Benzonium with B2 symmetry has
higher pseudo Juan-Teller stability energy.
3-2. Investigating pseudo Juan-Teller effect on
distortion of analog containing P 1,3-di(pyridine-2-yl)
Benzonium atom (compound No. 2)
Structural properties of compound No. 2 was examined
using B3LYP/6-311++G** theoretical level. The results
showed that compound No. 2 has C2V high symmetry,
and has low symmetry in point group. Deviations of this
arrangement with high symmetry are caused by psuedo
Juan-Teller effect, which is the only source of instability
for arrangements with high symmetry in aligned and
non-aligned states. The deviations are formed as a result
of combining the compound of ground state A1 and
excited level B2 by displacement b2, and another case
as a result of combining the ground state A1 and excited
level B1 through displacement b1, i.e., Energy difference
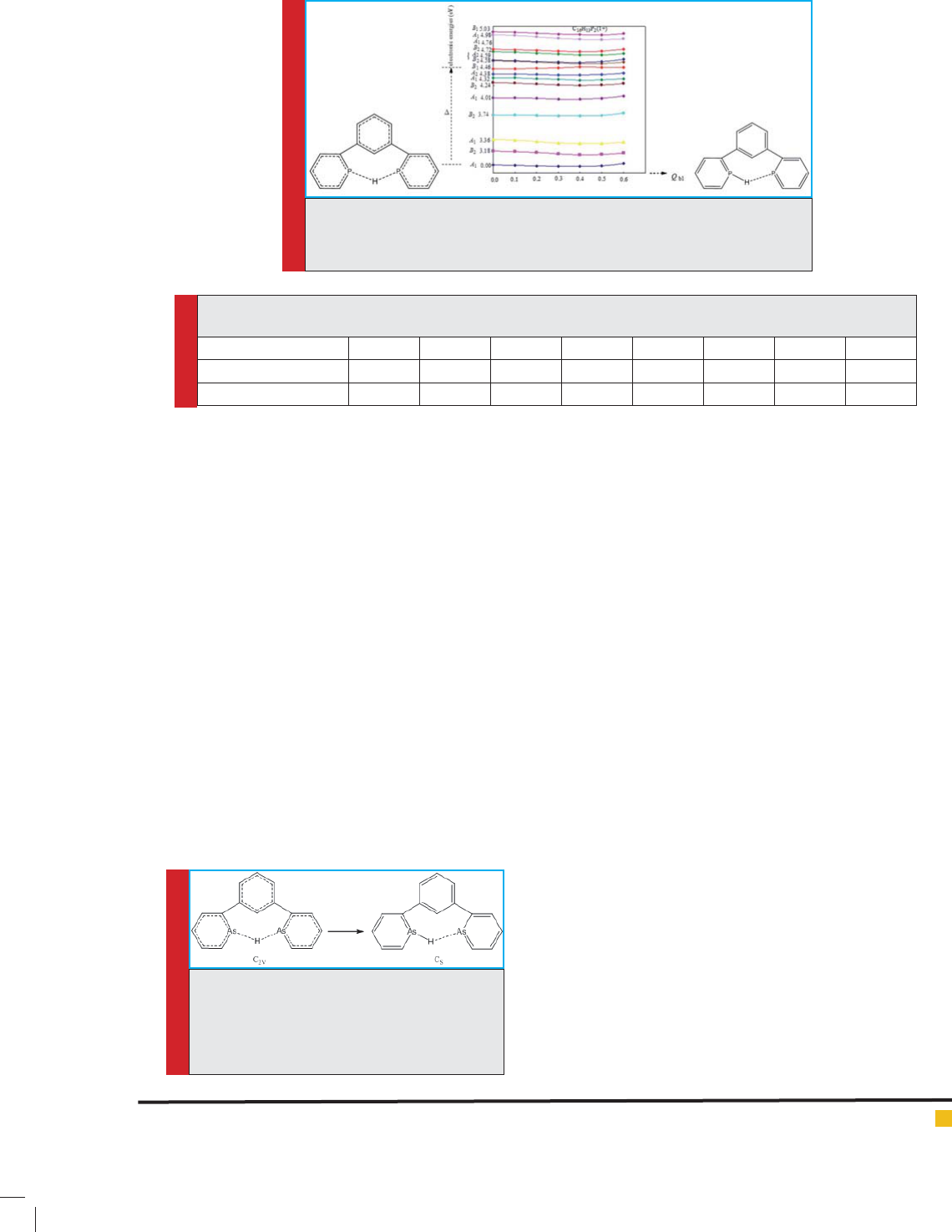
between ground state and excited state B2 ( rst case)
and between ground state and excited state B1 (second
case) is 5.10 and 4.46 eV, respectively.
