
Pharmaceutical
Communication
Biosci. Biotech. Res. Comm. 10(4): 601-611 (2017)
Evaluation of some biological properties of
Saussurea
costus
crude root extract
Emad M. Abdallah,
1
* Kamal A. Qureshi,
2
Ahmed M. H. Ali
1,3
and Gamal O. Elhassan
2
1
Department of Laboratory Sciences, College of Sciences and Arts at Al-Rass, Qassim University,
Al-Rass, Saudi Arabia
2
Department of Pharmaceutics, Unaizah College of Pharmacy, Qassim University, Saudi Arabia
3
Department of Zoology and Entomology, Faculty of Science, Assiut University, Assiut, Egypt
ABSTRACT
The current study aimed to evaluate some biological activities of Saussurea costus(S. costus) such as phytochemi-
cal constituents, antimicrobial activity and antifeedant potential on the larvae of Spodoptera littoralis. The results
revealed that the methanol extract of roots of S. costus are rich in some bioactive phytochemical compounds such as
alkaloids, phenols/polyphenols, avonoids, terpenoids, tannins, coumarins, quinines, steroids, cardiac glycosides and
resins. The antimicrobial screening revealed that, among 12 referenced microbial strains (10 bacteria and 2 fungi),
4 Gram-positive bacteria exhibited high susceptibility with the methanol and ethanol extracts of S. costus, namely
Bacillus cereus ATCC 10876 (IZ 16.0±0.0, 15.5±0.5 mm, MIC100, 50 mg/ml, MBC 200, 100 mg/ml), Staphylococcus
saprophyticus ATCC 43867 (IZ 14.5± 0.5, 15.5±0.5 mm, MIC50, 50 mg/ml, MBC100, 100 mg/ml), Staphylococcus
epidermidis ATCC 12228 (IZ 13.5±0.5, 14.5±0.5mm, MIC50, 50 mg/ml, MBC 200, 100 mg/ml) and Staphylococcus
aureus ATCC 29213 (IZ 11.0±0.0, 11.5±0.5 mm, MIC 100, 50 mg/ml, MBC 200, 100 mg/ml), respectively. Also, 1 fungal
strain (Aspergillus niger ATCC 6275) revealed high susceptibility with the extracts (IZ 26.0±1.0 mm, MIC and MFC
50mg/ml). Other microorganisms recorded weak or no effect. Furthermore, the ethanolic extract of S. costus pro-
vided an anitfeedant effect toward Spodoptera littoralis larvae at different concentrations. In conclusion, the current
ndings provide evidence that roots of Saussurea costus is rich in bioactive phytochemical compounds and it might
be a promising source of antimicrobial compounds as well as antifeedant activity against the larvae of Spodoptera
littoralis.
KEY WORDS: ANTIBACTERIAL, ANTIFUNGAL, PHYTOCHEMICAL,
SAUSSUREA COSTUS
, ANTIFEEDANT, INSECTICIDAL,
SPODOPTERA
LITTORALIS
, TRADITIONAL MEDICINE
601
ARTICLE INFORMATION:
*Corresponding Author: emad100sdl@yahoo.com
Received 21
st
Oct, 2017
Accepted after revision 24
th
Dec, 2017
BBRC Print ISSN: 0974-6455
Online ISSN: 2321-4007 CODEN: USA BBRCBA
Thomson Reuters ISI ESC and Crossref Indexed Journal
NAAS Journal Score 2017: 4.31 Cosmos IF: 4.006
© A Society of Science and Nature Publication, 2017. All rights
reserved.
Online Contents Available at:
http//www.bbrc.in/
DOI: 10.21786/bbrc/10.4/2

602 BIOLOGICAL PROPERTIES OF
SAUSSUREA COSTUS
BIOSCIENCE BIOTECHNOLOGY RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS
Emad M. Abdallah et al.
INTRODUCTION
Medicinal plants are used for healing purposes through-
out the human history; even in the current era, there
are up to 80% of the world population most of them are
living in the developing countries, rely on traditional
herbal medicine on their primary health care systems,
many of these herbal drugs prescribed in traditional
medicine have inadequate knowledge and untested by
scienti c methods (Ekor 2013 Qazi and Molvi 2016).
On the other side, Modern medicine stands helpless in
the front of the growing phenomenon of antimicrobial
resistance to antibiotics, which considered as a major
health problem and required prompt attention. This cri-
sis encouraged scholars and researchers to develop the
current antibiotics, synthesize new antibiotics or to nd
new alternatives. The latter option is preferable because,
in nature, plants arise as one of the largest pharmaceuti-
cal factories ever known and plants were the main source
of drugs for humankind since antiquity. Many medicinal
plants produce diverse groups of secondary metabolites
known as phytochemical compounds, which may sup-
press the microbial growth by different modes of action
such as interference with cellular metabolic processes,
cellular membrane perturbations or by modulating the
signal transduction or gene expression pathways (Omo-
jate et al., 2014 Mohamed et al. 2017).
Saussurea costus (Falc.) Lipschitz, synonymous with
Saussurea lappa C.B. Clarke, belongs to family Aster-
aceae, this family includes about 1000 genera and
30,000 species, widely distributed in different regions
in the world; However, numerous species are found in
India (Pandey et al., 2007). It is also distributed in Paki-
stan and some parts of Himalayas (Shah 2006). Saus-
surea costus(S. costus) is well known in Islamic medi-
cine, which enlisted in the Holy Ahadith said by Prophet
Muhammad (Peace be upon him) (Ahmad et al., 2009).
It is known in Arab countries as “Al-Kost Al-Hindi” and
used by traditional healers since the era of the Islamic
civilization. For example but not limited to, S. costusis
traditionally used as stimulant, antiseptic, carminative,
sedative, bronchodilator and astringent agent (Wani
et al., 2011). In the scienti c literature, the biological
activities of the roots of S. costus (synonymous with
S. lappa) are widely investigated. Scienti c investi-
gations revealed that it has anti-trypanosomal activ-
ity (Julianti et al, 2011), it has “complement-inhibitor”
substances helpful in the treatment of some diseases
related to excessive activation of the complement sys-
tem, like rheumatoid arthritis, respiratory distress and
systemic lupus erythematosus (Fan et al., 2014). It was
published that S. costus has a good anticancer activity
on the tested cell lines (Robinson et al., 2008). The etha-
nol extract of S. lappa (synonymous S. costus) recorded
a wide spectrum antimicrobial activity against some
human pathogens (Hasson et al., 2013). In addition,
many investigations reported other bioactive properties
of S. costus roots such as anti-ulcer, anti-in ammatory,
hepatoprotective, immunomodulator, hypoglycaemic,
spasmolytic, anticonvulsant, antidiarrheal and antiviral
activity (Zahra et al., 2014 Ghasham et al., 2017).
