The effect of Swedish massage on fasting glucose
levels, insulin resistance, cortisol, adrenaline and heart
rate in women with type II diabetes
Vahdat Boghrabadi
1
*, Hosein Nikkar
2
and Ali Hosseinzadeh Gonabadi
3
1
Sama technical and vocational training college, Islamic Azad University, Mashhad branch, Mashhad, Iran
2
Young researcher and elites club, Birjand branch, Islamic azad university, Birjand, Iran
3
Sama technical and vocational training college, Islamic Azad University, Shiraz branch, Shiraz, Iran
ABSTRACT
The aim of this study was to evaluate the effect of Swedish massage on some physiological factors in women with
type II diabetes. The experimental group included 12 women with type II diabetes and also had 12 patients with type
II diabetes in the control group. The subjects received Swedish massage for four weeks (three sessions a week) in the
back and in the abdomen respectively for 10 and 20 minutes. The blood samples were collected 24 hours before the
rst session of massage and 24 hours after the last session and the changes of factors were measured at rest, as well
as the mean blood pressure and resting heart rate before and 24 hours after the rst massage session of massage.
Independent and dependent T-test was used to analyze the data. Results of the study did not show any statistically
signi cant changes in fasting blood glucose levels and insulin resistance in experimental and control groups.Corti-
sol, adrenaline and heart rate changes were signi cant in experimental group (p <0/05) but not statistically signi -
cant in the control group. All factors were non-signi cant from the perspective of between-group changes.Overall,
this paper showed that massage as an external factor did not have signi cant impact on the physiological factors
affecting diabetes, it can only have positive effects on the heart rate and stress factors, which means massage can be
helpful as a relaxing factor.
KEY WORDS: SWEDISH MASSAGE, PHYSIOLOGICAL FACTORS, DIABETES TYPE II
42
ARTICLE INFORMATION:
*Corresponding Author: vahdat.boghrabadi@gmail.com
Received 27
th
Nov, 2016
Accepted after revision 28
th
March, 2017
BBRC Print ISSN: 0974-6455
Online ISSN: 2321-4007
Thomson Reuters ISI ESC and Crossref Indexed Journal
NAAS Journal Score 2017: 4.31 Cosmos IF : 4.006
© A Society of Science and Nature Publication, 2017. All rights
reserved.
Online Contents Available at: http//www.bbrc.in/
Biosci. Biotech. Res. Comm. Special Issue No 1:42-47 (2017)

Boghrabadi, Nikkar and Gonabadi
INTRODUCTION
Diabetes is a common diseases in Iran and worldwide.
This chronic disease is progressive and costly, and is con-
sidered as a public health problem and creates numer-
ous complications (Eslami, 2010; Mousavi, 2008). Type
II diabetes is a complex metabolic and endocrine disor-
der in which the interaction between multiple genetic
and environmental factors causes a variation of insulin
resistance and dysfunction of beta cells in pancreas and
ultimately leads to diabetes (Heidari Safa, 2011). Mas-
sage involves a series of movements and manual skills
that are applied regularly on human body tissues to
affect neuromuscular system and the general circulation
(Baumgart et al. 2011). Massage can be effective in the
balance of nervous system and the correction of physi-
cal balance (Bucher, 2002).
Diabetes is a source of tension for people, and has nega-
tive psychological effects other than physical ones, and
thus, these make the treatment and the control of the dis-
ease so dif cult for them and has destructive effects on
their quality of life (Moghaddasian and Ebrahimi, 2008).
According to the importance of moderating blood pressure
in people with type II diabetes, and despite the scienti c
evidences on the effects of massage, only a few studies
have speci cally examined the long-term effects of mas-
sage on mean blood pressure. These studies give different
results on the effectiveness (Williams and Hopper, 1999;
Ignatviciuce and Workman, 2006; Aourell et al. 2005) or
ineffectiveness (National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive
Kidney Diseases, 2010) of massages on the blood pressure.
