Medical
Communication
Biosci. Biotech. Res. Comm. 10(1): 178-183 (2017)
Comparative evaluation of pulpal vitality test accuracy
in different groups of teeth
Elnaz Mousavi
1
*, Narges Simdar
1
, Sara Mehri
2
, Maryam Ghamari
3
and Sepideh Arab
4
1
Assistant Professor, Department of Endodontics, Faculty of Dentistry, Guilan University of Medical Science,
Rasht, Iran
2
Dentist
3
Assistant Professor, Department of Endodontics, Faculty of Dentistry, Ghazvin University of Medical
Science, Ghazvin, Iran
4
Assistant Professor, Department of Orthodontic, Faculty of Dentistry, Tehran University of Medical Science,
Tehran, Iran
ABSTRACT
The vitality pulp tests are necessary for diagnosis of pulpal disease and differentiation between endodontic and non-
endodontic disease. Thermal and electrical tests are conventional method for evaluation pulp vitality. The aim of the
present study was to evaluate the accuracy of thermal and electrical tests to register pulp vitality in different group
of teeth. 184 teeth (81 male, 103 female) with unknown pulpal status that need endodontic treatment were examined.
After complete isolation, the thermal and electrical tests were performed. The cold, heat and electrical tests were done.
The interval between tests was conducted after 2 minutes. Based on information obtained the sensitivity, speci city,
accuracy, positive and negative predictive value were calculated. In total, 78 teeth with necrotic pulp and 106 teeth
with vital pulp were tested. The gold standard was established by direct pulp inspection of 184 teeth with endodontic
treatment. Based on information obtained the accuracy of cold test in anterior teeth was 78/8%, in premolar teeth
was 81.8% and in molar teeth was 80.5%. The accuracy of heat test in anterior teeth was 82.6%, in premolar teeth
was 78.1% and in molar teeth was 72.7%. The accuracy of electric pulp test in anterior teeth was 71.1%, in premolar
teeth was 74.5% and in molar teeth was71.4%. In anterior teeth the heat test has more accuracy than the other one.
In premolar and molar teeth the cold test has more accuracy than other test.
KEY WORDS: DENTAL PULP TESTS, DIAGNOSIS
178
ARTICLE INFORMATION:
*Corresponding Author: elnaz32@gmail.com
Received 12
th
Jan, 2017
Accepted after revision 27
th
March, 2017
BBRC Print ISSN: 0974-6455
Online ISSN: 2321-4007 CODEN: USA BBRCBA
Thomson Reuters ISI ESC and Crossref Indexed Journal
NAAS Journal Score 2017: 4.31 Cosmos IF : 4.006
© A Society of Science and Nature Publication, 2017. All rights
reserved.
Online Contents Available at: http//www.bbrc.in/

Elnaz Mousavi et al.
INTRODUCTION
Diagnosis in dentistry may be de ned as ‘the process
whereby the data obtained from questioning, examin-
ing and testing are combined by the dentist to identify
deviations from the normal. The diagnosis of dental pulp
status should be seen as a synthesis of history, clinical
examination, special tests, and radiological examination,
and not as the outcome of any one speci c test. Vitality
testing is an important aid in the diagnosis of pulp dis-
ease and apical periodontitis (Gopikrishna et al. 2009).
The complex anatomical structure and inaccessibility of
the dental pulp to clinical tests makes an accurate diag-
nosis of the health of the dental pulp often dif cult and
challenging to the dentist. The physical con nement of
the dental pulp, with its rich sensory nerve innervations
and microcirculatory components make the dental pulp
a unique tissue (Samuel et al. 2014).
Conventional pulp tests such as electric pulp tests and
thermal tests measure the neural component of the pulp
and are now considered as pulp sensibility tests (Lin et
al. 2008). Studies have shown that blood circulation, and
not the nerve innervation, is the accurate determinant of
the pulp vitality as it provides an objective differentia-
tion between vital and non-vital pulp (Yu and Abbott,
2007). Hence, pulpal circulation is the true determinant
of pulp vitality. The nerve bers of the pulp may be
resistant to necrosis than the vascular tissue and may be
reactive long after the surrounding tissues have degen-
erated (Gopikrishna et al. 2007).The conventional tests
are subjective and depend upon the patient’s perceived
response to the stimulus as well as the dentist’s interpre-
tation of that response. Pulp sensibility tests have limi-
tations, and false responses can occur (Bender, 2000).