Egyptian cotton leafworm, Spodoptera littoralis (Lep-
idoptera: Noctuidae), is responsible for causing devastat-
ing damage for numerous vegetables and crops (Kandil
et al., 2003; Adham, et al., 2009). This polyphagous pest
is widely distributed in Africa and Middle Eastern coun-
tries (Abdel-Rahim and Azab 2008; Rizk et al. 2010; El-
Zoghby et al. 2011). Several synthetic pesticides have
been used to manage the agriculture crops from insect
infestation. These synthetic insecticides cause seri-
ous hazard to the environment due to residual toxicity
(White, 1995; El- Torkey 2008; Rizk et al. 2010). There-
fore, scientists developed safe alternative insecticides
with no residual activity. In this regard, various phyto-
chemical plant extracts from several botanical sources
against the speci c pest have been evaluated (Kamaraj
et al., 2010). The current study aimed to investigate some
biological properties of the methanol extract of the roots
of S. costus, including the phytochemical constituents,
antimicrobial activity and antifeedant potential on the
larvae of Spodoptera littoralis.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
The dry roots of S. costus(Figure 1) were purchased from
a herbal market at Qassim region, Saudi Arabia. The
herbal seller showed the trademark of the package and it
has been con rmed that it was exported from India. The
authentication of plant material was con rmed at the
department of Laboratory Sciences, College of Sciences
and Arts, Al Rass, Saudi Arabia.
12 standard pathogenic test organisms were used in
this study; Bacillus cereus ATCC
®
10876
TM
, Staphylococ-
cus epidermidis ATCC
®
12228
TM
, Staphylococcus aureus
ATCC
®
29213
TM
, Staphylococcus saprophyticus ATCC
®
FIGURE 1. The dried roots of
Saussurea costus

BIOSCIENCE BIOTECHNOLOGY RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS BIOLOGICAL PROPERTIES OF
SAUSSUREA COSTUS
603
Emad M. Abdallah et al.
43867
TM
and Streptococcus pneumonia ATCC
®
49619
TM
,
Escherichia coli ATCC
®
25922
TM
, Proteus vulgaris ATCC
®
6380
TM
, Klebsiella pneumonia ATCC
®
27736
TM
, Pseu-
domonas aeruginosa ATCC
®
9027
TM
, Shigella exneri
ATCC
®
12022
TM
, Candida albicans ATCC
®
10231
TM
and
Aspergillus niger ATCC
®
6275
TM
.
The extraction of plant material was carried out by
following the maceration method. The roots of the plant
were crushed into small particles and then ne powder
was obtained by using electrical mixer grinder. The mac-
eration of plant material was carried out by mixing of
ne powder into 70 % ethanol and 80 % methanol sol-
vents separately. Then, all mixtures were incubated in a
shaker incubator at 40
o
C temp., 50 r.p.m. shaking speed
for up to 3 days in a well-tighten dark container. After
incubation, the mixtures were centrifuged at 5000 r.p.m.
for 15 minutes and then ltered through Whatman lter
paper No.1. The ltrates were subjected to evaporate the
solvents by using a rotary evaporator to get a semi-solid
mushy crude extract, which was dried in hot air oven at
45
o
C for 48 hrs. The dried crude extracts were kept in a
refrigerator until used (Ghasham et al., 2017). Methanol
crude extract was analyzed for potential phytochemi-
cal molecules, methanol and ethanol extracts were used
in the antimicrobial investigation, while ethanol crude
extract was employed in the antifeedant examination
against the larvae of Spodoptera littoralis.
In order to detect the various phytochemical constitu-
ents, the aqueous methanolic extract (100 mg/mL) was
used. The colourimetric tests listed below were used as
reported by (Ghasham et al. 2017, Sasidharan et al., 2011).
1 mL methanolic extract was mixed well with 1 mL of
1 % hydrochloric acid solution, followed by slight heat-
ing till the steaming. After that, 06 drops of Wagner’s
reagent were added into 1 mL of acidi ed extract. The
formation of a brownish-red precipitate was observed
for a positive test.
Carboxylic acid
2 mL of sodium bicarbonate solution was added to 1 mL
of methanolic extract. The formation of effervescence
was observed for a positive test.
Cardiac glycosides
1 mL methanolic extract was dissolved in 1 mL of chlo-
roform, followed by addition of 2-3 drops of the sul-
phuric acid solution at the side of the test tube to form
a layer. The formation of a brown ring at interphase was
observed for a positive test.
Coumarins
1 mL of methanolic extract was mixed with 1 mL of 10
% sodium hydroxide solution. The formation of yellow
colouration was observed for a positive test.
Emodins
1 mL of ammonia and 1.5 mL of benzene solutions were
added to 1 mL of methanolic extract. The formation of
red colouration was observed for a positive test.
Flavonoids
1 mL methanolic extract was added to 1 mL of 10 % lead
acetate solution. The formation of a yellow coloured
precipitate was observed for a positive test.
Leucoanthocyanins
1 mL of isoamyl alcohol was taken into a test tube, fol-
lowed by slow addition of 1 mL of methanolic extract.
The formation of red colouration at upper layer was
observed for a positive test.
Lipids
0.5 mL of methanolic extract was mixed with 5 ml of
ether. This mixture was allowed for evaporation on lter
paper and dried the lter paper. The formation of an
appearance of spot-on lter paper was observed for a
positive test.
Phenols/Polyphenols
1 mL methanolic extract was added into 0.5 mL of 10
% ethanolic ferric chloride solution. The formation of
blue-green to dark blue colouration was observed for a
positive test.
Phlobatannins
1 mL methanolic extract was added to 1 mL of 1 %
hydrochloric acid solution, followed by boiling the mix-
ture. The formation of a red precipitate was observed for
a positive test.
Quinones
1 mL of concentrated sulphuric acid was taken into a
test tube, followed by addition of 1 mL of methanolic
extract. The formation of red colouration was observed
for a positive test.
Resins
Few drops of acetic anhydride solution were added to 1
mL of methanolic extract, followed by addition of 1 mL
of concentrated sulphuric acid. The formation of orange
to yellow colouration was observed for a positive test.
Saponins
5 mL of puri ed distilled water was taken into a test
tube, followed by addition of 1 mL of methanolic extract
and the whole mixture was well stirred. The formation
of continuous effervescence was observed for a positive
test.

Emad M. Abdallah et al.
604 BIOLOGICAL PROPERTIES OF
SAUSSUREA COSTUS
BIOSCIENCE BIOTECHNOLOGY RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS
Steroids
1 mL methanolic extract was mixed with 1 mL of chlo-
roform, followed by addition of 2 mL of acetic anhy-
dride and then few drops of concentrated sulphuric acid
solution. The formation of dark green colouration was
observed for a positive test.
Tannins
2-3 drops of 1 % lead acetate solution were added to 1
mL methanolic extract. The formation of dark blue or
greenish grey colouration was observed for a positive
test.
Terpenoids
2.5 mL of methanolic extract was mixed with 1 mL of
chloroform and then 1.5 mL of concentrated sulphuric
acid solution was added. The formation of reddish brown
colour at the interface was observed for a positive test.
Volatile oil
0.5 mL of diluted sodium hydroxide and 0.5 mL of
diluted hydrochloric acid were added to 2 mL of metha-
nolic extract and mixed well. The formation of a white
precipitate was observed for a positive test.
