Biosci. Biotech. Res. Comm. Special Issue No 1:1-6 (2017)
The prevalence of overweight and obesity among adults
with intellectual and developmental disabilities in
Ahvaz, Iran
Sajed Salehi
1
, Gholamhossein Nassadj
1
, Kamal Shakhi
1
, Mohammad Hossein
Haghighizade
2
and Sheyda Javadipour
1
1
Musculoskeletal Rehabilitation Research Center, Ahvaz Jundishapur University of Medical Sciences,
Ahvaz, Iran
2
Department of Statistics, School of Public Health, Ahvaz Jundishapur University of Medical Sciences,
Ahvaz, Iran
ABSTRACT
The prevalence of overweight and obesity among people with intellectual and developmental disabilities (IDD) is 4
times more than any other people in the community, but a little research have been examined the prevalence of over-
weight and obesity among people with intellectual disabilities (ID) recently, So the present study aimed in order to
estimate the prevalence of overweight and obesity in ID people in Ahvaz, Iran.205 adults with IDD who had referred
to ve rehabilitation centers to receive rehabilitation services participated in this cross-sectional study. In addition
to demographic information of ID people, data on their height and weight were collected to measure the body mass
index (BMI). 69 percent of participants are male and 97 individuals had Down syndrome. The results of the present
study Demonstrated that the prevalence of overweight and obesity among people with ID is high and about 57
percent. The results showed that there is a statistically signi cant difference between gender, IQ level, family size;
and disability type with the prevalence of overweight and obesity.Implementation of intervention programs such as
physical activities over the week in supportive institutions, as well as increasing parent awareness of IDD people
about overweight and obesity could help to reduce the prevalence of overweight and obesity among people with IDD.
KEY WORDS: OVERWEIGHT, OBESITY, PREVALENCE, PEOPLE WITH INTELLECTUAL AND DEVELOPMENTAL DISABILITIES
1
ARTICLE INFORMATION:
*Corresponding Author: heyda.javadi@gmail.com
Received 27
th
Nov, 2016
Accepted after revision 21
st
March, 2017
BBRC Print ISSN: 0974-6455
Online ISSN: 2321-4007
Thomson Reuters ISI ESC and Crossref Indexed Journal
NAAS Journal Score 2017: 4.31 Cosmos IF : 4.006
© A Society of Science and Nature Publication, 2017. All rights
reserved.
Online Contents Available at: http//www.bbrc.in/
2 THE PREVALENCE OF OVERWEIGHT AND OBESITY AMONG ADULTS BIOSCIENCE BIOTECHNOLOGY RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS
Sajed Salehi et al.
INTRODUCTION
One of the most important health problems in many
countries is overweight or obesity of adults (Wille
et al. 2008; James et al. 2004). The prevalence of over-
weight and obesity in adults are estimated 6 billion
and 400 million respectively which have doubled in
the last 20 and it seems to increase as an epidemic and
common problem in communities in addition (World
Health Organization, 2008; World Health Organization,
2007). They cause many other diseases such as diabe-
tes, hypertension, gallbladder and osteoarthritis disor-
ders (James, 2001). Overweight and obesity is considered
as an epidemic and common problem in communities
it is increasing; moreover obesity and its related com-
plications impose signi cant costs on society (Obesity,
2000).
The prevalence of overweight and obesity among peo-
ple with IDD in United States is 4 times more than any
other people in the community (Rimmer and Yamaki,
2006; Mikulovic et al. 2011), but very few studies are
conducted regarding the prevalence of overweight and
obesity among people with IDD newly and the major-
ity of studies have addressed the prevalence of over-
weight and obesity in different age groups and among
adolescents and young people (Barzin et al. 2009). Hsieh
et al. in the United States showed that over 38% of peo-
ple with mental disabilities had a BMI more than 30 and
women are more obese than men in this study. In addi-
tion, people with Down syndrome have highest preva-
lence of obesity among different groups with IDD and
they plus had more health problems than other commu-
nity members (Hsieh et al. 2012).
The result of another study by Bhaumik et al.(2008)
in the UK showed that only 34.6% of people with IDD
had normal BMI and most of them had overweight
and obesity problem. Beside, in the study it is found
that people with IDD had higher blood pressure, poorer
nutritional status and more high-risk behaviors than
healthy people,(Bhaumik et al. 2008). People with ID
often have a mortality rate greater than the general
population, their health status is less than others and
the prevalence of obesity in them is higher than other
members of society due to immobility, lack of exer-
cise and poor nutritional status (Koritsas and Iacono,
2015).
