
Biotechnological
Communication
Biosci. Biotech. Res. Comm. 10(4): 783-789 (2017)
Antagonistic activity of ZrO
2
against typhoid fever
causing
Salmonella typhi
, isolated from retail poultry
shops in and around Tirupur District
A. Chithira, M.I. Farheena and A. Mohankumar
Division of Microbial Technology, PG and Research Department of Zoology, Chikkanna Government Arts
College, Tirupur, Tamilnadu, India
ABSTRACT
Recurrently typhoid fever, caused by Salmonella typhi, remains a signi cant cause of mortality and morbidity in
many regions of the world. So predominant pathogen S.typhi is one of the major causes of food and water borne
gastroenteritis in human and remains an important health problem. So fecal samples were collected from the poultry
retail shop in tirupur city. Totally 50 multidrug resistant Salmonella spp were isolated from 75 fecal samples and
con rmed by using routine laboratory techniques. Later, the antimicrobial pattern of this isolates were studied by
using 11 antibiotic discs which include Amikacin (10mcg), Co-trimoxazole (25mcg), Cipro oxacin (30mcg), Tetra-
cycline (30mcg), Cephalothin (30mcg), Ceftriaxone (30mcg), Entro oxacin (10mcg), Gentamicin (10mcg), Ampicillin
(10mcg), Trimethoprim (10mcg), Cefoxitin (30mcg). Among these strains (12%), (62%), (28%), (80%), (12%), (4%),
(6%), (26%), (36%), (100%), and (8%) were found to be exhibit a signi cance degree of resistance to different groups
of antibiotics. Further, plasmid pro le were performed for the ve multidrug resistance isolates and observed the
molecular weight was 1500bp and 700bp respectively. Recurrently, the metal oxide nanoparticles are currently the
most promising tools applied as antimicrobial agents for diagnosis of diseases. Nanoparticle Zirconium oxide was
used to against Salmonella spp. Different concentration of Zirconium oxide 50μl, 100μl and 150μl were used against
Salmonella spp. Among the three concentration of nanoparticle, maximum zone of inhibition 16mm was observed
against the isolate CH36 at 150μl concentration of nanoparticle. Minimum zone of inhibition 13mm was observed
against the isolate CH37. So hence the present study Zirconium oxide was used and it shows prominent antibacterial
activity against typhoid causing organism.
KEY WORDS: TYPHOID FEVER,
SALMONELLA TYPHI
, ANTIBIOTIC RESISTANCE, PLASMID PROFILE AND ZRO
2
783
ARTICLE INFORMATION:
*Corresponding Author: nanochithira@gmail.com
Received 21
st
Oct, 2017
Accepted after revision 29
th
Dec, 2017
BBRC Print ISSN: 0974-6455
Online ISSN: 2321-4007 CODEN: USA BBRCBA
Thomson Reuters ISI ESC and Crossref Indexed Journal
NAAS Journal Score 2017: 4.31 Cosmos IF: 4.006
© A Society of Science and Nature Publication, 2017. All rights
reserved.
Online Contents Available at:
http//www.bbrc.in/
DOI: 10.21786/bbrc/10.4/25

784 ANTAGONISTIC ACTIVITY OF ZRO
2
AGAINST TYPHOID FEVER CAUSING SALMONELLA TYPHI BIOSCIENCE BIOTECHNOLOGY RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS
A. Chithira et al.
INTRODUCTION
Typhoid fever is a major health problem in develop-
ing countries, for thousands of years, thriving in con-
ditions of poor sanitation, crowding and social chaos,
contaminated water, milk, food or fruits vegetables or
via convalescent or chronic carrier (Harish Menezes,
2011). Typhoid fever is the most serious form of enteric
fever and in 2000 it was estimated that the global num-
ber of typhoid causes exceeded 21,00,000 with more
than 2,00,000 death. Globally, up to 27 million infec-
tions occur per year, with over 2x10
5
attributable deaths
annually, predominantly among children under the age
of ve years (Clark et al., 2010). The predominant Sal-
monella species are Gram-negative rod shaped bacteria
that are members of the family Entero bacteriaceae and
are considered threatened food borne pathogens facing
food safety and public health. Salmonella is a serious
threat facing poultry industries as it has the ability to
infect chickens causing diarrhoea. In the last few years,
consumption of contaminated poultry, eggs, and their
products become the most common sources of foodborne
human salmonellosis (Mahmoud et al., 2015; Park et al.,
2015; Hsu et al., 2016). Arena et al., 2017; Pashazadeh
et al., 2017 and Kalupahana et al., 2017).