Considering the importance of moderating blood
sugar levels as well as regulating the amount of stress
hormones, especially cortisol and adrenaline in diabetics,
and considering the importance of the role of women in
society, the question is that whether Swedish massage in
women with type II diabetes can cause changes in physi-
ological indicators such as heart rate, insulin resistance,
as well as changes in hematological parameters such as
glucose, cortisol and adrenaline.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
This study has a quasi-experimental design in which the
preliminary test (pre-test) and nal (post-test) were con-
ducted in two experimental and control groups.
PARTICIPANTS
Statistical population of the research includes 50 old
women with the range of 40-45 years old with diabe-
tes type 2. Among the candidates, 24 people randomly
divided into two equal groups that comprised massage
group and a control group.
INCLUSION CRITERIA
Having at least one year from history of the disease.
All participants used the same drug conditions
Having les at Neyshabur Diabetes Prevention Association.
Non-Smokers
Having no history of regular physical activity at least for
the last six months.
The scope of their blood sugar levels be between 150 to 250
mg per dl.
EXCLUSION CRITERIA
Patients with diabetes type I
People with special diseases
People with hyperlipidemia and hypertension
People with complications of diabetes (neuropathy,
nephropathy, retinopathy)
Lack of regular participation in physical activity
METHOD
From 50 people who had been referred to the Neyshabur
Diabetes Clinic, 24 patients who had the conditions of
research selected and randomly divided into two groups:
experimental (n = 12) and control (n = 12). The experi-
mental group received Swedish massage for four weeks,
which were included three sessions per week, each ses-
sion lasting 30 minutes. In this period, the control group
did not perform any particular physical activity.
SWEDISH MASSAGES PROTOCOL
Swedish massage in every session consist of 10 minutes
of massage in the back and 20 minutes in the abdo-
men. This is performed with ef eurage (string), petris-
sage (rubbing) percussion (impact), and vibration move-
ments. Ef eurage is a slipping movement performed in
the hands to improve blood circulation. Petrissage is
performed to improve blood and lymph circulation. In
petrissage the muscular mass is put up and is rotated or
compressed slowly. In the percussion movement, throb-
bing movements which are light and fast and continu-
ous are performed by the edges of the hands or by palms
to the muscles. Vibration is performed by vibrating the
tips of ngers or by palms. The aim of the vibration
gesture is to help calm the muscles and increase blood
circulation is localized.
BLOOD SAMPLING AND MEASURING THE FACTORS
Blood samples were collected 24 hours before the rst
massage session and 24 hours after the last session,
while the subjects had been fasting for 12Hours.Glucose
test was done using enzymatic colorimetric by biosys-
tem’s kit.
BIOSCIENCE BIOTECHNOLOGY RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS THE EFFECT OF SWEDISH MASSAGE ON FASTING GLUCOSE LEVELS AND HEART RATE IN WOMEN 43
Boghrabadi, Nikkar and Gonabadi
Insulin resistance was calculated by the homeostasis
assessment of insulin resistance (HOMA-IR) according to
the following formula.
HOMA-IR = {[fasting insulin (μU / ml)] × [fasting glu-
cose (mmol / l)]} / 22.5.
Cortisol was evaluated by Vidas-Rosch kit and immu-
no uorescence method, by the Vedas mini blue machine
which is made in France, and Adrenaline was evaluated
using adrenaline ELISA kit LDN LABER DIAGOSTIKA
and Elisa method by ELISA reader machine version stat
fax 303 made in Germany.
STATISTICAL ANALYSIS
For survey the effect of massage on selected factors on
each factor, dependent t test was used and to compare
pretest and post-test data means in each group, the sta-
tistical independent t test was used. All the statistical
tests were performed at the 95 percent con dence level
(p <0.05).