According to our research, Iranian scienti c resources
show that no study has been conducted on the preva-
lence of overweight and obesity in individuals with IDD,
so this study was aimed to investigate the prevalence of
overweight and obesity among adults with IDD in Ahvaz
and its results could contribute in developing health care
programs to support these people.
MATERIAL AND METHODS
STUDY DESIGN AND DATA COLLECTION
This study has been designed and conducted to inves-
tigate the prevalence of overweight and obesity among
people with IDD in Ahvaz. 205 adults with IDD (like:
Down syndrome, cerebral palsy, autism spectrum disor-
ders and intellectual disability) who had referred to eight
rehabilitation centers (medical and vocational rehabili-
tation centers) to receive rehabilitation services par-
ticipated in this cross-sectional study. The demographic
information of the people with IDD have been obtained
from existing records in centers and this information
includes items such as: age, gender, language, IQ, race,
ethnicity, disability type, place of residence, educational
status and employment status. Data on their height and
weight has been collected over a period of two months
from May to July 2016 by two professionals.
STATISTICAL ANALYSIS
For calculating the overweight or obesity the body mass
index (BMI) was used such that rst the height is meas-
ured by the wall by stadiometer with accuracy of 0.5 and
then their weight was obtained by minimum clothing
and no shoes on a scale with an accuracy of 100 grams.
BMI was achieved by dividing weight (in kilograms) by
the square of height (in meters) and someone with a BMI
of less than 18.5 is underweight, between 18.6 and 25
is normal, between 25.1 and 30is overweight and the
one with the BMI higher than 30 is obese (International
Obesity Task Force, 2007). Data has been analyzed using
SPSS version 16 software. Descriptive statistics such as
mean, SD and frequency percentage are used to report
BMI, age and gender. As well, the Chi Square and ANOVA
tests have been applied used to evaluate the prevalence
of overweight and obesity in terms of gender, ethnicity,
location and different age groups.
Parents of all people with IDD were announced of the
purpose of the study and they signed the informed con-
sent. This research ethics code IR.AJUMS.REC 263.1395
has been con rmed by Jundishapour University of Med-
ical Sciences Ethics Committee.
RESULTS
The results showed that133 of participants (69%) were male
and 73 participants were female. 97 people with had Down
syndrome, 81 with intellectual disability (ID), 13 individuals
had autism, and 14 of participants had cerebral palsy (CP)
that 53% (108 cases) had IQ within the range of 51-70 and