A variety of food products, especially poultry and
other types of meat products, are the most important
sources of human Salmonella spp. infection, but water
borne outbreaks have also occurred birds are mainly
infected through feed, drinking water or environmental
sources. The organisms route of infection is the faecal –
oral route via food or water contaminated with faeces
or urine of previously infected persons or animals. Most
environmental concerns over land application of ani-
mal manure have focussed on either the effect of applied
nutrients, especially N and b.
Although poultry production is considered as sec-
ondary agricultural production systems and it has an
important role in high quality protein. Poultry provide
globally important sources of animal protein and are
amongst the most intensively reared of all livestock
species several microbial diseases have been affecting
the poultry and it is a major concern, both locally and
international levels. The low productivity is mainly due
to high mortality, which is caused particularly by bacte-
rial disease and the mortality has been estimated in the
range of 80-90% (Debnam and Jackson, 2005).
Food borne diseases are main problems, particularly
in developing countries and cause the majority of ill-
nesses and death around the world. Food is the most
important vehicle that transmits the microorganisms to
human (Varnam, 1991) among microorganisms Salmo-
nella still a major cause of food – borne human disease
in most parts of the world (Soultose et al., 2003 and
Carraminana et al., 2004).
Poultry and poultry products
are frequently contaminated with Salmonella that can
be transmitted to humans through the handling of raw
poultry carcasses and products, or through consump-
tion of undercooked poultry meat (Kimura et al., 2004).
Young chick, mortality up to 100%, week chicks, loss of
appetite, diarrhoea, and adult birds: no sings depression,
diarrhoea, and drop in egg production, low mortality.
The poultry farms bird u has become a lethal condi-
tion that is occurring around the world more frequently
(Julie et al., 2004).
The sub therapeutic use of antibiotics in poultry has
become a popular practice and these is a growing body
of scienti c evidence to the effect that the increasing
incidence of antibiotic resistant bacteria is closely asso-
ciated with the heavy use of these antibiotics in poultry
and other related agricultural practices. Despite the great
progress in antimicrobial development, many infectious
diseases, especially intracellular infections, remain dif -
cult to treat. One major reason is that many antimicrobi-
als are dif cult to transport to cell membranes and have
low activity inside the cell, there by imposing negligi-
ble inhibitory or bactericidal effects on the intracellular
bacteria (Zhang et al., 2010).
In 2013 many techniques were used by several
researchers to Salmonella spp. but these techniques
could not completely cure Salmonella spp. Pathogenic
bacteria still remain a major health concern, which are
responsible for causing a large number of deaths and
hospitalizations each year. Although we have current
treatments such as antibiotics, bacteria are gaining
resistance to these therapeutics at an alarming rate. That
is why new therapeutic and diagnostic treatments are
necessary if we want to be prepared against known and
unknown pathogenic bacterial infections. A large group
of these studies includes the implementation of nano-
technologies and nanomaterials to create new antibac-
terial nano-medicines that increased effectiveness and
ef ciency.
Moreover, nanotechnology is through to be technol-
ogy of the future with several opportunities for applica-
tions one of the most important nanotechnology appli-
cations areas that hold the expectations of providing
create bene ts for humanity in the future is medicine
(Neuberger et al., 2005). Therefore, it is important to
nd another ef cient treatment for Salmonella infection
instead of antibiotic. In the last few years, there has been
a growing interest in nanotechnology. Indeed, nano-
particles have been gaining importance in recent years
and became an effective revolution therapy against
pathogenic bacteria due to their bactericidal properties.
The nanoparticles size and surface area are signi cant
agents to which their bactericidal mechanism of action
attributed to several pathogens (Devi et al., 2017).

BIOSCIENCE BIOTECHNOLOGY RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS ANTAGONISTIC ACTIVITY OF ZRO
2
AGAINST TYPHOID FEVER CAUSING SALMONELLA TYPHI 785
A. Chithira et al.
ZrO
2
nanoparticles with antimicrobial activity when
embedded and coated and the surface can nd immense
applications in water treatment, synthetic textiles, bio-
medical and surgical device, food processing and pack-
aging. Moreover, the composites prepare using ZrO
2
and
polymers can nd better utilization due to the enhanced
antimicrobial activity.The multi drug resistant patho-
gens due to antigenic shift are ineffectively managed
with current medications. This resistance to medication
by pathogens has become a serious problem in public
health and therefore mandating the need to develop
new bactericides and virucides. Zirconium oxide nano-
particle (ZrO
2
), having a long history of general use as
an antiseptic and disinfectant, are able to interact with
disulphide bonds of the glycoprotein / protein contents
of microorganisms, viruses, bacteria, fungi. The ZrO
2
nanoparticle change the three dimensional structure
of proteins by interfering with S- bonds and block the
functional operation of the microorganisms. ZrO
2
nano-
particles with antimicrobial activity when embedded and
coated and the surface can nd immense applications in
water treatment, synthetic textiles, biomedical and sur-
gical device, food processing and packaging. Moreover,
the composites prepare using ZrO
2
and polymers can
nd better utilization due to the enhanced antimicrobial
activity.
