The effectiveness of pelvic oor exercises on symptoms
in females with stress urinary incontinence
Nitesh Malhotra
1
* and Aksh Chahal
2
*
1
Ph.D Scholar, Department of Physiotherapy, Shri Jagdishprasad Jhabarmal Tibrewala University, Churela,
Rajasthan 333001
2
Department of Physiotherapy, Shri Jagdishprasad Jhabarmal Tibrewala University, Churela, Rajasthan
333001 India
ABSTRACT
The aim of the present investigation is to depict the interventions of pelvic oor exercises in urinary incontinence. The
present study deals with the employment of pelvic oor exercises in subjects of varying age group from 30-60 years.
Tools employed for the study are B-SAQ validation, the Bladder Control Self-Assessment Questionnaire (B-SAQ) and
1 Hr pad test which was working as outcome measure. The study was designed to investigate the effect of pelvic oor
exercises on symptoms and botherness caused by urinary incontinence and achieving continence level was marked
through pad test. Results con rmed that there was a signi cant improvement in the symptoms scores of experimental
group in which pelvic oor muscles were employed in contrast with the control group. Pelvic oor muscles should be
done under the supervision of physiotherapist as geriatric population needs some external support in order to complete
the pelvic oor exercise protocol.
681
Medical
Communication
Biosci. Biotech. Res. Comm. 11(4): 681-686 (2018)
INTRODUCTION
Urinary incontinence is commonest problem in old age
affecting social, psychological and physical daily activi-
ties. The most prevalent urinary incontinence amongst
females is Stress urinary incontinence especially at
the age between 30-60 years. Generally it is believed
these reduced in muscle strength of urethra and muscle
around the sphincter is responsible for causing inconti-
nence. The intension of doing pelvic oor exercises is
to increase maximal urethral pressure and also increase
in re ex contractions sphincteric unit which can sus-
tain the rise in the intraabdominal pressure. Pelvic oor
muscle training exercises is the recognized and preferred
ARTICLE INFORMATION:
Corresponding Authors: malhotra.nitesh@gmail.com,
aksh.chahal@gmail.com
Received 12
th
Aug, 2018
Accepted after revision 21
st
Nov, 2018
BBRC Print ISSN: 0974-6455
Online ISSN: 2321-4007 CODEN: USA BBRCBA
Thomson Reuters ISI ESC / Clarivate Analytics USA
Mono of Clarivate Analytics and Crossref Indexed
Journal Mono of CR
NAAS Journal Score 2018: 4.31 SJIF 2017: 4.196
© A Society of Science and Nature Publication, Bhopal India
2018. All rights reserved.
Online Contents Available at: http//www.bbrc.in/
DOI: 10.21786/bbrc/11.4/19

Nitesh Malhotra and Aksh Chahal
682 THE EFFECTIVENESS OF PELVIC FLOOR EXERCISES ON SYMPTOMS IN FEMALES BIOSCIENCE BIOTECHNOLOGY RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS
conservative treatment for urinary incontinence, (Saps-
ford et al. 2001, Ferreira et al. 2004, Sinclair et al. 2011,
Kılıcin et al. 2016 and Aarthi et al., 2018).
Exercises for pelvic oor were introduced in 1948 by
Kegel, till date many randomized controlled studies and
systematic reviews have supported the ef cacy of these
exercises, (Cavkaytar et al. 2014). Many researchers
have reported that more than 68.4% of the women suf-
fered from SUI while 41.2% of the women reported with
mixed urinary incontinence, both showed improvement
after 8 weeks of Kegel’s exercises. The incidence of uri-
nary incontinence in female subjects in a Turkish com-
munity was determined and stress urinary incontinence
was found to be higher i.e. 33.7 % than any other type
of incontinences in females of different age groups. This
was explained through observational studies, based on
questionnaires, where it was found that out of total of
192 subjects having incontinence, 45.5% had stress uri-
nary incontinence (SUI), 19.8 % had urge urinary incon-
tinence and 34.6% had mixed incontinence (Bhanupriya
et al. 2015 and Kılıcin et al. 2016).