BIOSCIENCE BIOTECHNOLOGY RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS THE PREVALENCE OF OVERWEIGHT AND OBESITY AMONG ADULTS 3
Sajed Salehi et al.
Table 1. demographic information of people
with ID
Variables Categories
Frequency
n (%)
Gender Male 133(65)
Female 72(35)
Age (year) 15-25 132(64)
26-35 59(29)
36-44 14(7)
IQ <50 58(28)
51-70 109(53)
>70 38(19)
Race Persians 84(41)
Arabs 121(59)
Residential Area Urban 175(85)
Rural 30(15)
Education Diploma 16(8)
Under Diploma 189(92)
Occupation Supportive
Employment
70(34)
Sheltered
Employment
38(19)
Unemployed 97(47)
parent’s Education Illiterate 99(48)
Diploma 76(37)
Academic 30(15)
Family Size <7 76(37)
≥7 129(63)
Disability Type Down
Syndrome
97(47.3)
Intellectual
Disability only
81(39.5)
Autism 13(6.4)
Cerebral Palsy 14(6.8)
58 cases had the IQ range less than 50. Fifty nine percent
of respondents were Arabic speakers and 41% of them were
Farsi speakers; and about 73% of them lived in large fami-
lies (more than 7 members). Most people with intellectual
and developmental disabilities were urban dwellers and had
under diploma education. Only 15% of parents of persons
of these people had academic degree and about 88% of
them were covered by social security insurance. The demo-
graphic features of the participants have been reported in
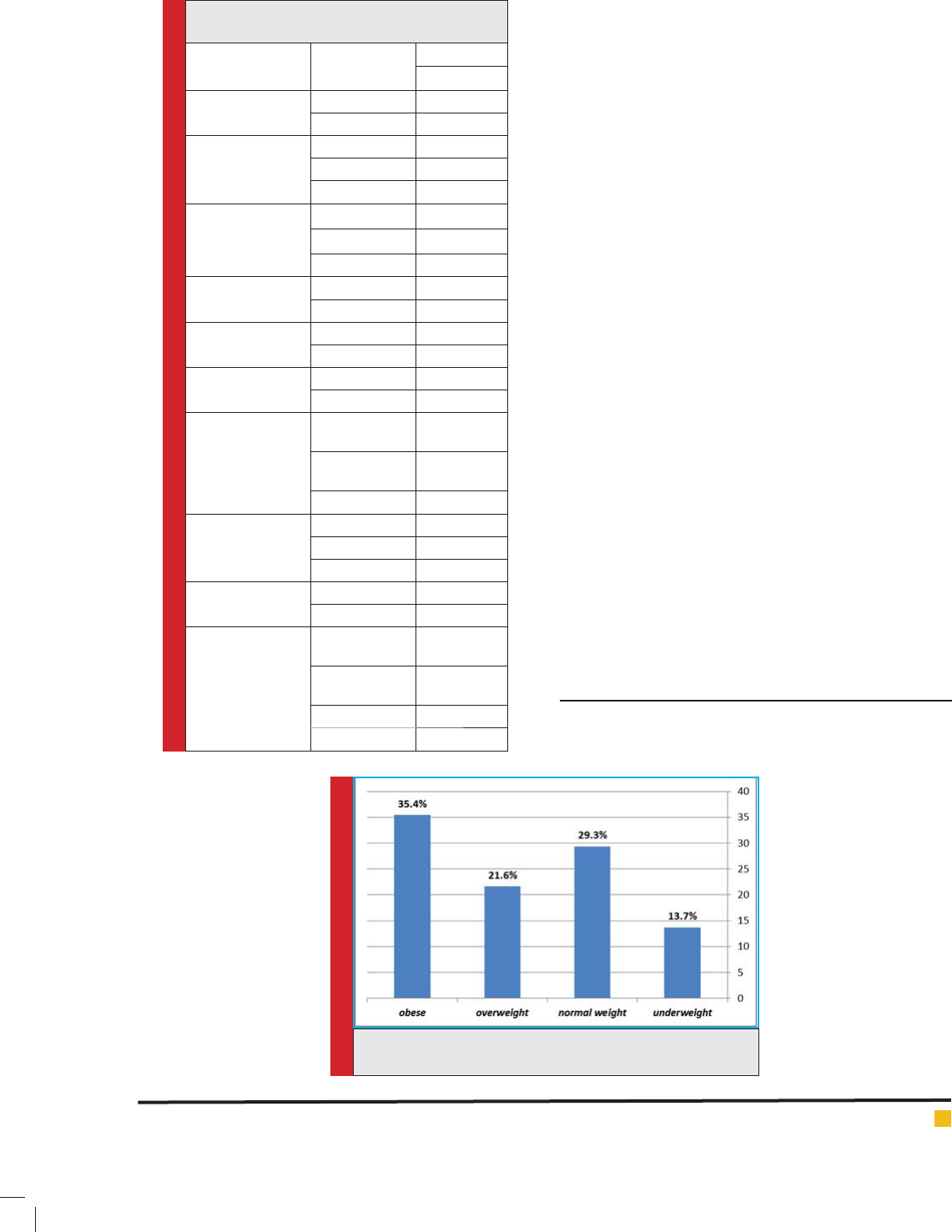
Table 1. As gure 1 suggests, 57% of the people with IDD
suffer from overweight and obesity, 13.7% are underweight
and only 29% have normal BMI. Among the various IDD,
prevalence of obesity is higher in people with Down syn-
drome than other types of disability (Figure 2). Based on
the results presented in Figure 3, the prevalence of over-
weight and obesity among women is higher than men.
The results presented in table 2 show there is a signif-
icant difference between gender of participants and the
prevalence of overweight and obesity (P=0.001), but sta-
tistically there is no difference between participants eth-
nicity and the prevalence of overweight and obesity (P=
0.32). ANOVA test results has demonstrated that there is
no signi cant difference between different age groups
and the prevalence of overweight and obesity (P=0.502).
The results also has depicted that the prevalence of over-
weight and obesity of people with an IQ less than 50 is
higher than the other groups (P=0.02). The prevalence of
obesity among large families (more than 7 members) has
a signi cant difference with smaller families (less than
7 members) (P=0.031). Table 2 shows the results of the
relationship between the prevalence of overweight and
obesity and demographic data of individuals with IDD.
DISCUSSION
The current research has been designed and performed
in order to estimate the prevalence of overweight and
FIGURE 1. BMI status for adults with Developmental and
Intellectual Disabilities

Sajed Salehi et al.