Recently the antibiotics such as tetracycline, amika-
cin, co-trimoxazole cipro oxacin, cephalothin, ceftri-
axone, entro oxacin, gentamicin, ampicillin, trimetho-
prim, cefoxitin are used for the poultry bacterial disease.
One of the earliest nanomedicine applications particu-
larly, an antimicrobial agent from ZrO
2
nanoparticle
for the treatment of various microbial diseases is being
emerged. However, studies related the ZrO
2
nanoparticle
against S.typhi is too limited. Hence, the present study
has been made an attempt to point out the bioactive
medical properties of metal oxide nanoparticle (ZrO
2
)
against Salmonella typhi isolated from retail poultry
shop in and around Tirupur District.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Sterile spatulas were used to collect samples of freshly
passed poultry droppings in sterile universal sampling
bottles. 75 samples were collected from different poul-
try retail shop in Tirupur city. The droppings were col-
lected from litter at random points and transported to
the laboratory where they were analyzed within one
hour from the time of collection. Pre-isolation enrich-
ment of the faecal samples were carried out by inoculat-
ing each sample directly in to tryptone soy broth (TSB)
and incubated at 35
o
C for 18-24 hrs. Immediately after
enrichment, the organisms were serially diluted from
10
-1
to 10
-9
and the dilutions 10
-4
to 10
-6
were plated on
to Xylose lysine decorboxylase media (XLD) agar it was
inoculated at 35
o
C for 24 hours onto XLD agar plate for
the isolation of strains of Salmonella spp. respectively.
The individual colonies with different morphology were
picked using sterile tooth pick and grown in Tryptone
soy broth and it was incubated at 37
o
C for 24 hours.
Further it was plated to check for purity.
The isolated bacteria were primarily identi ed on the
basis of the Gram staining, IMViC, Citrate Utilization,
Triple sugar Iron agar, Nitrate reduction, Motility, Cata-
lase, Oxidative. All Salmonella typhi. Strains used in this
study were grown in TSB broth at 37
o
C for 24 hours. The
following antibiotic discs: Amikacin, Co-trimoxazole,
Cipro oxacin, Tetracycline, Cephalothin, Ceftriaxone,
Entro oxacin, Gentamicin, Ampicillin, Trimethoprim,
Cefoxitin were used for antibiotic sensitivity assay.
Selected colonies were inoculated into nutrient broth
then incubated at 37
o
C for 12 hrs. These cultures were
used for further experiment.In this present study anti-
biotic susceptibility of Salmonella typhi was performed
using Kirby Bauer disc diffusion method (1979). Plasmid
were isolated from Salmonella typhi using the method of
alkaline lysis (Niels, 1994) and the presence of plasmid
was checked by 0.7% agarose gel was with visualized
under UV light on transilluminator and photographed.
Size of the plasmids was determined with the help of the
standard molecular marker.
The antibacterial activity of the ZrO
2
nanoparticles was
performed by using well diffusion method. About 20 ml
of sterile molten Mueller Hinton agar was poured into
the sterile petriplates. Triplicate plates were swabbed with
the overnight culture (10
8
cells /ml) of pathogenic bacte-
ria Salmonella spp. Different concentration of nanopar-
ticles (50μl, 100μl, 150μl) was prepared with DMSO. The
different concentrations of nanoparticles were screened
against fty isolates of Salmonella spp. The isolates were
selected on the basis of Salmonella spp. should above
50% antibacterial activity against the antibiotics tested:
Amikacin, Co-trimoxazole, Cipro oxacin, Tetracycline,
Cephalothin, Ceftriaxone, Entro oxacin, Gentamicin,
Ampicillin, Trimethoprim, Cefoxitin. The solid medium
was gently punctured with the help of cork borer to make
a well. Finally the nanoparticle samples with the concen-
tration: 50μl, 100μl, 150μl were added from the stock into
each well and incubated for 24h at 37±2
o
C. After 24 hrs
of incubation, the zone of inhibition was measured and
expressed as millimetre in diameter.
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Totally 75 samples were collected from different poultry
retail shops in Tirupur city. 50 isolates of Salmonella
typhi were isolated from the samples. The Salmonella
typhi strains were con rmed by comparing the results

A. Chithira et al.
786 ANTAGONISTIC ACTIVITY OF ZRO
2
AGAINST TYPHOID FEVER CAUSING SALMONELLA TYPHI BIOSCIENCE BIOTECHNOLOGY RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS
with standard biochemical test of Salmonella typhi such
as gram negative in rod shape as result of gram staining.
