
Biotechnological
Communication
Biosci. Biotech. Res. Comm. 10(4): 631-644 (2017)
Manipulating disease and pest resistance pathways in
plants for enhanced crop improvement
Paramita Ghosh, Anjanabha Bhattacharya* and Bharat Char
Maharashtra Hybrid Seeds Company Private Limited, Jalna-Aurangabad
Road, Dawalwadi, Jalna, Maharashtra, India
ABSTRACT
Plants are sessile organisms, therefore cannot escape challenges of their surrounding environment. The rich source
of nutrients plant possesses attracts various organisms. Biotic stress results from array of organisms such as bacteria,
fungi to various insects, pests and herbivores. Plants have evolved sophisticated mechanisms to protect themselves
against invaders. In this review, we explore the plant surveillance system, different nodes in the defence pathways
involved in plant protection and how it can be manipulated to get a resistant crop. Emerging technologies have
provided us with a vast number of potential candidate genes from plants, pathogens and other organisms. We here,
illustrate examples of technically useful solutions to make crops tolerant to pathogens and pests.
KEY WORDS: PLANT DEFENCE, BIOTIC STRESS, R GENE, DEFENCE SIGNALING TRANSDUCTION, NPR1, MAPK, GENETIC ENGINEERING
631
ARTICLE INFORMATION:
*Corresponding Author: anjanabha.bhattacharya@mahyco.com
Received 12
th
Nov, 2017
Accepted after revision 29
th
Dec, 2017
BBRC Print ISSN: 0974-6455
Online ISSN: 2321-4007 CODEN: USA BBRCBA
Thomson Reuters ISI ESC and Crossref Indexed Journal
NAAS Journal Score 2017: 4.31 Cosmos IF: 4.006
© A Society of Science and Nature Publication, 2017. All rights
reserved.
Online Contents Available at:
http//www.bbrc.in/
DOI: 10.21786/bbrc/10.4/5
ABBREVIATIONS
MAMPs - Microbe Associated Molecular Patterns,SAR -
Systemic Acquired Resistance, VOCS – Volatile Organic
Compound, R gene – Resistance Gene, HR – Hyper-
sensitive Reaction, ROS – Reactive Oxygen Species,
MAPK – Mitogen Activated Protein Kinase, avr – Aviru-
lence, ETI – Effector Triggered Immunity, NBS – Nuclear
Binding Site, LRR – Leucine Rich Repeat , pv. – pathover,
NO – Nitric Oxide, SA – Salicylic Acid, JA – Jasmonic
Acid, ET- Ethylene, NPR1 – Non Expressor of PR Genes
1,PR – Pathogenesis Related, LTP –Lipid Transfer Pro-
tein, PPO – Polyphenol Oxidase, POD – Peroxidase,
UV- Ultraviolet, HIPV – Herbivore Induced Plant Vola-
tile, QTL – Qualitative Trait Loci, SIPK - Salicylic Acid
Induced Protein Kinase, OS – Oral Secretion, FACs –
Fatty Acid –Amino Acid Conjugates, WIPK – Wound
Induced Protein Kinase, MEKK- Mitogen-Activated
Protein Kinase Kinase, ISR – Induced Systemic Resist-
ance, PRSV - Papaya Ring Spot Virus, ZFN – Zinc
Finger Nucleases, TALENs – TAL Effector Nucleases,
GM – Genetically Modi ed, RPP2 – Recognition of per-
onospora parasitica 2

632 MANIPULATING DISEASE AND PEST RESISTANCE PATHWAYS IN PLANTS BIOSCIENCE BIOTECHNOLOGY RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS
Paramita Ghosh et al.
INTRODUCTION
Plants are nutrient rich organisms and therefore many
invaders prey on their food reserve. Some of the invad-
ers are signi cant threats to crop production, world-
wide. In the process of co-evolution (Seidl and Thomma,
2017); plants, pathogens and insects have evolved vari-
ous strategies to avoid each others’ defence system. The
goal of producing crops with durable and increased
resistance to a broad spectrum of diseases and insects is
therefore, a major focus in plant research.
In nature, plants are continuously challenged by differ-
ent organisms, whereas, only few are successful in gain-
ing entry into a prospective host. Plants have developed
an elegant defence system with a wide variety of consti-
tutive and inducible defences to protect themselves from
damages of different biotic factors. Constitutive defences
include many preformed barriers such as waxy epider-
mal cuticles, cell walls and bark (specialized morphologi-
cal structures). Inducible defences include production of
repellents, toxic chemicals, pathogen-degrading enzymes,
anti-nutritional effects and deliberate cell suicide (Free-
man and Beattie, 2008). Plants often do not produce toxic
compounds or defence-related proteins until pathogens
are detected due to the metabolic cost associated with the
production and maintenance of such compounds. Plants
have evolved to live in environments where they are
very often exposed to different stress factors in combi-
nation. Plants have developed various mechanisms that
allow them to detect precise environmental changes and
respond to complex stress conditions, minimizing dam-
age (Saskia and Jorunn, 2011).
NATURE OF ATTACKERS
Plant pathogens can be broadly divided into biotrops and
necrotrophs. Bacteria and fungi can adapt to both lifestyles
(Freeman and Beattie, 2008).Viruses are quintessential bio-
trophs, although they eventually kill the host cell. Insects,
on other hand, cause damage by chewing and sucking.
Plants respond to the insects by producing protease inhibi-
tors and anti-feedants such as alkaloids [(Hanley et al.,
2007; Jeffery and Jonathan, 2001). Nematodes can adapt
to complex modes of parasitism by exhibiting variety of
parasitic modes affecting the development responses of
plants, causing galls, root knots or cysts (Jeffery and Jona-
than, 2001; Davis et al., 2004; Roland and Maurice,2011) .
Thus, plant immune system is highly polymorphic in their
capacity to recognize and respond to different stress fac-
tors (Jeffery and Jonathan, 2001).
PLANT SURVEILLANCE SYSTEMS
Although plants lack immune system comparable to
animals, they have developed sophisticated surveillance
mechanisms, which can respond rapidly before harmed.
These surveillance systems are linked to speci c pre-
programmed defence responses. Direct defences are
mechanical protection on the surface of the plants which
protects from all biotic factors (e.g., hairs, trichomes,
spines, thorns and thicker leaves) or toxic chemical pro-
duction.
Basal resistance is the rst line of pre-formed and
inducible defences. It is also known as innate immunity
(Freeman and Beattie, 2008; Owen and Zamir, 2010), and
protect plants against entire groups of pathogens (Free-
man and Beattie, 2008). Basal resistance is triggered
when plants recognize microbe-associated molecular
patterns (MAMPs). MAMPs include speci c proteins,
lipopolysaccharides, and components of cell wall com-
monly found in microbes. During evolution pathogens
also have developed counter measures that are able to
suppress basal resistance in certain plant species. If the
basal defence is somehow suppressed, plants respond
with hypersensitive response (HR) (Freeman and Beattie,
2008). In HR plants limit the pathogen’s access to water
and nutrients thereby sacri cing few cells in the infec-
tion site i.e. deliberate cell suicide (programmed cell
death). HR is more pathogen speci c than basal resist-
ance. It is triggered in presence of disease-causing effec-
tor molecules. Once the hypersensitive response is trig-
gered, plant tissues become highly resistant to a broad
range of pathogens. This phenomenon is known as sys-
temic acquired resistance (SAR) (Freeman and Beattie,
2008; Nelson et al., 2017), which represents readiness of
plant metabolites to defend plants, in case of a height-
ened attack.
Mechanical damage caused by insects is not gener-
ally considered “true” plant disease although plants have
developed surveillance systems designed to not only
recognize insect pests, but also to respond with speci c
defence mechanisms. General wounding can be different
from insect feeding in a way that elicitors are present
in insect saliva. In response to insect chewing, plants
release volatile organic compounds (VOCs), second-
ary metabolites and proteins that have toxic, repellent,
and/or anti-nutritional effects on the herbivores (Free-
man and Beattie, 2008; Saskia and Jorunn, 2011; Abdul
Rashid War et al., 2012). Sometimes volatiles released by
plants also attract bene cial predators (natural enemies)
that prey on the destructive pests (Abdul Rashid War
et al., 2012; Walling, 2000; Rashid and Chung, 2017).
Plants become phenotypically plastic when induced
defence is triggered as a result it decreases the chances
of the attacking insects to adapt to the induced chemi-
cals (Abdul Rashid War et al., 2012).
In addition, plants can defend themselves against
viruses by a variety of mechanisms which include RNA
silencing (Novina and Sharp, 2004, Csorba and Burgyan,
BIOSCIENCE BIOTECHNOLOGY RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS MANIPULATING DISEASE AND PEST RESISTANCE PATHWAYS IN PLANTS 633
Paramita Ghosh et al.
2016). Plants can recognize the foreign double stranded
RNA or DNA, produced by viruses in the host cell dur-
ing replication, and respond by digesting the genetic
strands into non recognizable fragments and thereby
stopping the infection. The interaction of plants with
symbionts, pathogen, herbivores, and the natural ene-
mies, both above and below the ground is the focus of a
large amount of research effort and has great potential
for utilization in crop protection.
With cultivation of huge areas of genetically iden-
tical crops, protection relies on a small number of in-
bred disease resistance genes per crop species and on the
wide-spread application of pesticides. Unfortunately, an
absolute control is very dif cult to achieve through pes-
ticides (Cesari, 2017), as pathogens can overcome disease
resistance genes and/or become resistant to pesticides
(Nelson et al., 2017; Zhonghua et al., 2005). Genetic
manipulation can help solve the problem by inserting
multiple genes as transgenes by careful selection from
wild parent of the same plant species or from different
plant species (Campbell et al., 2002). Therefore a search
is on for genes that can confer a durable broad-spectrum
resistance against biotic factors. To make it more envi-
ronment friendly the gene product should be safe for all
organisms and also reduce the need of harmful pesti-
cides. However, the success so far achieved is very less.
In majority of cases the tansgene results in unpredict-
able expression in different parts of the plants, this phe-
nomenon is not due to the transgene itself, per se (Ham-
mond-Kosack and Parker, 2003; Stuiverand Custers,
2001) . Therefore, optimization of transgene expression
patterns needs close attention. Inducible expression of
such gene is essential (Hammond-Kosack and Parker,
2003; Michelmore, 2003). A highly inducible promoter
speci c for defence gene expression can help the plant
in directed recourse allocation by metabolic and tran-
scriptional adaption during stress. Plant can optimize
source sink relationship thus increasing yield or biologi-
cal harvest index (Hammond-Kosack and Parker, 2003).
