Agricultural
Communication
Biosci. Biotech. Res. Comm. 10(1): 219-229 (2017)
Agronomic responses of maize to de cit and adequate
irrigation and levels of chemical fertilizers and bio
fertilizers
Safar Nasrolahzadeh
1
, Ali Shirkhani
2
* and Saeid Zehtab Salmasi
1
1
Department of Eco-physiology, Faculty of Agriculture, University of Tabriz, Tabriz, Iran
2
Crop Horticulture Research Department, Kermanshah Agricultural Resources Research and Education Center
(AREEO), Iran
ABSTRACT
In 2014, over 180 thousand hectares and 1.223 million tons of Maize produced in Iran. However Iran is a major importer of Maize
in the world. Kermanshah is located in Western Iran and Maize is the most important crop after wheat. Maize production in this
province has two major problems: water shortage caused and low percentage of organic matter in soil. In this research, effects of
vermicompost and Azotobacter as a boi- fertilizers and chemical fertilizers on yield and yield components of Maize under normal
and de cit irrigation was investigated in two sites in 2014 and 2015. Site included normal irrigation and de cient irrigation (65%
optimum water requirement) and each site was conducted as the factorial split plot in a randomized complete block design with three
replications. Treatments included Azotobacter in the main plots (non-inoculation and inoculation), vermicompost (consuming 0, 2, 4
and 6 ton/ha) and chemical fertilizers included N,P,K in tree levels (100% recommendation based on soil test, 50% recommendation
and no fertilizer) in the sub plots. Results showed that grain yield, 1000 kernels weight, number of kernels per row, number of kernels
per ear and plant height were decreased by de cient irrigation. Use of Azotobacter and vermicompost signi cantly increased these
traits in normal and de cit irrigation, Results also showed that using 6 ton/ha of vermicompost and Azotobacter in soil, 50% of the
corn fertilizer supplied. The results showed that combined use of bio-fertilizers with chemical fertilizers increased the yield and yield
component. Therefore the uses of biological fertilizers signi cantly reduce the consumption of chemical fertilizers and reduce the
adverse environmental effects. So biofertilizers could be considered as a suitable substitute for chemical nitrogen fertilizer in organic
agricultural systems. On the other hand from this experiment, application of vermicompost in combination with chemical fertilizers
showed better performance than only chemical fertilizers, even in 100% recommendation based on soil test treatments.
KEY WORDS: MAIZE, VERMICOMPOST, AZOTOBACTER, CHEMICAL FERTILIZER, INM, YIELD
219
ARTICLE INFORMATION:
*Corresponding Author: Ali.shirkhani@gmail.com
Received 27
th
Dec, 2016
Accepted after revision 24
th
Feb, 2017
BBRC Print ISSN: 0974-6455
Online ISSN: 2321-4007 CODEN: USA BBRCBA
Thomson Reuters ISI ESC and Crossref Indexed Journal
NAAS Journal Score 2017: 4.31 Cosmos IF : 4.006
© A Society of Science and Nature Publication, 2017. All rights
reserved.
Online Contents Available at: http//www.bbrc.in/

220 AGRONOMIC RESPONSES OF MAIZE TO DEFICIT AND ADEQUATE IRRIGATION BIOSCIENCE BIOTECHNOLOGY RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS
Nasrolahzadeh, Shirkhani and Salmasi
INTRODUCTION
Maize (Zea mays L.) is an important crop that used as
food, feed and industrial products. Maize is the third
most important cereal after wheat and rice all over the
world and the world’s largest grain crop in term of total
production on a MT basis. Maize is currently produced
on nearly 184 million hectares in 125 developing coun-
tries and is among the three most widely grown crops in
75 of those countries (FAOSTAT, 2015).
Kermanshah is located in western Iran and Maize
is the most important crop after wheat, grown on an
area of 45,000 ha with the production of 382,500 tones
with 8500 kg ha-1 average grain yield; the third and
rst place of Iran for area harvested and mean yield,
respectively. Maize production in this province has two
major problems: water shortage caused by drought in
recent years and low percentage of organic matter in
soil, which in most areas is less than one percent. Maize
is an irrigated crop in Iran and recent drought periods
in Iran imposed pressure on groundwater resources. The
groundwater is the primary source of irrigation of Maize
production in province and in recent years, the water
storage has gradually decreased in this region mainly
because of increasing annual irrigation and the dry cli-
mate (Agricultural Department of Kermanshah, 2015).
Drought is the most common abiotic environmental
stress limited the production at approximately 25 % of
the world agricultural land. Yield losses include more
than two- thirds of the total damage of abiotic stresses
due to drought, salinity and other factors. Maize, how-
ever, is highly sensitive to drought, speci cally two
weeks prior and post-silking (Tollenaar and Lee, 2011).
Among the abiotic stresses, drought is the most severe
limitation to Maize production. Water stress adversely
affects crop growth and yield in many regions of the
world. One of the most important constraints for agri-
culture is water limitation. Most recently, global warm-
ing may be worsening this situation in most agricultural
region (Jabasingh and Babu, 2014).
The drought stress decreases the Maize yield due to
three main mechanisms: 1- by reducing the amount of
photosynthetic active radiation received by vegetation
canopy (due to decreasing growth of leaves and leaf pre-
mature senescence), 2- by reducing ef ciency of energy
and 3- by reducing the harvest index (due to less allo-
cation of assimilates to crop economic yield) (Hlavinka
and et al., 2009). Adequate water and nutrient supply
are important factors affecting optimal plant growth
and successful crop production. Water stress is one of
the severe limitations of crop growth especially in arid
and semiarid regions of the world as it has a vital role
in plant growth and development at all growth stages
(Taleshi and Osoli, 2015)
The addition of organic matter to the soil usually
increases the water holding capacity of the soil. This
is because the addition of organic matter increases the
number of micropores and macropores in the soil either
by “gluing” soil particles together or by creating favour-
able living conditions for soil organisms. Certain types
of soil organic matter can hold up to 20 times their
weight in water. The consequence of increased water
in ltration combined with a higher organic matter con-
tent is increased soil storage of water (Reicosky, 2005).
Hudson (1994) showed that for each 1-percent
increase in soil organic matter, the available water hold-
ing capacity in the soil increased by 3.7 percent. Soil
water is held by adhesive and cohesive forces within
the soil and an increase in pore space will lead to an
increase in water holding capacity of the soil. As a
consequence, less irrigation water is needed to irrigate
the same crop. The use of biofertilizer in condition of
environmental stress can decrease effects of stress and
enhance soil water holding capacity, root growth and
yield (Li and Ni, 1996). By increasing soil organic mat-
ter content, composts improve soil physical properties
such as structural stability, total porosity and hydrau-
lic conductivity, aggregate formation and water hold-
ing capacity. However, the effect of composts on plant
available water varies, depending on soil type, the type
of compost and application rate (Nguyen et al., 2012).
Compost produced from organic dairy cattle manure
can result in higher soil water content under Kentucky
bluegrass (Poa pratensis L.) after 8 days without addi-
tion of water (Johnson et al. 2009). Also Gholipoor et
al. (2014) reported that vermicompost can alleviate the
deleterious effects of drought stress on grain yield of
chickpea. Moreover, the use of organic matter such as
animal manures, compost and vermicompost has long
been recognized in agriculture as bene cial for plant
growth and yield and the maintenance of soil fertility.