ANTIMICROBIAL TESTING
The antimicrobial potential of S. costus root extract was
evaluated using agar-well diffusion method as described
by (Abdallah, 2014) with some modi cations. Before to
the experimental phase, all identi ed microbial isolates
were sub-cultured in a tighten bottles containing either
Mueller-Hinton broth (18-24 hours, 35
o
C) for bacte-
ria or Sabouraud dextrose broth (48 hours, 25
o
C) for
fungi. After incubation, all turbid bottles- as a result of
growth-were transferred and kept in the fridge (4
o
C) to
keep the microbial growth at the exponential phase until
used. Autoclaved Bottles containing 20 ml of Mueller-
Hinton agar or Sabouraud dextrose agar was poured hot
on sterile Petri-dishes (90 mm in diameter) and left at
room temperature until solidi ed. Working microbial
strains were taken from the broth cultures (previously
prepared) and adjusted as McFarland standard, then 100
µl from each microbial strain was put over Mueller-Hin-
ton or Sabouraud dextrose agar plates (depending on the
type of microorganism) and distributed above the agar
using sterile cotton swabs. Wells were punched into the
agar with a sterile cork borer (6 mm in diameter). Then,
100 l from each extract (500 mg/ml) was dropped into
the wells, extracts were previously reconstituted in 10%
di-methyl-sulphoxide (DMSO) to make a concentration
500 mg/ml. 10 % DMSO did not show any inhibitory
effect on microorganisms. Another well (in the centre)
was loaded with 100 l of 5 mg/ml Chloramphenicol for
bacteria or 10 mg/ml clotrimazol for fungi. Plates were
incubated at 35°C for 24 hours for bacteria or at 25
o
C
for up to 48 hours for fungi. The antimicrobial activities
of the tested extracts were determined by measuring the
clear zone of inhibition in millimetre (mm) ± standard
error of the mean.
MIC, MBC AND MFC ASSAY
Only microorganisms that showed high antimicrobial
activity was tested for MIC, MBC and MFC. The mini-
mum inhibitory concentration (MIC) was determined
using microdilution method as described by Hassan
et al. (2009) with slight modi cation. Brie y, in a set of
sterile test tubes, serial two-fold dilutions were made to
get 6 tubes containing 1 ml of 200, 100, 50, 25, 12.5 and
6.25 mg/ml of the extract, respectively. Additional two
tubes were also used, one tube containing 1 ml of 10%
DMSO to serve as negative control and the other tube
containing 1ml of 5mg/ml chloramphenicol to serve as
positive control. Then, 1 ml of sterile Mueller-Hinton
broth and 100µl of the adjusted microbial strain were
added to each tube (8 tubes). Tubes were gently shake
and placed in the incubator at 35°C for 24 hours for
bacteria or at 25oC for up to 48 hours for fungi. The
lowest concentration (highest dilution) of the extract
that showed no visible microbial growth (no turbidity)
compared with the control tubes was considered as MIC.
The minimum bactericidal concentration (MBC) and
minimum fungicidal concentration (MFC) was evaluated
by determined by sub-culturing the test dilution on to
unseeded plates of Mueller-Hinton agar for bacteria or
Sabouraud dextrose agar for fungi and incubated further
for 18-24 h for bacteria or 48 h for fungi. The highest
dilution that revealed no single bacterial colony on the
plates was taken as MBC or MFC.
ANTIFEEDANT ASSAY AND STARVATION
PERCENTAGE
A strain of S. littoralis was reared in the laboratory.
Larvae were fed on fresh castor leaves, Ricinus commu-
nius. Adults were provided with 10% sugar solution. All
the bioassays were conducted at 26± 2° C and 65±5 %
R.H., with 8:16 L:D h photoperiod. The experiments were
carried out on the 4th instar larvae. Serious of ascend-
ing crude concentrations were prepared (0.6 %, 1.25 %,
2.5 %, 5%, 10 % and 20%) by dilution in 70 % etha-
nol. Control discs were sprayed with the solvent alone.
400 larvae were starved overnight, then divided into 8
groups of 50 larvae each, six different concentrations of
plant extract (S. costus), one group for the control and
one group as starved larvae. Equal discs of castor bean
leaves were rinsed in each treatment and in the control,
the treated and untreated leaves were shad-dried. All

Emad M. Abdallah et al.
BIOSCIENCE BIOTECHNOLOGY RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS BIOLOGICAL PROPERTIES OF
SAUSSUREA COSTUS
605
larvae control and treated leaves were weighted before
and after treatment for 3 days. The dried leaves were
placed individually in plastic Petri dishes. Ten larvae
were transferred into each cup and allowed to feed on
the treated and untreated leaves, the starved larvae were
left without feeding for 24h. Five replicates for each
treatment were carried out. The starvation percentages
of tested larvae were calculated (Mostafa 1969 ; Abdel-
Mageed et al. 1975).
Starvation (%) = C – E/C – S X 100
Where:
C = Mean weight gain of untreated larvae after 24 h;
E = Mean weight gain of treated larvae for each concen-
tration after 24 h; and
S = Mean weight gain of starved untreated larvae after
24 h.
The antifeedant index (AFI) was calculated according
to Sadek (2003).
AFI (%)= [(C-T) / (C + T)] X 100
Where:
C: the amount of food consumed (leaves) in the control;
and
T: the amount of food consumed (leaves) in the treat-
ment.
STATISTICAL ANALYSIS
Quantitative data were expressed as a mean ± standard
error of means. One-way analysis of variance ANOVA
was used and P < 0.05 was used in testing the statisti-
cal signi cance. Paired-Samples T-test was employed to
determine any signi cant differences between methanol
and ethanol extracts of the antimicrobial assay. The pro-
gram used was SPSS-Statistical Package, version 11.
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
PHYTOCHEMICAL SCREENING
The results of phytochemical screening suggest that,
Saussurea costus roots are rich source of various bioac-
tive constituents such as alkaloids, cardiac glycosides,
coumarins, avonoids, phenols, quinones, resins, ster-
oids, tannins and terpenoids. These results are summa-
rized in Table 1.
These phytochemical constituents are important
for the use of health care. The ndings of the present
study agreed with previous studies; Chaudhary (2015)
has reported that S. lappa (synonymous S. costus), is a
rich source of alkaloids, steroids, avonoids and resins.
Moreover, Pandey et al., 2007 have reported that many
bioactive molecules were identi ed and isolated from S.
costus, such as sesquiterpene lactones, costunolide, iso-
dehydrocostus, isozaluzanin-C, guiainolide, cynaropic-
rin, reynosin, santamarine and many more. Undoubt-
edly, the diverse biological activities of S. costus are
attributed to its richness in phytochemical compounds.
Accordingly, it is recommended that more studies may
lead to the understanding which molecules are respon-
sible for the antibacterial, antifungal and antifeedant
activities against Spodoptera littoralis larvae.
