
Environmental
Communication
Biosci. Biotech. Res. Comm. 10(4): 764-774 (2017)
Role of certain tree species in absorption of air
pollutants caused by heavy metals – Copper, Zinc and
Uranium in Tehran
Mehdizadeh Mojdehi Aida
1
and Ronassi Ali Arash
2
1
Ph.D. student Belarusian National Technical University, Minsk, Belarus
2
Assistant Professor, Department of Physics, Payame Noor University, Tehran, Iran
ABSTRACT
As environmental pollution to heavy metals is being increased every year, occurrence of serious risks to health of human, animals
and plants can be expected. Heavy metals with all of their destructive effects are the main pollutants in the air of big cities. Hence,
this study has been conducted with the objective of analysis of role of tree species in absorption of air pollution caused by copper
(Cu), zinc (Zn) and (U) uranium in Tehran. According to the climate of studied stations, especially wind velocity and direction, the
sampling operation was taken at the end of March and December. The number of samples was also determined based on number
of tree species studied (Pinus eldarica , Cupressus arizonica,Platanus orientails), organs of tree species (leaves), number of stations
(Mehrabad Airport, Damavand and Chitgar Park) and sampling time scopes (March and December). Sampling was done in frame of
statistical plan of completely random block in 3 iterations and the data analysis was done using analysis of variance and using SAS
software. The results obtained from this study show that the absorption of cooper, zinc and uranium metals in the leaves of studied
trees in polluted stations is more than control station. According to obtained results, uranium concentration in the leaves of studied
species increased respectively in Pinus eldarica Medw, Cupressus arizonica Greene and Platanus orientails. The leaves of Pinus eldar-
ica Medwin Mehrabad Airport station have shown highest absorption of this metal. Moreover, obtained results show that the cooper
absorbed by leaves of studied species is increased respectively in Pinus eldarica Medw, Cupressus arizonica Greene and Platanus
orientails. In terms of the effect of station on absorption of cooper, the species in the Mehrabad station have shown high absorption
of this metal. The concentration of absorbed zinc in leaves of studied species is also increased respectively in Pinus eldarica Medw,
Cupressus arizonica Greene and Platanus orientails and the zinc absorbed by species of Mehrabad station has shown the highest level.
It is concluded that the absorption level of Cu, Zn and U in leaves of studied trees in polluted stations has been higher than control
stations and Pinus eldarica Medw can be used as an index of absorption of heavy metals such as Cu, Zn and U.
KEY WORDS: TREE SPECIES, HEAVY METALS, COPPER, ZINC, URANIUM
764
ARTICLE INFORMATION:
*Corresponding Author:
Received 18
th
Oct, 2017
Accepted after revision 12
th
Dec, 2017
BBRC Print ISSN: 0974-6455
Online ISSN: 2321-4007 CODEN: USA BBRCBA
Thomson Reuters ISI ESC and Crossref Indexed Journal
NAAS Journal Score 2017: 4.31 Cosmos IF: 4.006
© A Society of Science and Nature Publication, 2017. All rights
reserved.
Online Contents Available at:
http//www.bbrc.in/
DOI: 10.21786/bbrc/10.4/23

Mehdizadeh Mojdehi Aida and Ronassi Ali Arash
INTRODUCTION
As environmental pollution to heavy metals is being
increased every year and can ultimately lead to seri-
ous risks to health of human, animals and plants, heavy
metals with all of their destructive effects can be the
main pollutants in the air of big cities. Therefore, one
of the most fundamental issues gaining attention of sci-
entists to heavy metals is lack of metabolism of these
metals in the body. According to increasing population
and the industrialization phenomenon of societies, more
and more use of fossil fuels, especially oil products to
produce electricity, transport systems and industrial
and house uses, has led to occurrence of environmental
problems because of production of hydrocarbons, pol-
luted gases and heavy metals (Naderi et al, 2012, Zhou
et al., 2017, Suvarapu and Baek, 2017).
As a result of rapid industrial growth over the dec-
ades, soil pollution to heavy metals has been increased.
Although heavy metals can be existed in soil naturally,
high percentages of these metals could be the outcome
of human activities such as use of chemicals,organic
modi ers, animal fertilizers, mineral processing, sew-
age sludge and waste from the iron and steel industry,
mines, road transport and so on .Vehicles can be one of
the main sources of producing heavy metals at the cit-
ies, which can cause pollution of soil around the roads
by production of pollutants and making them enter to
the environment and into the air. According to various
studies conducted in eld of heavy elements, the metals
such as cooper (Cu), lead (Pb) and zinc (Zn) have shown
high importance because of long half lifetime in body
of human and other animals and because of being toxic
(Suvarapu and Baek, 2017, Qiutong & Mingkui, 2017
and Sistani et al, 2017, Xu et al., 2017).