The new approaches to the use of organic amendments
in farming have proven to be effective means of improv-
ing soil structure, enhancing soil fertility and increas-
ing crop yields. Organic matter is excellent source of
plant-available nutrients and their addition to soil could
maintain high microbial populations and activities. In
recent years vermicompost an organic amendment has
been selectively and effectively used in soil conditioning
and in varying degrees to in uence the soil properties.
Among various sources of organic matter, vermicom-
posts have been recognized as having considerable
potential as soil amendments. Vermicomposts are prod-
ucts of organic matter degradation through interactions
between earthworms and microorganisms. The process
accelerates the rates of decomposition of the organic
matter, alters the physical and chemical properties of the
material, and lowers the C:N ratio, leading to a rapid

BIOSCIENCE BIOTECHNOLOGY RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS AGRONOMIC RESPONSES OF MAIZE TO DEFICIT AND ADEQUATE IRRIGATION 221
Nasrolahzadeh, Shirkhani and Salmasi
humi cation process in which the unstable organic mat-
ter is fully oxidized and stabilized (Arancon et al., 2005).
The cost of inorganic fertilizers is very high and
sometimes it is not available in the market for which the
farmers fail to apply the inorganic fertilizers to the crop
eld in optimum time. On the other hand, the organic
manure is easily available to the farmers and its cost is
low compared to that of inorganic fertilizers. One of the
main practices in sustainable agriculture is application of
biologic and organic fertilizers in order to provide plants
nutrients and to reduce the need for chemical fertilizers.
Vermicompost is an important type of non chemical fer-
tilizers. Bio-fertilizer is a densely populated preservative
of one or more types of useful terricolous microorgan-
ism, their metabolic phenomenon are used to provide the
nutrients needed by plants, control soil-borne diseases
and maintain the stability of soil structure (Vessey, 2003).
Furthermore, compost has a high nutritional value, with
high concentrations of especially nitrogen, phosphorus
and potassium, while the contamination by heavy metals
and other toxic substances are very low, and also positive
changes have been reported in the quality of wheat our,
because of increasing the amount of gluten after compost
treatment (Gopinath, 2008).
Many attempts have been tried to replace a part of
those harmful fertilizers by biofertilizer. Integrated
nutrient management strategies involving chemical fer-
tilizer and biofertilizer have suggested enhancing the
sustainability of crop production (Esmailpour et al.,
2013). Previous studies showed that the combination of
compost with chemical fertilizer further enhanced the
biomass and grain yield of crops (Sarwar et al., 2008).
Also the synergistic effect of combining farm and min-
eral fertilizers application has been con rmed. Kmetova
and Kovacik (2014) reported where the joint application
of vermicompost and nitrogen fertilizer increased the
rice crop of 15.6 % compared to the only application of
nitrogen fertilizer.
On the other hand, El-Afry et al (2012) reported that
application of Azotobacter in Wheat, act as protective
factors against irrigation water de cit and could over-
come the negative effects of drought stress. The use of
rhizosphere associated microorganisms as biofertilizers
is now being considered as having potential for improv-
ing plant productivity (Vessey, 2003). Biofertilizers are
able to x atmospheric nitrogen in the available form
for plants. Rhizosphere-associated nitrogen xing and
phosphate-solubilizing bacteria have been used as inoc-
ulum for nonlegume crop species such as Maize, rice,
wheat, and sugarcane (Mehnaz and Lazarovits, 2006).
Many attempts have been tried to replace a part of those
harmful fertilizers by biofertilizers in Maize to get yield
of a good quality without loss in its quantity (Kholy
et al., 2005). Inoculation of Maize and wheat seeds with
Azotobacter and Azospirillum increased plant growth,
nutrients uptake and yield (Dobbelaere, et al., 2001). El-
kholy and Gomma have succeeded to reduce the recom-
mended dose of chemical fertilizers in Maize and millet
by 50%, using biofertilizers without signi cant yield
loss. A pot experiment was conducted by Mudenoor et
al., (2007), to study the effects of seed treatment of micro
nutrient supplemented Azospirillum biofertilizer on dry
mater production and yield of Maize at Karnataka and
result indicated high shoot and root dry matter with seed
treatment of Azospirillum. Azospirillum spp. are com-
monly isolated bacteria from the rhizosphere of various
grasses and cereals and are well characterized as plant-
growth-promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR). Many pub-
lished reports exist on the use of Azospirillum spp. for
inoculation of cereals (Mehnaz and Lazarovits, 2006). In
France, Azospirillum lipoferum is used as commercial
fertilizer for Maize under the trade name AzoGreen-m
(Jacoud et al, .1999). Integrated plant nutrient manage-
ment (INM) is the combined use of mineral fertilizers
with organic resources such as cattle manures, crop resi-
dues, urban/rural wastes, composts, green manures and
biofertilizers (Kemal and Abera, 2015).
Various studies revealed that sustainable yield and
yield related parameters of maize are signi cantly
improved by integrated nutrient management (INM)
practices. INM including vermicompost showed best
results in yield parameters of maize like number of
grains per cob, weight of the cob, 100 seed weight and
yield (Kannan et al., 2013). Also Kemal and Abera (2015)
reported application of recommended dose of inor-
ganic fertilizer along with vermicompost at 6 ton/ha to
maize not only enhanced productivity of maize but also
improved soil fertility in terms of higher available N,
P, K and organic carbon content over the control and
recommended N, P and K, moreover.The objective of this
study was to determine the effect of biofertilizers and
chemical fertilizers on yield and yield components of
Maize under normal and de cit irrigation condition in
western Iran region and looking for the
best biological
treatments could be applied to the maize to get a high yield
in addition to
keep our environment clean and safe.
MATERIAL AND METHODS
Characterization of the experimental area
Field experiments were conducted for two years (2014–
2015) at the agricultural research farm, Agricultural and
Natural Resources Research Centre in Kermanshah, Iran.
This farm is located at 34.08 N, 46.26 E, 1345 m altitude,
silty clay soil, pH=7.5-8, 450 mm precipitation Medi-
terranean climate. Table 1 gives the properties of the
experimental eld.