ANTIMICROBIL SCREENING
In the current study, 6 mm inhibition zone (IZ) means
that there is no antimicrobial activity of the extract (the
zone of the hole on the agar plate is 6 mm), above 6 mm
to less than 10 mm means that there is a weak antimi-
crobial activity, from 10 mm to 12 mm means that there
is a moderate antimicrobial activity (the double of the
hole diameter), above 12 mm is noticeable or good anti-
microbial activity. Philip et al. (2009) considered that
IZ above 10 mm is good antimicrobial activity. Unlike
the antibiotics, there is no standard criterion in explain-
ing the IZ for the crude plant extracts. The results of
the antimicrobial activity are demonstrated in (Table 2)
and (Figures 2-6). The results of the antimicrobial ef -
cacy of methanolic and ethanolic extracts of S. costus
roots have shown that Gram-positive bacteria were more
susceptible. Bacillus cereus ATCC 10876 has recorded
the highest susceptibility (16.0±0.0, 15.5±0.5 mm), fol-
Table 1. phytochemical analysis of Saussurea
costus roots
Phytochemical constituents Test results
Alkaloids +
Cardiac glycosides +
Coumarins +
Flavonoids +
Phenol/Polyphenols +
Quinones +
Resins +
Steroids +
Tannins +
Terpenoids +
Carboxylic acid -
Leucoanthocyanins -
Lipids -
Emodins -
Phlobatannins -
Saponins -
Volatile oil -
+ = test positive, - = test negative
Emad M. Abdallah et al.
606 BIOLOGICAL PROPERTIES OF
SAUSSUREA COSTUS
BIOSCIENCE BIOTECHNOLOGY RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS
Table 2. The antimicrobial activity of the methanol and ethanol extracts of S. costus roots against
different microorganisms
Tested
Compound
Mean inhibition zones (IZ) in millimetre
Gram-positive bacteria Gram-negative bacteria Fungi
Sa Se Ss Sp Bc Ec Pa Pv Kp Sf As Ca
MeOH of S. costus
(500 mg/ml)
11.0
±0.0
13.5
±0.5
14.5
±0.5
6. 5
±0. 5
16.0
±0. 0
8.5
±0.5
9.5
±0.5
9.0
±0.0
6.0
±0.0
6.0
±0.0
26.0
±1.0
6.0
±0.0
EtOH of S. costus
(500 mg/ml)
11.5
±0.5
14.5
±0.5
15.5
±0.5
6. 5
±0. 5
15.5
±0. 5
8.5
±0.5
7.5
±0.5
9.0
±0.0
6.0
±0.0
6.0
±0.0
27.5
±0.5
7.5
±0.5
Chloramphenicol
(5 mg/ml)
34.0
±0.5
38.0
±3.0
36.5
±1.5
20.5
±1.0
34.0
±2.0
34.0
±1.0
19.5
±0.5
33.0
±1.0
33.5
±0.5
34.5
±0.5
--
Clotrimazole (10 mg/ml) - - - - - - - - - - 40.5
±1.5
36.0
±2.0
10% DMSO 6.0
±0.0
6.0
±0.0
6.0
±0.0
6.0
±0.0
6.0
±0.0
6.0
±0.0
6.0
±0.0
6.0
±0.0
6.0
±0.0
6.0
±0.0
6.0
±0.0
6.0
±0.0
*MeOH= methanol extract, EtOH=Ethanol extract, Sa= Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 29213, Se=Staphylococcus epidermidis ATCC
12228, Ss=Staphylococcus saprophyticus ATCC 43867, Sp=Streptococcus pneumonia ATCC 49619, Bc= Bacillus cereus ATCC 10876,
Ec=Escherichia coli ATCC 25922, Pa=Pseudomonas aeruginosa ATCC 9027 Pv=Proteus vulgaris ATCC 6380, Kp=Klebsiella pneumonia
ATCC 27736, Sf=Shigella exsneri ATCC 12022, As= Aspergillus niger ATCC 6275, Ca= Candida albicans ATCC 10231.
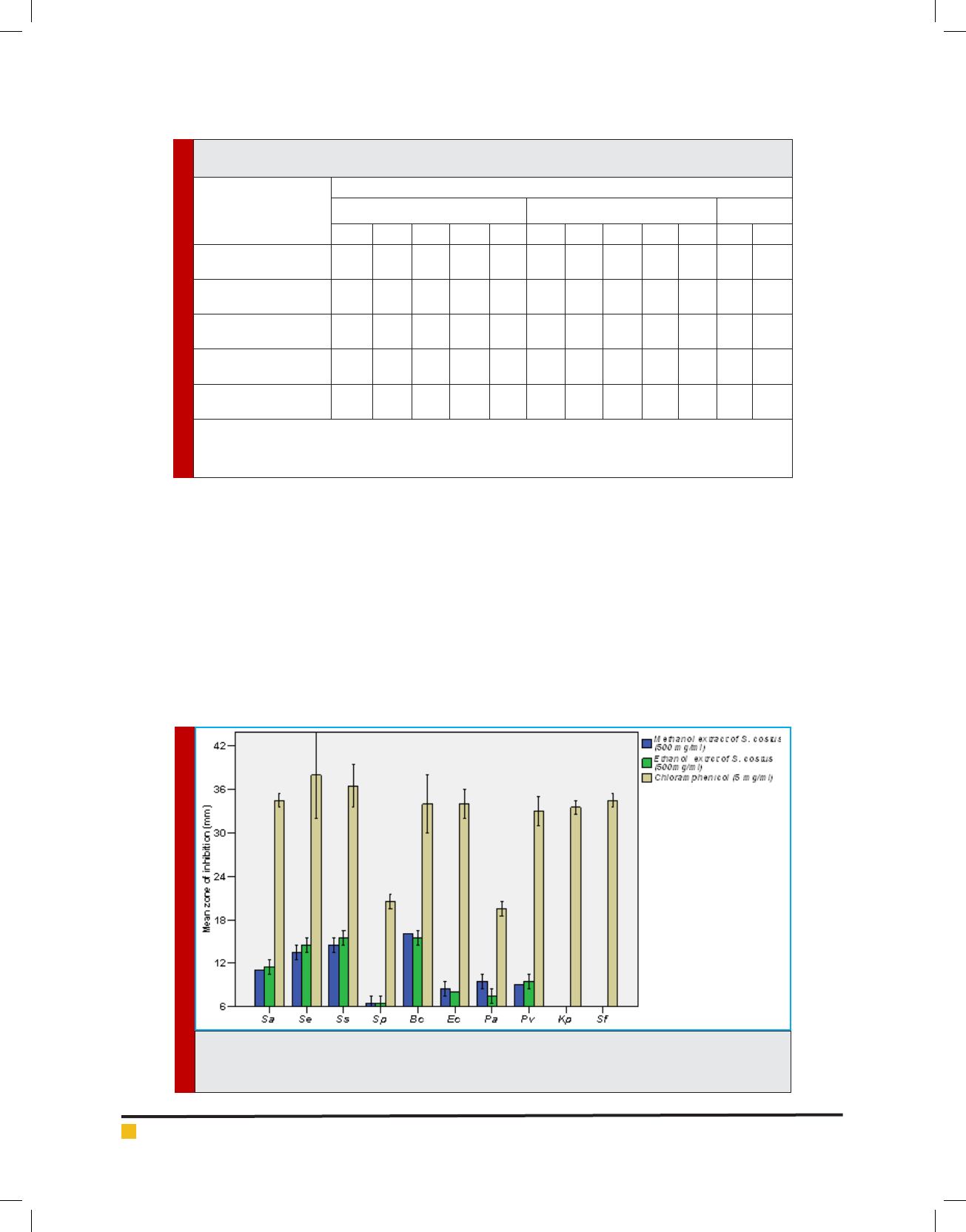
FIGURE 2. Mean zone of inhibitions of different bacterial strains due to the effect methanol and ethanol
extracts of S. costus compared with chloramphenicol*
*Abbreviations of the names of microorganisms are detiled under (Table2).