1. [Homo – 6 (A2) Lumo (B1), Homo – 5(B1)
Lumo+1(A2), Homo – 5 (B1) Lumo + 2 (A2),
Homo – 3 (B1) Lumo + 1(A2), Homo – 2 (A2)
Lumo (B1), Homo – 1(B1) Lumo + 2 (A2), Homo
(A2) – Lumo + 4(B1), Homo (A2) Lumo + 5 (B1)]
2. [Homo – 4 (B2) Lumo + 1(A2), Homo – 1(B1)
Lumo + 3 (A1)]
So, pseudo Juan-Teller results in (A1+B2) b2 and
(A1+B1) b1 problems.
Given the reduction in the energy difference of the
desired compound in B1 symmetry, it is expected that its
pseudo Juan-Teller energy would be higher (regardless
of other factors).
Figures 6 and 7 show the energy of ground level and
excited levels, as well as the deviations of arrangements
with high symmetry due to pseudo Juan-Teller effect.
The electron energy of a number of excited levels
for the structure of the compound No. 2, calculated in
B3LYP/6-311++G** theoretical level (eV), is reported
in Table 3, which shows that B2 excited level with an
approximate energy of 5.10 eV ( rst case) and B1 excited
level with an approximate energy of 4.46 eV ( rst case)
contribute in making pseudo Juan-Teller effect.
The value of thermodynamic parameters ΔG, ΔH, ΔS,
and ΔEe1 of the desired compound, shown in Table 2,
was calculated using B3LYP/6-311++G** method. The
results show that the value of ΔEe1 for compound No. 2
is 29.97 kCal/mol and 15.37 kCal/mol for B2 symmetry
and B1 symmetry, respectively, which implies that the
desired compound with B1 symmetry has lower pseudo
Juan-Teller stability energy, however, the energy differ-
ence between reference states has decreased.
FIGURE 5. Symmetrical transformation of C2V
of analog containing P 1,3-di(pyridine-2-yl)
Benzonium atoms in form of Cs (C2V Cs)
using calculations in B3LYP/6-311++G** theo-
retical level
FIGURE 6. Initial energy levels calculated (ground state and excited state with
B2 symmetry) in analog containing P 1,3-di(pyridine-2-yl)Benzoniumatoms,
and their changes by pseudo Juan-Teller effect ( rst case)
126 INVESTIGATING PSEUDO JAHN-TELLER EFFECT ON INTER-MOLECULAR HYDROGEN BOND BIOSCIENCE BIOTECHNOLOGY RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS
Elahe Jalali
3-3. Investigating pseudo Juan-Teller effect on
distortion of analog containing As 1,3-di(pyridine-2-yl)
Benzonium atom (compound No. 3)
As it was mentioned in previous structures, the structure
of compound No. 3 has C2V high symmetry, and has
low symmetry in point group. Deviations are the result
of combining the compound of ground state A1 and
excited level B2 by displacement b2, as well as the result
of combining the ground state A1 and excited level B1
through displacement b1. Combination of excited level
B2 with excited level B1 and combination of excited
level A2 with excited level A1 is done through displace-
ment a2. (It has to be noted that in the third case, the
ground state cannot combine with excited states as it
is aligned with them, so it doesn’t create psuedo Juan-
Teller effect, and devations with the combination of
non-aligned excited levels results in creation of psuedo
Juan-Teller effect.) Here, the pseudo Juan-Teller results
in (A1+B2) b2, (A1+B1) b1, (B2+B1) a2, and
(A2+A1) a2 problems.