Indole negative, MR-VP- positive, Voges Proskauer –
negative, Citrate positive, positive results were observed
in case of Catalase, Nitrate reduction, Motility, Tri-
ple sugar iron agar, Oxidase. Selective media like XLD
(Plate: 1) and Mac-Conkey agar media were used to iso-
late the Salmonella typhi. It showed black centre colony
and white colony respectively. These colonies were iso-
lated and stored for further experiment.
Antimicrobial susceptibility patterns were determined
by using commercial antimicrobial disc (HIMEDIA,
Mumbai): Amikacin (10mcg), Cotrimoxazole (25mcg),
Cipro oxacin (10mcg), Tetracycline (30mcg), Cepha-
lothin (30mcg), Ceftriaxone (30mcg), Entro oxacin
(10mcg), Gentamicin (10mcg), Ampicillin (10mcg), Tri-
methoprim (10mcg), and Cefoxitin (30mcg). Antimicro-
bial susceptibility testing was performed in accordance
with the standard guidelines of Kirby – Bauer (1979) disc
diffusion method.
Totally 11 antibiotic discs were used for this assay,
among that strain CH12 showed maximum resistance
of 72.72% and the antibiogram AK- TET- COT- CTR-
CEP- GEN- AMP-TR was recorded. Strain CH32 showed
minimum resistance of 9.09% and the antibiogram TR
was recorded (Plate: 2). The isolates were analyzed for
antibiogram as described to determine the antibiotic
susceptibility pattern along with the tendency of current
resistance against widely used drugs. Among 50 iso-
lates, 30 different antibiogram were found in this study
and the resistance was found against Amikacin (12%),
Cotrimoxazole (62%), Cipro oxacin (28%), Tetracycline
(80%), Cephalothin (12%), Ceftriaxone (4%), Entro oxa-
cin (6%), Gentamicin (26%), Ampicillin (36%), Trimeth-
oprim (100%), and Cefoxitin (8%) (Table: 1).
Five strains CH12, CH22, CH23, CH36 and CH37
showed more than 50% percentage frequency among the
fty isolates of Salmonella typhi.
MAR index for isolates = No. of antibiotics to which isolate is resistant
No. of antibiotics × No. of isolates
MAR index for isolates = No. of antibiotics resistant to the isolates
No. of antibiotics × No. of isolates
PLATE 1. Isolated colonies of
Salmonella typhi
PLATE 2. Antibiotic susceptibility test of Salmonella
typhi
Multiple Antibiotic Resistance (MAR) index was cal-
culated according to the formula
Maximum MAR index 0.7272 was showed by CH12
and minimum MAR index 0.0909 was showed by CH32.
Strains which showed more than 50% resistance was
taken for isolation of plasmid, by the following method
of Niels (1994), two fragments were obtained from the
strains: CH12, CH22, CH23, CH36, and CH37, but all