lowed by Staphylococcus saprophyticus ATCC 43867
(14.5±0.0, 15.5±0.5 mm), Staphylococcus epidermidis
ATCC 12228 (13.5±0.5, 15.5±0.5 mm) and Staphylococ-
cus aureus ATCC 29213 (11.0±0.0, 11.5±0.5 mm), respec-
tively. While, Streptococcus pneumonia ATCC 49619
has shown very weak susceptibility, which was 6.5±0.5
mm for methanolic and ethanolic extracts. On the other
side, the Gram-negative bacteria exhibited weak or no
susceptibility at all. Weak susceptibility was found with
Pseudomonas aeruginosa ATCC 9027 (9.5±0.5, 7.5±0.5
mm), Proteus vulgaris ATCC 6380 (9.0±0.0, 9.0±0.0 mm)
and Escherichia coli ATCC 25922 (8.5±0.5, 8.5±0.5 mm)
for methanolic and ethanolic extracts, respectively.
While, Klebsiella pneumonia ATCC 27736 and Shi-
gella exneri ATCC 12022 revealed no susceptibility
against the tested extract, which agrees with the results
of Mohamed et al. (2017) who stated that, methanolic
extract of S. costus roots has signi cant level of anti-
bacterial activity against Staphylococcus aureus and
Bacillus subtilis (Gram-positive) and showed no effect
against Escherichia coli and Pseudomonas aeruginosa
(Gram-negative). Interestingly, these results are in
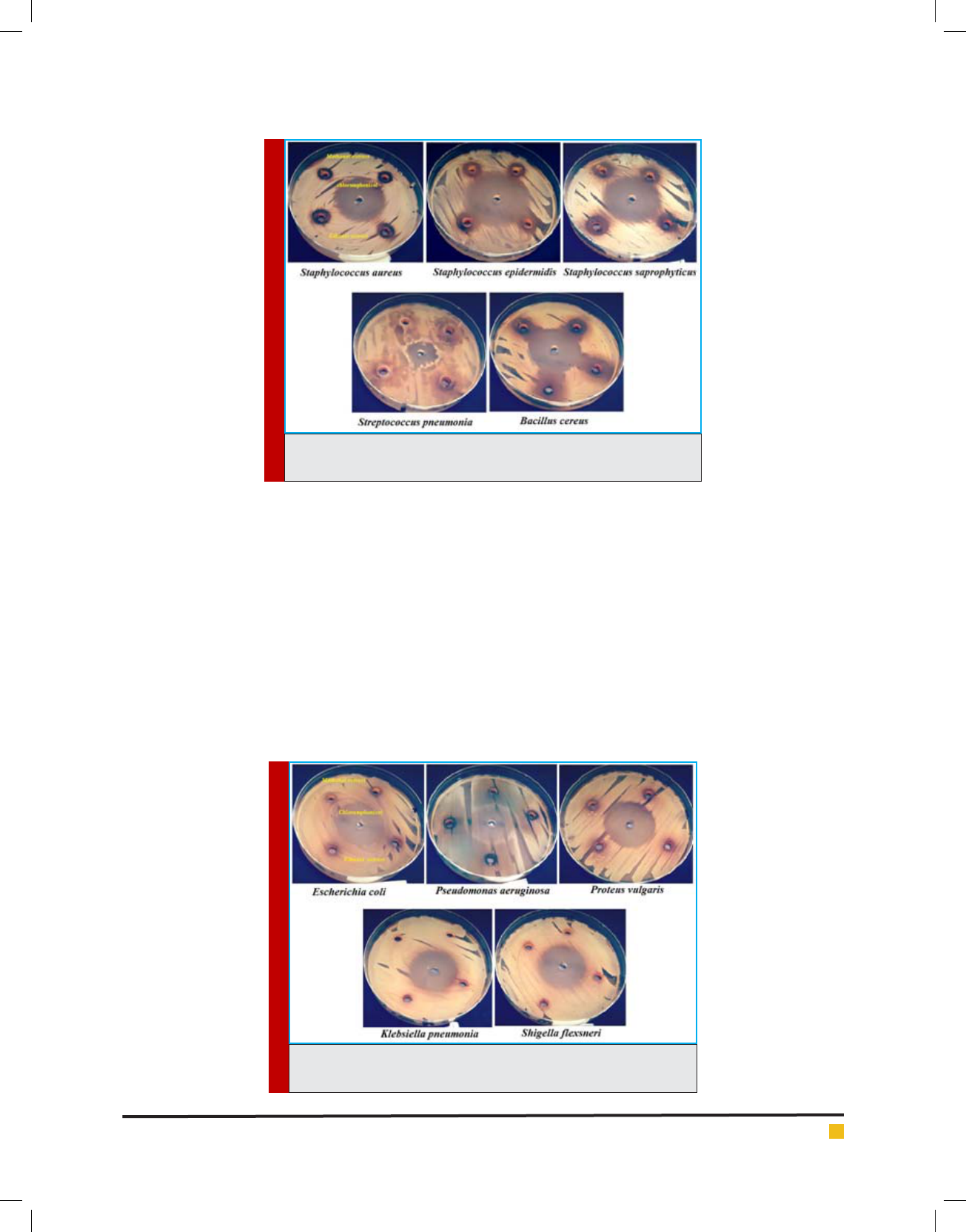
Emad M. Abdallah et al.
BIOSCIENCE BIOTECHNOLOGY RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS BIOLOGICAL PROPERTIES OF
SAUSSUREA COSTUS
607
FIGURE 3. Susceptibility of gram-positive bacteria to methanol and eth-
anol extracts of S. costus roots compared with chloramphenicol
FIGURE 4. Susceptibility of gram-negative bacteria to methanol and
ethanol extracts of S. costus roots compared with chloramphenicol
agreement in-partial with the ndings of Hasson et al.
(2013), in their study they have reported that S. lappa
(synonymous S.costus) has exhibited signi cant level
of antibacterial activity against different Gram-posi-
tive and Gram-negative pathogenic bacteria, includ-
ing Staphylococcus aureus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa,
Acinetobacter baumanii, Escherichia coli and Klebsiella
pneumonia.
After comparing the results of our ndings with the
results of Hasson et al., 2013, we have concluded that,
the former study has used 99.9 % ethanol as a solvent to
extract the crude and in our study, we used 70 % Ethanol
and used 80 % methanol. It is well known that absolute
ethanol can collect non-polar constituents better than
70 % ethanol. Whereas, methanol can collect some non-
polar and polar constituents from the plant materials.