4 THE PREVALENCE OF OVERWEIGHT AND OBESITY AMONG ADULTS BIOSCIENCE BIOTECHNOLOGY RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS
FIGURE 2. Prevalence of overweight and obesity by gender
of ID people
FIGURE 3. Overweight and obesity prevalence by disbility type of ID people
Table 2. BMI status and its relation with participant variables
Variables Categories
BMI Status BMI Status
overweight p-value Obesity p-value
Gender
Male 26.75
0.001
32.06
0.001
Female 29.23 36.47
Age groups (year)
15-25 27.74
0.502
33.25
0.67226-35 28.83 34.16
36-44 28.39 33.92
IQ
<50 28.63
0.02
36.54
0.00151-70 26.18 32.37
>70 26.35 33.74
Residential Area
Urban 29.32
0.012
35.24
0.001
Rural 26.07 31.15
Family Size
<7 27.14
0.03
31.78
0.02
≥7 29.59 35.41
Disability Type
Down Syndrome 29.34
0.01
36.32
0.001
Intellectual Disability only 27.88 32.63
Autism 27.31 30.82
Cerebral Palsy 26.8 30.01
Sajed Salehi et al.
BIOSCIENCE BIOTECHNOLOGY RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS THE PREVALENCE OF OVERWEIGHT AND OBESITY AMONG ADULTS 5
obesity among adults with IDD in Ahvaz. The results
showed that the prevalence of overweight and obesity in
adults with IDD is about 36% which indicates the high
rate of obesity in this group. Hsieh et al.(Hsieh et al.
2012) in their research on adults with ID living in the
American community have noted that the prevalence of
obesity in the population was about 38% which in keep-
ing with the results of the present research. A study by
Mikulovic et al.(Mikulovic et al. 2011) on people with ID
showed that 19% of 535 cases have overweight which
in consistent with the results of the current. In Miku-
lovic study the prevalence of obesity among people with
ID is reported about 4% which is inconsistent with the
present results. The reason for this high difference in
the prevalence is perhaps due to the individuals that in
Mikulovic study only persons with ID are studied while
in our study, most individuals have Down syndrome that
usually the prevalence is high in this population com-
pared to other people.
The ndings of various studies indicate that the prev-
alence of overweight among men is less than women;
the results also show that women are more obese than
men (Hsieh et al. 2012). The results of these studies are
consistent with the present study, the present study
showed that the prevalence of overweight (22.6% Vs
28.7%, P=0.001) and obesity (32.5% Vs 48.4%, P=0.001)
in women is higher than men. Yamaki and Rimmer
research’s results on obesity consideredthat the preva-
lence of obesity in people with Down syndrome is higher
than other disabilities and it is about 71%, as well peo-
ple with ID have the second place in the prevalence of
obesity among people with IDD (9). The present study
considered that people with Down syndrome have the
highest prevalence of obesity among other disabilities.
In the present research, people with CP had the lowest
prevalence of obesity which is consistent with Rimmer
and Yamaki research.
El Raghi et al.in Sudan stated that there is no signi -
cant correlation between age and the prevalence over-
weight and obesity (P =0.4) (El Raghi et al. 2016). Emer-
son in his research on adults with ID showed that there is
no signi cant difference between the prevalence of obe-
sity and different age groups (Emerson, 2005) which is
consistent with the present research ndings. The results
revealed that the prevalence of obesity among families
with more than 7 members and people with the IQ less
than 50 is more than other groups. El Raghi indicates
that there is no signi cant difference between the prev-
alence of obesity and IQ which is not consistent with
the results of the present study (El Raghi et al. 2016).
The reason might be due to the fact that people with
50> IQ due to the cultural issues and they may cause
harm to others are kept at home and have low mobil-
ity and this lifestyle has led to gain extra weight and
obesity compared to the other groups. Another inter-
esting result of this study is that there is a signi cant
difference between the prevalence of overweight and
obesity in terms of the place of residence such that the
prevalence of overweight and obesity in rural dwellers is
lower than urban dwellers. Hseih et al.in their study to
determine the factors in uencing obesity among people
with intellectual disabilities found that urban lifestyle
compared to rural lifestyle leads to higher prevalence
of obesity and overweight which is consistent with the
present study (Hsieh et al. 2012).
LIMITATIONS AND ADVANTAGES
The participants of this study were the ones who referred
to educational and supportive institutions and these peo-
ple might not be the representative of the entire people
with IDD in Ahvaz. Additionally, in this study the effect
of factors such as diet habits, movement restrictions and
drug usage are not studied on overweight and obesity.
One of the most important advantages of the present
study is that this is the rst study conducted to estimate
the prevalence of overweight and obesity among people
with IDD in Iran.