the strains were plasmid born Salmonella spp. 100bp
DNA ladder (MEDOX, Chennai), was used to know the
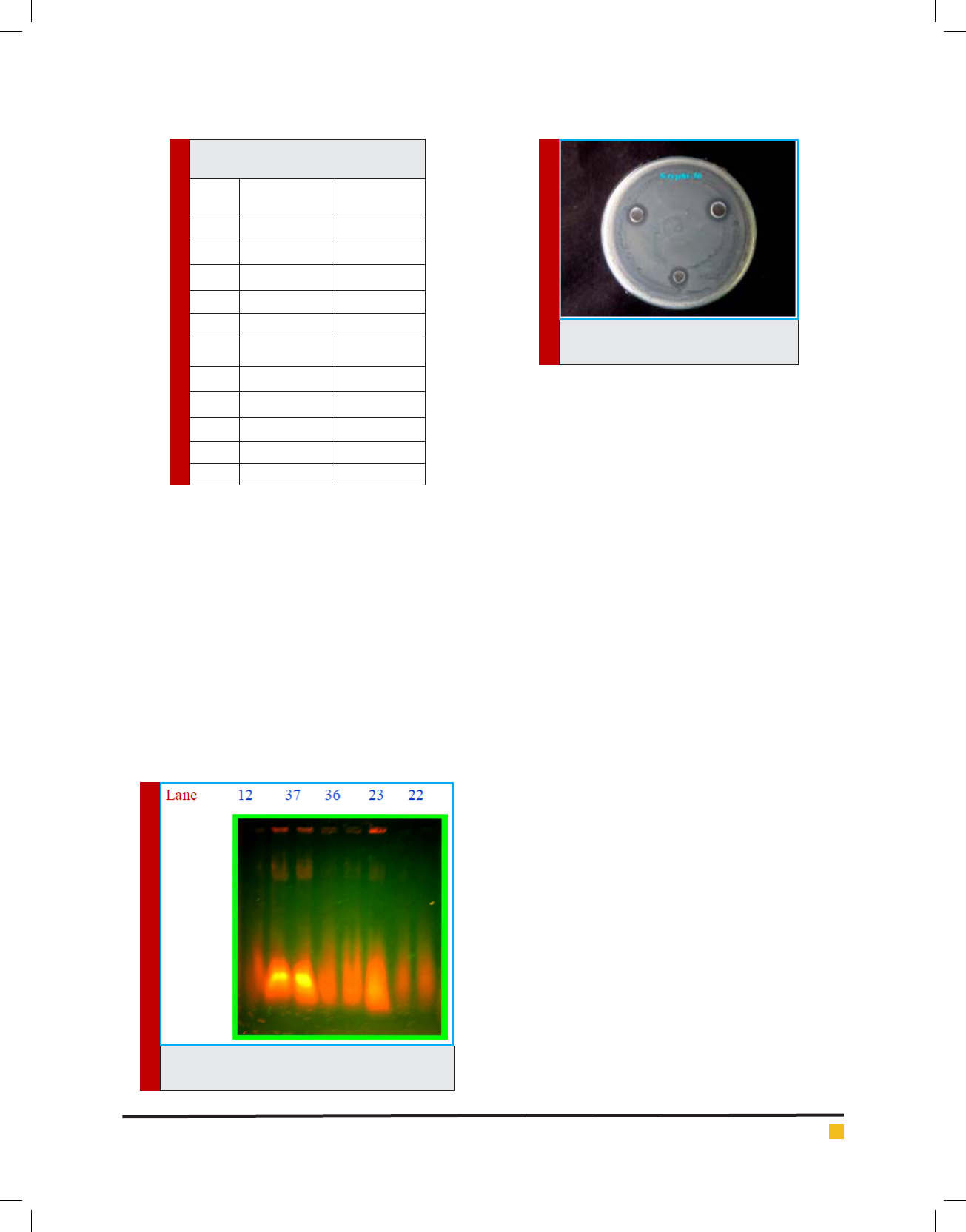
A. Chithira et al.
BIOSCIENCE BIOTECHNOLOGY RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS ANTAGONISTIC ACTIVITY OF ZRO
2
AGAINST TYPHOID FEVER CAUSING SALMONELLA TYPHI 787
molecular weight of the strain, it showed 1500 bp and
700 bp (Plate:3). The medical application of nanopar-
ticles is gaining popularity with an increasing number
of nanoparticle based therapeutics currently in clinical
development. We expect that with the introduction of
safer nanomaterials together with novel engineering
approaches that result in optimally designed nanoparti-
cles, enter the clinic in future.
Different concentration of nanoparticle Zirconium
oxide 50μl, 100μl, and 150μl were prepared with Dime-
thyl sulphoxide (DMSO), well diffusion method was used;
Different concentration of nanoparticle were impreg-
nated into well on the seeded Mueller Hinton Agar (MHA)
media. The plates were incubated at 37
o
C for 24hrs. Zone
of inhibition was recorded (Plate 4). The strains CH12,
CH22, CH23, CH36 and CH37 which showed more than
50% resistant against 11 antibiotics were used to test
against Zirconium oxide Nanoparticle. Salmonella spp.
Among the three concentrations of nanoparticles
tested against ve strains, maximum zone of inhibition
(16mm) was observed against CH36 at 150μl, followed
by 15mm against CH23 at 150μl. The minimum zone
(13mm) was recorded in the strain CH37. Although in
many areas of endemic city in Asia and the Indian sub-
continent typhoid outbreaks in Sub-Sharan Africa are
rarely documented, and data on incidence and antimi-
crobial susceptibility patterns are scarce. The observed
rise in MDR S.typhi in Kenya is particularly alarming.
For example during the period of their study, most of the
S.typhi isolates from blood culture of patients prior to
1993 were fully sensitive to all antimicrobials (Bhay et al.
2005). But in the present study the strain CH12 showed
maximum resistance 72.72% against all the antibiotics
tested. Salmonella typhi recorded 100% resistance to tet-
racycline, 66.7% resistance to gentamicin and ampicillin
respectively. These antibiotics are very common and are
readily available as over the counter drugs to consumers
in Nigeria (Funso Omojaasola and Folakemi Omojaasola,
2001). 80% of resistance showed by tetracycline, 26%
resistance to gentamicin, and ampicillin showed 36% of
resistance in the present study.