The statistical analysis (Paired-Samples T test) showed
that, there was no signi cant difference between anti-
bacterial activity of 70 % ethanolic and 80 % methanolic
extracts, which means that the effective antibacterial
compounds are present in the non-polar fraction. This
consumption is supported with the ndings of Pandey et
al. (2008), mentioned that, the essential oil of S. costus
roots has exhibited better antibacterial effects as com-
pared with the methanolic extract. In addition, S. costus
has showed high signi cant level of antifungal activity
Emad M. Abdallah et al.
608 BIOLOGICAL PROPERTIES OF
SAUSSUREA COSTUS
BIOSCIENCE BIOTECHNOLOGY RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS
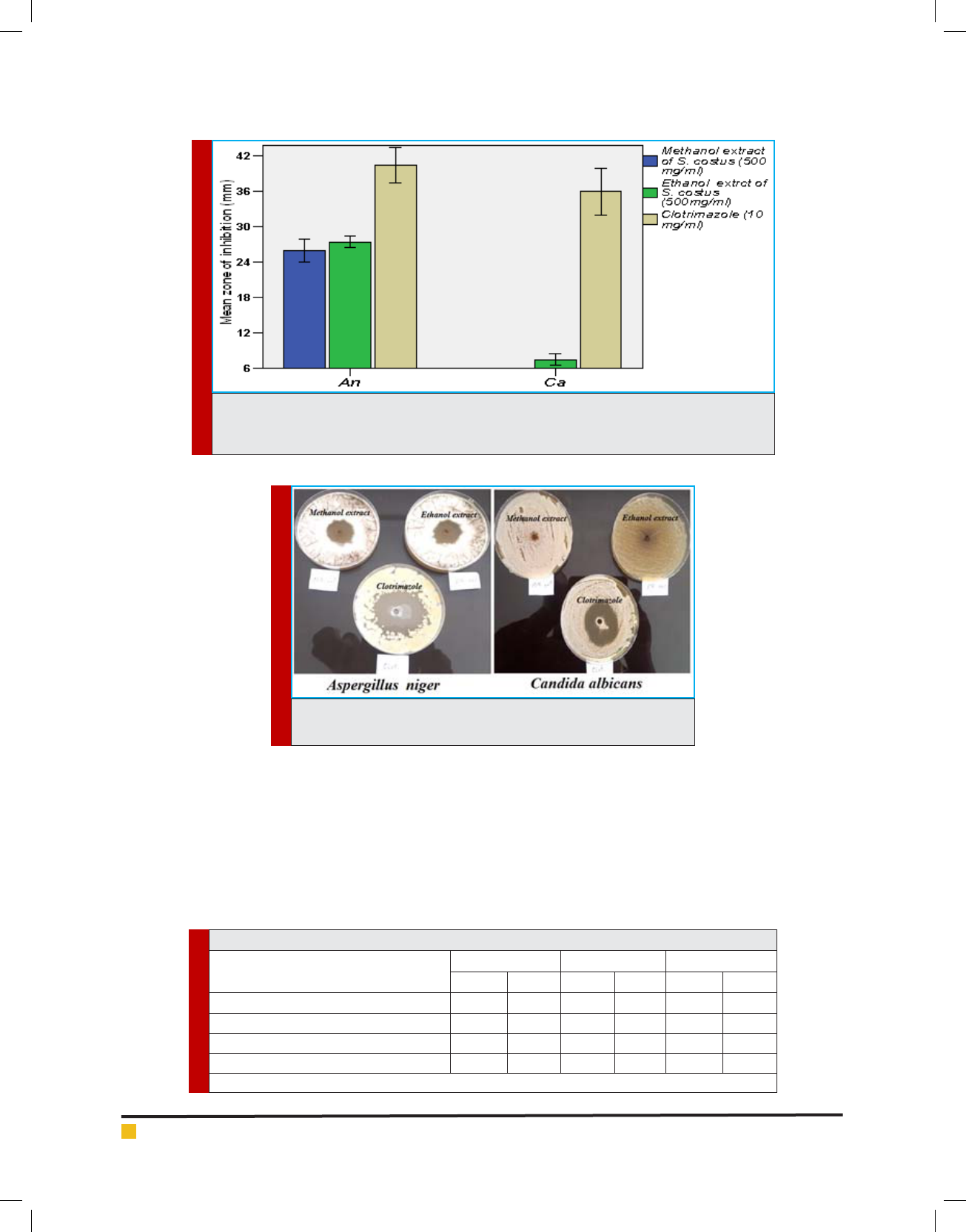
FIGURE 5. Mean zone of inhibitions of different fungal strains due to the effect methanol and
ethanol extracts of S. costus compared with clotrimazole*
*An=Aspergillus niger, Ca= Candida albicans
FIGURE 6. Susceptibility of fungalstrains to methanol and ethanol
extracts of S. costus roots compared with clotrimazole
Table 3. MIC and MBC of the methanolic and ethanolic extracts of the S. costus roots
Bacterial strain MIC mg/ml MBC mg/ml MBC/MIC
MeOH EtOH MeOH EtOH MeOH EtOH
Staphylococcus saprophyticus ATCC 43867 50 50 100 100 2 2
Staphylococcus epidermidis ATCC 12228 50 50 200 100 4 2
Bacillus cereus ATCC 10876 100 50 200 100 2 2
Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 29213 100 50 200 100 2 2
*MeOH= methanol extract, EtOH=Ethanol extract.
against Aspergillus niger ATCC 6275 and weak effect
against Candida albicans ATCC 10231.
It disagrees with the ndings of Mohamed et al.
(2017) who reported good antifungal activity of S. lappa
against Candida albicans. This contradiction is related
to the solvent used in extraction, as reported by Patil et
al. (2009) that, diethyl ether fraction has showed promi-
nent fungicidal activity against Candida albicans. How-
ever, the antimicrobial activity resulted from the current
investigation was not competitor to chloramphenicol or
clotrimazole. These referenced antibiotics are present in
a pure form (single compound), while the extracts are
investigated as a crude. Therefore, the antimicrobial ef -
cacy of S. costus roots could be competitor to antibiot-
Emad M. Abdallah et al.
BIOSCIENCE BIOTECHNOLOGY RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS BIOLOGICAL PROPERTIES OF
SAUSSUREA COSTUS
609
Table 4. MIC and MFC of the methanolic and ethanolic extracts of the S. costus roots
Fungal strain MIC mg/ml MFC mg/ml MFC/MIC
MeOH EtOH MeOH EtOH MeOH EtOH
Aspergillus niger ATCC 6275 50 50 50 50 1 1
*MeOH= methanol extract, EtOH=Ethanol extract.
Table 5. Antifeedant activity of ethanolic extract of S.
costus against 4th instar larvae of S. littoralis.
Concentration
Antifeedant index (%) ±SE
Mean*
Days post-treatment
1st 2nd
0.6% 28.39± 4.22e 26.01± 1.64d 27.20 %
1.25% 39.54± 3.27cd 39.75± 5.50c 39.64%
2.5% 35.16± 3.36de 38.34± 3.21c 36.75%
5% 46.58± 1.96c 43.03± 2.52bc 44.80%
10% 58.34± 4.75b 50.90± 2.67b 54.60%
20% 85.36± 2.24a 70.16± 3.23a 77.76%
*Data are expressed as mean ± SE (n=5), total mean of each treatment
at different time intervals, values were analyzed by one-way ANOVA,
where means within each column followed by different letters are
signi cantly different (P< 0.05 by LSD).