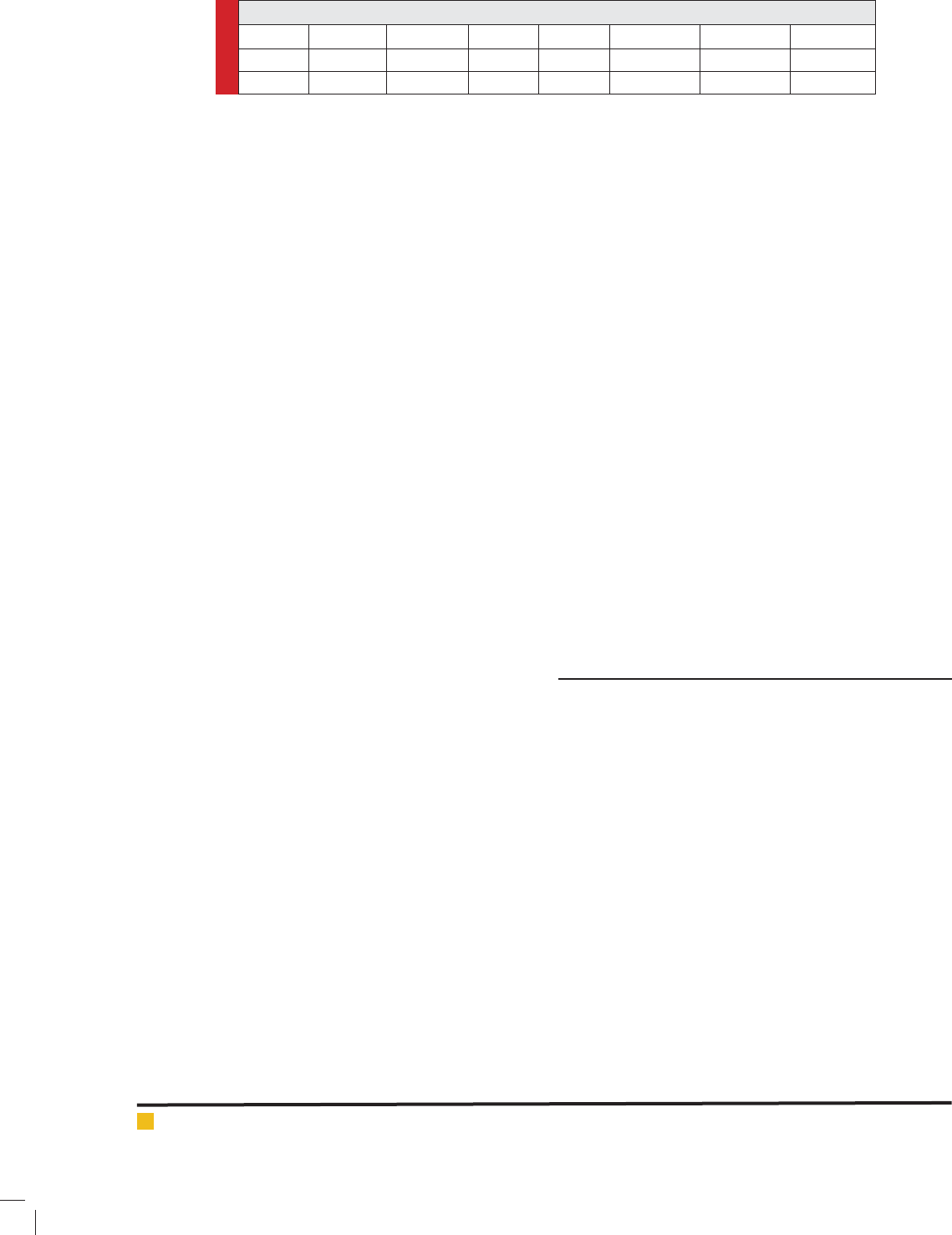
Nasrolahzadeh, Shirkhani and Salmasi
222 AGRONOMIC RESPONSES OF MAIZE TO DEFICIT AND ADEQUATE IRRIGATION BIOSCIENCE BIOTECHNOLOGY RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS
Application of the treatments
In this research, effects of vermicompost and Azotobac-
ter as a boi- fertilizers and chemical fertilizers on yield
and yield components of Maize under normal and de cit
irrigation was investigated in two sites. Sites included
normal irrigation and de cient irrigation (65% opti-
mum water requirement) and each site was conducted as
the factorial split plot in a randomized complete block
design with three replications and three factors. Treat-
ments included Azotobacter in the main plots (non-
inoculation and inoculation), vermicompost (consuming
0, 2, 4 and 6 ton/ha) and chemical fertilizers included
N,P,K in tree levels (100% recommendation based on soil
test, 50% recommendation and no fertilizer) in the sub
plots. The Maize cultivar used was “KSC 704” (a grain
Maize cultivar that is commonly planted in the region).
Entire experimental area was chisel-plowed in the fall
and plowed in the spring before planting. Soil samples
were taken before the imposition of treatments and were
analyzed for physical and chemical characteristics.
Experiment plots were seeded with 75 cm row to row
distance and plant density was 75000 plant/ha (conven-
tional plant density). Maize was planted in May 2014
and 2015 and by experimental planter. Seeds were sown
5 cm deep. Before planting 7g inoculation with 1g had
107 active and live bacteria, were used inoculating
seeds. Seeds which must mix with Azotobacter soaked
with sugar water with concentration 2% and with ratio
2kg inoculation 100kg seeds. Plot dimensions using in
this study will be 7m long by 3m wide, each plot will
be consisted four rows spacing at 0.75m. Vermicompost
used in this study has been produced by the activity
of Eisenia foetida worm produced from cattle manure.
The amount of acidity and electrical conductivity of its
aqueous solution are 7.5 and 14.65 dS/m, respectively.
Phosphorus and potassium fertilizers were mixed by soil
before cultivation. A quarter of urea fertilizer at plant-
ing, one-fourth of 6 to 8 leaf stage, and the remaining
fertilizer was applied prior to owering, before planting
all quantities of vermicompost was mixed with soil to a
depth of 30 cm. Weeds were removed manually across
the growing season.
Irrigation
Maize is an irrigated crop in Iran; therefore, it is not
dependent on the seasonal rainfall. Irrigations were car-
ried out at 7 day intervals. Water treatments (de cit and
adequate irrigation) were initiated during middle veg-
etative growth stage (around V6). Beginning on these
dates, water was applied at weekly intervals based on
the amount of evapotranspiration for the previous week
as determined by the on-site weather station using a
modi ed version of the Penman FAO equation (O’Neill
et al., 2004). The adequate irrigation treatment received
the amount of water required to fully replace the pre-
vious week evapotranspiration while the de cit treat-
ment received 65 % this amount. This was continued
throughout the remainder of the growing season. Water
entrance to plots was measured by counter and Hydro x
irrigation system
Variables
Each plot was harvested at maturity for yield and yield
components. The Maize ears located 6 m2 from each plot
were harvested by hand, then allowed drying at 80°C
to a constant weight and then seed yield was obtained.
Before nal harvesting Maize yield components includ-
ing the number of ears per plant and the number of
seeds per ear were determined on ve randomly selected
plants in the center rows of each plot. 100-seed weight
was measured according to the recommendation of the
International Seed Testing Association (ISTA).
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Grain yield
The yield of maize was signi cantly in uenced by de -
cient irrigation (Table 2); Results showed that during the
both research years, grain yield was decreased from 8.2
ton/ha to 4.4 ton/ha by de cient irrigation. Water de cit
in maize is one of limiting factors of yield and at the
time of pollination, drought may have severe impact on
yield (Moser et al., 2006). These results are consistent with
previous work; Dagdelen et al. (2006) reported that water
de ciency signi cantly affected maize yield and the
highest maize yield was obtained from the full irrigation
treatments. Stone et al. (2001) reported that water de cit
reduces crop growth and morphological characteristics
of maize plant. Pandey et al. (2000) reported that yield
reduction (22.6 - 26.4%) was found with de cit irrigation
and this was associated with decrease in kernel number
and weight. Also Karam et al. (2003) stated that water
de ciency signi cantly reduced dry matter accumulation
and as a result grain yield deceased in maize.
Table 1. Soil characteristics
Depth Cm av.P ppmav.K PpmN%O.C%Mn PpmFe ppmZn ppm
0-3011.66400.080.87.25.90.58
30-607.86400.10.96.43.80.52
Nasrolahzadeh, Shirkhani and Salmasi
BIOSCIENCE BIOTECHNOLOGY RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS AGRONOMIC RESPONSES OF MAIZE TO DEFICIT AND ADEQUATE IRRIGATION 223
Analysis of variance showed that Azotobacter
increased grain yield about 89 kg/ha in all treatments
(Table 4). In addition the use of vermicompost at 2, 4
and 6 ton/ha consistently and signi cantly increased
grain yield in normal and de cit irrigation (Table 4).