The resistance pattern of 101 strains of S.typhi to
11 drugs was determined by using the plate dilution
method. All 101 strains tested were inhibited by Cepha-
lothin; Gentamicin, (Olarte and Galindo, 1973), similar
method was followed in the present investigation, 50
strains of S.typhi isolated were inhibited by Cephalothin
(12%) and Gentamicin (26%).A total of 323 S.typhi iso-
lates from three hospitals covering the Nairobi region of
Kenya, 54 (16.7%) isolates were fully susceptible to all
eight antibiotics tested, (Kariuki et al. 2010), 50 strains of
S.typhi isolated from retail poultry shop in around Tiru-
pur, in all isolates (2%) was fully susceptible to all eleven
antibiotics tested. Further the authors were reported that
Table 1. Antibiotic Resistant Percentage
of Salmonella typhi
S: No Antibiotics
Percentage of
resistant
1 Amikacin 12%
2 Ceftriaxone 4%
3 Cipro oxacin 28%
4 Cephalothin 12%
5 Entro oxacin 6%
6 Gentamicin 26%
7 Ampicillin 36%
8 Cefoxitin 8%
9 Tetracycline 80%
10 Trimethoprim 100%
11 Co trimoxazole 62%
PLATE 3. Isolation of plasmid from Salmonella
typhi
PLATE 4. Activity of Zro
2
Nanoparticle
against of Salmonella typhi

A. Chithira et al.
788 ANTAGONISTIC ACTIVITY OF ZRO
2
AGAINST TYPHOID FEVER CAUSING SALMONELLA TYPHI BIOSCIENCE BIOTECHNOLOGY RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS
a total of 74 (22.9%) isolates were resistant to ampicillin
or tetracycline, similar results was recorded in the study
but total of fty isolates showed 36% and 80% resistant
to Ampicillin and tetracycline respectively.
One hundred and thirty two (132) bacteria were iso-
lated from 1000 cow dung samples, among that 18 iso-
lates of Salmonella typhi were cultured. 100% resistance
to tetracycline by all the isolates, ampicillin showed
85.6% resistance (Omojowo and omojasola, 2013), in
the present research work 75 faecal samples of retail
poultry shop, were collected among them, 50 isolates of
Salmonella typhi were isolates, ampicillin showed 36%
resistance against all tested antibiotics and tetracycline
showed 80% resistance.Six strains of Salmonella typhi
were resistant to ampicillin, trimethoprim, tetracycline
and gentamicin, these strains were isolated from the
blood with typhoid patients. These strains showed mul-
tiple antibiotics resistance (MDR) and all the six strains
were harbored plasmid about 50 kb (Pai et al. 2003).
Similar results was obtained, fty strains of Salmo-
nella typhi were showed resistant to all tested antibiot-
ics expect trimethoprim and all strains showed multiple
antibiotic resistant. These strains were harboured plas-
mid about 1500 bp and 700 bp.
Hirose et al. (2001) focused the antibiotics suscep-
tibilities of 62 strains of S.enterica serovar typhi of
S.enterica serovar paratyphi were investigated with 18
antibiotics. Eighteen S.enterica serovar typhi isolates and
ve S.enterica serovar paratyphi A isolates were resist-
ant to one or more antimicrobial agents among which
10 S.enterica serovar typhi isolates were susceptibility
against cipro oxacin. But our ndings showed the iso-
lates Salmonella typhi were showed antibiotics suscep-
tibility against all tested antibiotics except trimethoprim,
and these strains were resistant to one or more antibiotics.
Sisak et al. (2006) isolated 126 Salmonella spp from
pigs were tested against 14 antibiotics. They found
that the isolates showed resistance 1-8 antibiotics,
S.typhimurium strains were found to the most resist-
ant to streptomycin (91.5%), sulphonamides (88.1%),
ampicillin (86.4%), and chloramphenicol (83.0%), in the
present study, eleven antibiotics were tested against the
isolates, among that ampicillin showed lesser percentage
of inhibition while compare with work done by Sisak
et al. (2006), but it showed 36% resistance only. Ashok
et al. (2010) reported that they collected data for 2007
and 2008, ampicillin showed 18.2% and 52.8% of resist-
ance against Salmonella typhi, there as tetracycline
showed resistance of 9% and 33.4%, none of the anti-
biotics resistance against cipro oxacin and ceftriaxone
antibiotics, there uses controversy while compare the
results with present study, tetracycline showed second
highest resistance (80%), cipro oxacin 28%, ceftriaxone
4% showed resistance.
The antibacterial potential of metal oxide nanoparti-
cles viz, Al
2
O, Fe
3
O4, CeO
2
, ZrO
2
and MgO against poul-
try pathogens: Klebsiella spp., E.coli, Staphylococcus spp.
and Salmonella spp. The ZrO
2
showed maximum antibac-
terial activity against Salmonella spp. followed by E.coli
respectively. The author reported in their study that, the
ZrO
2
nanoparticles could be used as effective antibacterial
agent against poultry pathogens. In the present investiga-
tion, ZrO
2
was used as a nanoparticles against the Sal-
monella spp isolates which is isolated from retail poultry
shop. Totally ve isolates CH12, CH22, CH23, CH36, and
CH37 of Salmonella typhi were tested against different
ZrO
2
concentration (50μl, 100μl, and 150μl), as the zone of
inhibition were rapidly increased from 50μl - 150μl con-
centration of nanoparticles. Among ve isolates tested,
CH36 showed maximum zone of inhibition (16mm).