ENGINEERING PLANTS WITH INCREASED
RESISTANCE AGAINST PATHOGEN AND
INSECTS: TARGET GENES
(First generation strategies)
R gene
R genes (resistance genes) are important components
of plant surveillance system. A diverse array of defence
mechanism is triggered when R genes recognize patho-
gen or insects (Cesari, 2017). PR-gene induction, accu-
mulation of inhibitory metabolites and oxidative burst
response by production of reactive oxygen species, are
some of the downstream responses triggered by R genes
which lead to hypersensitive response (Owen and Zamir,
2010 ).
Pathogens possessing avr genes can overcome basal
immunity of plants by blocking perception of PAMP
or by inhibiting MAP kinase signaling cascade, which
is known as effector- triggered susceptibility. In case
of effector triggered immunity, the pathogen’s effec-
tor molecules are recognized by R proteins either by
direct or indirect interactions. Thus, enhancing the plant
resistance and it is faster than PTI. To trigger ETI, R pro-
teins must recognize speci c avirulence proteins (Avr)
in order to generate resistance. However, mutation in
either avr gene or R gene can change the scene i.e it will
result in compatibility and therefore loss of resistance. R
genes encode proteins which have nuclear binding sites
(NBS) and leucine rich repeat (LRR) domains (NBS-LRR
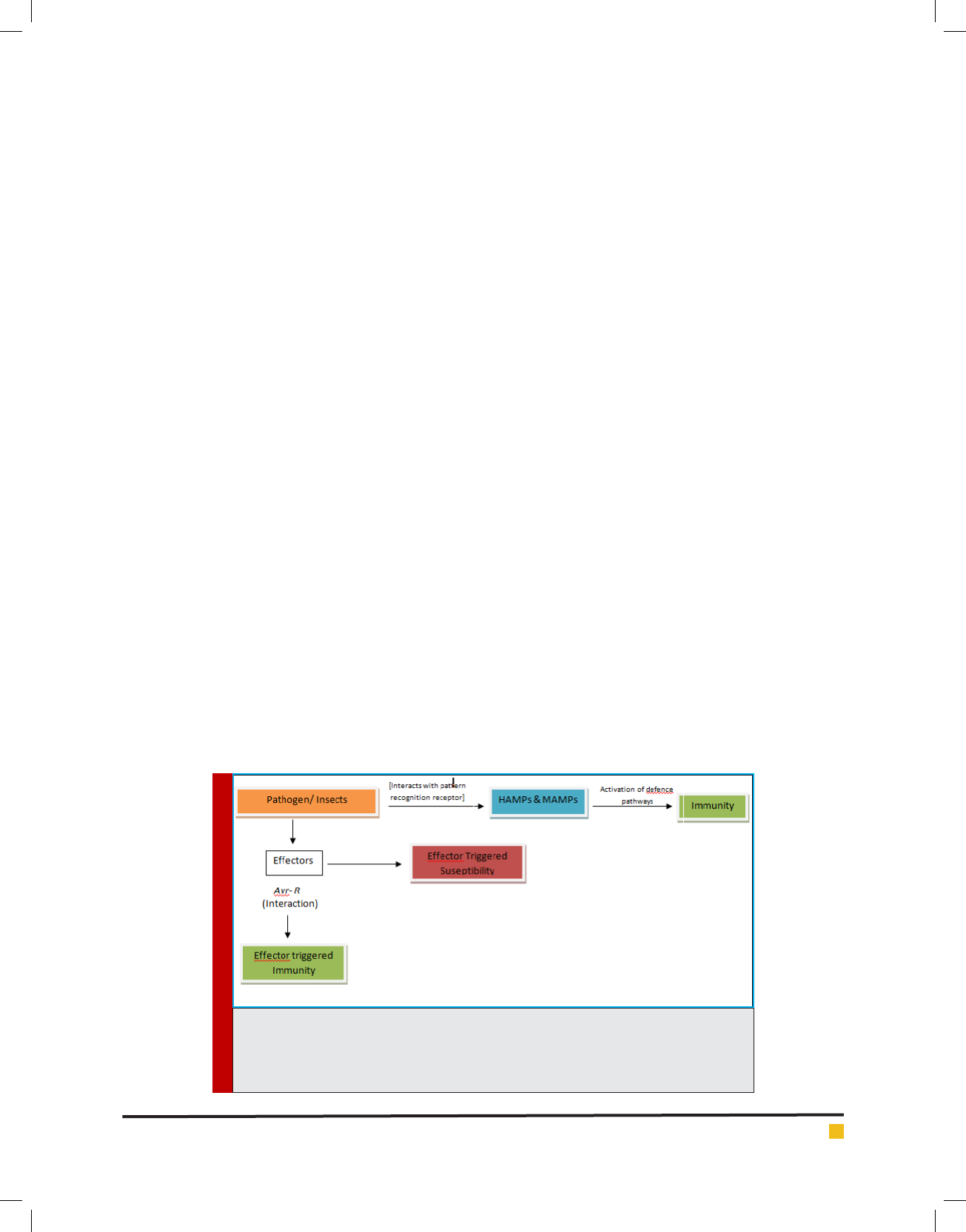
FIGURE 1. Shows pathogen triggered immunity when pathogen/herbivore associated
molecular patterns are recognized by the cell receptors. However in presence of effectors,
pathogens can surpass this immunity. In presence of R gene, effector triggered immunity
induces defence response in plants.

634 MANIPULATING DISEASE AND PEST RESISTANCE PATHWAYS IN PLANTS BIOSCIENCE BIOTECHNOLOGY RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS
Paramita Ghosh et al.
proteins) (Cesari, 2017; Jeffery and Jonathan, 2001; Mari
et al.,2013, Nelson et al., 2017).
Functional R genes conferring resistance against an
array of different biotic factors such as bacteria, virus,
fungus, nematodes and even insect pathogens have
been isolated (Cesari, 2017, Zhao et al., 2005; Vossen
et al., 2005; Reinink et al., 1989; Brotman et al., 2002).
Even though the mode of action as well as the effector
molecules of pathogens and insects are very different, R
genes encode only a few classes of proteins. NBS –LRR
class of proteins are the largest class of R gene which
encodes ‘nucleotide binding site with leucine rich repeat
(Jeffery and Jonathan, 2001). It is reported that NB-LRR
type R genes can confer resistance to multiple pathogens
even though the pathogens belong to taxonomically dis-
tinct families (Mari et al., 2013). It is also termed as MDR
or multiple disease resistance. In a maize recombinant
inbred line (RIL) a QTL, qMdr have been identi ed for
resistance to several diseases i.e, Norther blight, grey leaf
spot and souther leaf blight. The molecular mechanism
underlying the resistance is yet not known. In a research
it is found that a gene, ZmCCoAOMT2, which encodes
a caffeoyl-CoA O-methyltransferase is associated with
conferring quantitative resistance to both southern leaf
blight and gray leaf spot (Yang et al., 2017).
Bacterial effectors are delivered through type III
secretion system, which can be up to 30 per strain, and
by mimicking or inhibiting eukaryotic cellular functions
colonization is achieved (Abramovitch et al. 2006). An
example of a speci c R-gene, Rxo1 from maize con-
ferred resistance to bacterial streak disease caused by
Xanthomonas oryzae pv. Oryzicola(Zhao et al., 2005),
when introduced in rice. In another instance, R gene
RCT1 from Medicago truncatula expressed in alfalfa
conferred resistance to Colletotrichum trifolii (Yang et
al., 2008), RPI-BLB2 from wild potato gave resistance
to Phytophtohora infestans in day to day cultivated
potato (Vossen et al., 2005). Some of the R gene work
in pairs and are functional only when both genes are
present (Mari et al.,2013 ). Some of the examples of such
R gene pairs are RPP2A/RPP2( Sinapidou et al., 2004),
Pi5-1/Pi5-2 ( Lee et al., 2009) and Lr10/RGA2 (Loutre
et al., 2009). Examples in wheat rust, Sr31 from rye was
effective against all Pgt races for many years until the
appearance of Ug99 (Pretoriusetal.,2000).
Many single R genes responsible for resistance against
insects are mapped in cereal crops, including wheat con-
ferring resistance to Hessian y (Hatchet et al., 1970).
For decades, R genes have been used to control Hessian
y infestation in wheat. It is evident in support of gene-
for- gene model in plant- insect interactions.
Some of the insect resistant R genes that are effec-
tive against aphids include: the lettuce Nr gene which
gives resistance against aphid species Nasanova ribis-
nigri (Reinink et al., 1989), the Vat gene from melon
confers resistance against the melon/cotton Aphis gos-
sypii aphid (Brotman et al., 2002), in another instance,
the Sd1 gene gives resistance against Dysaphis devecta
aphid in apples (Walling, 2000; Roche et al. 1996), the
RAP1 gene gives resistance against the Pea Aphid in
Medicago truncatula (Stewart et al., 2009), and the Mi-1
gene in tomatoes (Rossi et al., 1998) found to be responsi-
ble for resistance against different organisms, the potato
aphid Macrosiphum euphorbiae, the root-knot nema-
todes Meloidogyne spp., and the white y Bemisia tabaci
(Nombela et al. 2003). The diverse resistance conferred
by the Mi-1 gene makes it is a very useful tool for inte-
grated pest management. While, Bph14 confers resist-
ance to the rice brown planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens
(Zhang et al., 2009). However, a constitutive expression
of a R gene can have a negative impact in absence of
attackers. Constitutive expression of R gene can be det-
rimental to plants and therefore needs to be expressed
with inducible promoters (Belbahri et al., 2001; Takakura
et al., 2004).
For decades, R genes have been used in conventional
breeding programme (Balconi et al., 2012) ; however, the
resistance is only against a strain of pathogen or a par-
ticular species of insect. Traditional breeding strategies
most often use only one R gene at a time. Pyramiding
multiple R genes can promise a long lasting resistance
as the pathogen has to accumulate mutation in multiple
Avr genes to escape resistance. Effective combinations of
R and APR gene by pyramiding or stacking can be con-
sidered for effective rust resistance (Jeffrey et al., 2014).