In the previous studies as explained with different
outcome measures and exercise protocols including
other intervention to enhance the muscle contraction
like biofeedback, duration and number of contraction
per day can also be a cause for difference in results
output. Therefore pelvic oor exercises are accepted as
an ef cient intervention for SUI, many queries related
to protocol adapted are still not yet explained. Other
adjunct treatment like interferential therapies did not
prove bene cial over pelvic oor exercises in SUI as
recently reported by Aarthi et al. 2018).
For application of a competent treatment concern
should be not only towards the pathology but also
towards the social, socio-economical status and emo-
tional aspect. Earlier surgical intervention was usually
considered as foremost choice of treatment, last few
years inclination towards conservative treatment has
increased. As per the opinion from The International
Continence Society, conservative treatment should be
the rst choice in incontinent patients (Dumoulin et al.
2016).
Researchers also employed different type of exer-
cises protocol for primiparous women and their sexual
ef cacy by employing 8 weeks of pelvic oor exercises
and found improvement in the outcome measure and
strength of pelvic oor muscles (Luginbuehl et al. 2015,
Malhotra et al 2018). Aforementioned studies employed
for Pelvic oor exercises combination with additional
treatment but there is limited study on the age group 30
– 60 years of ages. Therefore, there is need to determine
that whether the stress urinary incontinence can alone
be treated with PFMT on different age groups. The aim
of the study is to evaluate the effectiveness of pelvic
oor muscle exercise in female subjects with different
age groups having stress urinary incontinence
MATERIAL AND METHODS
The 42 female subjects between the ages of 30-60 were
included in the study and were divided into two groups,
Control (Group A) & Experimental (Group B) and. The
study was performed at RLJT Hospital & Research Cen-
tre, Jhunjhunu. The group allocation was done blinded
through randomly and data acquisition, data reduction,
data analysis was been blinded, the demographic data
of name, age, height weight and BMI were recorded
subjects present with stress urinary incontinence based
on patients history ,both parous and nulliparous , pre
and post menopausal and hemodynamicaly stable and
physically t for therapeutic exercises these subjects
who were included in study, subjects having any his-
tory of organ prolapse ,suffering from vaginal or urinary
tract infection, tumors or infectious disease or under
some kind of medications affecting incontinence were
excluded. Total study period was for 8 weeks, readings
were taken at baseline, on 4
th
week and 8
th
week of the
study. Experimental groups were asked to come are to
come every weekends and perform the exercise and fol-
low up while control group B were only explained the
exercises. Also both groups were asked to follow up on
4
th
and 8
th
weeks.
B-SAQ validation, the Bladder Control Self-Assess-
ment Questionnaire (B-SAQ) and 1 Hr pad test was
employed as outcome measure, following the method of
Sahai et al (2014). The B-SAQ contained 8- questions
that assessed the symptoms such as number of times a
patient is required to void, dif culty in holding urine,
nocturia and urine leaks, for which there were associ-
ated scores. Responses to both were scored on a 4-point
Likert scale. Total of both the score can give a signi cant
illustration of patients to seek help or medical advice.
1 hour pad test: the test was performed on all the
female subjects, where they were given pre-weighed
pads and were asked to wear the same, few subjects
were requested to wear two pads due to increased symp-
toms of incontinence. All subjects were asked to drink
500 ml of plain water at room temperature in 15 min-
utes of span, following which they asked to conduct
certain activities like simple walking, climbing up and
down a ight of stairs, standing up-down from sitting
(10 times), cough vigorously (10 times), on spot jog for
1 minute, pick up objects with bending (5 times) and
washing hands in running water (1 minute). All patients
were strictly asked not to void their bladder for 1 hour
and later the pads were weighed, for which the calcula-
tions were done on the basis of pad weight in grams i.e.
Nitesh Malhotra and Aksh Chahal
BIOSCIENCE BIOTECHNOLOGY RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS THE EFFECTIVENESS OF PELVIC FLOOR EXERCISES ON SYMPTOMS IN FEMALES 683
1-10 gms signi ed mild incontinence, 11 to 50 gms sig-
ni ed moderate and more than 50 gms indicated severe
incontinence respectively.