Mrithunjai singh et al. (2008) found that the nanopar-
ticles increase chemical activity due to crystallographic
surface structure with their large surface to volume
ratio. They used silver ions and silver based compounds
including silver nanoparticles, there has promoted
research and this effect was size and dose dependent and
was more pronounced against Gram – negative bacteria
than Gram – positive organisms, in the present investi-
gation, ZrO
2
was used as a nanoparticles, this showed
maximum activity, the activity was dependent on dose.
CONCLUSION
Development of resistance to antibiotics by bacteria is
inevitable, not only because of their rates in mutation
and transferability of drug resistant genes. This con-
stitutes a signi cant public health risk due to possible
cross-contamination with antibiotic resistant bacteria of
food and drinking water meant for public consumption,
which always culminates in human illnesses, mostly
typhoid fever. The growing incidence of multi-drug
resistant Salmonella typhi has become a global phenom-
enon and antibiotic resistant bacteria are increasingly
isolated from a wide array of sources, in the clinical
environments, poultry. There is some scienti c evidence
of the growing rate of recovery of antibiotic resistant
S. typhi from poultry products. So It is concluded from
the present study that species of Salmonella typhi iso-
lated from retail poultry shop in around Tirupur Dt. The
rapid emergence of drug resistant strains of microbial
Salmonella typhi pathogen especially those with multi
drug resistance characteristics and the organism link
with a plasmid. Due to the development of drug resistant
urgently need new therapeutic among drug to combat
the infectious disease. So in this study the biomedical
properties of metal oxide nanoparticles was used in dif-
ferent concentration to treat against multidrug resistant
Salmonella typhi.

A. Chithira et al.
BIOSCIENCE BIOTECHNOLOGY RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS ANTAGONISTIC ACTIVITY OF ZRO
2
AGAINST TYPHOID FEVER CAUSING SALMONELLA TYPHI 789
REFERENCES
Arena, E.T., Tinevez J, Nigro G, Sansonetti P.J, Marteyn B.S,
(2017). The infectious hypoxia: occurrence and causes during
Shigella infection. Microbes Infect, 19(3): 157-165.
Ashok, R., K. Peter, N. Joselyne, and N. Emma, (2010). Antimi-
crobial susceptibility patterns of Salmonella typhi from Kigali,
Rwanda. Shiraz E- Medical Journal, 11(3): 117 - 121.
Carraminana, J. J., C. Rota, I. Agustin, and A. Herrera, (2004).
High Prevalence of multiple resistance to antibiotics in Sal-
monellae serovars isolated from a poultry slaughter house in
Spain. Vet. Microbia., l 104: 133-139.
Clark, T. W., C. Daneshvar, M. Pareek, N. Perera, and I. Stephen-
son, (2010). Enteric fever in a UK regional infectious diseases
unit: A10 year retrospective review. J Infect., 60(2): 91-98.
Crump, J. A., S. P. Luby, and E. D. Mintz,(2004). The global
burden of typhoidal fever. Bull World Health Organ, 82: 346-
353.
Debnam, A. L., and C. R. Jackson, (2005). Effect of growth pro-
motant usage on enterococci species on a poultry farm. Avian
Dis., 49: 361-365.
Devi, G.K., Kumar K.S, Parthiban R, Kalishwaralal K, (2017).
An insight study on HPTLC ngerprinting of Mukia maderas-
patna: Mechanism of bioactive constituents in metal nano-
particle synthesis and its activity against human pathogens.
Microb. Pathog, 102: 120-132.
Harish, B. N., and G. A. Menezes, (2011). Antimicrobial resist-
ance in typhoidal Salmonellae. Indian Journal of Medical
Microbiology, 29(3): 223-9.
Hsu, Y. M., Yu B, Tseng C. S, Chang C. H, Chen D.S., Su C.H,
Chen Y.S, (2016). Preventive activities of Scutellariae radix,
Gardeniae fructus, and probiotics in Salmonella enterica sero-
var typhimurium infection in chickens. Anim. Feed Sci. Tech-
nol, 214: 121–129.
Hyunjoo Pai., Jeong Hum Byeon, Sunmi Yu, Bok kwon Lee,
and Shukho Kim, (2003). Salmonella enterica serovar typhi
strains isolated in Korea containing a multidrug resistance
class 1 integron. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy,
47(6): 2006 – 2008.