However, it is a lengthy process to introduce a R gene
into an elite cultivar by conventional breeding. R-genes
from unrelated plant species can be introduced through
genetic engineering, which often remain functional in
the new host plant (Collinge et al., 2008) . The limitation
of this technology being that resistance is conferred only
against a single pathogen similar to breeding (Balconi
et al., 2012). Additionally, R-gene only confers resist-
ance against pathogens that essentially act as a sink for
the host plant’s metabolism i.e. biotrophs.
Shuf ing of multiple R genes can also be consid-
ered rather than only pyramiding. Plant pathogen Clad-
osporium fulvum elicitors are recognition by Cf genes in
tomato which belongs to the Hcr9 gene clusters (Brande
et al., 2004). Studies have shown that Hcr9s are com-
posed of sequences that have been generated by sequence
exchange between individual homologues, Intra and
intergenic recombination, gene conversion, point muta-
tion, duplication and translocation. Therefore, shuf ing
multiple R genes might increase recognition speci ci-
ties and engineering R gene for novel disease resistance
speci cities in plants can be achieved (Cesar, 2017). For
example, gene shuf ing done in tomato Cf4 and Cf9 R
BIOSCIENCE BIOTECHNOLOGY RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS MANIPULATING DISEASE AND PEST RESISTANCE PATHWAYS IN PLANTS 635
Paramita Ghosh et al.
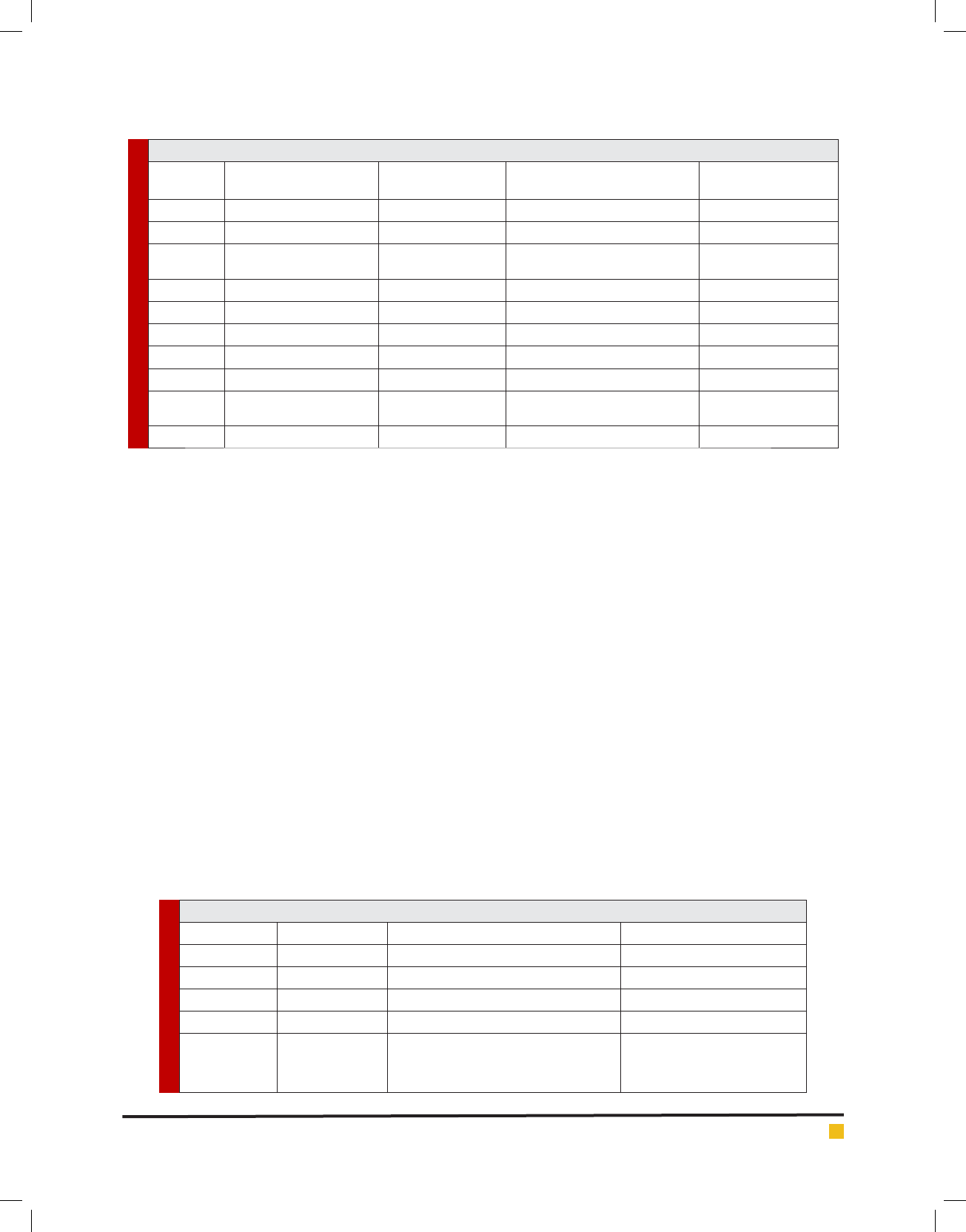
Table I. List of R gene against different pathogens
R gene Source (Donor)
Examples of
transgenic crop
Against Pathogen References
Rox1 Maize Rice Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzicola Zhao et al., 2005
RCT1 Medicago truncatula Alfalfa Colletotrichum trifolii Yang et al., 2008
RPI-BLB2
Potato
(Solanum bulbocastanum)
Potato Phytophtohora infestans Vossen et al., 2005
Bs2 Pepper Tomato Xanthomonas campestris Tai et al., 1999
Rpg1 Barley Barley Stem rust Brueggeman et al., 2002
Ve1 and Ve2 Tomato Potato Verticillium spp. Kawchuk et al., 2001
RRS1-R Arabidopsis Arabidopsis Ralstonia solanacearum Deslandes et al., 2002
Pi-d2 Rice Rice Chinese rice blast Chen et al., 2006
RPW8 Arabidopsis Arabidopsis, tobacco
Broad spectum resistance against
powdery mildew
Xiao et al., 2003
Pto Tomato Tomato Pseudomonas syringae Frederick et al., 1998
Table II. List of R gene against different insects
R gene Source (Donor) Against Insect Reference
Nr gene lettuce Aphid species Nasanova ribisnigri Reinink et al., 1989
melon Vat gene Melon Melon/cotton Aphis gossypii aphid Brotman et al., 2002
Sd1 gene Apple Dysaphis devecta aphid Roche et al., 1996; Walling, 2000
RAP1 gene Pea Pea Aphid in Medicago truncatula Stewart et al., 2009
Mi-1.2 gene Tomato
Potato aphid Macrosiphum euphorbiae, the
root-knot nematodes Meloidogyne spp., and
the white y Bemisia tabaci
Rossi et al., 1998
genes lead to the identi cation of sequences required for
the Avr-dependent HR in tomato (Brande et al., 2001).
SIGNAL TRANSDUCTION NETWORK
Plants can sense changes in their environment through
signaling pathways (Pankaj and Atle, 2013). When
pathogen elicitors interact with host receptors, signal
transduction cascades are likely to be activated includ-
ing oxidative burst (ROS), calcium uxes, ion channel
uxes, NO production (Bollwell et al., 1999) and vari-
ous protein kinases. Subsequently, transcriptional and/
or post transcriptional activation of transcription factors
takes place which lead to the induction of defence gene.
Plant hormones which play important role in defence
are SA, JA and ET. SA is primarily involved in the pro-
tective response against biotrophic and hemi-biotrophic
pathogens and systemic acquired resistance (SAR) (Grant
and lamb, 2006). Some mutants insensitive to SA shows
enhanced susceptibility to biotrophic pathogens. Methyl
salicylate is a mobile inducer of SAR and is induced
when the plant is infected with a pathogen in tobacco
plants (Park et al., 2007). After pathogen challenge the
elevated level of SA increases the expression of PR
genes, therefore increasing resistance. Whereas the level
of JA and ET are elevated against necrotrophic pathogen
and herbivorous insects (Park et al., 2007).
Most often the SA and JA/ET defence pathways are
antagonistic, however reports of synergistic interaction
also exist (Kunkel and Brooks, 2002; Mur et al., 2006;
Schenk et al., 2000) . Speci c biotic factors regulate the
positive or negative cross talk between SA and JA/ET
pathways (Adie et al., 2007). In nature it is not one factor
that affects the plant but several attackers, here plants
have to employ complex regulatory mechanisms to cope
with the complex situation. The mechanism by which
plant is able to prioritize the responses is not known.
Non expressor of PR genes 1 (NPR1) is one of the
important components of SA signaling. NPR1 plays
an important role in SA-JA interaction (Dong, 2004).
Downstream of NPR1 are several WRKY transcription
factors which is also important is SA-dependent defence
response. WRKY70 maintains the balance between the
SA and JA pathways (Li et al., 2004; Li et al., 2006).
Another key component which is involved in mediating
the antagonism between SA and JA signaling in Arabi-

636 MANIPULATING DISEASE AND PEST RESISTANCE PATHWAYS IN PLANTS BIOSCIENCE BIOTECHNOLOGY RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS
Paramita Ghosh et al.
dopsis is mitogen activated protein kinases (Petersen
et al., 2000). In the second generation strategies, these
signaling nodes will be discussed. The goal of effective
and sustainable disease resistance can be achieved by
the knowledge of signal transduction pathways (David
et al., 2010), as the increased understanding has made
it clear that successful pathogen process through patho-
genicity factors (effectors). The disease resistance gene
are mostly downstream genes and often do not act as
speci c receptors produced by pathogens and insects.
A complex signaling network is also established when
herbivorous insects attack a plant. To identify new mol-
ecules important for ne tuning of plant defence signal-
ing, there is a need of dynamic modeling and simula-
tion of signal transduction pathways (Beckers and Spoel,
2006; Erb et al., 2009).
Various plant protectant and defence gene are acti-
vated by the primary and secondary signals. The defence
gene products include glutathione S-transferases, per-
oxidases, cell wall proteins, proteinase inhibitors, hydro-
lytic enzymes (e.g., -1,3-glucanases and chitinases),
pathogenesis-related PR proteins (Balconi et al., 2012).