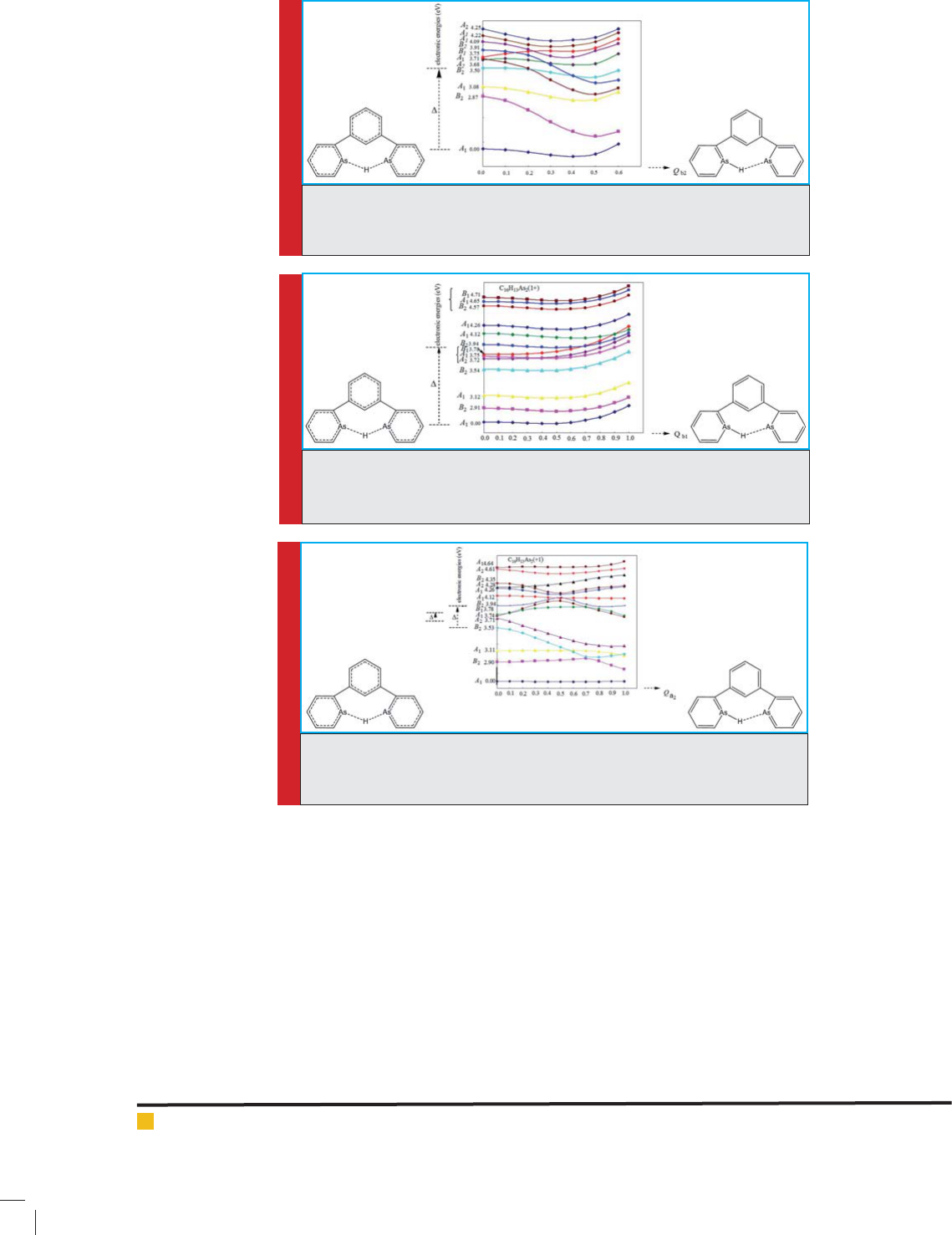
Figures 9, 10, and 11 show the energy of ground level
and excited levels, as well as the deviations of arrange-
ments with high symmetry due to pseudo Juan-Teller
effect. The energy difference between ground level and
excited level B2 ( rst case), shown in Figure 9, and
between ground level and excited level B1 (second case),
shown in Figure 10, and between a pair of excited levels
of B2 and B1 and another pair of excited levels of A2
and A1 (third case), shown in Figure 11, along with the
combination of orbitals is 3.50, 3.78, and 0.03-0.25 eV,
respectively.