Patients were explained about the anatomy and phys-
iology of pelvic oor muscle a group class was conducted
for both the groups on another day was an live demon-
stration video to explain how to perform the exercises in
the protocol, also exercises in three different position i.e.
Lying, sitting and standing an muscle contraction and
stopping while passing the urine For experimental group
the patients were explained and asked to perform correct
pelvic oor muscle exercise in three different positions:
Lying down supine with one pillow below the hips, sit-
ting on chair and standing with legs both slightly kept
apart. Patients were asked to perform exercises in lying
position for rst two weeks 10- 15 repetition. Contract-
ing the muscle with a hold of 2-4 seconds of hold in
each contraction without holding breath they were also
asked to perform 2-3 sets per , with minimum of 20-30
contractions in a day. At 3
rd
and 4
th
week there was an
addition of sitting position, number of set remained the
same, by increasing the number of repetition to 30-40
in each set and 60-120 contractions over all through-
out the day. Remaining 4 weeks, the protocol was added
with an additional position of standing and keeping the
number of sets as constant, the contraction per set was
increased to 50-60 per set and minimal number of con-
tractions per day ranged from 150 to 180. Telephonic
and message reminders were sent on phone to encour-
age the subjects twice a week and queries were noted
down and answered either on telephone or during the
follow up visits.
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
The data analysis was done with help of SPSS software
version 19 was applied , To isolate the variable that dif-
fer from the others Turkey test was applied for multiple