RESEARCH FINDINGS
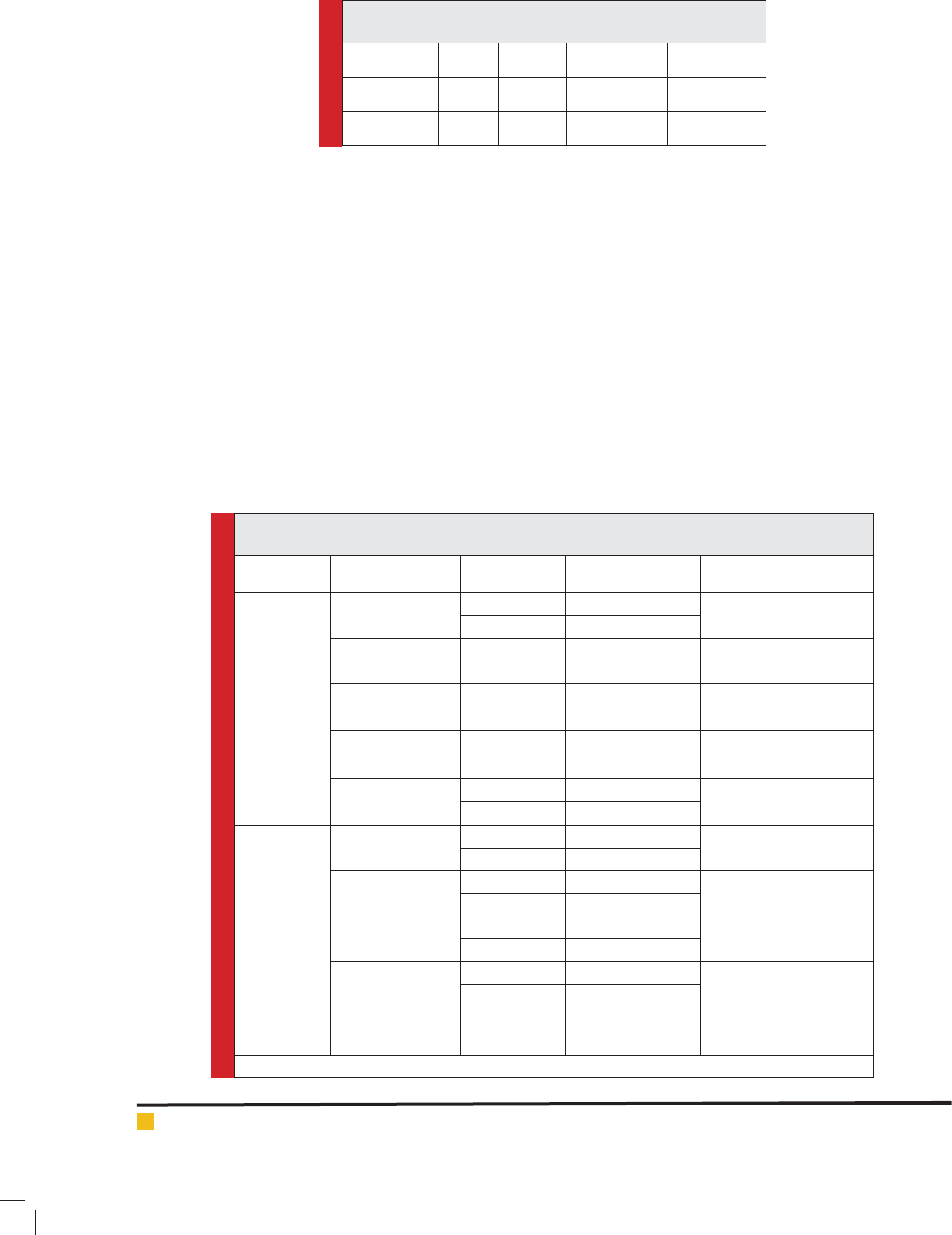
In Table 1, descriptive information of the participants of
the two groups has been shown.
In Table 2 the results of paired t-test for intergroup
changes during the four-week are presented.