Although, application of vermicompost led to increase
in grain yield, the highest grain yield was related to
integrated treatments 6 ton/h vermicompost and 100%
chemical fertilizers recommendation based on soil test.
Results also indicated that the use of 6 ton/ha ver-
micompost and Azotobacter in soil, 50% of the maize
fertilizer supplied. The results showed that combined use
of bio-fertilizers with chemical fertilizers increased the
grain yield. Therefore the uses of biological fertilizers
signi cantly reduce the consumption of chemical ferti-
lizers and reduce the adverse environmental effects.
On the other hand from this experiment, application
of vermicompost in combination with chemical fertiliz-
ers showed better performance than only chemical ferti-
lizers, even in 100% recommendation based on soil test
treatments. It can be stated that the increase in growth
parameters of maize are due to greater availability of
nitrogen in full organic and integrated treatments. In
full chemical treatments most of nitrogen would be
leached from the soil pro le. In addition, high porosity
and water holding capacity of vermicompost that helps
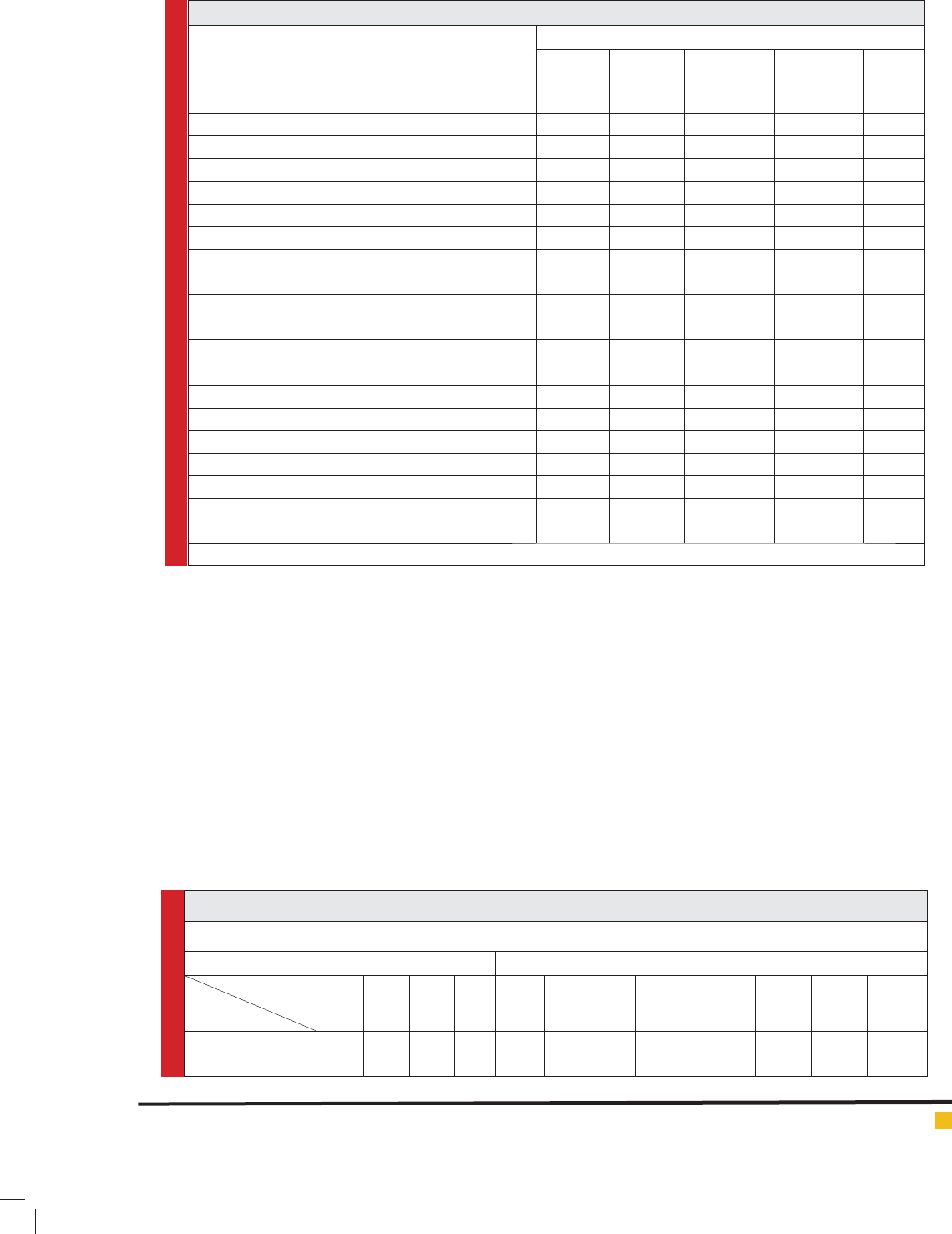
Table 2. AOVA table of fresh and dry yield of data 2014 and 2015 (in brief).
S O V df MS
Yield kernel
weight
Number of
kernels per
row
Number of
kernels per
ear
Plant
height
Replication 2 ns ns ns ns ns
Year 1 ns ns ns ns ns
Year* replication 2 ns ns ns ns ns
Irrigation 1 ** ** * ** **
Error 8 - - - - -
Azotobacter 1 ns ns ns Ns ns
Azotobacter * Irrigation 1 ns ns ns Ns ns
Year*Vermicompost * Irrigation 1 ** ** ** ** **
Error 8 - - - - -
N P K 2 ** ** * ** **
Azotobacter * N P K 2 ns ns ns Ns ns
Irrigation* N P K 2 ** ** ** ** **
Azotobacter *Irrigation* N P K 2 ** ** * ** **
Vermicompost 3 ** ** * ** **
Vermicompost *Irrigation 3 ** ** ** ** **
N P K*Vermicompost *Irrigation 6 ** ** ** ** **
N P K*Vermicompost *Irrigation* Azotobacter 6 ** ** ** ** **
Year* N P K*Vermicompost *Irrigation* Azotobacter 24 ** ** ** ** **
C.V. 8.8 9.6 8.9 10.5 11.1
ns: not- signi cant; * signi cant at 5-% (P<0.05), ** signi cant at 1-% (P<0.01)
Table 3. Effects of chemical fertilizer and vermicompost on yield
Chemical Fertilizers included N P K
100% Recommendation50% RecommendationNo Fertilizer
642064206420
Vermicompost
(ton/ha)
Irrigation
10.710.310.310.210.38.587.375.95.34.4Normal 100%
5.55.45.34.75.34.84.74.14.23.83.12.8De cient 65%

Nasrolahzadeh, Shirkhani and Salmasi
224 AGRONOMIC RESPONSES OF MAIZE TO DEFICIT AND ADEQUATE IRRIGATION BIOSCIENCE BIOTECHNOLOGY RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS
in better aeration and drainage. Moreover use of 6 ton/
ha vermicompost and Azotobacter in treatments with
no chemical fertilizers produced 7 and 4.4 ton/ha grain
yield in normal and de cit irrigation respectively. Appli-
cation of organic manures either alone or integrated
with chemical amendments for maize, performed better
than all amendments tested in laboratory trails studied
by Mujeeb et al. (2010). Recommendation of organic
matter alone with synthetic fertilizers could be helpful
for enhancing stagnant wheat grain yield was reported
by Tahir et al. (2011). Similarly Fanuel and Gifole (2012)
recommended applying combination of compost at 5 ton
ha-1 along with inorganic fertilizer to obtain better yield
of maize.