In eld of role of tree species in adsorption of air
pollution caused by heavy metals, various studies have
been conducted. Cheraghi et al (2012) have conducted a
study under the title of “analysis of heavy metals in bed,
leaves and stem of Avicennia marina in Khuzestan” and
have determined concentration of heavy metals such as
Cu, Pb, Ni and Cd in sediments of Imam Khomeini Port
Zone and Avicennia Marina and analysis of mobility
of these metals based on enrichment percentage. 9 sta-
tions were selected in theMangrove stations and some
samples of leaves and stem of Mangrove were collected,
along with sediments of the zone. The results showed
that concentration of metals in step of plants was more
than leaves. Moreover, there was signi cant correlation
between concentration of metals in stem and sediments
(Cheraghi et al, 2012).
Maddah et al (2013) measured the amount of sedi-
ment in extracts resulted from stem, shoot and leaves
and soil of owerpots at the end of Nov using ICP
device. The results showed that P.Sylvetris specie is the
suitable specie forphytoremediation of lead. In the con-
centration of 800ppm, the contamination of Pb in stem
and shoots is more than leaves; although in concentra-
tion of 1600ppm, the highest accumulation of lead is in
stem and leaves. Comparing different horizons of soil
showed that Pb has been mainly contaminated in sur-
face horizon (Maddah et al, 2013).
Kardar et al (2015) has studied cadmium adsorption in
organs of Fraxinus excelsior and Cupressus arizonica in
Isfahan. To this end, some samples of leaves and surface
steps of trees were prepared linearly and randomly in 3
iterations in late spring and summer and the cadmium
concentration in them was measured using atom adsorp-
tion device. The results show that cadmium absorption
level in areal organs of Cupressus arizonica happens
more than Fraxinus excelsior and cadmium absorption
in leaves of studied species is more than stem. Moreo-
ver, cadmium absorption in different organs of species
in polluted station was more than other stations and the
highest level of cadmium absorption was observed in
September and the lowest level was observed in June
(Kardar et al, 2015).
Kord et al (2011) has conducted a study under the
title of re nement of soil polluted to Zn by means of
tree species of Pinus Eldarica Medw, Cupressus arizon-
ica Greene, Robinia peseudoacacia,Fraxinus rotundifolia
Mill andUlmus carpinifolia var umbraculifera Rehd in
Tehran. For this purpose, in summer in polluted stations
(Azadi, Bahman and Bazar) and control station (Agh-
dasieh), a transect was selected due to wind direction
and sampling was done in 3 iterations from leaves and
surface stems of trees in frame of absolutely random
statistical plan and the Pb concentration in each sample
was measured using atom absorption device model Var-
ian220. The results showed that Pinus eldarica Medw,
Cupressus arizonica Greene and Robinia peseudoacacia
species have shown respectively highest Pb concentra-
tion in aerial organs (14.39ppm, 11.91ppm and 9.72ppm)
and highest coef cient of Pbtransfer from the under-
ground to the limb (respectively 3.49, 2.99 and 2.82).
Accordingly and due to adequate coping conditions, the
3 species have been used to re ne Pb-contaminated soil
in similar zones (Kord et al, 2011).
Afshari et al studied heavy metal pollution using pol-
lution factor in soil of lands with various uses in cen-
tral zone of Zanjan Province. To evaluate 241 samples
of surface soil based on systematic approach, nesting
was done in depth of 0-10c of agricultural, farming and
urban uses. The results showed that 1time more of the
pollutant is in eld soil and 0.4, 5.0 and 2.0 and 1 of
total Pb, Zn, Cd and Cu in samples soils and respectively
the overall concentration of Fe, Mg, Co and Ni is lower
than eld concentration of these metals. High amounts
BIOSCIENCE BIOTECHNOLOGY RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS ROLE OF CERTAIN TREE SPECIES IN ABSORPTION OF AIR POLLUTANTS 765

Mehdizadeh Mojdehi Aida and Ronassi Ali Arash
of pollution factor of Pb, Zn, Cd and Cu was observed
in urban uses and the pollution factor of Fe, Mg, Cr, Co
and Ni was observed in agricultural and farming uses.
Finally, the results showed that the metals in rst group
are mostly under the effect of human activities and the
metals in second group are mostly affected by mother
materials in the zone.
Shabanian and Chanor (2013) studied thebiodegrada-
bility of wooden species used in urban foresting of San-
andaj. Contamination of some heavy metals such as Pb,
Zn, Cd and Mg was measured in leaves ofOriental plain,
elm, asparagus, Croissant and black pine in Sanandaj’s
City Center (as polluted zone) and the area of Kurdis-
tan University (as control zone). The results showed that
contamination of Pb, Zn and Cd in leaves of majority of
species in polluted zone was signi cantly higher than
control zone at the level of 95%. In the polluted zone,
the highest contamination of Pb and Cd was observed
inCroissant, most Zn contamination was observed in
asparagus and the most Mg contamination was observed
in elm, (Shabanian and Chanor 2013).