PR proteins
Other potential candidates for manipulation are patho-
genesis related (PR) genes, which shows promising activ-
ities against biotic factors i.e. pathogens as well as insect
pests. Pathogenesis related (PR) genes could increase the
level of pre-existing barriers (Owen and Zamir, 2010;
Hammond-Kosack and Parker, 2003). Naturally occur-
ring PR proteins are constitutively expressed at low lev-
els and are induced to high levels challenged by patho-
gens or application of either salicylic acid or jasmonic
acid (Ferreira et al., 2007) . PR proteins include several
groups of unrelated proteins. Seventeen classes of PR
protein have been examined, and numbered chronologi-
cally in order of discovery i.e. PR-1 to PR-17 (Balconi
et al., 2012). PR-2 ( b -1,3-glucanases), PR-3, -4, -8 and
-11 (chitinases) target the pathogen cell wall (Owen and
Zamir, 2010; Honee, 1999), PR-1 and PR-5 (thaumatin-
like proteins and osmotins) are termed as permatins as
they target the membrane, PR-10 has weak ribonuclease
activity therefore may target pathogen RNA or play a
role in defence against viruses, PR-6 proteins (protein-
ase inhibitors) may target nematodes, whereas the PR-7
protein (an endoproteinase) may be involved in micro-
bial cell wall dissolution (Jorda et al., 2000) . The PR-9
family may enhance resistance to multiple pathogens by
catalyzing ligni cations which helps in cell wall rein-
forcement (Passardi et al., 2004). Since PR-10 family has
weak ribonuclease activity it can be used against viruses
(Park et al., 2004), PR-12 (defensins), PR-13 (thionins)
and PR-14 (lipid transfer proteins) predicts antibacte-
rial and antifungal activities (Epple et al., 1997) , some
proteins generating hydrogen peroxide and are toxic to
pathogen and pest, PR-15 (oxalate oxidases) and PR-16
(oxalate oxidase-like proteins) belongs to this family
(Hu et al., 2003). PR-17 (uncharacterized) is detected in
infected tobacco, wheat and barley (Christensen et al.,
2002).
Most investigated PR proteins are chitinases and 1–3
glucanases (Owen and Zamir, 2010). Over-expression of
chitinase have been moderately successful against fun-
gal pathogens. Studies have found chitinase have role
in insect resistance as well. The combined expression of
chitinases and 1–3 glucanases have proven to enhance
resistance by synergistic effect (Anand et al., 2003; Jach
et al., 1995; Jongedijk et al., 1995; Zhu et al., 1994).
Chitinases originating from Trichoderma harzianum
(biocontrol agent), exhibit higher anti-fungal activity
(Dana et al., 2006; Baranski et al., 2008; Kumar et al.,
2009). Ectopic expression of thionins and defensins has
conferred broad spectrum disease resistance, though the
resistance is at low level (Punja, 2001). For example rad-
ish defensin RS-AFP2 (Kostov et al., 2009) when over-
expressed in tomato resulted in up to 90% reduction
in disease against agriculturally important pathogens.
Lipid transfer proteins (LTP) are one of the important
PR proteins which act as a potential mobile signal for
systemic acquired resistance (SAR) in plants (Maldonado
et al., 2002). LTP activates SAR over-expression of LTP
might result in deleterious effect (Walters, 2007) , so far
no such effect is observed. A highly inducible promoter
can be used to over-express this gene in order to achieve
the goal of disease resistance.
The plant defensive metabolites are termed as second-
ary metabolites play an important rolein plant defense
against herbivore and other interspecies defense, thus
increasing the tness of the plant. They can be either
constitutively stored (phytoanticipins) as inactive forms
or induced in response to the insect or microbe attack
(phytoalexins)(King et al., 2014). Herbivore induced plant
volatiles (HIPVs) play very important role in defense by
either attracting the natural enemies of the herbivores
or by acting as feeding and/or oviposition deterrent
(Rashid and Chung, 2017). HIPV are released by healthy
plants as well, however a different blend of volatiles is
produced in response to herbivory and is very speci c
for a particular insect-plant system (Liu et al., 2012). For
example, plants tend to release volatile compounds in
response to aphid –attack to attract parasitoid wasps.
In corn, plants release terpenoids in response to aphid
attack. Many other volatile compounds like MeSa, C
6
volatiles etc in uence plant-insect, pest and pathogen
interaction.
Metabolite engineering can play an important role
in developing plant with insect resistance. Increas-
ing the ux of defence related secondary metabolites

BIOSCIENCE BIOTECHNOLOGY RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS MANIPULATING DISEASE AND PEST RESISTANCE PATHWAYS IN PLANTS 637
Paramita Ghosh et al.
by engineering the respective pathways can be of great
importance in developing crops with insect resistance
(Sanchez -Vallet et al., 2013). There are some reports of
metabolic engineering of dhurrin, a cyanogenic glyco-
side in transgenic A. thaliana plants which, resulted in
minor effects on the whole metabolome and transcrip-
tome (Dudareva et al., 2013 ). Resistance to green peach
aphid (Myzus persicae) feeding have been enhanced by
metabolic engineering of raf nose in the phloem of A.
thaliana (Jirschitzka et al., 2013). In another instance,
manipulation of plant volatile emissions has enhanced
the effectiveness of biological control agents. This can
be used as a strategy to ght insect pests in an ecologi-
cally sound manner (Degenhardt et al., 2009).
SECOND GENERATION STRATEGIES
Master switch genes
Over-expression of a single defence-related gene is gen-
erally unable to provide high levels of resistance against
a broad range of biotic factors like pathogen and her-
bivores. The knowledge of pathogen-induced signal-
ing pathways in plants suggests that modi cations of
existing innate signaling pathways or expression of
‘masterswitch’ genes such as kinases and transcription
factors (Owen and Zamir, 2010; Hammond-Kosack and
Parker, 2003; Sarah and Paul 2005), which regulate a
large number of defence genes could increase resistance
against biotic factors (Owen and Zamir, 2010; Sarah
and Paul 2005). The disadvantage encountered by this
approach could be the harmful effect on plant develop-
ment, due to potential yield loss which is common with
over-expression of large number of genes at a time con-
stitutively (Owen and Zamir, 2010). Therefore, the ideal
candidates are the genes that activate partial pathways
or augment pathways.
Transcription Factors
Transcriptome and QTL data analysis suggested tran-
scription factors to be promising candidates for genetic
engineering to increase disease resistance characteristics
in plants (Sarah and Paul 2005) . They might behave as
master switch gene by taking care of the expression of
several genes in a single pathway. Therefore capable of
making large changes in single trait causing very few
disturbance on other traits (Doebley and Lukens, 1998).
A good example is WRKY transcription factors (Owen
and Zamir, 2010; Sarah and Paul 2005).
WRKY transcription factors are involved in SA- medi-
ated defence pathways. Several WRKYs have the poten-
tial for increasing disease resistance, among them the
most studied are WRKY70 from Arabidopsis [50].Sev-
eral other transcription factor families that have roles
in plant defence could yield useful master switch genes
like WRKY, ERF, TGA, MYB, Dof, GRAS, bHLH, GT1 and
the Whirly factor Why1(Desvaux et al., 2004). The only
limitation being, transcription factors mostly consist of
large multigene families and identifying the best candi-
date can be dif cult due to the functional redundancy
(Eulgem et al., 2000). However, several of Arabidop-
sis WRKY has been identi ed have good functionality
against pathogens (Sarah and Paul 2005).
MAP Kinase
Potential candidate master –switch genes which also
play vital roles under different stress are protein kinases
(Sarah and Paul 2005) . MAP kinase (MAPK) signaling is
a necessarypart of many defence-signalling pathways.
When tobacco MAPK, SIPK is over-expressed it led to
activation of defence responses and HR-like cell death
showing the potential role of these genes (Zhang and
Liu, 2001) . Enhanced resistance to virulent P. syringae
and Botrytis cinerea was observed when MKK4a, MKK5a
were over expressed transiently and MEKK1 was acti-
vated constitutively (Asai et al., 2002) . Other potential
protein kinases are calcium dependent sensor proteins
that changes Ca
2+
defence response (Romeis et al., 2001)
. In response to herbivore-induced cues such as insect
oral secretions (OS) and oviposition uid compounds,
plants undergo a change in transcriptomes, proteomes,
and metabolomes. The major components of the oral
secretion of insects are fatty acid-amino acid conju-
gates (FACs) which activate the mitogen-activated pro-
tein kinase (MAPK) pathway. The MAPK pathway not
only play an important role in signaling transduction
in responses to a number of stresses including cold,
heat, ROS, UV, drought, pathogen and insect attack but
also regulate plant growth and development (Wu et al.,
2007). On application of FACs in oral secretion of M.
sexta leads to activation of several compounds/mol-
ecules of MAPKs, salicylic acid induced protein kinase
(SIPK) and wound-induced protein kinase (WIPK), JA,
SA and ethylene. In another case brown plant hopper N.
lugens induces expression of putative OmMKKI (MAPK).
Several FAC elicitors have been isolated from various
lepidopteran species (Wu et al., 2007; von Dahl et al.,
2007) .
NPR1
One of the most promising candidates of second gen-
eration strategy is NPR1 (Cao et al., 1994). Pathogen or
insect pest resistance can be achieved through signaling
modi cation. The Npr1 gene was discovered originally
from various independent genetic screens. The Arabi-
dopsis mutants npr‐1 do not respond to inducers of sys-
temic acquired resistance (SAR) such as salicylic acid
(Cao et al., 1994; Delaney et al., 1995; Shah et al., 1997)
638 MANIPULATING DISEASE AND PEST RESISTANCE PATHWAYS IN PLANTS BIOSCIENCE BIOTECHNOLOGY RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS
Paramita Ghosh et al.
or lost the ability to accumulate PR transcripts and were
also hypersensitive to biotrophic pathogens (Pieterse et
al., 2004). NPR1 acts as a switch between the signal-
ing pathways involving ethylene/jasmonic acid (ET/JA)
(ISR) and salicylic pathway (SAR), therefore resistance
to both necrotrophic and biotrophic pathogens depends
on modulation of NPR1 gene (Li et al., 2004; Cao et
al., 1994; Pieterse et al., 2004) . NPR1 is the key master
switch as it constitutes a node which links SAR, ISR, SA,
JA, ethylene, and also R gene-mediated resistance (Piet-
erse et al., 2004). The activation of NPR1 gene is through
redox pathways by SA accumulation in the cytosol and
then translocated to the nucleus, however without bind-
ing to DNA directly it acts through transcription factors,
which in turn induces expression of several PR genes
(Pieterse et al., 2004). NPR1 is constitutively expressed
at low levels, when challenged by pathogen or treated
with SA, transcript accumulation increases up to two-
fold. SA gives better defence against piercing and suck-
ing insect pests than the chewing pests (Zhao et al.,
2009).