Nagananda et al., (2010) in their experiments observed
that inoculation of maize with Azotobacter and Azos-
Table 4. Effects of Azotobacter and vermicompost on yield
Azotobacter
InoculationNon-inoculation
64206420
Vermicompost
(ton/ha)
Irrigation
5.14.74.43.94.94.64.33.8Normal 100%
9.58.27.97.39.38.27.87.3De cient 65%
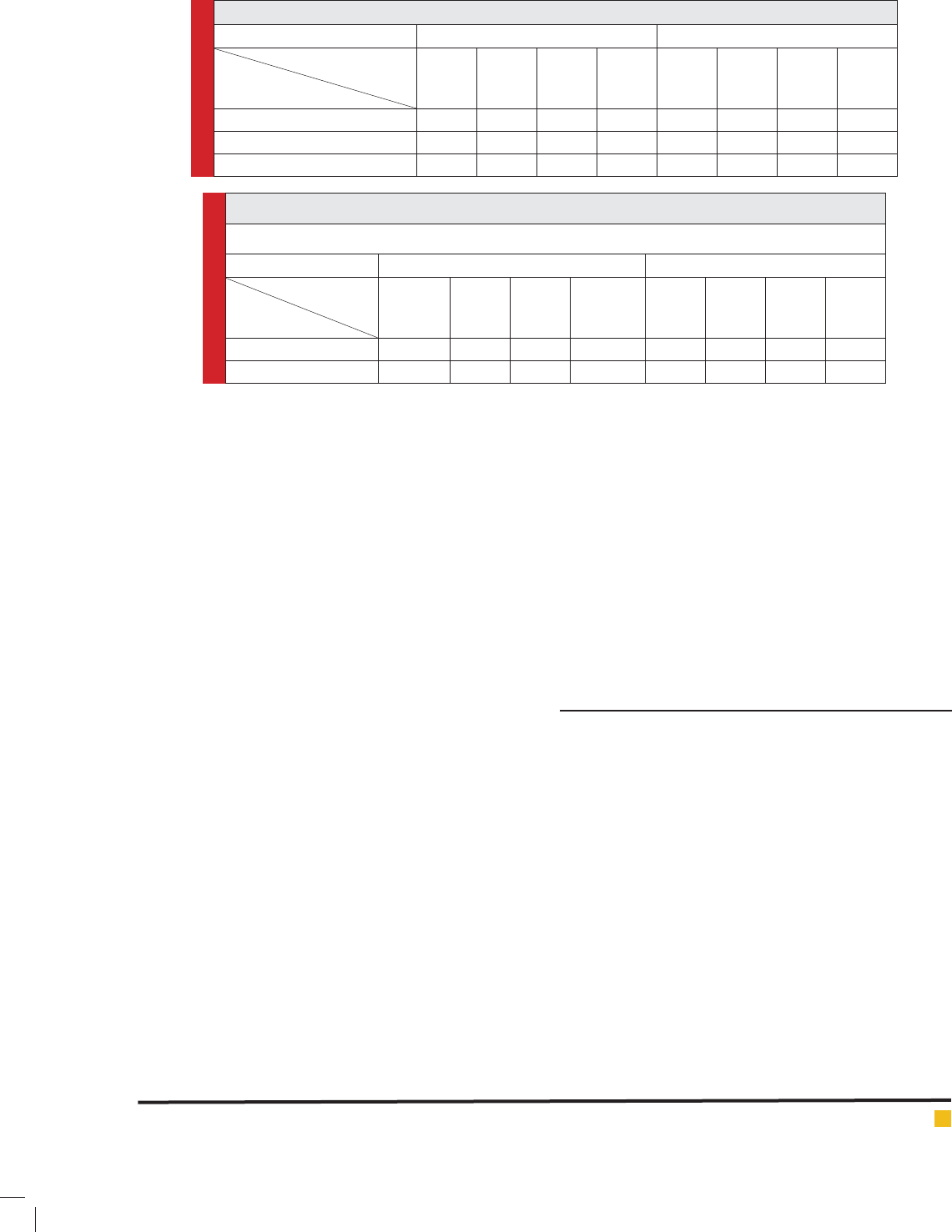
Table 5. Effects of Chemical and bio fertilizer on yield
Normal IrrigationDe cient Irrigation
64206420
Vermicompost
(t/ha)
NPK
Recommendation
Azotobacter
6.85.75.14.34.13.732.6
No Fertilizernon-inoculation
75.95.44.44.43.93.12.8
No FertilizerInoculation
108.47.97.25.14.74.63.9
50% non-inoculation
10.48.58.17.45.34.94.84.3
50% Inoculation
10.510.210.2105.45.25.24.8
100% non-inoculation
10.610.310.310.25.55.45.34.7
100% Inoculation
FIGURE 1. Effect of vermicompost and imigation on grain yield

Nasrolahzadeh, Shirkhani and Salmasi
BIOSCIENCE BIOTECHNOLOGY RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS AGRONOMIC RESPONSES OF MAIZE TO DEFICIT AND ADEQUATE IRRIGATION 225
pirillum bacteria, leads to yield increasing in sections of
nitrogen fertilizer.
1000 kernel weight
The results of this study showed that vermicompost and
chemical fertilizers had a signi cant effect on 1000 ker-
nel weight during both the years (Table 6). Vermicom-
post and Azotobacter increased 1000 kernel weight
and also chemical fertilizers. The heaviest 1000 kernel
weight 331.8 g was recorded in the plots where 6 ton/
ha vermicompost and 100% chemical fertilizer were
applied but with use of 6 ton/ha vermicompost and
50% chemical fertilizer 1000 kernel weight was 327.3 g
and no signi cant different was observed. Also without
chemical fertilizer and with use of 6 ton/ha vermicom-
post and Azotobacter, 1000 kernel weight was 315.7 g
and 263g in normal and De cient Irrigation condition
respectively.
Ramasamy et al. (2011) reported vermicompost
increased kernel weight in maize. Similarly, Cheema,
et al. (2010) found that applying 50% N from poultry
manure and remaining from urea fertilizer produced
maximum grain yield of maize and grain weight per cob.
Kalhapure and et al. stated that (2013) Azotobacter and
compost increased 1000-grain weight in maize. Similar
results were described by Yazdani et al. (2009) that grain
weight of maize increased with the application of phos-
phate solubilizing microorganisms.