comparison analyze the mean and standard deviation
within group and ANOVAs test were applied to calcu-
late the difference between groups. Forty subjects were
included in the study having a mean age of 46.05±6.04
and were divided in experimental and 41.15±7.12 in
control group. The mean height in respective groups
were 162±6.69 cm and 58.55±5.09 cm, mean weight was
64±6.50 and 67.3±5.54 in kg, The mean BMI was also
calculated as 25.23±2.44 and 24.63±2.13 respectively
for experimental and control group.
Amongst the 42 participant in the study, 2 women
could not complete the study there was no signi cant
difference seen in Group A (Control) before treatment
and after treatment, but there was a statistical difference
seen amongst Group B (Experimental Group) subjects at
4th week and 8
th
week of treatment.
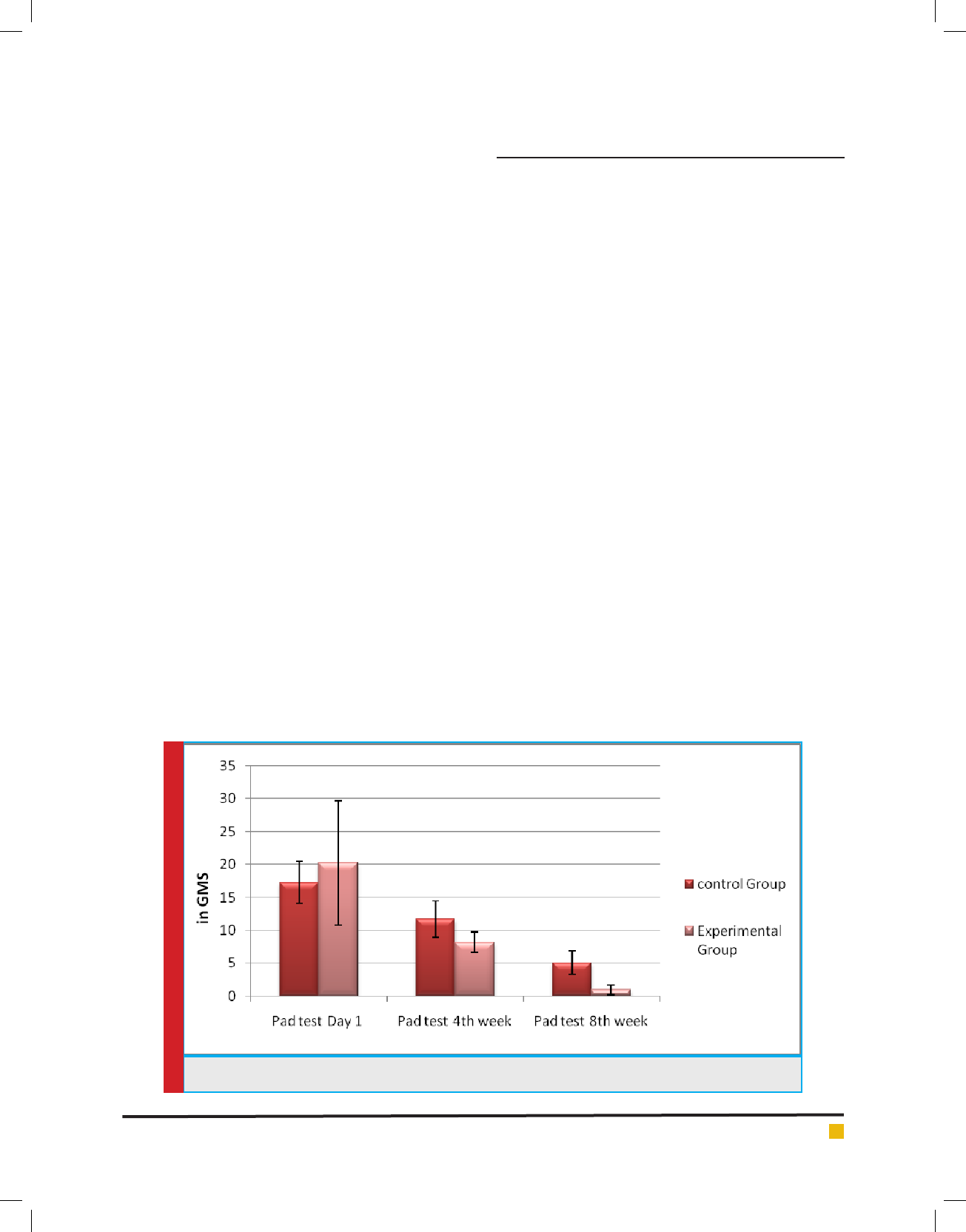
As shown in gure I, the pad test demonstrates the
signi cant improvement at 4
th
and 8
th
week for patient
who was engaged in exercises and with regular follow-
ups Group B, there was an improvement seen in the pad
test performed for women in control group (Group A)
but was not statistically signi cant.
Explaining through gure 1 & table 2 there was no
signi cant difference found in between baseline data
and 4
th
week and at end of 8
th
week in Group A (Control
group), similarly when compared within intergroups as
explained through table 3, there was a signi cant dif-
FIGURE 1. Illustrates about the mean and standard deviation difference in the score in Pad test
Nitesh Malhotra and Aksh Chahal
684 THE EFFECTIVENESS OF PELVIC FLOOR EXERCISES ON SYMPTOMS IN FEMALES BIOSCIENCE BIOTECHNOLOGY RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS
Table 1. Illustrates the mean and standard deviations
in demographic data.