1. [Homo – 4 (B2) Lumo + 2 (A1), Homo – 1(B1)
Lumo+1(A2)]
2. [Homo – 1 (B1) Lumo + 2 (A2)]
3. [Homo – 4 (B2) Lumo (B1), Homo (A2) – Lumo
+2 (A1), Homo 3(B1) – Lumo (B1), Homo (A2) –
Lumo + 1(A2), Homo (A2) – Lumo + 3 (A2), Homo
4 (B2) – Lumo + 2(A1), Homo 1(B1) – Lumo
+ 1 (A2), Homo 1(B1) – Lumo + 2 (A1)]
Comparison between the rst and second case shows
that according to the reduction in energy difference in
the rst case, its pseudo Juan-Teller energy is higher,
and comparison between the three cases indicates that
the pseudo Juan-Teller of the third case is the highest (in
case just one single factor of energy difference between
ground level and excited level (Δ) is considered).
The electron energy of a number of excited levels
for the structure No. 3, calculated in B3LYP/6-311++G**
theoretical level (eV), is reported in Table 4. It shows that
the excited level B2 with an approximate energy of 3.50
eV ( rst case), and the excited level B1 with an approxi-
FIGURE 7. Initial energy levels calculated (ground state and excited state with
B1 symmetry) in analog containing P 1,3-di(pyridine-2-yl)Benzoniumatoms,
and their changes by pseudo Juan-Teller effect (second case)
Table 3. Investigating the energy of excited levels (eV) of analog containing P 1,3-di(pyridine-2-yl)Benzonium
atoms in symmetrical transformation (C2V Cs) (two cases).
B
2
A
1
B
2
A
2
B
1
B
2
A
1
B
2
1. C
16
H
13
P
2
(+1) 3.15 3.32 3.71 4.33 – 4.55 4.94 5.10
2. C
16
H
13
P
2
(+1) 3.18 3.36 3.74 4.38 4.46 4.58 4.76 –
FIGURE 8. Symmetrical transformation of C2V
of analog containing As 1,3-di(pyridine-2-yl)
Benzonium atoms in form of Cs (C2V Cs)
using calculations in B3LYP/6-311++G** theo-
retical level
BIOSCIENCE BIOTECHNOLOGY RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS INVESTIGATING PSEUDO JAHN-TELLER EFFECT ON INTER-MOLECULAR HYDROGEN BOND 127
Elahe Jalali
FIGURE 9. Initial energy levels calculated (ground level and excited level with
B2 symmetry) in analog containing As 1,3-di(pyridine-2-yl)Benzoniumatoms,
and their changes by pseudo Juan-Teller effect ( rst case)
FIGURE 10. Initial energy levels calculated (ground level and excited level
with B1 symmetry) in analog containing As 1,3-di(pyridine-2-yl)Benzoniu-
matoms, and their changes by pseudo Juan-Teller effect (second case)
FIGURE 11. Initial energy levels calculated (B2, B1, A2, and A1 excited lev-
els) in analog containing As 1,3-di(pyridine-2-yl)Benzoniumatoms, and their
changes by pseudo Juan-Teller effect (third case)
mate energy of 3.78 eV ( rst case) contribute in creating
pseudo Juan-Teller effect.
The value of thermodynamic parameters ΔG, ΔH, ΔS,
and ΔEe1 of the desired compound, shown in Table 2,
was calculated using B3LYP/6-311++G** method.
The results show that the value of ΔEe1 for the com-
pound No. 3 is 21.74 kCal/mol, 11.87 kCal/mol, and 1.06
kCal/mol for the rst, second, and third case, respec-
tively, which implies that the desired compound in the
third state has lower pseudo Juan-Teller stability energy.