Electric pulp tests are known to be unreliable in imma-
ture teeth and in teeth undergoing orthodontic move-
ment (Myers, 1998). Furthermore, false responses are
known to occur when the electric current is conducted
to adjacent periodontal tissues, adjacent teeth and even
to remnant in amed pulp tissue with liquefactive pulp
necrosis. In traumatized teeth, Electric pulp tests are less
reliable than cold tests It is also reported pulpal sensibil-
ity testing with Endo Ice and pulp tester are more accu-
rate and reliable methods of determining pulpal vitality,
(Chen et al. 2011 and Jespersen et al. 2014).
Cold tests are known to elicit false-negative responses
in elderly patients because of the amount of thermal
insulation provided by secondary dentin (Emshoff et al.
2004). Commonly available agents for cold tests are CO
2
snow, ice, and refrigerant sprays (eg, tetra uoroethane,
butane, propane, isobutane, dicholoro uoromethane
and ethyl chloride). Cold tests and electric pulp tests are
pulp sensibility tests that have been established as use-
ful aids in the assessment of pulp status despite being
subjective and patient-dependent (Emshoff et al. 2004).
Nonetheless, the lack of pulp sensibility is often associ-
ated with advanced pulp necrosis (Chen et al. 2011).
Currently, there is no reliable and acceptable pulp
testing method for the pediatric age-group. The aim of
the current study was to determine sensitivity and speci-
city of cold, heat and electric test on pulpal vitality
tests in different dental type.
MATERIAL AND METHODS
PATIENTS
A total 184 teeth (81 male, 103 female) with unknown
pulpal referred to Endodontic Department of dental clinic
of international branch of Guilan University of Medical
Sciences during 2015 were examined. Patients aged 12-81
(mean 37.94 years old). They informed about the study
and signed the form. The inclusion criteria were not suf-
fering systemic disease or administration of NSAID drugs.
STUDY PROTOCOL
Then peri-apical radiography was done on teeth and
those with calci cation and decay without pulp invasion
were included into as case group. The next tooth in the
same arc with no calci cation or decay kept as control.
At rst, primary diagnosis was done in all pulp based
on observation followed by observation. After complete
isolation, the thermal and electrical tests were performed
in case and control teeth. The cold test by ethyl chol-
oride and heat test by gutta percha and electrical test
with electrical pulp tester (Parkel/USA) were done. Two
minutes interval between tests was conducted. The pain
response of the patients was recorded as normal, high
and highest (+, ++ and +++). Based on information
obtained the sensitivity, speci city, accuracy, positive
and negative predictive value were calculated for each
method in different groups of teeth.
STATISTICAL ANALYSIS
The obtained data was analyzed using SPSS ver. 21
using One Way ANOVA. For treatments showing a main
effect by ANOVA, means were compared using chi squar
test. P<0.05 was considered as signi cant differences
between treatments.
RESULTS
The results of the accuracy of thermal and electrical tests
to register pulp vitality in different group of teeth are
presented in gures 1-14. A total 184 teeth (81 male,
103 female) with unknown pulpal status that need endo-
BIOSCIENCE BIOTECHNOLOGY RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS EVALUATION OF PULPAL VITALITY TESTS ACCURACY IN DIFFERENT GROUPS OF TEETH 179

Elnaz Mousavi et al.