Characteristics Group A Group B
Age (Mean ± SD) 41.15±7.12 46.05±6.04
Height (In cm) (Mean ± SD) 158.55±5.09 162±6.69
Weight(In kg) (Mean ± SD) 67.3±5.54 64±6.50
BMI (Mean ± SD) 24.63±2.13 25.23±2.44
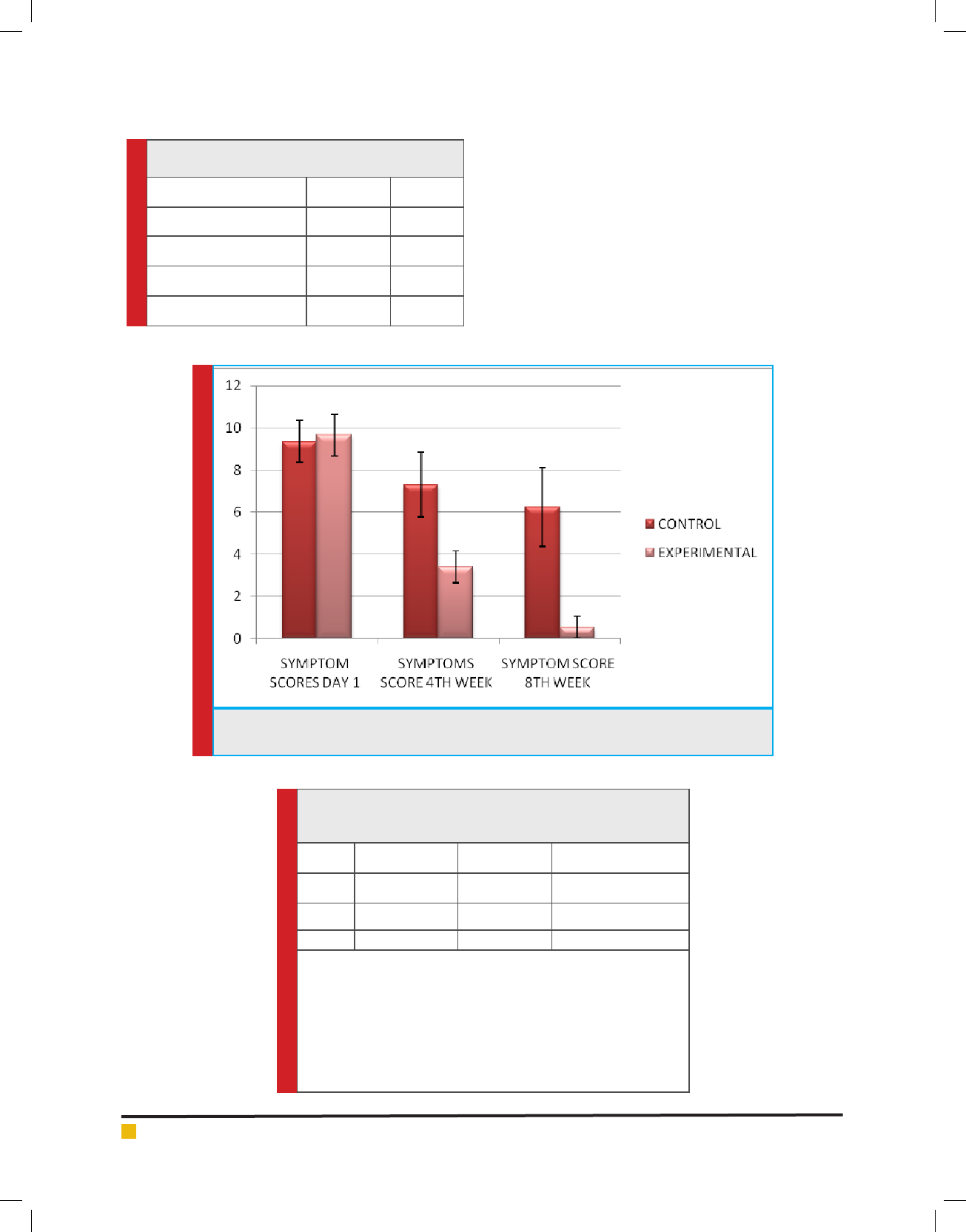
FIGURE 2. Explains about the mean and standard deviation difference in the symptom score in
B-SAQ
Table 2. As explained in the above table comparison illustrates the
pad test day 1 proved to be statistically signi cant for 4th week
and 8th week
Statistics Control group Experimental group
Day 1 Median (Q1,Q3) 17(15, 18) 19(13, 23)
4
th
week Median (Q1,Q3) 11(9,13) 8(7,9) ,@
8
th
week Median (Q1,Q3) 5(3,27) 1(0,1.75) ,,#
Q1: rst quartile, Q3: third quartile
. Statistically signi cant (p <0.001) reductions at 4th week and 8th week compared
to Day 1 in patients with Experimental group
. Statistically signi cant (p <0.001) reduction from week 4th to 8th week in patients
with Experimental group
@. Statistically signi cant (p <0.001) differences in mean pad test scores between
Control group & Experimental group regimes at 4th week
#. Statistically signi cant (p <0.001) differences in mean pad test scores between
conventional and advance physiotherapy regimes at 8th week
ference seen in pad test results for experimental groups,
bringing the P at signi cant value of <0.001.