CONCLUSION
The results of the present study showed that the preva-
lence of overweight and obesity among adults with IDD
is high (57%); and it is higher than other community
groups which necessitates the intervention. Implemen-
tation of intervention programs such as physical activi-
ties over the week in supportive institutions, as well as,
increasing parent awareness of intellectual and develop-
mental disabilities people about overweight and obesity
could help to reduce the prevalence of overweight and
obesity among people with intellectual and develop-
mental disabilities.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This research was a part of MSc thesis of Mr .Sajed Salehi
and supported by the Research Affairs Deputy,Ahvaz
Jundishapur University of Medical Sciences, Ahvaz,
Iran. The authors of the current study warmly appreciate
all the people with IDD and their families due to take
part in our research.
REFERENCES
Barzin M, Mirmiran P, Ramezankhani A, Hatami H, Azizi F.
(2009): Prevalence of obesity in young tehranian males (18-
25y) entering military service (Shahrivar 1386). Iranian Jour-
nal of Endocrinology and Metabolism. Mar 15;10(6):605-13.

6 THE PREVALENCE OF OVERWEIGHT AND OBESITY AMONG ADULTS BIOSCIENCE BIOTECHNOLOGY RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS
Sajed Salehi et al.
Bhaumik S, Watson JM, Thorp CF, Tyrer F, McGrother CW.
(2008): Body mass index in adults with intellectual disability:
distribution, associations and service implications: a popula-
tion‐based prevalence study. Journal of Intellectual Disability
Research. Apr 1;52(4):287-98.
El Raghi HA, Abdel-Aziz SB, Shalaby SF, El-Khider RK. (2016):
Prevalence of Obesity in Mentally Disabled Children Attend-
ing Special Education Institutes in Khartoum State. Journal of
Childhood Obesity.
Emerson E. (2005): Underweight, obesity and exercise among
adults with intellectual disabilities in supported accommoda-
tion in Northern England. Journal of Intellectual Disability
Research. Feb 1;49(2):134-43.
Hsieh K, Rimmer J, Murthy S. (2012): Prevalence and Associ-
ated Factors of Obesity in Adults with Intellectual Disabilities
Living in the Community. Conference: 140st APHA Annual
Meeting and Exposition. Available at: https://www.research-
gate.net/publication/266817266_Prevalence_and_associated_
factors_of_obesity_in_adults_with_intellectual_disabilities_
living_in_the_community.
International Obesity Task Force. (2007): The Global Challenge
of Obesity and the International Obesity Task Force. [cited Feb
18] Available from: URL http://www.iuns.org/features/obesity/
obesity.htm.
James PT, Leach R, Kalamara E, Shayeghi M. (2001): The world-
wide obesity epidemic. Obesity research. Nov 1;9(S11):228S-
33S.
James PT, Rigby N, Leach R. (2004): The obesity epidemic,
metabolic syndrome and future prevention strategies. Euro-
pean Journal of Cardiovascular Prevention & Rehabilitation.
Feb 1;11(1):3-8.
Koritsas S, Iacono T. (2015): Weight, nutrition, food choice, and
physical activity in adults with intellectual disability. Journal
of Intellectual Disability Research. Jan 1.1-10.
Mikulovic J, Marcellini A, Compte R, Duchateau G, Vanhelst
J, Fardy PS, Bui-Xuan G. (2011): Prevalence of overweight in
adolescents with intellectual de ciency. Differences in socio-
educative context, physical activity and dietary habits. Appe-
tite. Apr 30;56(2):403-7.
Obesity WH. preventing and managing the global epidemic.
Report of a WHO consultation. World Health Organ Tech Rep
Ser. 2000 Jun 3;894:1-253.
Rimmer JH, Yamaki K. (2006): Obesity and intellectual disabil-
ity. Mental retardation and developmental disabilities research
reviews. Jan 1;12(1):22-7.
Wille N, Erhart M, Petersen C, Ravens-Sieberer U. (2008): The
impact of overweight and obesity on health-related quality of
life in childhood–results from an intervention study. BMC Pub-
lic Health. Dec 23;8(1):421.
World Health Organization. (2006): The World Health Organi-
zation Warns of the rising threat of heart disease and stroke
as overweight and obesity rapidly increase. Sep 22 [cited 2008
May 2] Available from: URL: http: //www.who.int/mediacen-
tre/news/releases/2005/pr44/en /index.html.
World Health Organization. (2008): WHO European Ministerial
Conference on Counteracting Obesity Conference Report 2007
[cited March 15] Available from: URL: http: //www.euro.who.
int/ document/E90143.pdf.