Sistani et al (2017) conducted a cross-sectional and
descriptive-analytical research under the title of “heavy
metals contamination in adjacent soil of Kerman Steel
Industry: evaluation of metal enrichment and degree
of pollution”. In this study, they found that the most
concentration has been belonged to steel and concen-
tration of other metals such as Pb, Cd has been signif-
icantly under the effect of steel complexes and some
plans should be made for the surrounding area to reduce
emission of pollutants. Therefore, this study has been
conducted to investigate the amount of heavy metal
absorption in some tree species in Tehran.
MATERIAL AND METHODS:
In this study, to measure the amount of heavy metal
absorption in some tree species in Tehran, urban areas
such as parks, boulevards, streets and highways and
industrial districts used various tree species are selected
as stations and research station. Then, during certain
time intervals, through sampling leaves, stems and
shoots of species, the contamination of each organ was
determined. Accordingly, species with highest level
of heavy metal absorption and with higher resistance
against these metals were detected and were used in the
zones polluted to these metals.
As the status of pollution caused by studied heavy
metals is not same in whole city, sampling operation
should be taken in form of an index of pollution sta-
tus, so that it can consider minimum and maximum
and average levels of pollution. To this end and due to
reports of air pollution by Environmental Protection
Agency and Transport and Traf c Agency of Tehran,
Mehrabad Airport station was selected as station with
high air pollution; Damavand Station was selected as
station with low pollution. Chitgar station was selected
as control station due to low pollution to be the basis for
comparison with other polluted stations.
After determining the polluted and control stations,
the studied species were identi ed and selected in each
station. The desired species were selected based on
majority in Tehran and dominance in all studied area
from Evergreen and Easter species andBroad leaf and
needle leaf species. The tree species existed in all studied
stations in common were detected and board leaf Pla-
tanus orientails and needle leaf Pinus Eldarica Medw
andCupressus arizonica Greene were selected to take
required comparisons to determine heavy metal absorp-
tion level among different organs like leaves.
Sampling was done on leaves of trees in such way
that leaf samples were carefully separated from petiole
location. Moreover, according to position of the leaves
on the crown of tree, an arrangement was taken to select
leaves from whole crown of tree. Number of samples
was also determined due to number of studied tree spe-
cies (Pinus Eldarica Medw, Cupressus arizonica Greene,
Platanus orientails), organs of tree species (leave), num-
ber of stations (Mehrabad Airport, Damavand and Chit-
gar Park) and sampling time scopes (March and Decem-
ber) and iteration of examinations (3 iterations). Hence,
according to the climate of studied stations, especially
wind speed and direction, sampling was done in late
March and late December.
In this study, the effect of various factors such as tree
species, research stations, and time intervals of sampling
and concentration of heavy metals in leaves of trees was
studied. In frame of absolutely random block plan and
in 3 iterations, sampling was done and the data analy-
sis was done using analysis of variance and using SAS
software. Drawing diagrams and graphs was also done
using Excel software.
RESULTS
The results obtained from analysis of variance of mean
square in leaves of tree species for 3 elements of Cu, Zn
and U in time scope of March and December in 3 studied
zones are presented in table 1.
According to table 1, the results obtained from analy-
sis of variance in March showed that the effect of specie
is signi cant for all studied properties at the probability
level of 1% and the results have been insigni cant for
Cu concentration in leaf. Moreover, the results obtained
from analysis of variance in December showed that the
effect of specie for all studied properties is signi cant at
the probability level of 1% and the results obtained from
766 ROLE OF CERTAIN TREE SPECIES IN ABSORPTION OF AIR POLLUTANTS BIOSCIENCE BIOTECHNOLOGY RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS

BIOSCIENCE BIOTECHNOLOGY RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS ROLE OF CERTAIN TREE SPECIES IN ABSORPTION OF AIR POLLUTANTS 767
Mehdizadeh Mojdehi Aida and Ronassi Ali Arash
Table 1. analysis of variance of studied properties (March and December)
Sources of
variations
Degrees of
freedom
Mean Square
March December March December March December
Leaf Cu Leaf Cu Leaf Zn Leaf Zn Leaf U Leaf U
Specie 2 **35.65 **1.45 **1.23 **1.47 **0.98 **0.85
Station 2 **43.55 **1.64 **1.32 **10.21 **0.21 **032/
Specie×Station 3 **2.36 **0.08 **0.12 **0.09 *0.12 **0.9
Error 30 0.35 0.09 0.05 0.01 0.18 0.15
Coef cient of variation (%) 10.38 15.35 8.11 15.11 0.17 0.75
FIGURE 1. The effect of station on Zn concentration (ppm) in leaves of studied trees (March)
uranium concentration in leaf and Cu contamination in
leaf are not signi cant.
According to gure 1, the results of mean compar-
isons showed that the mutual effect of station on Zn
concentration in leaves of these trees was signi cant at
the level of 95% (p<0.05). On the other hand, the results
of multiple comparisons using Duncan test showed that
the highest Zn concentration in Pinus eldarica Medw
leaf was at Mehrabad Airport station (1.07ppm) and the
lowest concentration was at Chitgar station in Platanus
orientails (1.00ppm).