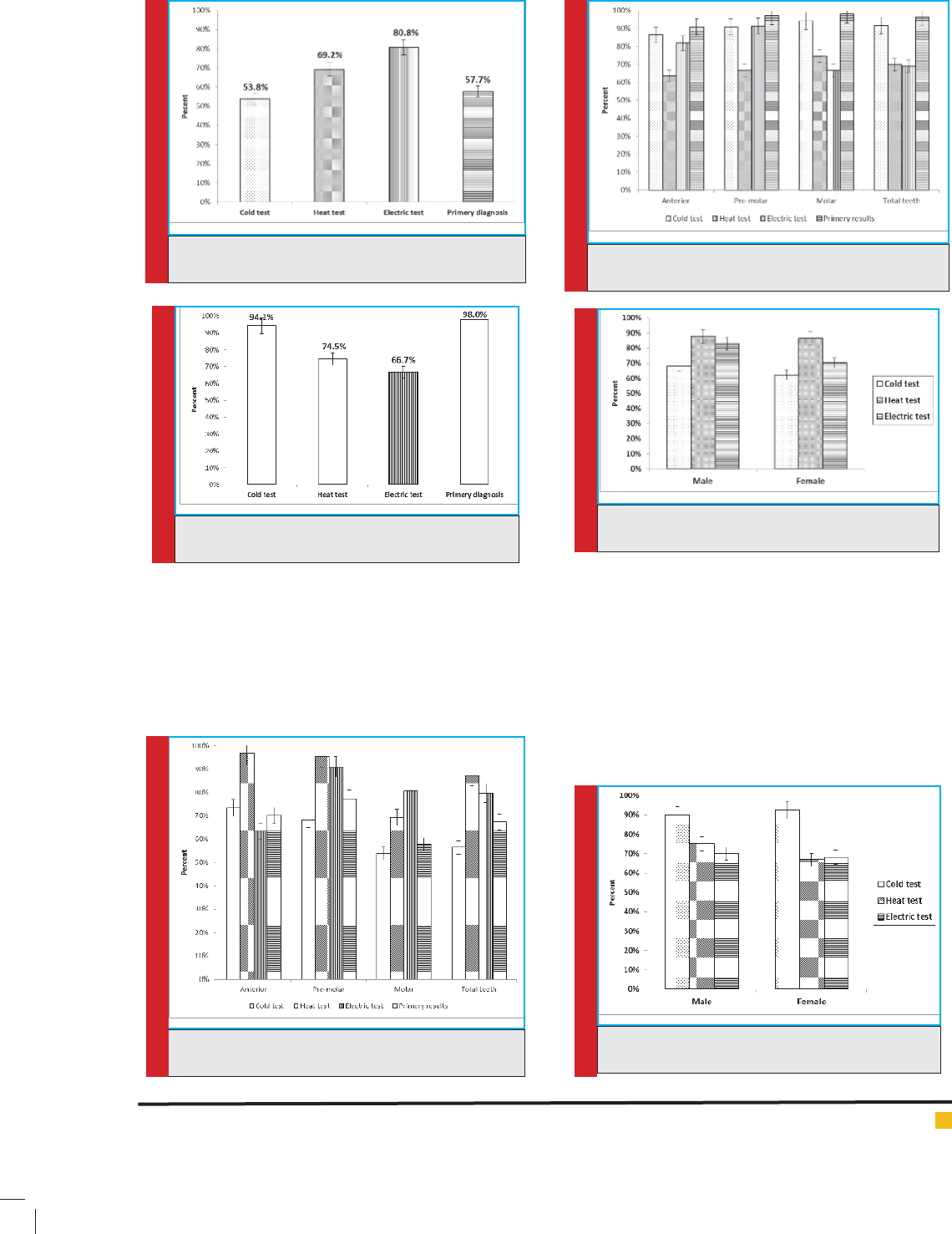
FIGURE 1. the sensitivity of the tests for determine pulp
vitality in teeth
FIGURE 2. the Speci city of the tests for determine
pulp vitality in teeth
FIGURE 3. the sensitivity of the tests for determine
pulp vitality in anterior teeth
dontic treatment were examined. In total, 78 teeth with
necrotic pulp and 106 teeth with vital pulp were tested.
As seen in gure 1, the heat test had the highest sensi-
tivity (87.2%) compared to the other tests for determine
pulp vitality in teeth.
As observed in gure 2, primary test (96.2%) and cold
test (91.5%) had the highest accuracy of the tests for
determine pulp compared to the other tests, respectively.