SA-mediated expression of proteins by NPR1 include
the WRK70 transcription factors this lead to suppres-
sion of JA-dependent signaling events (Li et al., 2004;
Ndamukong et al., 2007). However, nuclear localization
of NPR1is not required for direct regulation of JA-path-
ways which indicates a dual function between the cyto-
solic and nuclear located NPR1 (Glazebrook et al., 2003;
Spoe et al., 2003; Yuan et al., 2007).
As both SA and JA dependant pathways are controlled
by NPR1, it can be targeted to achieve broad spectrum
disease resistance through genetic engineering. There
are several instances where over-expression of NPR1
has resulted in resistance against both biotrophic (Cao
et al., 1994; Lin et al., 2004). Necrotrophic (Lin et al.,
2004; Makandar et al., 2006; Wally et al., 2009) patho-
gen in several plant species as well as against insect pest
in tobacco plants. Over-expression of NPR1 resulted in
quicker and higher intensity of PR proteins for longer
duration. The function of NPR1 remained unchange
when AtNPR1 was expressed in different crop like rice
(Fitzgerald et al., 2004) , wheat (Makandar et al., 2006),
carrot (Wally et al., 2009) tobacco ( Meur et al., 2008)
and tomato (Lin et al., 2004) indicating the conserved
functionality of the signaling system as well as the
NPR1 like proteins.
However, when AtNPR1 or the rice ortholog OsNH1
was expressed in transgenic rice, the constitutive expres-
sion of PR genes lead to stunted growth of plants and
more light sensitivity apart from desired increase in dis-
ease resistance (Chern et al., 2005). Green tissue speci c
expression of AtNPR1 in rice reduced such developmen-
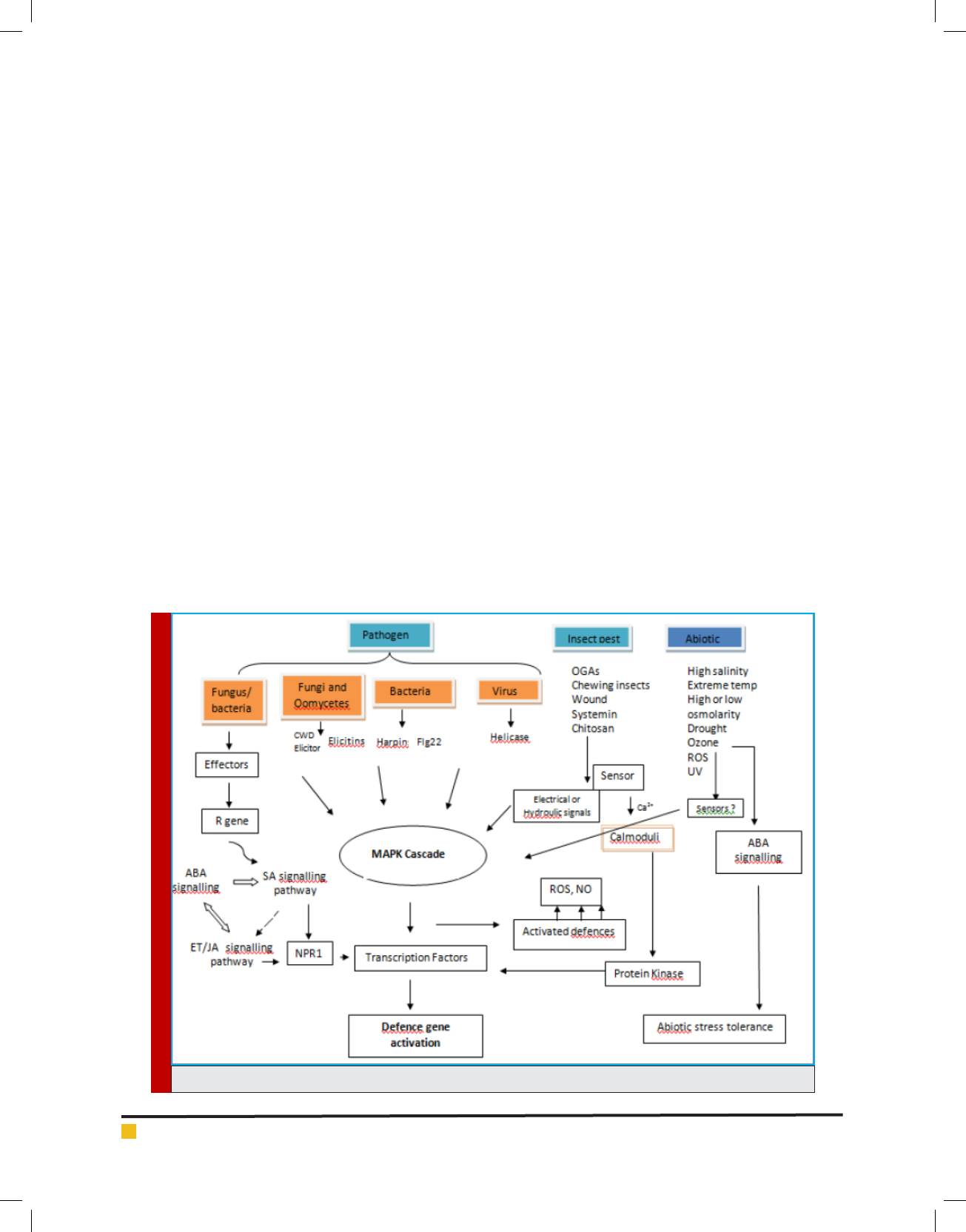
FIGURE 2. A summary of role of MAPK, NPR1 and transcription factors in plant defence.

BIOSCIENCE BIOTECHNOLOGY RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS MANIPULATING DISEASE AND PEST RESISTANCE PATHWAYS IN PLANTS 639
Paramita Ghosh et al.
tal abnormalities and conferred resistance to the sheath
blight pathogen without compromising the growth and
yield parameters (Molla et al., 2016)
MANIPULATION THE EXPRESSION OF
TARGET GENES
Expressing Avr protein
De Wit (1992) proposed an interesting exploitation of R
gene response, where a plant can be designed to express
an active Avr protein under the control of a pathogen-
responsive promoter for which the plant has a R gene.
The induced Avr product would induce responses which
would result in incompatible reaction to a wide range of
pathogens (Dewit, 1992). The pathogen inducible pro-
moter (hsr203J) in tobacco resulted in successful exploi-
tation of HR elicitor cryptogein (Keller et al., 1999). The
main bene t is resistance against a wide range of patho-
gens. However the real value of this strategy is yet to be
exploited.
Synthetic modi cations of PR proteins
To enhance the effectiveness of PR proteins, synthetic
modi cations such as linking a single chain antibody
gene against a particular pathogen can be done (Peschen
et al., 2004). The antibodies would then attach to the
invading pathogen’s cell wall and the antimicrobial pro-
teins would effectively degrade the fungi. It has been
demonstrated against Fusarium graminearum. It was
highly effective against nine different species of the
Fusarium genus, in Arabidopsis, however, not effective
against unrelated pathogens (Peschen et al., 2004). This
method has been also implemented in transgenic wheat,
which reduced the disease symptoms against Fusarium
head blight (Li et al., 2008).
Toxic gene products to engineer local cell death
One of the rst strategies applied for increased dis-
ease resistance in plants was generation of an ‘HR-like’
local cell death arti cially by expressing a toxic gene
(Li et al., 2008). This strategy is only successful when
‘HR’ is restricted to infection sites otherwise uncon-
trolled cell death will occur even in uninfected tissues
which is undesirable. Components of the pathogen can
be expressed as toxic genes. But the promoters used so
far have undesired background expression in uninfected
tissues. Moreover, the toxicity level of the gene product
needs to be studied well before the product is marketed.
RNAi
A useful tool inhibiting pathogen expression is through
RNAi (Csorba and Burgyan, 2016; Novina and Sharp,
2004) technology. It inhibits the expression at both the
transcriptional and post transcriptional levels in plants.
RNAi has been exploited to develop many virus resist-
ant plants (Fuentes et al.,2016). For example, papaya
ringspot virus (PRSV) coat protein protected papaya in
Hawaii has already been commercialized.
Stacking antimicrobial compounds
Expressing antimicrobial proteins, phytoalexins and
enzymes in plant cell reinforcement or in the breakdown
of pathogen infection structures has also been tried. The
limitation of this strategy is resistance towards a speci c
pathogen. However to broaden the spectrum of resist-
ance, stacking of antimicrobial peptides could be a rea-
sonable approach (Van der Biezen, 2001).
Targeting inducible promoters
With the signi cant advances in sequencing technolo-
gies for transcriptome analysis, number of important
crop genomes have been sequenced, which make it fea-
sible for high throughput recognition of promoters and
putative cis elements. Cis regulatory elements function
as molecular switches in respose to various stress signals
(Kazuko and Kazuo, 2005). Transcription factors inter-
act with cis acting elements in the promoter region and
forms a complex to initiate transcription thus can help
in formation of initiation complex when activated and
act as molecular switches to determine transcription ini-
tiation events. Therefore, it is important to determine the
elements in the stress responsive promoters to under-
stand the molecular switches of stress inducible genes.
Apart from this, plant pathogen molecular interaction
has shown that the promoter region also plays an impor-
tant role in pathogen recognition (Patrick et al., 2009) .
In gene for gene interaction pathogen effector interacts
with the promoter region for activation of R gene. For
example, some bacterial effectors like TAL effectors Avr
BS3 and AVR Xa27 interact with the promoter region
and activate the corresponding R genes (Patrick et al.,
2009).
The current limitation of development of resistant
transgenic crops using genetic transformation is una-
vailability of the right kind of promoter. Strong syn-
thetic inducible promoters can be designed to address
the issue of biotic stress. Promoters can be designed to
not only recognize speci c predators but also effector
molecules from different pathogen and pests, thus giv-
ing a broad spectrum resistance against several biotic
factors. It is also possible to use bidirectional promoters
to activate two genes at the same time.