According to gure 2, the results of mean compari-
sons showed that the mutual effect of station on Cu con-
centration in leaves of these trees was signi cant at the
level of 95% (p<0.05). On the other hand, the results of
multiple comparisons using Duncan test showed that the
highest Cu concentration in Pinus eldarica Medw leaf
belonged to Mehrabad Airport station being 2.04 ppm
and the lowest concentration belonged to Chitgar sta-
tion inPlatanus orientails which was 1.63 ppm.
According to gure 3, the results of mean compari-
sons showed that the mutual effect of station on U con-
centration in leaves of these trees was signi cant at the
level of 95% (p<0.05). On the other hand, the results of
multiple comparisons using Duncan test showed that the
highest U concentration in Pinus Eldarica Medw leaf
was at Mehrabad Airport station being 0.99 ppm and
the lowest concentration at Chitgar station in Platanus
orientails was 1.00ppm.
According to gure 4, the results of mean compar-
isons showed that the mutual effect of station on Zn
concentration in leaves of these trees was signi cant at
the level of 95% (p<0.05). On the other hand, the results
of multiple comparisons using Duncan test showed that
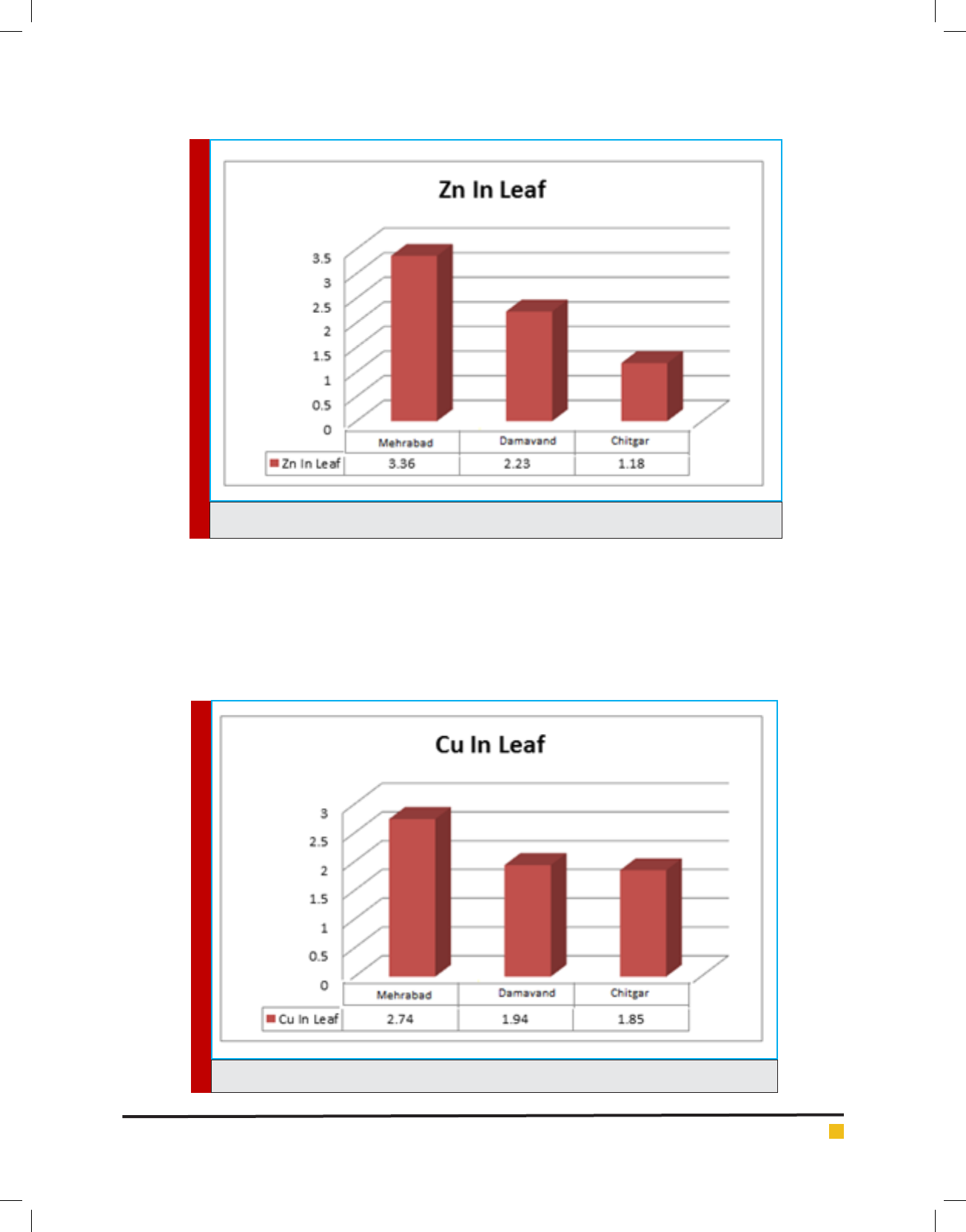
the highest Zn concentration in Pinus Eldarica Medw
leaf was at Mehrabad Airport station (3.36 ppm) and
768 ROLE OF CERTAIN TREE SPECIES IN ABSORPTION OF AIR POLLUTANTS BIOSCIENCE BIOTECHNOLOGY RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS
Mehdizadeh Mojdehi Aida and Ronassi Ali Arash
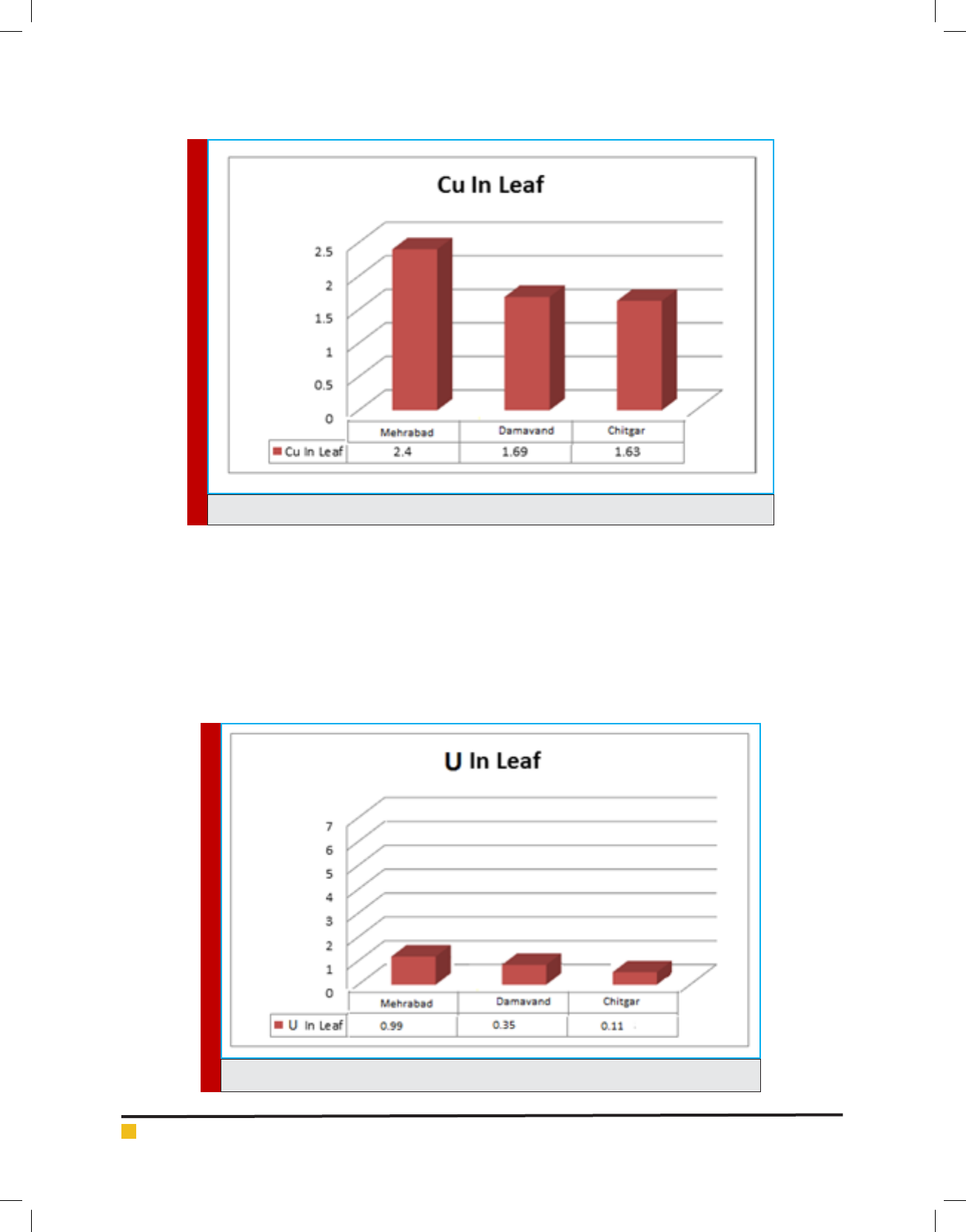
FIGURE 2. Cu concentrations (ppm) in leaves of studied trees (March) from various stations
FIGURE 3. The effect of station on U concentration in leaves of studied trees (March)
the lowest concentration at Chitgar station in Platanus
orientails was 1.18 ppm.
According to gure 5, the results of mean compari-
sons showed that the mutual effect of station on Cu con-
centration in leaves of these trees was signi cant at the
level of 95% (p<0.05). On the other hand, the results of
multiple comparisons using Duncan test showed that the
highest Cu concentration in Pinus Eldarica Medw leaf
belonged to Mehrabad Airport station being 2.74 ppm
and the lowest concentration was at Chitgar station in
leaves of Cupressus arizonica Greene being 1.85 ppm.