As Table 2 shows, a course of massage can cause sig-
ni cant changes in cortisol, adrenaline and heart rate
in the experimental group. It means twelve sessions
of massage can have a positive impact on mentioned
factors. While in control group, who did not receive
Table1. Pro le of subjects in two experimental and control
groups
Group Count Age (y) Height (cm) Weight (kg)
Experimental 12 51±5/15 161/38±7/92 71/3±11/77
Control 12 51±4/16 157/26±6/74 71/7±9/03
Table 2. Results of paired t-test variables measured in two groups.
Group Variable Test M±SD t Value
Experimental
Glucose (mmol/L)
Pre- test 136/92±30/69
-2/14 0/056
Post- test 145/75±32/4
Insulin Resistance
Pre- test 3/87±2/38
-0/78 0/44
Post- test 3/56±1/47
Cortisol (mcg)
Pre- test
184/5±63/93
-2/34 0/03*
Post- test 154/5±54/08
Adrenaline (ACTH)
Pre- test 0/27±0/15
-3/24 0/008*
Post- test
0/14±0/09
Heart Rate (bpm)
Pre- test 83/91±7/22
-2/21 0/04*
Post- test
80±7/03
Control
Glucose (mmol/L)
Pre- test 141/92±2894
0/48 0/63
Post- test 146/08±36/37
Insulin Resistance
Pre- test 4/37±3/41
-1/26 0/23
Post- test 3/86±2/98
Cortisol (mcg)
Pre- test 166/08±64/16
2/05 0/06
Post- test 193/42±53/78
Adrenaline (ACTH)
Pre- test 0/28±0/18
0/36 0/72
Post- test
0/3±0/17
Heart Rate (bpm)
Pre- test
83/25±7/56
0/2 0/84
Post- test 83/41±5/83
* Signi cance level (p <0.05)
44 THE EFFECT OF SWEDISH MASSAGE ON FASTING GLUCOSE LEVELS AND HEART RATE IN WOMEN BIOSCIENCE BIOTECHNOLOGY RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS
Boghrabadi, Nikkar and Gonabadi
any massage, none of the factors showed signi cant
changes.
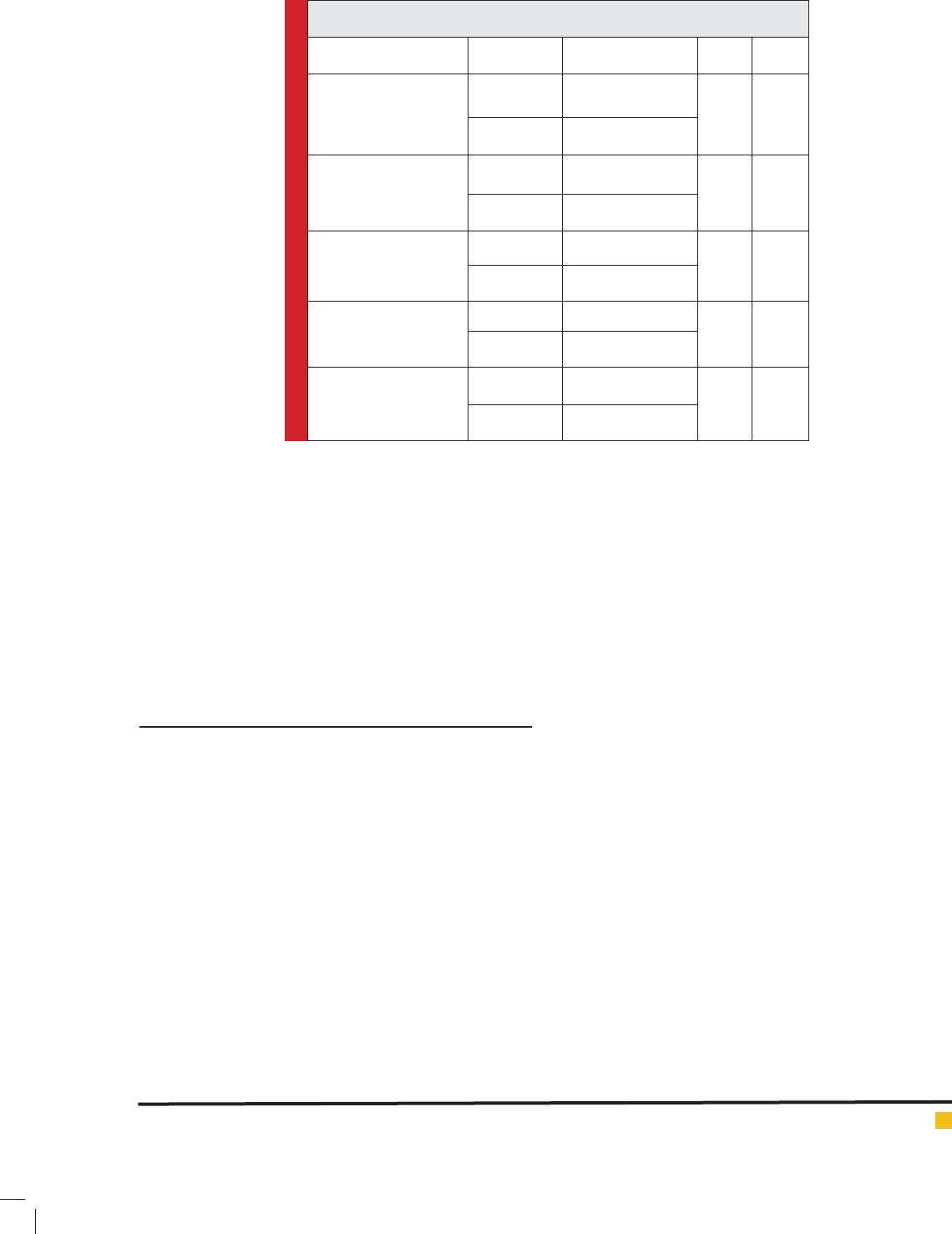
As in Table 3, independent t-test results show that
no signi cant differences were obtained comparing
experimental and control groups in effectiveness of one
session Swedish massage on aforementioned factors. In
other words, people with diabetes who have been receiv-
ing Swedish massage did not show any statistically sig-