CONCLUSION
Durable pest and disease resistance so far has been
achieved by traditional breeding and chemical appli-
cations. However, conventional breeding has prioritize

640 MANIPULATING DISEASE AND PEST RESISTANCE PATHWAYS IN PLANTS BIOSCIENCE BIOTECHNOLOGY RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS
Paramita Ghosh et al.
quality parameters and agronomic adaptation over
resistant breeding. Therefore, new improved genomic
tools are required to empower the process of genetic
analysis and crop improvement. High through put
sequencing and complete genome sequencing of many
crops allows understanding of many metabolic path-
ways and disease resistance mechanisms. Understanding
of omics are shedding light on the different compounds
associated with plant defense. Using new technologies,
it might be possible to achieve more durable and long
term resistance through various genetic approaches.
The wide spread application of pesticides can also be
reduced through this technology. There are several suc-
cess stories of plant genetic engineering which include
herbicide resistant for weed control and insect resistance
for lepidopteran insect control. However, transgenic dis-
ease resistance crop and resistance against sap suck-
ing insects represent a very small portion of transgenic
crops. Also the scope is wide with the advancement of
genome editing tools like CRISPR-Cas9 and new digital
phenotyping technologies, to develop a more sustain-
able agriculture that involves adaptation to changing
climates. The global food demand needs to be ful lled
and therefore, it is the need of the hour to combat yield
losses caused by diseases and sap sucking insect pests
on a global scale. Also, an increased and stable yield is
required to address decreasing land availability issues.
Engineering disease resistance with new tools available
needs to be made a priority.
REFERENCES
Abdul Rashid War, Michael Gabriel Paulraj,Tariq Ahmad,Abdul
Ahad Buhroo, Barkat Hussain, Savarimuthu Ignacimuthu,
andHari Chand Sharma (2012) Mechanisms of plant defence
against insect herbivores. Plant signaling and Behavior 7:10,
1306-1320.
Abramovitch, R. B., Anderson, J. C., & Martin, G. B. (2006)
Bacterial elicitation and evasion of plant innate immunity.
Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology, 7(8):601-611.
Adie BA,Pérez-Pérez J,Pérez-Pérez MM,Godoy M,Sánchez-
Serrano JJ,Schmelz EA,Solano R. (2007) ABA is an essential
signal plant resistance to pathogens affecting JA biosynthe-
sis and the activation of defence in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell
19:1665-1681.
Anand A, Zhou T, Trick HN, Gill BS, Bockus WW, Muth-
ukrishnan S. (2003) Greenhouse and eld testing of transgenic
wheat plants stably expressing genes for thaumatin-like pro-
tein, chitinase and glucanase against Fusarium graminearum.
Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology 54:1101-11.
Asai T,Tena G,Plotnikova J,Willmann MR,Chiu WL,Gomez-
Gomez L,Boller T,Ausubel FM,Sheen J. (2002) MAP kinase
signalling cascade in Arabidopsis innate immunity. Nature
415:977–983.
Baranski R, Klocke E, Nothnagel T. (2008) Chitinase CHIT36
from Trichoderma harzianum enhances resistance of trans-
genic carrot to fungal pathogens. Journal of Phytopathology
2008; 156:513-21.
Beckers GJM, Spoel SH. (2006) Fine-tuning plant defence sig-
nalling: salicylate versus jasmonate. Plant Biology 8:1–10.
Belbahri L, Boucher C, Candresse T, Nicole M, Ricci P, Keller
H. (2001) A local accumulation of the Ralstonia solanacearum
PopA protein in transgenic tobacco renders a compatible
plant-pathogen interaction incompatible. The Plant Journal
28:419-30.
Bollwell, G.P. (1999) Role of active oxygen species and NO in
plant defence. Current Opinion in Plant Biology 2:287–294.
Brande B.H. Wulff, Marco Kruijt, Peter L. Collins, Colwyn M.
Thomas, Andrea A. Ludwig, Pierre J.G.M. De Wit and Jonathan
D.G. Jones (2004) Gene shuf ing-generated and natural vari-
ants of the tomato resistance gene Cf-9 exhibit different auto-
necrosis-inducing activities in Nicotiana species. The Plant
Journal 40: 942–956.
Brande B. H. Wulff, Colwyn M. Thomas, Matthew Smoker, Mur-
ray Grant,and Jonathan D. G. Jones (2001) Domain Swapping
and Gene Shuf ing Identify Sequences Required for Induction
of an Avr-Dependent Hypersensitive Response by the Tomato
Cf-4 and Cf-9 Proteins. The Plant Cell 13:255–272.
Brotman Y, Silberstein L, Kovalski I, Périnin C, Dogimont C,
Pitrat M, ,Klingler J,Thompson A,Perl-Treves R. (2002) Resist-
ance gene homologues in melon are linked to genetic loci con-
ferring disease and pest resistance. Theoretical and Applied
Genetics 104(6-7):1055-1063.
Campbell, M.A. Matthew A. Campbell, Heather A. Fitzger-
ald,PamelaC.Ronald. (2002) Engineering pathogen resistance
in crop plants. Transgenic Research 11:599–613.
Cao H, Bowling SA, Gordon AS, Dong XN. (1994) Charac-
terization of an Arabidopsis mutant that is nonresponsive to
inducers of systemic acquired-resistance. Plant Cell 6:1583-92.
Carlotta Balconi , Piergiorgio Stevanato , Mario Motto and
Enrico Biancardi. (2012) Breeding for biotic stress resistance /
tolerance in plants. Crop Production for Agricultural Improve-
ment pp 57-114.
Cesari S. (2017) Multiple strategies for pathogen perception by
plant immune receptors. New Phytologist nph.14877
Chern M, Fitzgerald HA, Canlas PE, Navarre DA, Ronald PC.
(2005) Overexpression of a rice NPR1 homolog leads to con-
stitutive activation of defence response and hypersensitivity to
light. Molecular Plant-Microbe Interactions 18:511-20.
Christensen A, Ho Cho B, Naesby M, Gregersen PL, Brandt
J, Madriz-Ordeñana K, Collinge DB, Thordal-Christenen H.
(2002) The molecular characterization of two barley proteins
establishes the novel PR-17 family of pathogenesis-related
proteins. Molecular Plant Pathology 3:135–144.
Collinge DB, Lund OS, Thordal-Christensen H. (2008) What
are the prospects for genetically engineered, disease resistant
plants? European Journal of Plant Pathology 121:217-31.

BIOSCIENCE BIOTECHNOLOGY RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS MANIPULATING DISEASE AND PEST RESISTANCE PATHWAYS IN PLANTS 641
Paramita Ghosh et al.
Csorba T. and Burgyan J, (2016) Antiviral Silencing and Sup-
pression of Gene Silencing in Plants. Springer International
Publishing Switzerland.
Dana MD, Pintor-Toro JA, Cubero B. (2006) Transgenic
tobacco plants overexpressing chitinases of fungal origin show
enhanced resistance to biotic and abiotic stress agents. Plant
Physiology 142:722-30.
David B. Collinge, Hans J.L. Jørgensen, Ole S. Lund, and
Michael F. Lyngkjær (2010) Engineering Pathogen Resistance
in Crop Plants: Current Trends and Future Prospects. Annual
Review of Phytopathology 48:269-91.
Davis EL,Hussey RS,Baum TJ (2004) Getting to the roots of
parasitism by nematodes. Trends in Parasitology 20(3):134-41.
Degenhardt J, Hiltpold I, Kollner TG, Frey M, Gierl A, Gershen-
zon J, Hibba BE, Ellersieck MR, Turlings TCJ. (2009) Restoring
a maize root signal that attracts insect-killing nematodes to
control a major pest. Proceedings of the National Academy of
Sciences, USA 106:13213-13218.
Delaney TP, Friedrich L, Ryals JA. (1995) Arabidopsis signal‐
transduction mutant defective in chemically and biologically
induced disease resistance. Proceedings of the National Acad-
emy of Sciences USA 92:6602‐6606.
Desveaux D, Subramaniam R,Després C, Mess JN,Lévesque
C, Fobert PR, Dangl JL, Brisson N. (2004) A “Whirly” tran-
scription factor is required for salicylic acid-dependent dis-
ease resistance in Arabidopsis. Developmental Cell 6(2):229–
240.
Doebley J. and Lukens L (1998) Transcriptional regulators and
the evolution of plant form. Plant Cell 10:1075–1082.
De Wit PJGM. (1992) Molecular characterization of gene-for-
gene systems in plant-fungus interactions and the application
of avirulence genes in control of plant-pathogens. Annual
Review of Phytopathology30:391-418.
Dong X. (2004) NPR1, all things considered. Current Opinion
in Plant Biology 7:547-552.
Du B, Zhang W, Liu B, Hu J, Wei Z, He R, Zhu L, Chen R,
Han B and He G
. (2009) Identi cation and characterization of
Bph14, a gene conferring resistance to brown planthopper in
rice. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences USA,
106:22163-22168.
Dudareva N, Klempien A, Muhlemann JK, Kaplan I. (2013) Bio-
synthesis, function and metabolic engineering of plant volatile
organic compounds. New Phytologist 198:16-32.
Epple P, Apel K, Bohlamann H. (1997) Overexpression of an
endogenous thionin enhances resitance of Arabidopsis against
Fusarium oxysporum . Plant Cell 9:509–520.
Erb M, Flors V, Karlen D, de Lange E, Planchamp C,
D’Alessandro M, Turlings TCJ, Ton J. (2009) Signal signature of
aboveground-induced resistance upon belowground herbivory
in maize. The Plant Journal 59:292–302.
Eulgem, T.E, Rushton PJ, Robatzek S,Somssich IE. (2000) The
WRKY superfamily of plant transcription factors. Trends Plant
Science 5:199–206.
Ferreira RB, Monteiro S, Freitas R, Santos CN, Chen Z, Batista
LM, Duarte J,Borges A,Teixeira AR. (2007) The role of plant
defence proteins in fungal pathogenesis. Molecular Plant
Pathology 8:677-700.
Fitzgerald HA, Chern MS, Navarre R, Ronald PC. (2004) Over-
expression of (At)NPR1 in rice leads to a BTH-and environ-
ment-induced lesion-mimic/cell death phenotype. Molecular
Plant-Microbe Interactions 17:140-51.