Explaining through gure 2 the result signi es that
symptoms score of B-SAQ were signi cantly improved
from day 1 4
th
week and at 8
th
for group B week but
there no signi cant improvement in the scores for con-
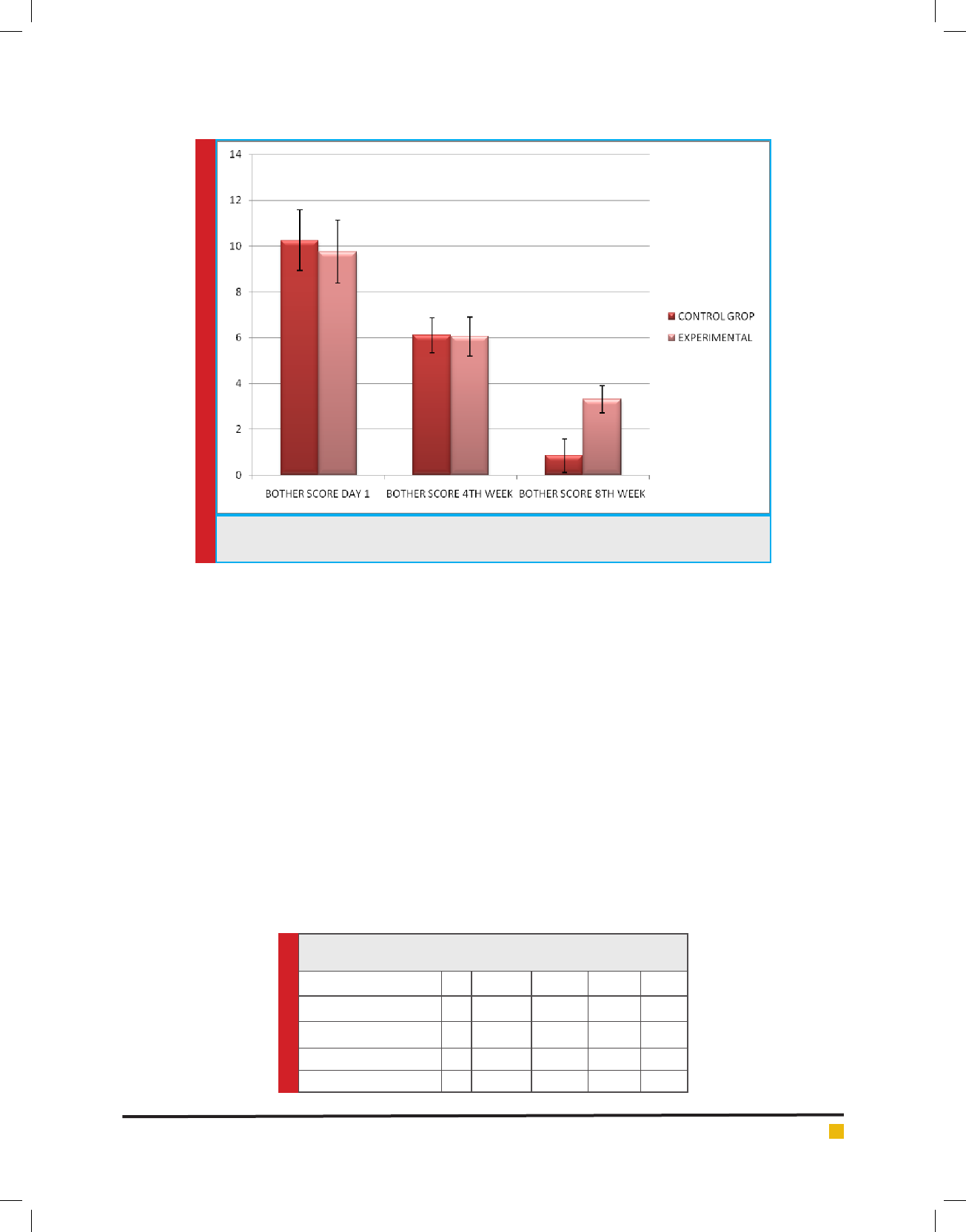
trol group, gure 3 explains about the bothers score in
B-SAQ in shows neither the experimental group nor the
control group brings a signi cant change.