According to gure 6, the results of mean comparisons
showed that the mutual effect of station on U concentra-
tion in leaves of these trees was signi cant at the level of
95% (p<0.05). On the other hand, the results of multiple
comparisons using Duncan test showed that the highest
BIOSCIENCE BIOTECHNOLOGY RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS ROLE OF CERTAIN TREE SPECIES IN ABSORPTION OF AIR POLLUTANTS 769
Mehdizadeh Mojdehi Aida and Ronassi Ali Arash
FIGURE 4. The effect of station on Zn concentration in leaves of studied trees (December)
FIGURE 5. The effect of station on Cu concentration in leaves of studied trees (December)
U concentration in Pinus Eldarica Medw leaf belonged to
Mehrabad Airport station being 0.99 ppm and the low-
est concentration belonged to Chitgar station in leaves of
Cupressus arizonica Greene which was 0.22 ppm.
According to gure 7, the results of mean compari-
sons showed that the mutual effect of specie on Zn con-
centration in leaves of these trees was signi cant at the
level of 95% (p<0.05). On the other hand, the results of
multiple comparisons using Duncan test showed that the
highest Zn concentration was in Pinus Eldarica Medw
leaf (1.61 ppm) and the lowest concentration was in
leaves of nlatanus orientails (1.29 ppm).
According to gure 8, the results of mean compar-
isons showed that the mutual effect of species on Cu

770 ROLE OF CERTAIN TREE SPECIES IN ABSORPTION OF AIR POLLUTANTS BIOSCIENCE BIOTECHNOLOGY RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS
Mehdizadeh Mojdehi Aida and Ronassi Ali Arash
FIGURE 6. The effect of station on U concentration in leaves of studied trees (December)
FIGURE 7. The Zn concentration ppm in leaves of studied trees (March)
concentration in leaves of these trees was signi cant at
the level of 95% (p<0.05). On the other hand, the results
of multiple comparisons using Duncan test showed that
the highest Cu concentration was in the leaves of Pinus
eldarica Medw (2.61 ppm) and the lowest concentration
belonged to Platanus orientails which was 1.08 ppm.
According to gure 3, the results of mean compari-
sons showed that the mutual effect of specie on U con-
centration in leaves of these trees was signi cant at the
level of 95% (p<0.05). On the other hand, the results
of multiple comparisons using Duncan test showed that
the highest U concentration belonged to Pinus Eldarica
Medw leaf to 0.91 ppm and the lowest concentration
belonged to Platanus orientails to 0.17 ppm.
According to gure 10, the results of mean compari-
sons showed that the mutual effect of specie on Zn con-

BIOSCIENCE BIOTECHNOLOGY RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS ROLE OF CERTAIN TREE SPECIES IN ABSORPTION OF AIR POLLUTANTS 771
Mehdizadeh Mojdehi Aida and Ronassi Ali Arash
FIGURE 8. The Cu concentration ppm in leaves of studied trees (March)
FIGURE 9. The U concentration in leaves of studied trees (March)
centration in leaves of these trees was signi cant at the
level of 95% (p<0.05). On the other hand, the results
of multiple comparisons using Duncan test showed that
the highest Zn concentration belonged to Pinus eldarica
Medw leaf to 2.47 ppm and the lowest concentration
was in Cupressus arizonica Greene (2.05 ppm).
According to gure 11, the results of mean compari-
sons showed that the mutual effect of specie on Cu con-
centration in leaves of these trees was signi cant at the
level of 95% (p<0.05). On the other hand, the results of
multiple comparisons using Duncan test showed that the
highest Cu concentration was in Pinus eldarica Medw

772 ROLE OF CERTAIN TREE SPECIES IN ABSORPTION OF AIR POLLUTANTS BIOSCIENCE BIOTECHNOLOGY RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS
Mehdizadeh Mojdehi Aida and Ronassi Ali Arash
FIGURE 10. The Zn concentration in leaves of studied trees (December)
FIGURE 11. The Cu concentration in leaves of studied trees (December)
(2.38 ppm) and the lowest concentration was in Cupres-
sus arizonica Greene being 1.97 ppm.
According to gure 12, the results of mean compari-
sons showed that the mutual effect of specie on U concen-
tration in leaves of these trees was signi cant at the level
of 95% (p<0.05). On the other hand, the results of multiple
comparisons using Duncan test showed that the highest
Uranium concentration was in Pinus eldaricaleaves which
was 0.27 ppm and the lowest concentration of 0.11 ppm
was in the leaves of Cupressus arizonica.
DISCUSSION AND CONCLUSION
This study has been conducted with the aim of anal-
ysis of the role of three tree species in absorbing the
air pollution caused by Cu, Zn and Uranium in Tehran.