Freeman and G.A Beattie. (2008) An overview of plant defences
against pathogen and herbivores. The Plant Health Instructor.
DOI:10.1094/PHI-I-2008-0226-01.
Fuentes A,Carlos N,Ruiz Y,Callard D,Sánchez Y,Ochagavía
ME,Seguin J,Malpica-López N,Hohn T,Lecca MR,Pérez R,Dor-
este V,Rehrauer H, Farinelli L, Pujol M, Pooggin MM (2016)
Field Trial and Molecular Characterization of RNAiTrans-
genic Tomato Plants That ExhibitResistance to Tomato Yel-
low Leaf Curl Geminivirus. Mol Plant Microbe Interact
29(3):197-209.
Glazebrook J, Chen WJ, Estes B, Chang HS, Nawrath C, Metraux
JP, Zhu T,Katagiri F. (2003) Topology of the network integrat-
ing salicylate and jasmonate signal transduction derived from
global expression phenotyping. Plant Journal 34:217-28.
Grant M and Lamb C (2006) Systemic immunity. Current Opin-
ion in Plant Biology 9:414-420.
Hammond-Kosack, K.E. and Parker, J.E. (2003) Deciphering
plantpathogen communication: fresh perspectives for molec-
ular resistance breeding. Current Opinion in Biotechnology
14:177–193.
Hanley ME, Lamont BB, Fairbanks MM, Rafferty CM. (2007)
Plant structural traits and their role in antiherbivore defence.
Perspec. Plant Ecol Evol Syst 8:157-78.
29. Hatchet JH, Gallun RL (1970) Genetics of ability of Hessian
y, Mayetiola-Destructor Diptera –Cecidomyiidae to survive
on wheats having genes for resiatnce. Annals of the Entomo-
logical Society of America 63:1400-1407.
Honee G (1999) Engineered resistance against fungal plant
pathogens. European Journal of Plant Pathology 105:319–326.
Hu X, Bidney DL, Yalpani N, Duvick JP, Crasta O, Folkerts O,
Lu G. (2003) Over expression of a gene encoding hydrogen
peroxide-generating oxalate oxidase evokes defence responses
in sun ower. Plant Physiology 133:170–181.
http://www.nap.edu/read/2116/chapter/5
Jach G, Gornhardt B, Mundy J, Logemann J, Pinsdorf E, Leah
R, Schel J, Maas C. (1995) Enhanced quantitative resistance
against fungal disease by combinatorial expression of differ-
ent barley antifungal proteins in transgenic tobacco. The Plant
Journnal 1995; 8:97-109.
.Jeffrey G. Ellis, Evans S. Lagudah, Wolfgang Spielmeyer and
Peter N. Dodds (2014) Thepast,presentandfutureofbreedingrustr
esistantwheat. Frontiers in plant science vol5, article 641.
Jeffery L. DangI and Jonathan D.G. Jones (2001) Plant patho-
gens and integrated defence responses to infection. Nature Vol
411.

642 MANIPULATING DISEASE AND PEST RESISTANCE PATHWAYS IN PLANTS BIOSCIENCE BIOTECHNOLOGY RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS
Paramita Ghosh et al.
Jirschitzka J, Mattern DJ, Gershenzon J, D’Auria JC. (2013)
Learning from nature: new approaches to the metabolic engi-
neering of plant defense pathways. Current Opinion in Bio-
technology 24, 320-328.
Jongedijk E, Tigelaar H, Vanroekel JSC, Bresvloemans SA, Dek-
ker I, Vandenelzen PJM, Cornelissen BJC, Melchers LS. (1995)
Synergistic activity of chitinases and beta-1,3-Glucanases
enhances fungal resistance in transgenic tomato plants.
Euphytica 85:173-80.
Jordá L, Conejero V, Vera P (2000) Characterization of P69E
and P69F , two differentially regulated genes encoding new
members of the subtilisin-like proteinasi family from tomato
plants. Plant Physiology 122:67–74.
Kazuko Yamaguchi-Shinozaki and Kazuo Shinozaki (2005)
Organization of cis-acting regulatory elemens in osmotic and
cold -stress-responsive promoters. Trends in plant science. Vol.
10 No.2.
Keller H, Pamboukdjian N, Ponchet M, Poupet A, Delon R, Ver-
rier JL, et al. (1999) Pathogen-induced elicitin production in
transgenic tobacco generates a hypersensitive response and
nonspeci c disease resistance. Plant Cell 11:223-35.
King SRF, McLellan H, Boevink BC, Armstrong MR, Bukharova
T, Sukarta O, Win J, Kamoun S, Birch PRJ, Ban eld MJ. (2014)
Phytophtora infestans RXLR effector PexRD2 interacts with
host MAPKKKe to suppress plant immune signaling. Plant
Cell.113.120055.
Kostov K, Christova P, Slavov S, Batchvarova R. (2009) Consti-
tutive expression of a radish defensin gene Rs-Afp2 in tomato
increases the resisstance to fungal pathogens. Biotechnology &
Biotechnological Equipment 23:1121-5.
Kumar V, Parkhi V, Kenerley CM, Rathore KS. (2009) Defence-
related gene expression and enzyme activities in transgenic
cotton plants expressing an endochitinase gene from Tricho-
derma virens in response to interaction with Rhizoctonia
solani. Planta 230:277-91.
Kunkel BN, Brooks DM. (2002) Cross talk between signaling
pathways in pathogen defence. Current Opinion in Plant Biol-
ogy 5:325-331.
Lee SK, song MY, Seo YS, Kim HK, Ko S, et al.(2009) Rice Pi5-
mediated resistance to Magnaporthe oryzae requires the pres-
ence of two CC-NBLRR genes. Genetics 181:1627-1638.
Li HP, Zhang JB, Shi RP, Huang T, Fischer R, Liao YC. (2008)
Engineering fusarium head blight resistance in wheat by
expression of a fusion protein containing a fusarium-speci c
antibody and an antifungal peptide. Molecular Plant-Microbe
Interactions 2008; 21:1242-8.
Li J, Brader G, Palva ET. (2004) The WRKY70 transcription fac-
tor: A node of convergence for jasmonate-mediated and salic-
ylate-mediated signals in plant defence. Plant Cell 16:319-31.
Li J, Brader G, Kariola T, Palva ET (2006) WRKY70 modulates
the selection of signaling pathways in plant defence. The Plant
Journal 46:477-491.
Lin WC, Lu CF, Wu JW, Cheng ML, Lin YM, Yang NS,
Black L,
Green SK, Wang JF, Cheng CP.
(2004) Transgenic tomato plants
expressing the Arabidopsis NPR1 gene display enhanced resist-
ance to a spectrum of fungal and bacterial diseases. Transgenic
Research 13:567-81.
Liu T, Liu Z, Song C, Hu Y, Han Z, She J, Fan F, Wang J, Jin C,
Chang J, Zhou JM, Chai J. (2012) Chitin-induced dimerization
activates a plant immune receptor. Science 336:1160-1164.
Loutre C, Wicker T, Travella S, Galli P, Sco eld S, et al. (2009)
Two different CC-NBS-LRR genes are required for Lr10 –medi-
ated leaf rust resistance in tetraploid and hexaploid wheat.
Plant Journal 60: 1043-1054.
Magdalena Rossi,Fiona L. Goggin,Stephen B. Milligan,Isgouhi
Kaloshian,Diane E. Ullman, and Valerie M. Williamson (1998)
The nematode resistance gene Mi of tomato confers resistance
against the potato aphid. Proceedings of the National Academy
of Sciences USA 95:9750–9754.
Makandar R, Essig JS, Schapaugh MA, Trick HN, Shah J. (2006)
Genetically engineered resistance to Fusarium head blight in
wheat by expression of Arabidopsis NPR1. Molecular Plant-
Microbe Interactions 19:123-9.
Maldonado AM, Doerner P, Dixon RA, Lamb CJ, Cameron RK.
(2002) A putative lipid transfer protein involved in systemic
resistance signaling in Arabidopsis. Nature 419:399-403.
Mari Narusaka, Kubo Y, Hatakeyama K, Imamura J, Ezura H,
Nanasato Y, Tabei Y, Takano Y, Shirasu K, Narusaka Y.(2013)
Interfamily Transfer of Dual NB-LRR Genes Confers Resistance
to multiple pathogens. . Public Library of Science (PLOS) one
8:e55954.
Meur G, Budatha M, Srinivasan T, Kumar KRR, Gupta AD,
Kirti PB. (2008) Constitutive expression of Arabidopsis NPR1
confers enhanced resistance to the early instars of Spodoptera
litura in transgenic tobacco. Physiologia Plantarum 133:765-
75.
Michelmore, R.W. (2003) The impact zone: genomics and
breeding for durable disease resistance. Current Opinion in
Plant Biology 6:397–404.
Molla KA,Karmakar S,Chanda PK,Sarkar SN,Datta SK,Datta
K (2016). Tissue-speci c expression of Arabidopsis NPR1 gene
in rice for sheath blight resistance without compromising phe-
notypic cost. Plant Sci 250:105-114.
Mur LA, Kenton P, Atzorn R, Miersch O and Wasternack C.
(2006) The outcomes of concentration include synergy, antag-
onism, and oxidative stress leading to cell death. Plant Physi-
ology 140:249-262.
Ndamukong I, Al Abdallat A, Thurow C, Fode B, Zander M,
Weigel R, Gatz C. (2007) SA-inducible Arabidopsis glutare-
doxin interacts with TGA factors and suppresses JA-responsive
PDF1.2 transcription. The Plant Journal 50:128-39.
Nelson R, Wiesner-HanksT, Wisser R and Balint-Kurti P (2017)
Navigating complexity to breed disease-resistant crops. Nature
Reviews Genetics (Advanced publication)
Nombela, G., Williamson, V. M., & Muñiz, M. (2003). The root-
knot nematode resistance gene Mi-1.2 of tomato is responsible
for resistance against the white y Bemisia tabaci. Molecular
Plant-Microbe Interactions 16(7):645-649.

BIOSCIENCE BIOTECHNOLOGY RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS MANIPULATING DISEASE AND PEST RESISTANCE PATHWAYS IN PLANTS 643
Paramita Ghosh et al.
Novina, C.D. and Sharp, P.A. (2004) The RNAi revolution.
Nature 430:161–164.