FIGURE 2. Effect of vemicompost and azotobacter on kernel weight
Table 6. Effects of chemical fertilizer and vermicompost on 1000 kernel weight
De cient Irrigation Normal Irrigation
Vermicompost (ton/ha)
Chemical Fertilizers
02460246
No Fertilizer 213.6 235.2 240 263 260.3 269.7 281.1 316
50% Recommendation 240.5 259.3 271.7 283 288.5 304.2 319.8 326.9
100% Recommendation 274.8 278.6 279.8 284.6 327.6 330.7 331.4 337.3
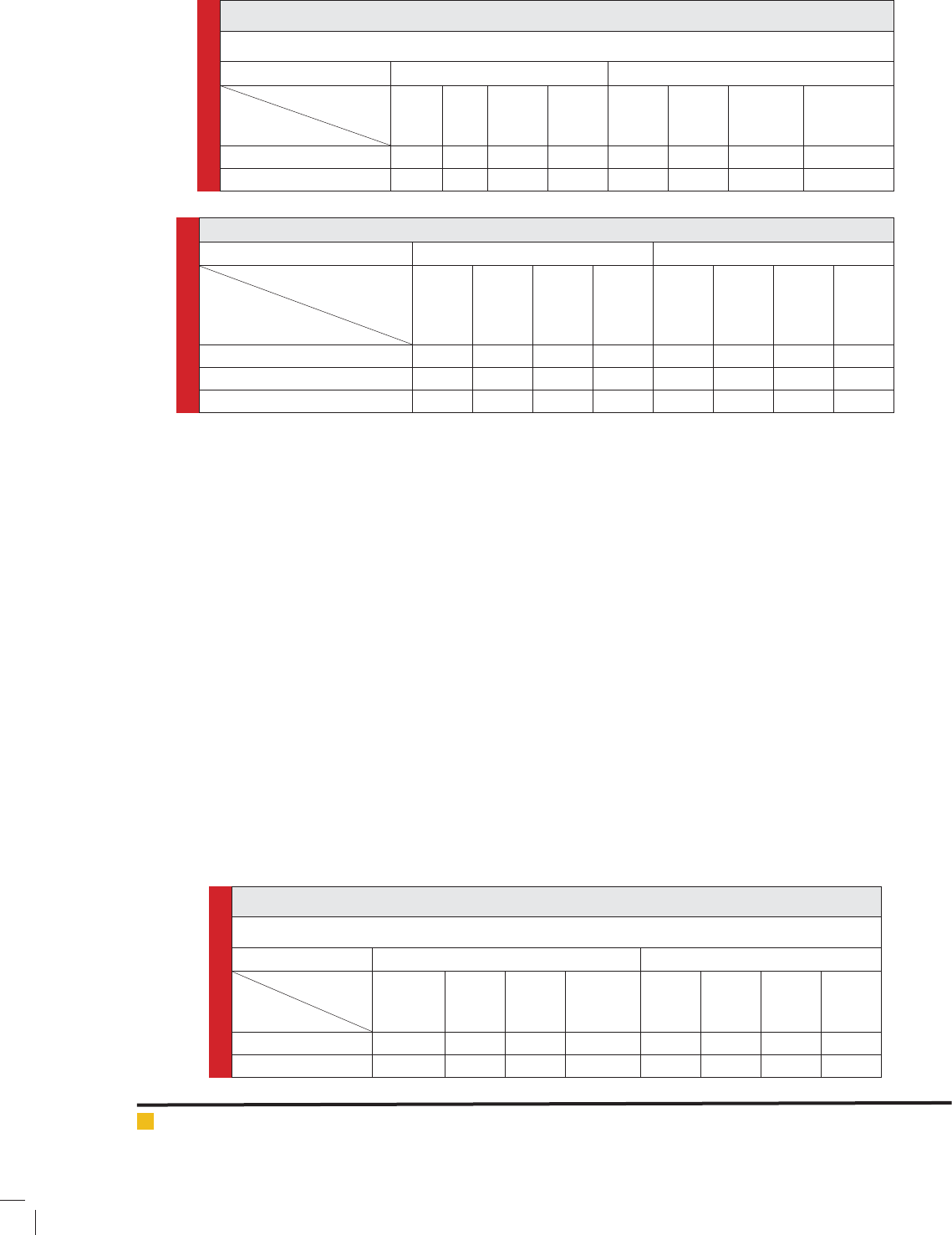
Table 7. Effects of chemical fertilizer and vermicompost on number of kernels per row
De cient Irrigation Normal Irrigation
Vermicompost (ton/ha)
Chemical Fertilizers
02460246
No Fertilizer 33.4 33.2 35.5 36 39.1 39.3 45 45,6
50% Recommendation 36.5 36.3 38.3 38.7 46.8 47 48.4 48.6
100% Recommendation 39 39.3 40 40.5 48.3 48.3 49 49
Nasrolahzadeh, Shirkhani and Salmasi
226 AGRONOMIC RESPONSES OF MAIZE TO DEFICIT AND ADEQUATE IRRIGATION BIOSCIENCE BIOTECHNOLOGY RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS
Whereas results of this experiment showed that
drought stress reduced 1000 kernel weight from 307.8 g
to 260.3 g. In de cient irrigation condition by increase
vermicompost and chemical fertilizer kernel weight was
increased. Nevertheless, uses of vermicompost and Azo-
tobacter in this condition were increased kernel weight.
Karam et al. (2003) stated that water de ciency signi -
cantly reduced dry matter accumulation. Grain yield
reduced to 37% due to a decline of 18% in kernel weight
and of 10% in kernel number under water stress condi-
tions. Increase in 1000-grain weight of common mil-
let due to the application of humic acid was informed
by (Veysel et al., 2011). Beigzade et al. (2013) reported
bacteria (Azospirillum + Pseudomonas) increased grain
weight in maize.
Number of kernels per row
Number of kernels per row was affected by water short-
ages. Number of kernels per row in normal and de cient
irrigation was 46.2 and 37.1 respectively. In addition
Analysis of variance of the data showed the main effects
of chemical fertilizers and biofertilizers and interaction
of chemical and biofertilizers were signi cant. Simi-
larly with other traits in de cient irrigation condition
by increase vermicompost and chemical fertilizer kernel
weight was increased. The maximum number of kernels
per row 49 was observed in 100% chemical fertilizer,
but Number of kernels per row in treatment with 50%
chemical fertilizer and 6 ton/ha vermicompost and use
of Azotobacter was 48.5. Results showed that using 6
tons of vermicompost and Azotobacter, reduced use of
chemical fertilizers by 50%. Whereas this trait in condi-
tion with use of 6 ton/ha vermicompost and Azotobacter
without chemical fertilizer was 45.6. Moreover Azoto-
bacter increased number of kernels per row from 40.2 to
43.2 (Table 7 and 8)
INM including vermicompost showed best results in
yield parameters of maize like number of grains per cob,
weight of the cob, 100 seed weight and yield (Kannan et
al., 2013). Beigzade et al. (2013) showed that phospho-
Table 8. Effects of Azotobacter and vermicompost on number of kernels per row
Azotobacter
InoculationNon-inoculation
64206420
Vermicompost
(ton/ha)
Irrigation
48.14847.847.647.2474241Normal 100%
39.539.337.637.636.736.53534.7De cient 65%
Table 9. Effects of chemical fertilizer and vermicompost on number of kernels per ear
De cient Irrigation Normal Irrigation
Vermicompost
(ton/ha)
Chemical Fertilizers
02460246
No Fertilizer 405 461.8 471.5 512.7 464.1 659 662.6 674.2
50% Recommendation 495.6 523.3 545.8 581.4 680.4 729.4 749.9 751.1
100% Recommendation 551.6 556.4 568.5 594.9 718.6 735.3 757.1 763.2
Table 10. Effects of Azotobacter and vermicompost on number of kernels per ear
Azotobacter
InoculationNon-inoculation
64206420
Vermicompost
(ton/ha)
Irrigation
734.9731.8721.7623.6724.1714.6707.5618.7Normal 100%
571.3526.5526.5490.8554.7521.3509.1480.7De cient 65%
Nasrolahzadeh, Shirkhani and Salmasi
BIOSCIENCE BIOTECHNOLOGY RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS AGRONOMIC RESPONSES OF MAIZE TO DEFICIT AND ADEQUATE IRRIGATION 227
rus fertilizer and bacteria (Azospirillum + Pseudomonas)
growth had a signi cant effect on number of grains per
row, but interaction effect of these two factors had not
signi cant effect on mentioned trait. Baral and Adhikari
(2013) reported that the numbers of kernels per row was
signi cantly in uenced by Azotobacter
Number of kernels per ear
Results showed that de cient irrigation decreased num-
ber of kernels per ear and the other hand vermicompost,
Azotobacter and chemical fertilizers had a signi cant
effect on number of kernels per ear (Table 3). Maximum
number of kernels per ear was recorded to inoculation
with Azotobacter, 6 ton/ ha vermicompost and 100%
chemical fertilizer (763.2) and with use of Azotobacter,
6 ton/ ha vermicompost and 50% chemical fertilizer this
treat was 749.4. So, biofertilizers was decreased chemi-
cal fertilizer 50% (Table 9 and 10).