FIGURE 4. the Speci city of the tests for determine
pulp vitality in anterior teeth
FIGURE 5. the sensitivity of the tests for determine
pulp vitality in pre-molar teeth
FIGURE 6. the Speci city of the tests for determine pulp
vitality in pre-molar teeth
Among the various tests, the heat test had highest
sensitivity (96.7%) for determine pulp vitality in anterior
teeth ( gure 3).
Furthermore, the heat test had lowest Speci city
(63.3%) of the tests for determine pulp vitality in ante-
rior teeth ( gure 4).
The results of the sensitivity of the tests for determine
pulp vitality in pre-molar teeth is presented in gure 5.
As seen, heat test (95.5%) and electric test (90.9%) had
180 EVALUATION OF PULPAL VITALITY TESTS ACCURACY IN DIFFERENT GROUPS OF TEETH BIOSCIENCE BIOTECHNOLOGY RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS
Elnaz Mousavi et al.
FIGURE 7. the sensitivity of the tests for determine
pulp vitality in molar teeth
FIGURE 8. the Speci city of the tests for determine
pulp vitality in molar teeth
FIGURE 10. the Speci city of the tests to determine
pulp vitality in various teeth
FIGURE 12. the Speci city of the tests to determine
pulp vitality in patients based on the gender
FIGURE 9. the sensitivity of the tests to determine pulp
vitality in various teeth
the highest sensitivity of the tests for determine pulp
vitality in pre-molar teeth, respectively.
Also, the heat test had lowest Speci city (66.7%) for
determine pulp vitality in pre-molar teeth ( gure 6).
As seen in gure 7, for the sensitivity of the tests for
determine pulp vitality in molar teeth, the electric test
was highest (80.8%) compared to the other tests.
FIGURE 11. the sensitivity of the tests to determine
pulp vitality in patients based on the gender
According to the gure 8, primary test (98%) and cold
test (94.1%) had higher Speci city of the tests for deter-
mine pulp vitality in molar teeth
The sensitivity of the tests to determine pulp vital-
ity in various teeth is shown in gure 9. As observed
heat test had better sensitivity for anterior, pre-molar
and total teeth while electric test had higher sensitivity
for molar ( gure 9).
BIOSCIENCE BIOTECHNOLOGY RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS EVALUATION OF PULPAL VITALITY TESTS ACCURACY IN DIFFERENT GROUPS OF TEETH 181

Elnaz Mousavi et al.
FIGURE 13. the sensitivity of the tests to determine
pulp vitality in patients based on the age
FIGURE 14. the Speci city of the tests to determine
pulp vitality in patients based on the age
Based on the results of the gure 10, primary test and
cold test had highest Speci city to determine pulp vital-
ity in various teeth compared to the other tests.
The heat and electric tests had highest sensitiv-
ity to determine pulp vitality in both men and women
( gure 11).
Interestingly, the cold test had highest Speci city to
determine pulp vitality in both gender ( gure 12).
As seen in gure 13, cold and heat tests had similar
sensitivity to determine pulp vitality in patients aged
<40 years old while only heat test had higher sensitivity
to determine pulp vitality in patients aged >40.
Furthermore, cold test had higher Speci city to deter-
mine pulp vitality in patents based on their age ( gure 14).
DISCUSSION
The key to developing a treatment plan for oral reha-
bilitation is a correct diagnosis, and in endodontic treat-
ment, it is important to identify the status of the pulp
tissues. To determine the sensitivity of the pulpal nerves,
dentists use thermal and electrical tests (Newton et al.
2009). The ideal test should be easy to use, fast, inexpen-
sive, noninvasive, painless, reproducible, and accurate
(Jafarzadeh and Abbott, 2010). Sensitivity, speci city,
and positive and negative predictive values were previ-
ously developed to characterize the accuracy of given
tests (Dastmalchi et al. 2012).
The sensitivity value indicates the ability of a test
to identify teeth that are diseased. The speci city value
tests the ability of a procedure to identify teeth without
disease (Chen and Abbott, 2011). Therefore, it is impor-
tant to determine the positive and negative predictive
values to identify the probability of a correct diagno-
sis with thermal and electrical pulp tests (Saeed et al.