Pankaj Barah and Atle M. Bones (2013) Controlling crop dis-
eases using induced resistance:challenges for the future. Jour-
nal of Experimental Botany 64:1263–1280.
Park CJ, Kim KJ, Shin R, Park JM, Shin YC, Paek KH (2004)
Pathogenesis-related protein 10 isolated from hot pepper func-
tions as a ribonuclease and an antiviral pathway. The Plant
Journal 37:186–198.
Park SW, Kaimoyo E, Kumar D, Mosher S,Klessig DF. (2007)
Methyl salicylate is a critical mobile signal for plant systemic
acquired resistance. Science 318:113-116.
Passardi F, Penel C, Dunand C (2004) Performing the para-
doxical- How plant peroxidases modify the cell wall. Trends in
Plant Science 9:534–540.
Patrick Romer, Sabine Recht, and Thomas Lahaye (2009) A
single plant resistance gene promoter engineered to recognize
multiple TAL effectors from disparate pathogens. Proceedings
of the National Academy of Sciences vol. 106, no. 48.
Peschen D, Li HP, Fischer R, Kreuzaler F, Liao YC. (2004) Fusion
proteins comprising a Fusarium-speci c antibody linked to
antifungal peptides protect plants against a fungal pathogen.
Nature Biotechnology 22:732-8.
Petersen M, Brodersen P, Naested H, Andreasson E, Lind-
hart U, Johansen B,Nielsen HB,Lacy M, Austin MJ, Parker
JE, Sharma SB, Klessig DF, Martienssen R, Mattsson O,
Jensen AB, Mundy J. (2000) Arabidopsis map kinase 4 nege-
tively regulates syatemic acquired resistance. Cell 103:1111 -
1120.
Pieterse CM, Van Loon L. (2004) NPR1: the spider in the web
of induced resistance signaling pathways. Current Opinion in
Plant Biology7:456-64.
Pretorius,Z.,Singh,R.,Wagoire,W.,andPayne,T.(2000).Detec-
tion of virulence to wheat stem rust resistance gene Sr31in
Pucciniagraminis. f. sp. tritici in Uganda. PlantDis. 84:203–
203.
Punja ZK. (2001) Genetic engineering of plants to enhance
resistance to fungal pathogens—a review of progress and future
prospects. Canadian Journal of Plant Pathology 23:216-35.
Rashid MH, and Chung YR (2017) Induction of Systemic
Resistance against Insect Herbivores in Plants by Bene cial
Soil Microbes. Frontiers in Plants Science 08:1816.
Roche PA, Alston FH, Maliepaard CA, Evans KM, Vrielink R,
Dunemann F, Markussen T, Tartarini S, Brown LM, Ryder C,
King GJ. (1996) RFLP and RAPD markers linked to the rosy leaf
curling aphid resistance gene (Sd1) in apple. Theoretical and
Applied Genetics 94:528e33.
Reinink K, Dieleman FL. (1989) Comparison of sources of
resistance to leaf aphids in lettuce (L. sativa L.). Euphytica
40:21-29.
Roland N. Perry , Maurice Moens (2011) Introduction to Plant-
Parasitic Nematodes; Modes of Parasitism. Chapter Genomics
and Molecular Genetics of Plant-Nematode Interactions pp
3-20Date: 27.
Romeis, T, Ludwig AA,Martin R, Jones JDG. (2001) Calcium-
dependent protein kinases play an essential role in a plant
defence response. The EMBO Journal 20:5556–5567.
Sanchez-Vallet A, Saleem-Batcha R, Kombrink A, Hansen
G, Valkenburg DJ, Thomma BPHJ, Mesters JR (2013) Fungal
effector Ecp6 outcompetes host immune receptor for chi-
tin binding through intrachain LysM dimerization. eLife 2:
e00790.
Saskia A Hogenhout and Jorunn IB Bos. (2011) Effector pro-
teins that modulate plant – insect interactions. Current Opin-
ion in Plant Biology 14:422-428.
Schenk PM, Kazan K, Wilson I, Anderson JP, Richmond T,
Somerville SC, and Manners JM (2000) Coordinated plant
defence responses in Arabidopsis revealed by microarray anal-
ysis. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences USA
97:11655-11660.
Sarah J. Gurr and Paul J. Rushton (2005). Engineering plants
with increased disease resistance: what are we going to
express? Trends in Biotechnology 23: 275–282.
Shah J, Tsui F, Klessig DF (1997) Characterization of a salicylic
acid‐insensitive mutant (sai1) of Arabidopsis thaliana, identi-
ed in a selective screen utilizing the SA‐inducible expres-
sion of the tms2 gene. Molecular Plant‐Microbe Interactions
10:69‐78.
Seidl MF and Thomma BPHJ. (2017) Transposable Elements
Direct The Coevolution between Plants and Microbes. Trends
Genet 33(11):842-851.
Spoe et al., 2003; Spoel SH, Koornneef A, Claessens SMC, Kor-
zelius JP, Van Pelt JA, Mueller MJ, Buchala A J, Métraux J P,
Brown R, Kazan K, Van Loon LC, Dong X and Pietersea CMJ.
(2003) NPR1 modulates cross-talk between salicylate- and jas-
monate-dependent defence pathways through a novel function
in the cytosol. The Plant Cell 15:760-70.
Stuiver, M.H. and Custers, J.H.H.V. (2001) Engineering disease
resistance in plants. Nature 411:865–868.
Sinapidou E, Williums K, Nott L, Bahkt S, Tor M, Crute I,
Bittner-Eddy P and Beynon J. (2004) Two TIR:NB:LRR genes
are required to specify resistance to Peronospora parasitica iso-
late Cala2 in Arabidopsis. The Plant Journal 38:898-909.
Stewart, S. A., Hodge, S., Ismail, N., Mans eld, J. W., Feys, B.
J., Prospéri, J. M. & Powell, G. (2009). The RAP1 gene confers
effective, race-speci c resistance to the pea aphid in Medicago
truncatula independent of the hypersensitive reaction. Molecu-
lar plant-microbe interactions 22(12):1645-1655.
Takakura Y, Ishida Y, Inoue Y, Tsutsumi F, Kuwata S. (2004)
Induction of a hypersensitive response-like reaction by pow-
dery mildew in transgenic tobacco expressing harpin(pss).
Physiological and Molecular Plant Pathology 64:83-9.
van der Biezen, E.A. (2001) Quest for antimicrobial genes to
engineer disease-resistant crops. Trends in Plant Science 6:89–
91.
van der Vossen EA, Gros J, Sikkema A, Muskens M, Wouters D,
Wolters P, Pereira A,Allefs S. (2005) The Rpi-blb2 gene from
Solanum bulbocastanum is an Mi-1 gene homolog confer-

644 MANIPULATING DISEASE AND PEST RESISTANCE PATHWAYS IN PLANTS BIOSCIENCE BIOTECHNOLOGY RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS
Paramita Ghosh et al.
ring broad-spectrum late blight resistance in potato. The Plant
Journal 44:208-22.
von Dahl CC, Winz RA, Halitschke R, Kühnemann F, Gase K,
Baldwin IT. (2007) Tuning the herbivore-induced ethylene
burst: the role of transcript accumulation and ethylene per-
ception in Nicotiana attenuata. The Plant Journal 51:293-307.
Wally O and Punja ZK. (2010) Genetic engineering for increas-
ing fungal and bacterial disease resistance in crop plants. GM
Crops 1:4,199-206.
Wally O, Jayaraj J, Punja ZK (2009) Broad-spectrum disease
resistance to necrotrophic and biotrophic pathogens in trans-
genic carrots (Daucus carota L.) expressing an Arabidopsis
NPR1 gene. Planta 231:131-41.
Walling LL. (2000) The myriad plant responses to herbivores.
Journal of Plant Growth Regulation 19:195-216; PMID:11038228.
Walters D, Heil M. (2007) Costs and trade-offs associated with
induced resistance. Physiological and Molecular Plant Pathol-
ogy 71:3-17.
Wu JQ, Hettenhausen C, Meldau S, Baldwin IT. (2007) Her-
bivory rapidly activates MAPK signaling in attacked and unat-
tacked leaf regions but not between leaves of Nicotiana atten-
uata. Plant Cell 19:1096- 122.
Yang Q., He Y., Kabahuma M. et al., (2017) A gene encoding
maize caffeoyl-CoA O-methyltransferase confers quantitative
resistance to multiple pathogens.
Nature Genetics49:1364–1372.
Yang SM, Gao MQ, Xu CW, Gao JC, Deshpande S, Lin SP, et al.
(2008) Alfalfa bene ts from Medicago truncatula: The RCT1
gene from M. truncatula confers broad-spectrum resistance to
anthracnose in alfalfa. Proceedings of the National Academy
of Sciences USA 105:12164-9.
Yuan Y,Zhong S,Li Q,Zhu Z,Lou Y,Wang L,Wang J,Wang
M,Li Q,Yang D,He Z. (2007) Functional analysis of rice NPR1-
like genes reveals that OsNPR1/NH1 is the rice orthologue con-
ferring disease resistance with enhanced herbivore susceptibil-
ity. Plant Biotechnology Journal 5:313-24.
Zhang, S. and Liu, Y. (2001) Activation of salicylic acid-
induced protein kinase, a mitogen-activated protein kinase,
induces multiple defence responses in tobacco. Plant Cell 13,
1877–1889.
Zhonghua Ma
1
, Themis J. Michailides (2005), Advances in
understanding molecular mechanisms of fungicide resistance
and molecular detection of resistant genotypes in phytopatho-
genic fungi. Crop Protection 24:853–863.
Zhao BY, Lin XH, Poland J, Trick H, Leach J, Hulbert S. (2005)
A maize resistance gene functions against bacterial streak dis-
ease in rice. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences
USA 102:15383-8.
Zhao LY, Chen JL, Cheng DF, Sun JR, Liu Y, Tian Z. (2009) Bio-
chemical and molecular characterizations of Sitobion avenae–
induced wheat defence responses. Crop Protection 28:435-42;
http://dx.doi. org/10.1016/j.cropro.2009.01.005.
Zhu Q, Maher EA, Masoud S, Dixon RA, Lamb CJ. (1994)
Enhanced protection against fungal attack by constitutive
coexpression of chitinase and glucanase genes in transgenic
tobacco. Nature Biotechnol 1994; 12:807-12.c