The results of B3LYP/6-311++G** calculations for
the three compound 1, 2, and 3 show that the major
cause of deformation of con gurations with C2V high
symmetry to Cs low symmetry con gurations is pseudo
Juan-Teller effect. The energy difference (Δ) between the
reference states from compound 1 to compound 3 (i.e.,
5-35-5.55 eV, 4.46-5.10 3 eV, and 0.03-0.25-3.5-3.78 eV
for compounds 1, 2, and 3, respectively) decreases. So, it
is expected that the pseudo Juan-Teller energy for these
deformations (C2V Cs) increases from compound (1)
to (3). The results obtained bu applying this method to
determine the energy of the ground state from compound
(1) to (3) for B2 symmetry (79.02, 27.97, and 21.74 kcal-
mol-1 for compound 4, 5, and 6, respectively) and for
128 INVESTIGATING PSEUDO JAHN-TELLER EFFECT ON INTER-MOLECULAR HYDROGEN BOND BIOSCIENCE BIOTECHNOLOGY RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS

Elahe Jalali
B1 symmetry (48.01, 15.35, and 11.78 21.74 kcalmol-1
for compound 1, 2, and 3, respectively) decreases, which
implies that the compound (1) has the highest pseudo
Juan-Teller stability energy.
CONCLUSION
The results obtained by calculations in B3LYP/6–
311++G** theoretical level shows that the pseudo Juan-
Teller effect explains C2V high symmetry structural
deformation to Cs low symmetry structure in the follow-
ing compounds:
1,3-di(pyridine-2-yl)Benzonium (compound 1)
Analog containing P 1,3-di(pyridine-2-yl)Benzonium atom
(compound 2)
Analog containing As 1,3-di(pyridine-2-yl)Benzonium
atom (compound 3)
It was found that the hydrogen bond of compounds (1)
to (3) have C2V high symmetry con guration.
By Q transformations, the rst three compounds
(1 to 3) transform from C2V high symmetry base con-
guration to Cs low symmetry excited con guration.
It is associated with decreasing the electron energy of
ground state electron con gurations and increasing the
electron energy of excited state electron con gurations.
This study addressed the mixing of electron ground state
with electron excited states in the direction of applying
normal coordination, describing leaving high symme-
try and transforming into low symmetry. Therefore, the
distortion of C2V high symmetry having hydrogen bond
in compounds (1)-(3) is due to pseudo Juan-Teller effect
(PJTE), (A1+B2) b2, and (A1+B1) b1, which is cre-
ated by combining the ground state and excited states.
It has to be noted that meanwhile, the energy difference
(ΔE) between reference states from compound (1) to (3)
(i.e., 5.33-5.5 eV, 4.46-5.10 eV, 0.03-0.25-3.5-3.78 eV
for 1,3-di(pyridine-2-yl)Benzonium, analog containing
P atom, and analog containing As atom, respectively)
decreases. Furthermore, examining pseudo Juan-Teller
for these deformations (C2V Cs) showed that the
pseudo Juan-Teller stability energy decreases from com-
pounds (1) to (3).
REFERENCES
Bersuker, I. B. (2006): The Jahn-Teller Effect; Cambridge Uni-
versity Press: New York.
Bersuker, I. B. Chem. (2001): Rev., 101. 1967.
G. C. Pimcntel, A. L. M. Clellan. (1976): The Hydrogen Bond
North-Holand, Amsterdam.
J. C. Speakman. (1975): The Hydrogen Bond and other Inter-
molecular Forces, Vol. 27 of Monograpbs for Teachers, The
Chemical Society, London.
L. Pauling, (1960): The Nature of the Chemical Bond and the
structure of Molecules and Crystals, 3
rd
Ed. Cornell University
Press, Ithaca, NY.
W.C. Hamilton, j. A. Ibers, W. A. Benjamin. (1962): the Hydro-
gen Bondilling solid, Sanfrancisco.
Table 4. Investigating the energy of excited levels (eV) of C2V analog containing As
1,3-di(pyridine-2-yl)Benzonium atoms with symmetrical arrangement (C2V Cs) (three
cases).
B
2
A
1
B
2
A
2
A
1
B
1
1. C
16
H
13
As
2
(+1) 2.87 3.08 3.50 3.68 3.71 3.75
2. C
16
H
13
As
2
(+1) 2.91 3.12 3.53 3.72 3.75 3.78
3. C
16
H
13
As
2
(+1) 2.90 3.11 3.53 3.71 3.74 3.78
BIOSCIENCE BIOTECHNOLOGY RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS INVESTIGATING PSEUDO JAHN-TELLER EFFECT ON INTER-MOLECULAR HYDROGEN BOND 129