2011). As seen in this study the accuracy of heat test in
anterior teeth was 82.6%, in premolar teeth was 74.5%
and in molar teeth was 72.7%. The accuracy of electric
pulp test in anterior teeth was 71.1%, in premolar teeth
was 78.1% and in molar teeth was71.4%. The accuracy
of cold test in anterior teeth was 78/8%, in premolar
teeth was 81.8% and in molar teeth was 80.5%. Evalua-
tion of pulp vitality is an important diagnostic aspect of
treating traumatized teeth. The methods currently used
are thermal and electrical stimulation. However, thermal
and electric testing has limitations in providing accu-
rate diagnosis (Goho et al. 1999). Several studies have
compared different tests to assess sensitivity, but none
of them calculated the positive and negative predictive
values (Newton et al. 2009; Setzer et al. 2012).
In this study, anterior teeth the heat test had more
accuracy than the other one. Studies have shown that
cold testing and electric pulp testing are equally reliable
for over 80% of cases in the diagnosis of vital and non-
vital pulps (Weisleder et al. 2009). However, this evidence
does not con rm the validity of the test in the assess-
ment of the pulpal condition. This appears currently to
be a signi cant limitation in the diagnosis of diseases
of the pulp (Mejàre et al. 2012) attempts to correlate the
actual threshold value evoked by electric pulp testing
with the condition of pulp remain to be elucidated. Pulp
nerve bers are more resistant to necrosis than vascular
tissue, and thermal or electric testing of only pulp neural
response may also result in false positive results if only
the pulp vasculature is damaged (Goho et al. 1999).
In the current study, premolar and molar teeth the
cold test has more accuracy than other tests. It is reported
that pulpal sensibility testing with Endo Ice and pulp
tests are accurate and reliable methods of determining
pulpal vitality (Jespersen et al. 2014).
Patients aged 21–50 exhibited a more accurate
response to cold. Sex, tooth type, number of restored
surfaces, presence of caries, and recent analgesic use did
not signi cantly alter the results of pulpal sensibility
testing in this study. Previous studies have demonstrated
no gender related differences in perception threshold
(Lin et al. 2007; Jespersen et al. 2014) and our ndings
was similar to the previous reports. Peterson et al. (1998)
182 EVALUATION OF PULPAL VITALITY TESTS ACCURACY IN DIFFERENT GROUPS OF TEETH BIOSCIENCE BIOTECHNOLOGY RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS

Elnaz Mousavi et al.
on the ability of thermal and electrical tests to register
pulp vitality reported the sensitivity, speci city, positive
predictive value and negative predictive value were cal-
culated for each method. The sensitivity was 0.83 for the
cold test, 0.86 for the heat test and 0.72 for the electrical
test. The speci city was 0.93 for the cold test, 0.41 for
the heat test and 0.93 for the electrical test. The positive
predictive value was 0.89 for the cold test, 0.48 for the
heat test and 0.88 for the electrical test, and the negative
predictive value was 0.90 for the cold test, 0.83 for the
heat test and 0.84 for the electrical test. This indicated
that the probability of a non-sensitive reaction repre-
senting a necrotic pulp was 89% with the cold test, 48%
with the heat test and 88% with the electrical test. It also
indicated that the probability of a sensitive reaction rep-
resenting a vital pulp was 90% with the cold test, 83%
with the heat test and 84% with the electrical test.
CONCLUSION
In a diagnostic test (cold, heat, and electrical), it is nec-
essary to know the probability that the test will provide
the correct diagnosis. In anterior teeth the heat test has
more accuracy than other one. In premolar and molar
teeth the cold test has more accuracy than other tests.
REFERENCES
Bender IB. (2000)Reversible and irreversible painful pulpitides:
diagnosis and treatment. Aust Endod Journal 26:10–4.
Chen E, Abbott PV. (2011) Evaluation of accuracy, reliability,
and repeatability of ve dental pulp tests. J Endod 37:1619–23.
Chen E, Abbott PV. Evaluation of accuracy, reliability, and repeat-
ability of ve dental pulp tests .J Endod 2011;37:1619–1623.