The pelvic oor muscles constitute the core muscles
of the pelvis; the study was designed to investigate the
effect of pelvic oor exercises on symptoms and bother-
Nitesh Malhotra and Aksh Chahal
BIOSCIENCE BIOTECHNOLOGY RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS THE EFFECTIVENESS OF PELVIC FLOOR EXERCISES ON SYMPTOMS IN FEMALES 685
FIGURE 3. Explains about the mean and standard deviation difference in the bother score in
B-SAQ
ness caused by urinary incontinence and achieving con-
tinence level were marked through pad test. There was
a signi cant improvement in the symptoms scores of
experimental group in contrast with the control group.
The bother score when compared in both the groups at
baseline and 4
th
week there was no statistical signi -
cant difference seen. The present study showed a signi -
cant decrease in symptoms and levels of incontinence,
also there was an improvement reduction in frequency,
urgency and nocturia in experimental group when
compared to the control group in a 12 weeks protocol.
Supervised protocol for pelvic oor exercises proved
to be a most effective method for improvement in the
symptoms in urinary incontinence. In a study by Sha-
ron et al. (2010), it has been explained that this sever-
ity impacted the quality of life it was found that 30
% of female subjects and 18% of male subjects were
reported with micturition dribbling and severity from
mild to moderate, also female were more affected than
men associated with other variable representing increase
in the micturition dribble .this study showed that the
increase in symptoms were disturbing quality of life. A
signi cant improvement was seen in quality of life and
self esteem frequency of urination and amount of urine,
(Johromi et al. 2014).
In a study performed by Ali et al. (2011) the effect of
Kegels exercises on women aged between 25-54 years
suffering from urinary incontinence was carried out, it
was found that the average score before administering
the exercises was 53.15 and after the treatment there was
a signi cant improvement to 73.82, bringing the signi -
cant level to p=0.0001. A study performed by another
researcher on 30 patients affected with urinary inconti-
nence in Imam Reza and Gharazi hospital at Sirjan city
Iran with a aim to investigate the effect of kegels exer-
cises on incontinent female subject for 3 month showed
Table 3. Illustrates the mean and standard deviation questionnaire
at different time interval for both control and experimental group
Source of Variation DF SS MS F P
Between Subjects 19 59.500 3.132
Between Treatments 5 1254.367 250.873 230.716 <0.001
Residual 95 103.300 1.087
Total 119 1417.167 11.909

Nitesh Malhotra and Aksh Chahal
686 THE EFFECTIVENESS OF PELVIC FLOOR EXERCISES ON SYMPTOMS IN FEMALES BIOSCIENCE BIOTECHNOLOGY RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS
a signi cant improvement in reduction frequency of uri-
nation and was lessened by 30 % concluded that kegels
exercises can become a suitable method to treat urinary
incontinence, (Baba et al. 2006). Through the present
study we explain that it is better to do pelvic oor exer-
cises under supervision of a physiotherapist, learning of
the correct technique of exercises to strengthen the mus-
cle for required results, 2 months of exercises protocol
results in the improving the strength and symptoms.
Limitation of the study : Considering small sample
size dif cult to draw and rm conclusion Explaining
and recognizing the correct pelvic oor muscle and
skilled exercises learned by patient as treatment can
result in positive effect but if not can result in negative
effect increasing frequency of urination and dribbling.