Grain yield of maize is product of three yield compo-
nents i.e. the number of ears per unit of area, the number
of grains per ear and the unit grain weight (Gardner et
al., 1985). Variation in any one of these components,
keeping the size of other components constant, contrib-
utes to increase or decrease in grain yield, and thus any
management factor which increase any of these compo-
nents, will increase the nal grain yield.
3.5 Plant height
Inoculation with Azotobacter and use of vermicompost
signi cantly in uenced the plant height. Two years
mean revealed that maximum plant height (236.5) was
recorded with the application of recommended dose of
chemical fertilizer plus 6 ton/ha vermicompost and Azo-
tobacter inoculation and in normal irrigation. Minimum
plant height (147.1) was observed in de cient Irrigation
and without chemical and bio fertilizer. In both irrigation
treatments with increasing of chemical and bio fertilizer
plant height was increased (Table 11 and 12). Baral and
Adhikari (2013) reported Azotobacter increased plant
height in maize. Alnoaim and Hamad (2004), reported
that by using of bio-fertilizers with using of N fertilizer
the highest plant height, number of tiller and grain yield
of rice (Oryza sativa) were achieved. Maize plant height
increased application with 10 t/ha farm yard manure
(Karki, et al., 2005).
CONCLUSION
Although the vermicompost and Azotobacter were not
able to provide all the nutritional requirements for
Maize but the results indicated that the use of 6 ton/
ha vermicompost and Azotobacter in soil, 50% of the
maize fertilizer supplied and that means a 50% reduc-
tion in the consumption of chemical fertilizers and less
pollution of the soil and the environment. On the other
hand, the results showed that under de cient irrigation
vermicompost and Azotobacter increased grain yield. As
a general conclusion these results suggested that inte-
grating organic sources with 50% of recommended NPK
fertilizers are appropriate for sustainable crop produc-
tion in normal and de cient irrigation.
REFERENCES
Alnoaim AA, Hamad SH.(2004). Effect of bio-fertilization
along with different levels of nitrogen fertilizerapplication on
Table 11. Effects of chemical fertilizer and vermicompost on plant height
De cient Irrigation Normal Irrigation
Vermicompost
(ton/ha)
Chemical Fertilizers
02460246
No Fertilizer 147.1 164.6 168 171 201.9 208.9 213.8 219.3
50% Recommendation 158.2 167.3 168.5 174.5 216.5 220.6 229.1 235.5
100% Recommendation 162.1 175.2 175.1 177.5 230.7 231 236 237.4
Table 12. Effects of Azotobacter and vermicompost on plant height
Azotobacter
InoculationNon-inoculation
64206420
Vermicompost
(ton/ha)
Irrigation
174.2172.6171.4156.8171.5170.5166.7154.9Normal 100%
229.1224.8219.1218232.3227.8221.2214.7De cient 65%

Nasrolahzadeh, Shirkhani and Salmasi
228 AGRONOMIC RESPONSES OF MAIZE TO DEFICIT AND ADEQUATE IRRIGATION BIOSCIENCE BIOTECHNOLOGY RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS
the growth and grain yield of hassawi rice (Oryza sativa L.).
Basic and Applied Sci. 5:215-225.
Arancon, N., Edwards, C., Bierman, P, Metzger, J., and Chad
Lucht. (2005). Effects of vermicomposts produced from cattle
manure, food waste and paper waste on the growth and yield
of peppers in the eld. Pedobiologia 49 297—306.
Baral, B and Parbati Adhikari.(2013). Effect of Azotobacter on
growth and yield of Maize. SAARC J. Agri., 11(2): 141-147.
Beigzade, m., Maleki, A., Ataollah Siaddat, S. Malek, M.(2013).
Effect of combined application of phosphate fertilizers and
phosphate solubilizing bacteria on yield and yield components
of maize single cross 704. International Journal of Agriculture
and Crop Sciences. Vol., 6 (17), 1179-1185
Cheema,M, Farhad, W., Saleem,M., Khan,H., Munir, A.,
Wahid,M., Rasul,F., and H. M.Hammad.( 2010). Nitrogen man-
agement strategies for sustainable maize production. Crop
Environ.,1: 49-52. Crop Prod., vol. 2, pp. 23-27.
Dagdelen, N., E. Yılmaz, F. Sezgin and T. Gurbuz.(2006). Water-
yield relation and water use ef ciency ofcotton and second
crop Maize in western Turkey. Agric. Water Management 82(1-
2): 63-85.
Dobbelaere, S., A. Croonenborghs, A. Thys, D. Ptacek, J. Van-
derleyden, P. Dutto, C. Labandera Gonzalez, J. Caballero-Mel-
lado, F. Aguirre, Y. Kapulnik, S. Brener, S. Burdman.(2001).
Response of agronomically important crops to inoculation
with Azospirillum. Austuralian J. Plant Physiol., 28: 871-879.
DOI:10.1071/PP01074
El-Afry, M., El-Nady, M. and E. B. Abdelmonteleb. (2012). Ana-
tomical studies on drought stressed wheat plants treated with
some bacterial strains. Acta Biologica Szegediensis. Volume
56(2):165-174.
El-Kholy, M.A., S. El-Ashry and A.M. Gomaa.(2005). Biofertili-
zation of maize crop and its impact onyield and grains nutrient
content under low rates of mineral fertilizers. J. Applied Sci-
ence Res.,1(2): 117-121.
Fanuel,L., and G. Gifole.( 2012). Response of maize (Zea mays
L.) to integrated fertilizer application inwolaita. South Ethiopia
Advances in Life Science and Technology. ISSN 2224-7181,
vol. 5. Available: www.iiste.org.
Gholipoor,M., A. Karamzadeh, A. and Gholami, A.(2014). Ver-
micompost as a soil supplement to relieve the effects of low
intensity drought stress on chick pea yield ICHS Acta Horti-
culturae 1018: I International Symposium on Organic Matter
Management and Compost Use in Horticulture.DOI 7660/Acta-
Hortic.2014.1018.22
Gopinath KA, Saha S, Mina BL, Pande H, Kundu S and Gupta
HS.( 2008). In uence of organic amendments on growth,
yield and quality of wheat and on soil properties during
transition to organic production. Nutr Cycl Agroecosys 82:
51-60.
Gardner FP, Pearce RB and Mitchell RL (1985). Physiology of
Crop Plants (Iowa State Univ. Press) Ames, Iowa..
Hlavinka, P., Trnka, M., Semeradovaa, D., Dubrovsky, M.,
Zalud, Z. and Mozny, M. (2009). Effect of drought on yield
variability of key crops in Czech Republic. Agric. Forest Mete-
orology 149:431-442.
Hudson, B.D (1994). Soil organic matter and available water
capacity. J. Soil Wat. Con., 49(2):189-194.