Table 6. Starvation percentage (%) of the 4
th
instar larvae of S. littoralis treated with
the ethanolic extract of S. costus
Treatments Time Average weight
(mg/larva)
Difference*
(mg/larva)
Starvation (%) Average
0.6
0 min
24h
48h
63.13
74.30
93.62
--------
+11.17
+30.49
-------
25.09
24.18
24.63%
1.25
0 min
24h
48h
69.10
76.24
84.12
--------
+7.14
+15.02
-------
42.38
52.05
47.21%
2.50
0 min
24h
48h
60.11
70.00
70.73
--------
+9.89
+10.62
-------
30.58
59.98
45.28%
5
0 min
24h
48h
60.83
64.20
72.31
--------
+3.37
+11.48
-------
58.55
58.43
58.49%
10
0 min
24h
48h
68.23
64.75
77.80
--------
-3.48
+9.57
-------
87.94
61.87
74.90%
20
0 min
24h
48h
68.00
63.25
65.78
--------
-4.75
-2.22
-------
93.39
83.11
88.25%
Control
0 min
24h
48h
68.10
85.12
112.01
--------
+17.02
+43.91
-------
-------
-------
-------
-------
-------
Starved larvae 0 min
24h
48h
61.68
55.39
50.09
--------
-6.29
-11.59
-------
-------
-------
-------
-------
-------
ics if the bioactive compound (s) isolated and studied
in a future studies. This hypothesis is boosted by the
results of MIC, MBC and MFC as shown in (Tables 3
and 4), which revealed that, the methanolic extract was
bacteriostatic to Staphylococcus saprophyticus, Staphy-
lococcus epidermidis, Bacillus cereus and Staphylococ-
cus aureus at 50, 50, 100 and 100 mg/ml, respectively;
and the bactericidal activity was at 100, 200, 200, 200
mg/ml, respectively. As well, the ethanolic extract was
bacteriostatic to Staphylococcus saprophyticus, Staphy-
lococcus epidermidis, Bacillus cereus and Staphylococ-
cus aureus at 50, 50, 50 and 50 mg/ml, respectively; and
the bactericidal activity was detected at 100, 100, 100,
100 mg/ml, respectively. In addition, the methanolic and
ethanolic extracts were bacteriostatic and bactericidal
to Aspergillus niger at 50 mg/ml. The values of MBC/
MIC were ranging between 2-4 for bacterial strains and
1 for fungal strain. Djeussi (2013) has stated that, the

Emad M. Abdallah et al.
610 BIOLOGICAL PROPERTIES OF
SAUSSUREA COSTUS
BIOSCIENCE BIOTECHNOLOGY RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS
plant extract is a bactericidal when the ratio of MBC/
MIC equals 4 and bacteriostatic when MBC/MIC ratio is
>4. Accordingly, S. costus roots may possess new natu-
ral antimicrobial agents that require isolation of these
novel and natural bioactive molecules.
ANTIFEEDANT PROPERTIES
The antifeedant potential results of the ethanolic extract
of S. costus on the larvae of Spodoptera littoralis are
presented in (Table 5), the crude methanol extract
exhibited antifeedant effect on the 4
th
instar larvae of
S. littoralis. The antifeedant activity are varying from
27.2%, 39.64%, 36.75%, 44.8%, 54.6 to 77.76% at 0.6,
1.25, 2.5, 5, 10 and 20% concentrations, respectively. It
was noticed that the antifeedant activity on the larvae
increased by days in all concentrations after treatment.
Data in (Table 6) shows the starvation percentage of the
4
th
instar larvae of S. littoralis treated with the ethanolic
extract of S. costus. The starvation percentage same as
antifeedant activity which increased with the increas-
ing of the concentration during 48 hours. The root of
S. lappa which have the essential oil and the alkaloid
considered as insect repellent (Kapoor, 2001). The Costu-
nolide that isolated from root extract of S. lappa showed
80% antifeedant activity to citrus pest Papilio demoleus
(Vattikonda et al., 2014). The plant extract of of S. cos-
tus may be useful for effective control of S. littoralis at
larval stages.
CONCLUSION
Roots of Saussurea costus(S. costus) are widely used
in the traditional medicine; it is frequently mentioned
in the Islamic medicine as well as ancient Indian and
Chinese medicine. the current investigation revealed the
presence of many bioactive phytochemical molecules,
antimicrobial activity, and antifeedant effect against
Spodoptera littoralis larvae, which offers a scienti c
basis for traditional uses of S. costus roots as antimicro-
bial and insect repellent. We recommend further future
studies using different solvents and extraction systems
as we assume that there are perhaps more bioactive
compounds in the non-polar or aromatic fraction. More-
over, it is worthy to separate and identify these bioactive
compounds from the roots of S. costus in order to get
new natural and effective drugs.
SOURCE OF SUPPORT
Nil
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
None declared
REFERENCES
Abdallah, E. M. (2014): Antimicrobial properties and phyto-
chemical constituents of the methanol extracts of Euphorbia
retusa Forssk. and Euphorbia terracina L. from Saudi Arabia.
South Asian J. Exp. Biol. 4(2): 48-53.
Abdel-Mageed, M. I., Shaaban, A. M. and Zidan, Z. H. (1975):
The effectiveness of dursban, Du-Ter brestan and their com-
bination against the cotton leafworm Spodoptera littoralis
(Boisd.). Bull. Ent. Soc. Egypt, Econ. Ser. 9:283-292.
Abdel-Rahim, E.F.M. and Azab, A.M.A. (2008): Bio-residual
activity of some conventional and inconventional insecti-
cides against eld strain cotton leaf worm,Spodoptera littora-
lis(Boisd). Egypt. J. Agric. Res. 86: 2141-2155.
Adham, F.K., Rashad, E.M.,Shoukry, I.F. and Nasr, E.E. (2009):
Host plants shifting affects the biology and biochemistry of
Spodoptera littoralis (boisd.) (lepidoptera: noctuidae). Egypt.
Acad. J. Boil. Sci. 2: 63- 71.
Ahmad, M., Khan, M. A., Marwat, S. K., Zafar, M. and Khan, M. A.
(2009): Useful Medicinal Flora Enlisted in Holy Quran and Ahad-
ith. American-Eurasian J. Agric. Environ. Sci. 5(1): 126-140.
Choulhary, G.P. (2015): Phytochemical and pharmacological
study of Saussurea lappa Clarke: a review. European J. Phar-
maceu. Med. Res. 2(7): 120-125.
Djeussi, D. E., Noumedem, J.A., Seukep, J.A., Fankam, A.G.,
Voukeng, I. K., Tankeo, S. B., et al. (2013): Antibacterial activi-
ties of selected edible plants extracts against multidrug-resist-
ant Gram-negative bacteria. BMC Complement. Altern. Med.
13: 164.
Ekor, M. (2013): The growing use of herbal medicines: issues
relating to adverse reactions and challenges in monitoring
safety. Front. Pharmacol. 4: 177.