This study has been conducted in 3 stations including
Mehrabad Airport, Damavand and Chitgar stations. In
this study, it was found that absorption of heavy met-
als (Cu, Zn and Uranium) in leaves of studied trees in
polluted stations was more than control station and
it is increased respectively in Chitgar, Damavand and
Mehrabad stations. As the environment plays key role
in absorption of metals by plant species, it seems that
Mehrabad Airport has shown higher level of absorption
of the metal in leaves of tree species than other stations
due to high concentration of metals in the air. Heydari
et al (2005) have claimed that Pb absorption by plants
can be increased due to concentration of this metal in
the environment. Marry et al (1996) have also men-
tioned in their investigations that Pb absorption level by
plants is in signi cant correlation with concentration of
this metal in the environment.

BIOSCIENCE BIOTECHNOLOGY RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS ROLE OF CERTAIN TREE SPECIES IN ABSORPTION OF AIR POLLUTANTS 773
Mehdizadeh Mojdehi Aida and Ronassi Ali Arash
Cheraghi et al (2012) showed that concentration of
metals in stem of plants was more than leaves. Moreo-
ver, signi cant correlation was observed between con-
centration of metals in stem and the sediments. Maddah
et al (2013) found that forest pine is suitable specie for
PbPhytoremediation. In concentration of 800ppm, the
contamination of Pb is in highest level in stem and
shoots; although in concentration of 1600ppm, the Pb
contamination is mostly in stem and leaf.
The results obtained from the present study show that
the absorption of these metals in tree species studied
varies during different times and the process is increased
in December and March. As absorption of these elements
in plants is a physiologic phenomenon, absorption is
decreased in cold months of the year with reduction of
temperature and reduction of breathing. Poorfarhadi
(1994) and Shahmansuri (1995) studied role of different
seasons in absorption level of Pb in plants and found
that the most absorption of Pb is in summer.Organiza-
tion of Parks and Green Space of Tehran Municipality
(1994) has also reported most Pb contamination level in
plants in late September.
Kardar et al (2015) found that absorption of Cd in
different organs of plant species in polluted station
has been more than other stations and the highest cd
absorption level has been attributed to September and
the lowest level is observed in June. Shabanian and
Cheraghi (2013) showed that contamination of Zn, Pb
and Cd in leaves of majority of species in polluted zone
has been signi cantly higher than control zone at the
level of 95%. In polluted zone, the contamination of Pb
and Cd has been observed in cedar and Zn in elm and
Mg are also observed mostly inRobinia peseudoacacia.
In this study, in the studied treatments, absorption of
metals existed in needle leaf trees has been more than
broad leaf trees, so that its increasing process has been
observed respectively inPinus Eldarica Medw, Cupressus
arizonica Greene and Platanus orientails. It seems that
parameters such as being evergreen, more numbers of
leaves, high growth speed, the Cu contamination in soil
and ability of transfer from underground to aerial organs
can affect increased absorption of metals in needle leaf
plants. Lasat (2000) has found that growth speed of spe-
cies and the coef cient of Cu transfer from underground
to shoots could be the most important factor to increase
the element in shoots (leaf and branches). Safdari (2005)
has also mentioned that air pollutants can have more
effect on needle leaf plants because of being evergreen
and because of wider surface of leaf against the air ow.
Moreover, as one of the secondary results of this
study, it could be mentioned that through conducting
a eld study in the zones with probability of emission
of radioactive mainly caused by heavy metals such as
surrounding areas of nuclear stations and the places for
disposal of radioactive materials, through planting tree
species with high absorption capability of heavy met-
als, especially radioactive metals such as U235, U238
and Pu239 found in nuclear wastes abundantly, a reli-
able method could be found in long-term to measure
the amount of emission of radioactive materials from
thenuclear disposal plant or reservoirs. Particularly, it
could be applied in positions or places, at which Geiger
Müller meters or other nuclear sensors can’t be applied
for any reason.
The results obtained from this study show that the
Cu absorbed by leaves of studied species is increased
FIGURE 12. The U concentration in leaves of studied trees (December)

774 ROLE OF CERTAIN TREE SPECIES IN ABSORPTION OF AIR POLLUTANTS BIOSCIENCE BIOTECHNOLOGY RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS
Mehdizadeh Mojdehi Aida and Ronassi Ali Arash
respectively in Pinus eldarica Medw, Cupressus ari-
zonica Greene and Platanus orientails. Also, the high-
est absorption level of this metal is observed in leaf of
Pinus Eldarica Medw. In terms of the effect of station in
absorption of Cu, the species in Mehrabad Airport sta-
tion have shown highest level of Cu contamination. The
Zn contamination is also increased in leaves of stud-
ied species includingPinus eldarica Medw, Cupressus
arizonica Greene and Platanus orientailsand the Pinus
eldarica Medwleaves have shown the highest contami-
nation of this metal. The effect of stations on this metal
has been also similar to two mentioned metals and has
shown highest concentration in species in Mehrabad
Station. In this study, it seems that due to the results
obtained, uranium concentration absorbed by studied
species is increased respectively in Pinus eldarica Medw,
Cupressus arizonica Greene and Platanus orientails.