ni cances compared to people who did not.
DISCUSSION AND CONCLUSION
The results of this study showed signi cant reduction in
cortisol, adrenaline and heart rate in women with type II
diabetes in the experimental group after 12 sessions of
massage (p <0/05).
However, according to the between-group results, no
statistically signi cant decline was observed in experi-
mental group compared to the control group. The results
of cortisol levels, were consistent with the results of the
research performed by Christopher Moyer (2004), but
were con icted with the results of studies performed by
Sicree (2010), French et al (2010) and Anderson and col-
leagues (2001).
As mentioned about the relationship between stress
and diabetes, one of the most important psychological
factors in uencing diabetes is stress. Scientists have dif-
ferent comments about the relationship between stress
and diabetes; The reaction of the organism when faced
an unusual disorder is an over activity of the hypotha-
lamic/pituitary/adrenal axis; In the neuroendocrine sys-
tem or hypothalamic/pituitary/adrenal cortex axis, stress
(such as exams, paragliding, etc.) leads to the release
of corticotropin increasing agents by stimulating para-
ventricular nuclei of hypothalamus. This agent causes
synthesis of adrenocorticotropin in the anterior pituitary
gland and thus stimulation of adrenal and secretion of
glucocorticoids (like cortisol) (Kreyer, 2003). Therefore,
stimulating the central sympathetic/adrenal and hypo-
thalamic/pituitary/adrenal cortex axes will result in
secretion of catecholamines and glucocorticoids and an
increase in heart rate, blood pressure, respiratory rate
and metabolism (Goyman and Wing eld, 2004). Mas-
sage may alter the activity of the autonomic nervous
system (ANS) responses from sympathetic to parasym-
pathetic responses. In this case, cardiovascular activity
and stress hormones are reduced and the person feels
relaxed and comfortable.