Dastmalchi N, Jafarzadeh H, Moradi S.(2012) (Comparison of
the ef cacy of a custom-made pulse oximeter probe with digi-
tal electric pulp tester, cold spray, and rubber cup for assessing
pulp vitality. J Endod 38:1182–6.
Emshoff R, Emshoff I, Moschen I, Strobl H. (2004) Diagnos-
tic characteristics of pulpal blood ow levels associated with
adverse outcomes of luxated permanent maxillary incisors.
Dent Traumatol 20:270–5.
Goho C. (1999)Pulse oximetry evaluation of vitality in primary
and immature permanent teeth Pediatr Dent 21:109-113
Gopikrishna V, Pradeep G, VenkaTeshbabu N. (2009) Assess-
ment of pulp vitality: a review. International Journal of Paedi-
atric Dentistry 19: 3–15.
Gopikrishna V, Tinagupta K, Kandaswamy D. (2007) Evalua-
tion of ef cacy of a new custom-made pulse oximeter dental
probe in comparison with the electrical and thermal tests for
assessing pulp vitality. J Endod 33:411-4.
Jafarzadeh H, Abbott PV.(2010) Review of pulp sensibility
tests. Part I: general information and thermal tests. Int Endod
J 43:738–62.
Lin J, Chandler N, Purton D, Monteith B (2007) Appropriate
electrode placement site for electric pulp testing rst molar
teeth. Journal of Endodontics 33, 1296-8.
Lin J, Chandler NP.(2008) Electric pulp testing: A review. Int
Endod Journal; 41:365-74.
Mejàre IA, Axelsson S, Davidson T.(2012) Diagnosis of the
condition of the dental pulp: a systematic review. International
Endodontic Journal 45, 597-613.
Myers JW. (1998) Demonstration of a possible source of error
with an electric pulp tester. J Endod 24:199–200.
Newton CW, Hoen MM, Goodis HE. (2009) Identify and deter-
mine the metrics, hierarchy, and predictive value of all the
parameters and/or methods used during endodontic diagnosis.
J Endod 35:1635–44.
Newton CW, Hoen MM, Goodis HE. (2009) Identify and deter-
mine the metrics, hierarchy, and predictive value of all the
parameters and/or methods used during endodontic diagnosis.
J Endod 35:1635–44
Peterson K, Soderstrom C, Kiani-Anaraki M, Ltvy G.(1999)
Evaluation of the ability of thermal and electrical tests to reg-
ister pulp vitality. Endod Dent Traumatol 15: 127-1 3 1.
Rutsatz C, Baumhardt SG, Feldens CA. (2012) Response of pulp
sensibility test is strongly in uenced by periodontal attach-
ment loss and gingival recession. J Endod 38:580–3.
Saeed MH, Mazhari NA, Al-Rawi NH. (2011) The ef cacy of
thermal and electrical tests to register pulp vitality. J Int Dent
Med Res 4:117–22.
Samuel SS, Thomas AM, Singh N. A (2014) Comparative study
of pulse oximetry with the conventional pulp testing meth-
ods to assess vitality in immature and mature permanent
maxillary incisors Journal of Health and Research 1(4): 235-
240.
Setzer FC, Kataoka SH, Natrielli F. (2012) Clinical diagnosis of
pulp in ammation based on pulp oxygenation rates measured
by pulse oximetry. J Endod 38: 880–3.
Villa-Chavez C E., Patino-Marın N, Loyola-Rodrıguez JP, Zav-
ala-Alonso NV, Martınez-Castanon GA, Medina Solıs CE.(2013)
Predictive values of thermal and electrical dental pulp tests: A
clinical study. J Endod 39:965–969.
Weisleder R, Yamauchi S, Caplan DJ, Trope M, Teixeira FB
(2009) The validity of pulp testing: a clinical study. Journal of
the American Dental Association 140, 1013-7.
Yu C, Abbott PV. (2007)An overview of the dental pulp: Its
functions and responses to injury. Aust Dent J 52:S4-16.
BIOSCIENCE BIOTECHNOLOGY RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS EVALUATION OF PULPAL VITALITY TESTS ACCURACY IN DIFFERENT GROUPS OF TEETH 183