The highest uranium contamination is also observed in
Pinus eldarica Medwleaves. As it was mentioned, the
concentration of uranium in studied species in polluted
stations is more than control station and the leaves of
Pinus eldarica Medwin Mehrabad Station have shown
highest contamination of this metal. Therefore, it could
be observed in this study that absorption of Cu, Zn and
U in studied trees in polluted zones has been higher than
control station and Pinus eldarica Medwcan be applied
as an indicator species for contamination of heavy met-
als such as Cu, Zn and Uranium.
REFERENCES
Afshari Ali, Khademi Hossein and Delavar Mohammad Amir
(2015). Evaluation of Heavy Metal Contamination Using Pol-
lution Factor in Soil Land with Different Uses in the Central
District of Zanjan Province. Journal of Water and Soil Science,
Vol. 25, No. 2.4, 2015, p. 41-52
Baek SO (2017).Determination of heavy metals in the ambient
atmosphere. Toxicol Ind Health. 2017 Jan;33(1):79-96.
Cheraghi, M., Dadalahi Sohraab, Saffahieh A., Ghanemi K. and
Dorky A. (2012). Investigation of the accumulation of heavy
metals in the bed, leaves and roots of the plant (Avicennia
marina). In Khuzestan province. Journal of Marine Science and
Technology, Volume 11, Number 4, Pages 46-5646
Kardar Saeed, Fatemi Talab Seyed Reza, Saeb Keivan, Kha-
demi Amin (2015). Investigation of the role of Asteroid and
Silver Cousin Types in heavy metal cadmium biomass process-
ing (Isfahan case study). Natural Ecosystems of Iran. Article
7, Volume 6, Issue 2, Successive Issue 19, Summer 2013, Page
89-96
Kord Behrooz, Khademi Amin and Abbasi Sarapour (2011)
.Production of lead element by some tree species in urban
polluted soils (Tehran). Biostatistics: Autumn 2011, Volume 5,
Issue 3 (18); p 109-119.
Maddah Seyedeh Mahdokht, Jalilpour Babak, Shirvani Anush-
irvan, Moraghebi Farhang, Firouzeh Faezeh (2013). Evaluation
of Lead Biomonitoring Ef ciency in Soil by Pinus sylvestris
Forest Pine Saplings. Plant and Ecosystems:Summer2013, No
35, Issue 9; p 11-20.
Marry, R.H.; Tiller, K.G. and Alston, A.M.,)1986. (The effect of
contamination of soil with copper, lead and arsenic on the growth
and composition of plant. Journal of Plant and Soil, 91: 115-128.
Naderi, Mohammad Reza, Daneshahrki, Abdul Razaq, Naderi,
Rezvan (2012). A review of the planting of soils contaminated
with heavy metals. Man and the environment.10. No. 4 (23rd
year 34), 35-49
Parks & Green Space Organization of Tehran, (1994) Informa-
tion on the area and number of Tehran parks.
Poorfarhadi, K. (1994). Investigation of Tehran’s air leads cap-
ture by evergreen plants and determination of resistant spe-
cies. Master’s Degree Program in Environmental Economics,
Faculty of Natural Resources, University of Tehran., 108E
Safdari, Vahid Reza, Parsapajouh, Davood, Hamsi, Amir
Hooman, Dendrochemistry studies in order to investigate the
effects of Tehran air pollution on Pinus eldarica. Environmen-
tal Science and Technology, No. 26, 2005
Shah Mansouri, M (1995). Ecological survey of lead-contam-
ination in the river, Journal of Water and Sewage, No. 3-11:
Shanbanian, Naghi and Lamaghi, Chanor (2013). Comparison of
heavy metal biopsy by wood species used in urban forestry in
Sanandaj. Forest and Poplar Researches of Iran,21 (1), 154-165.
Sistani N., Moin al-Dini Mazeher, Khorasani Nematollah,
(2017). Po llution of Heavy Metals in Soils Adjacent to Kerman
Steel Industries: Evaluation of Metal Bene t and Degree of
Contamination. Journal of Health and Environment, Journal
of Research. Iranian Society of Environmental Health. Volume
10, Number 1, Spring 2017, p 75-86
Suvarapu LN, Baek SO (2017). Determination of heavy met-
als in the ambient atmosphere. Toxicol Ind Health. 2017 Jan;
33(1):79-96
Zhou, X., Chen, Q., Liu, C., & Fang, Y. (2017). Using Moss to
Assess Airborne Heavy Metal Pollution in Taizhou, China.
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public
Health,14(4), 430. http://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph14040430
Xu Qiutong and Zhang Mingkui (2017). Heavy Metals Accu-
mulated in Vegetable Soils in the Coastal Plain of Eastern Zhe-
jiang Province, China. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 142, 410-416.
2017 Apr 28.