Kalupahana, R.S., Rajapaksa D.I.G, Fernando P.S, Thilakar-
athne D.S, Abeynayake P,(2017). Occurrence and characteriza-
tion of nontyphoidal Salmonella in retail table eggs in Kandy
district of Sri Lanka. Food Control, 72: 244-248.
Kenji Hirose., Kazumichi Tamura, Hiroko Sagara and Haruo
watannabe, (2001). Antibiotic susceptibility of Salmonella
enteric serovar paratyphi A isolated from patients in Japan.
Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy, 45(3): 956 -958.
Kimura, A. C., V. Reddy, and R. Marcus, (2004). Chicken con-
sumption is a newly identi ed risk factor for sporadic Sal-
monellae enteric serotype enteritidis infections in the United
States. Clin. Infect. Dis., 38: 244-252.
Mahmoud, B.S.M., Chang S, Yuwei W, Nannapaneni R, Sharma
C.S, Coker R, (2015). Effect of X-ray treatments on Salmonella
enterica and spoilage bacteria on skin-on chicken breast llets
and shell eggs. Food Control, 57: 110-114.
Mritunjai Singh., Shinjini singh, S. Prasad, and I. S. Gambhir,
(2008). Nanotechnology in medicine and antibacterial effect
of silver nanoparticles. Digest Journal of Nanomaterials and
Biostructures, 3(3): 115 – 122.
Namagirilakshmi, S., Selvaraj P, Nanjappan k, Jayachandran S,
Visha P, (2016). Turmeric (Curcuma Longa) as an alternative to
in-feed antibiotic on thegut health of broiler chickens. Tamil-
nadu. J. Vet. Anim. Sci, 6: 148–150.
Neuberger, T., B. Schopf, H. Hofmann, M. Hofmann, B. Von
Rechenberg, (2005). Superparamagnetic nanoparticles for bio-
medical applications: possibilities and limitations of a new
drug delivery system. Magn. Magn. Mater., 293: 483-496.
Niels Bohr., (1998). An improved method for the isolation of
supercoiled plasmid DNA. Current Science, 74: 572 – 573.
Park, S., Choi S, Kim H, Kim Y, Kim B, Beuchat L.R, Ryu J, (2015).
Fate of mesophilic aerobic bacteria and Salmonella enterica on
the surface of eggs as affected by chicken feces, storage tem-
perature, and relative humidity. Food Microbiol, 48: 200-205.
Samuel Kariuki., Gunturu Revathi, John Kiiru, M. Doris mengo,
Joyce Mwituria, Jane Muyodi, Agnes Munyalo, Y. Yik Teo, E.
Kathryn Holt, A. Robert Kingsley, and Gordon Dougan, (2010).
Typhoid in Kenya is associated with a dominant multidrug
resistant Salmonella enterica serovar typhi haplotype that is
also widespread in Southeast Asia. Journal of clinical Microbi-
ology, 48(6): 2171-2176.
Shi, R., Yang X, Chen L, Chang H, Liu H, Zhao J, Wang X,
Wang C, (2014). Pathogenicity of Shigella in Chickens. PLoS
ONE, 9(6): e100264.
Sisak, F., H. Havlickova, H. Hradecka, I. Rychlik, I. Kolackova,
and R. Karpiskova, (2006). Antibiotic resistance of Salmo-
nella spp. isolates from pigs in the Czech Republic. Veterinarni
Medicina., 51(5): 303- 310.
Soultose, N., P. koidis, and R. H. Madden, (2003). Prevalence of
listeria and Salmonellae in retail chicken in Northern Ireland.
Appl. Microbiol., 37: 421-423.
Tseng, C., Yen Y, Chang C, Hsu Y, (2014). Polymorphism of
gene cassette promoter variants of class 1 integron harbored
in S. choleraesuis and typhimurium isolated from Taiwan. Bio-
medicine, 4: 1–6.
Varnam, A. H., (1991). Food borne pathogens 1st Edn. Wolfe
publication Ltd, 71-76.
Xiangqian, Li., X. U. Huizhong, Zhe-sheng Chen, and Guofang
chen, (2011). Biosynthesis of nanoparticles by microorganisms
and their applications. Journal of Nanomaterials, 10: 1155.
Xu, L.J, Wang C.Q, Hu G.Z, Kang X.T, Ren J, et al (2004). Dis-
covery on shigellosis of ock in china and studies on the path-
ogenic specialty. Chin J Prev Vet Med, 26: 281–286.
Zhang, L., D. Pornpattananangkul, C. M. J. Hu, and C. M.
Huang, (2010). Development of nanoparticles for antimicrobial
drug delivery. Current Medicinal Chemistry, 17: 585-594.