Jacoud, C, Job, D, Wadoux, P, Bally, R (1999) Initiation of root
growth stimulation by Azospirillum lipoferum CRT1 during
maize seed germination. Can J Microbiol 45: 339–342
Jabasingh, C and S. Saravana Babu. (2014). Impact of Water
Stress on Protein Content of Zea mays L. Journal of Academia
and Industrial Research (JAIR). Volume 2, Issue 12 May 2014.
Johnson G.A., Qian Y.L., Davis J.G. (2009): Topdressing Ken-
tucky bluegrass with compost increases soil water content and
improves turf quality during drought. Compost Science and
Utilization, 17: 95–102.
Kalhapure, A., B.T. Shete, B. and M.B. Dhonde. (2013). Inte-
grated Nutrient Management in Maize (Zea mays L.) for
Increasing Production with Sustainability. International Jour-
nal of Agriculture and Food Science Technology. ISSN 2249-
3050, Volume 4, Number 3 (2013), pp. 195-206.
Kannan,R., Dhivya,M., Abinaya,D., Lekshmi Krishna,R., and S.
Krishnakumar, Effect of integrated nutrient management on
soil fertility and productivity jn maize, Bull. Env. Pharmacol.
Life Sci., vol. 2, pp. 61-67, 2013.
Karam, F., J. Breidy, C. Stephan and J. Rouphael. (2003). Evap-
otranspiration, yield and water use ef ciency of drip irrigated
Maize in the Bekaa Valley of Lebanon. Agric. Water Manage-
ment 63(2): 125-137.
Karki, T.B., Kumar, A. and Gautam, R.C. (2005).In uence of
Integrated Nutrient Management on Growth, Yield, Content
and Uptake of Nutrients and Soil Fertility Status in Maize (Zea
mays). Indian Journal of Agricultural Sciences 75 (10): 682-5.
Kemal, and Merkuz Abera.(2015). Contribution of integrated
nutrient managment practices for sustainable crop productiv-
ity, nutrient uptake and soil nutrient status in maize based
cropping systems. Journal of Nutrients, 2015, 2(1):1-10.home-
page: http://www.pakinsight.com/?ic=journal&journal=87
Kmetova, M and Kováˇ
c
ik, P.(2014). The impact of vermicom-
post application on the yield parameters of maize (Zea mays
L.) observed in selected phenological growth stages (BBCH-
SCALE). Acta fytotechn. zootechn., 17, 2014(4): 100–108. DOI:
10.15414/afz.2014.17.04.100–108
Li WJ, Ni YZ .(1996). Researches on application of microbial
inoculants in crop production. Researches and application of
En technology, Agriculture University Press, Beijing, China,
pp: 42-84.
Mehnaz, S and Lazarovits, G.(2006). Inoculation Effects of
Pseudomonas putida, Gluconacetobacter azotocaptans, and
Azospirillum lipoferum on Maize Plant Growth Under Green-
house Conditions. Volume 51, 326–335. DOI: 10.1007/s00248-
006-9039-7
Moser, S. B., Feil, B., Jampatong, S. and Stamp, P.(2006).
Effects of pre- anthesis drought, nitrogen fertilizer rate, and
variety on grain yield, yield components, and harvest index of
tropical maize. Agric. Water Management 81:41-58.

Nasrolahzadeh, Shirkhani and Salmasi
BIOSCIENCE BIOTECHNOLOGY RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS AGRONOMIC RESPONSES OF MAIZE TO DEFICIT AND ADEQUATE IRRIGATION 229
Mudenoor, M. G., Geete, Goudar and Savalgi, V. P.(2007).
Response of maize (Zea mays) to seed treatment of micronu-
trients supplemental Azospirillum biofertiilizer. International
Journal of Plant Science. 2:197-201.
Mujeeb, F., Rahmatullah, J., Akhtar and Ahmad, R. (2010).
Integration of organic and inorganic P sources for improv-
ing P use ef ciency in different soils. Soil and Environment,
29:122-127.
Nagananda GS, Bhattacharya Das AS, Kalpana T.(2010). In
vitro studies on the effects of bio fertilizers (Azotobacter and
Rhizobium) on seed germination and development of Trigo-
nella foenum-graecum L. using a Novel glass marable contain-
ing liquid medium. International journal of botany 6 (4): 394-
403.
Nguyen, T., Fuentes, S. and Marschner, P. (2012). Effects of
compost on water availability and gas exchangein tomato dur-
ing drought and recovery. Plant Soil Environ., 58, 2012 (11):
495–502
O’Neill, P., Shanahan, J., Schepers, Jand Bob Caldwell.(2004).
Agronomic Responses of Maize Hybrids from Different Eras to
De cit and Adequate Levels of Water and Nitrogen. Agron. J.
96:1660–1667. Doi:10.2134/agronj2004.1660–1667.
Pandey, R.K., J.W. Maranville and A. Admou.(2000). De cit
irrigation and nitrogen effects on maize in a Sahelian environ-
ment I. Grain yield and yield components. Agric. Water Man-
agement 46: 1-13.
Ramasamy, P., Baskar, K. and S. Ignacimuthu. (2011). In uence
of vermicompost on kernel yield of Maize (Zea mays L.). Elixir
Agriculture 36 : 3119-3121.
Reicosky, D.C.( 2005). Alternatives to mitigate the greenhouse
effect: emission control by carbon sequestration. In: Simpósio
sobre Plantio direto e Meio ambiente; Sequ¨ estro de carbono
equalidade da agua, pp. 20-28.. Anais. Foz do Iguaçu, 18–20
de Maio 2005.
Sarwar, G., Schmeisky, H., Hussain, N., Muhammad, S., Ibra-
him, M. and Safdar, E. 2008.Improvmentof soil physical and
chemical properties with compost application in Rice-wheat
cropping system. Pak. J. Bot., 40(1): 275-282.
Stone P.J., D.R. Wilson, P.D. Jamieson and R.N. Gillespie.
(2001). Water de cit effects on sweet Maize. II. Canopy devel-
opment. Aust.J.Agric. Res. 52: 115-126.
Tahir, M., Ayub, M., Javeed, H.M.R., Naeem, M., Rehman, H.,
Waseem, M. and Ali, M. (2011). Effect of different organic mat-
ter on growth ad yield of wheat (Triticum aestivum L). Pakistan
Journal of life and Social Sciences, 9: 63-66.
Taleshi, |K. and , Osoli, N. (2015). In uence of Drought Stress,
Vermicompost and N Fertilizer on Saf ower Leaves Antioxi-
dant Enzymes Activity. International Conference on Chemical,
Agricultural and Biological Sciences (CABS-2015) Sept. 4-5,
2015 Istanbul (Turkey). http://dx.doi.org/10.17758/ERPUB.
ER915042
Tollenaar, M. and Lee, E.A. (2011). Strategies for enhancing
grain yield in maize. Pl. Breed. Rev. 34: 37-81.
Vessey, JK (2003) Plant growth promoting rhizobacteria as
biofertilizers. Plant Soil 255: 571–586.
Veysel, S., A. Kusvuranand S. Babat. (2011). The effect of dif-
ferent humic acid fertilization on yield and yield components
performances of common millet (Panicummi liaceum L.). Sci-
enti c Research and Essays Vol. 6, pp. 663-669.
Yazdani, M., M. A. Bahmanyar, H. Pirdashti and M. A. Esmaili.
(2009). Effect of Phosphate Solubilization Microorganisms
(PSM) and Plant Growth Promoting Rhizobacteria (PGPR) on
Yield and Yield Components of Maize (Zea mays L.). Int.J.Biolo.
Life Sci., 5:2 2009.