CONCLUSION
Pelvic oor muscle exercises can be considered as an
empowerment methods for improvement in the symp-
toms and bother score also improving on pelvic oor
muscle strength. So it is recommended that these types
of exercising protocol can be utilized in improving the
strength and quality of life in patient suffering from
incontinence
REFERENCES
Aarthi M, Sankarganesh A. and Sivakumar V.P.R. (2018) Inter-
ferential Therapy Versus Pelvic Floor Exercise for the Man-
agement of Stress Urinary Incontinence in Women. Journal of
physiotherapy research Vol.2 No.1(1): Pages 1-7
Baba Mohammadi H and Khalili H. (2006) The effect of pelvic
oor exercise in the treatment of urinary incontinence in the
elderly, Ghrzy and Imam Reza hospitals in Sirjan city. Yazd
Journal of Medical Sciences and Health Services.Vol 3: Pages
61.
Bhanupriya, Singh N. and Goel N.(2015) Prevalence and Risk
Factors of Urinary Incontinence Among Women Delivering in
a Tertiary Care Center of Northern India. Obstetrics & Gynecol-
ogy International Journal.Vol.3 No. 4: Pages 1-4
Cavkaytar S.1., Kokanali M.K., Topcu H.O., Aksakal O.S. and
Do
g
˘anay M. (2015) Effect of home-based Kegel exercises on
quality of life in women with stress and mixed urinary incon-
tinence. Vol.35 No.4:Pages 407-410
Dumoulin C., Hunter K.F., Moore K., Bradley C.S., Bur-
gio K.L., Hagen S., Imamura M., Thakar R.,Williams K. and
Chambers T. (2016) Conservative management for female uri-
nary incontinence and pelvic organ prolapse review 2013:
Summary of the 5th International Consultation on Inconti-
nence. Neurourology and urodynamics .Vol. 35 No.1:Pages
15-20
Ferreira P.H., Ferreira M.L. and Hodges P.W. (2004) Changes in
recruitment of the abdominal muscles in people with low back
pain ultrasound measurement of muscle activity. Spine. Vol.
29:Pages 2560–2566
Jahromi M.K., Ramezanli S., Taheri L. and Rahmanian A. (2014)
Management of Stress Urinary Incontinence in Females with
Diabetic Mellitus (Type 2). Journal of Diabetes & Metabolism.
Vol 5 No.3: Pages 1-5
Kılic M. (2016) Incidence and risk factors of urinary inconti-
nence in women visiting Family Health Centers; Springer Plus.
Vol.5 No.1,1331:Pages 1-9
Luginbuehl H., Lehmann C., Baeyens J.P.,Kuhn A. and
Radlinger L (2015) Involuntary re exive pelvic oor muscle
training in addition to standard training versus standard train-
ing alone for women with stress urinary incontinence: study
protocol for a randomized controlled trial : BioMed Central Vol
16 No. 524: Pages 1-8
Malhotra N. and Chahal A. (2018) Effect of pelvic oor exer-
cise on non-speci c lower back pain in post-partum women
Biosciences Biotechnology Research Communications Vol.11
No. 3: Pages 469-475
Sahai A, Dowson C., Cortes E., Seth J., Watkins J., Khan
M.S.,Dasgupta P.,Cardozo L.,Chapple C.,De- Ridder D.,Wagg
A. and Kelleher C. (2014) Validation of the bladder control self-
assessment questionnaire (B-SAQ) in men. British Journal of
Urology Vol.113 No.5: Pages 783-788
Sapsford R.R, Hodges PW, Richardson CA, Cooper DH, Mark-
well SJ and Jull GA. Co-activation of the abdominal and pelvic
oor muscles during voluntary exercises. Neurourology and
Urodynamics.Vol. 20: Pages 31–42.
Shah Ali S. H, Kashanian M. and Azari A. (2011) The effect of
pelvic oor exercises on quality of life in women with stress
urinary incontinence. The Bring knowledge Magazine. Vol.15:
Pages 159-162
Sinclair A.J. and Ramsay I.N. (2011) The psychosocial impact
of urinary incontinence in women.The Obstetrician & Gynae-
cologist.Vol. 13: Pages 143–148.
Tennstedt S.L, Chiu G.R., Link C.L., Litman H.J., Kusek J.W.
and McKinlay J.B.(2010 ) The effects of severity of urine leak-
age on quality of life in Hispanic, white and black men and
women: the Boston community health (bach) survey.Urology.
Vol. 75No1: Pages 27-33