The pressure applied during the therapeutic mas-
sage, stimulates the vagus nerve activity, which in turn
leads to reduced stress hormones levels and physiologi-
cal arousal and then parasympathetic response from the
ANS (Bjorntorp et al. 1999).
The cause of variation with French et al (2010) nd-
ings, may be due to the small number of massage ses-
sions per week (one session per week) by Vandal. The
samples taken by Vandl were urine samples while in this
study they were blood samples of participants receiving
massage 3 sessions a week. The variation of ndings
Table 3. Comparing the changes of physiological factors in the two groups
Variable Group Means variations t Value
Glucose (mmol/L)
Experimental 8/83
0/49 0/37
Control 4/16
Insulin Resistance
Experimental -0/3
0/36
0/88
Control -0/51
Cortisol (mcg)
Experimental -30
-3/1
0/75
Control 27/33
Adrenaline (ACTH)
Experimental -0/31
-2/05
0/29
Control 0/23
Heart Rate (bpm)
Experimental -3/66
-2/06
0/16
Control 0/16
BIOSCIENCE BIOTECHNOLOGY RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS THE EFFECT OF SWEDISH MASSAGE ON FASTING GLUCOSE LEVELS AND HEART RATE IN WOMEN 45

Boghrabadi, Nikkar and Gonabadi
with Edward et al (2010) ndings may be due to the pres-
ence of both sexes (male and female) and participants’
age (45 to 72 years). The results of this study reported
a signi cantly decrease in heart rate of women with
type II diabetes in experimental group after 12 massage
sessions (p <0/05). However, no statistically signi cant
decline was observed when comparing the results of the
two (experimental and control) groups.
These ndings are consistent with Zolriasatian and
colleagues (2013), Ramezanpour and colleagues (2010),
Hassanvand and colleagues (2010), Rahmani Anaraki
and colleagues (2001), and Moyer and colleagues (2004)
ndings. No research was found to be in contrast with
the present study ndings.
Massage increases blood ow to the arteries, veins,
and regional blood ow and stroke volume. It improves
lymph drainage and increases serotonin, dopamine
and cortisol levels (French, 2010). Therapeutic massage
also stimulates the central nervous system parasympa-
thetic tone and reduces the heart rate and respiratory
rate and thereby makes one feel relieved (Sara no,
2002).
CONCLUSION
12 sessions of Swedish massage in women with type
2 diabetes were unable to cause signi cant changes
in glucose levels and insulin resistance. However, this
study showed that massage can be somewhat effec-
tive in reducing stress hormones levels such as corti-
sol and adrenaline, as well as reducing the heart rate at
rest.
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
This article is as a result of research project with the title
of “The effect of 12 sessions of Swedish massage on the
cortisol and adrenaline in women with type II diabetes
“that did with nancial support of Sama technical and
vocational training college of Mashhad.
REFERENCES
Anderson RJ, Freedland KE, Clouse RE and Lustman PJ. (2001):
The prevalence of comorbid depression in adults with diabetes:
A meta-analysis. Diabetes Care; 24(6):1069-78.
Aourell M, Skoog M, Carlson J. (2005): Effect of Swedish mas-
sage on blood pressure. Complementary Therapies in Nursing
and Midwifery: 242-246.
Baumgart S, Müller-Oerlinghausen B, Schendera CFG. (2011):
Ef cacy of massage therapy on depression and anxious disor-
ders as well as on depressiveness and anxiety as comorbidity –
A systematic overview of controlled studies. Physikalische
Medizin, Rehabilitations medizin, Kurort medizin; 21(4): 167-
82.
Bjorntorp P, Holm G, Rosmond R. (1999): Hypothalamic
arousal, insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabet
Med. 16(5):373-83.
Bucher L, Melander j, Cohen RA.Shock. (2002): Critical Care
Nursing. London. St, Louisco; 1: 40-41.