El-Torky, H. M. (2008): Physico-chemical studies on formu-
lated plant extracts and their effect on Spodoptera littoralis
(Boisd.) (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). Bull. Ent. Soc. Egypt. Econ.
Ser. 34: 111-118.
El-Zoghby, F. A., Salem, M.H., Gadelhak, G.G. and El-Sabrout,
A.M. (2011): Effect of Melilotus indica crude extracts and cascade
(IGR) on Spodoptera littoralis (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) reproduc-
tive organs. Bull. Ent. Soc. Egypt. Econ. Ser. 37: 121-136.
Fan, W., Liu, F., Bligh, S.W.A., Shi, S. and Wang, S. (2014):
Structure of a homofructosan from Saussurea costus and anti-
complementary activity of its sulfated derivatives. Carbohyd.
Polym. 105: 152–1
Ghasham, A.A., Muzaini, M.A., Qureshi, K.A., Elhassan, G.O.,
Khan, R.A., Farhana, S.A., Hashmi, S., El-Agamy, E. and
Abdallah, W.E. (2017): Phytochemical Screening, Antioxidant
and Antimicrobial Activities of Methanolic Extract of Ziziphus
mauritiana Lam. Leaves Collected from Unaizah, Saudi Arabia.
Int. J. Pharm. Res. Allied Sci. 6(3):33-46.
Hassan, A., Rahman, S., Deeba, F. and Mahmud, S.C. (2009):
Antimicrobial activity of some plant extracts having hepato-
protective effects. J. Med. Plants Res. 3(1): 020-023.
Hasson, S.S.A., Al-Balushi, M.S., Alharthy, K., Al-Busaidi, J.Z.,
Aldaihani, M.S., Othman, M.S., Said, E.A., Habal, O., Sallam,

Emad M. Abdallah et al.
BIOSCIENCE BIOTECHNOLOGY RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS BIOLOGICAL PROPERTIES OF
SAUSSUREA COSTUS
611
T.A., Aljabri, A. and Idris, M.A. (2013): Evaluation of anti-
resistant activity of Auklandia (Saussurea lappa) root against
some human pathogens. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Biomed. 3(7): 557-
562.
Julianti, T., Hata, Y., Zimmermann, S., Kaiser, M., Hamburger,
M. and Adams, M. (2011): Antitrypanosomal sesquiterpene lac-
tones from Saussurea costus. Fitoterapia 82:955–959.
Kamaraj, C., Abdul Rahuman, A., Mahapatra, A., Bagavan, A.
and Elango, G. (2010): Insecticidal and larvicidal activities of
medicinal plant extracts against mosquitoes. Parasitol. Res.
107: 1337-1349.
Kandil, M.A., Abdel-Aziz,N.F. and Sammour, E.A. (2003). Com-
parative toxicity of chlor uazuran and leufenron against cot-
ton leafworm Spodoptera littoralis (Boisd). Egypt J. Agric. Res.
2: 645-661.
Kapoor, L.D. (2001): Handbook of Ayurvedic Medicinal Plants.
Washington D. C: CRS Press; 2001.
Mohamed, A., Aldaw, M., Ismail, E., Abu-algasim A. and Karar,
E. (2017): Evaluation of antimicrobial activity of different sol-
vent extracts of Saussurea lappa , World J. Pharm. Pharmaceu.
Sci. 6(9): 12-18.
Mostafa, O. K. (1969): Studies on antifeeding and repellents
to economic lepidoptera. M.Sc. Thesis, Faculty of Agriculture
Cairo University, Egypt, pp. 65-68.
Omojate, G. C., Enwa, F. O., Jewo, A. O. and Eze, C, O. (2014):
Mechanisms of antimicrobial actions of phytochemicals
against enteric pathogens – a review. J. Pharm. Chem. Biol.
Sci. 2(2):77-85.
Pandey, M.M., Rastogi, S. and Rawat, A.K.S. (2007): Saussurea
costus: Botanical, chemical and pharmacological review of an
ayurvedic medicinal plant. J. Ethnopharma. 110: 379–390.
Pandey, M.M., Singh, M., Rastogi, S. and Rawat, A.K.S. (2008):
Antimicrobial activity of methanolic extract and oil of Saus-
surea costus roots. Nigerian J. Nat. Prod. Med. 12:95-98.
Patil, S.M., Patil, M.P., Sapkale, G.N. and Umbare, R.P. (2009):
Antimicrobial activity of Saussurea lappa Clarke roots. Res. J.
Pharmacog. Phytochem. 1(1): 51-53.
Philip, K., Malek, S.N.A., Sani, W., Shin, S.K., Kumar, S., Lai,
H.S., Serm, L.G. and Rahman, S.N.S.A. (2009): Antimicrobial
activity of some medicinal plants from Malaysia. American J.
Appl. Sci. 6: 1047-1058.
Qazi, M.A. and Molvi, K.I. (2016): Herbal Medicine: A Compre-
hensive Review. Inter. J. Pharmace. Res. 8(2): 1-5.
Rizk, G.A., Hashem H.F. and Mohamed, S.A. (2010): Plants in
pest control.2-Evaluation of some plant extracts against the
cotton leaf worm, Spodoptera littoralis (Boisd.). Bull. Ent. Soc.
Egypt. Econ. Ser. 36: 213-222.
Robinson, A., Kumar, T.V., Sreedhar, E., Naidu, V.G.M., Krishna,
S.R., Babu, K.S., Srinivas, P.V.M and Rao, J.M. (2008): A new
sesquiterpene lactone from the roots of Saussurea lappa:
Structure–anticancer activity study. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Let.
18: 4015–4017.
Sasidharan, S., Chen, Y., Saravanan, D., Sundram, K.M. and
Yoga Latha, L. (2011): Extraction, isolation and characteriza-
tion of bioactive compounds from plants’ extracts. Afr. J. Tra-
dit. Complement. Altern. Med. 8(1): 1-10.
Shah, R. (2006): Nature’s Medicinal plants of Uttaranchal:
(Herbs, Grasses & Ferns). Vol. I and II. Gyanodaya Prakashan,
Nanital, Uttarakhand. India.
Vattikonda,S. R., Amanchi, N. R. and Sangam, S. R. (2015):
Effect of Costunolide a plant product of Saussurea lappa on
feeding behaviour of Papilio demoleus L. (Lepidoptera: Papil-
ionidae) Larvae. Res. J. Recent Sci. 4 (7): 55-58.
Wani, B.A., Wani, F.M., Khan, A., Bodha, R.H., Mohiddin, F.A.
and Hamid, A. (2011): Some herbs mentioned in the Holy
Quran and Ahadith and their medicinal importance in contem-
porary times. J. Pharm. Res. 4(11): 3888-3891.
White, L. (1995): Chemical control. Integrated management of
insects in stored products. Dekker, Inc; New York. Basel. Hong
Kong, pp. 287- 330.
Zahra, K,, Tabassum, S., Sabir, S., Chaudhari, S.K., Arshad, M.,
Qureshi, R. and Amgad, M.S. (2014): A review of therapeutic
potential of Saussurea lappa-An endangered plant from Hima-
laya. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Med. 7(S1): S60-S69.