Eslami M. (2010): The relationship between depression and
self-care behaviors in depressed and non-depressed diabetic
patients, Journal of Diabetes and Lipid Disorders 3 (10): 313-
318.
Zolriasatein Fereshteh, Bahraini Saina, Hariri Gholam Reza,
Khodakarim Soheila. (2013): Comparing the effect of foot
massage on physiological parameters of male and female
patients admitted to Intensive Care Units of hospitals related
to Beheshti University of Medical Sciences. Journal of Nursing.
Volume 11. Number Two.
French HP, Brennan A, White B, Cusack T (2010): Manual ther-
apy for osteoarthritis of the hip or knee - a systematic review.
Manual Therapy 16 (2): 109–17.
Goymann W, Wing eld JC. (2004): Allostatic load, social sta-
tus and stress hormones: The costs of social status matter.
Anim Behav. 67(3):591-602.
Heidari Safa M. (2011). Treatment of type II diabetes, New
Journal of Medicine, 512: 83-270.
Rahmani Anaraki Hossein, Abdollahi Ali Akbar, Nasiri Hos-
sein, Vakili Mohammad Ali (2001): The effect of massage in
the back on physiological indicators of patients in inten-
sive care unit. Academic Journal of Gorgan University of
Medical Sciences. Volume 3, Number 2 (Autumn and Winter
2001).
Ignatviciuce D, Workman M.L. (2006): Medical Surgical Nurs-
ing. 5 thed. Elsevier sunders: 786
Kreyer I. (2003): Endocrine stress responses in critical care
nurses: A possible relation to job turnover [dissertation].
Zurich: University of Zurich.
Moghaddasian S, Ebrahimi H. (2008): Three dimensions of
quality of life in patients with diabetes, Nursing and Midwifery
Journal. Tabriz University of Medical Sciences 3 (10): 38-44.
Mousavi. (2008): General health status and depression in
patients with type II diabetes, Journal of Science and Health,
3 (1): 44-48.
Moyer CA, Rounds J, Hannum JW. (2004): A meta-analysis of
massage therapy research. Psychol Bull. Jan; 130(1):3-18.
National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive Kidney Diseases.
(2010): The diabetes epidemic among African Americans.
Retrieved September 23, from http://diabetes.niddk.nih.gov/
dm/pubs/africanamerica
Ramezanpour Mohammadreza, Rashidlamir Amir, Heaari
Mohsen (2010): Comparison of Three Methods of recov-
ery (slow swimming, sitting and massage) on heart rate and
blood lactate levels in adult swimmers. Sports and Biomotor
46 THE EFFECT OF SWEDISH MASSAGE ON FASTING GLUCOSE LEVELS AND HEART RATE IN WOMEN BIOSCIENCE BIOTECHNOLOGY RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS

Boghrabadi, Nikkar and Gonabadi
Sciences: Fall-Winter (2010): Volume 2 Number 4; from page
37 to page 46.
Sara no, E. P. (2002): Health psychology: Biopsychosocial
interactions. New York: Wiley.
Hasanvand Shirin, Naja Saeed, Forouzi Mansoureh, Moham-
mad Alizadeh Sakineh, Dr. Haghdoost Aliakbar (2010): The
effect of massage in the back in blood pressure and radial
pulse on patients with essential hypertension referring to
Khorramabad Shohadaye Ashayer Clinic of Cardiology. Jour-
nal of Lorestan University of Medical Science. Volume 12,
Number 3.
Sicree R, et al. (2010): The Global Burden, Diabetes and
Impaired Glucose Tolerance, IDF Diabetes Atlas, fourth
edition.
Williams L, Hopper P. (1999): Understanding Medical-Surgical
Nursing, Philadelphia, A. Davis Company, Vol: 292.
BIOSCIENCE BIOTECHNOLOGY RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS THE EFFECT OF SWEDISH MASSAGE ON FASTING GLUCOSE LEVELS AND HEART RATE IN WOMEN 47