Pharmaceutical
Communication
Biosci. Biotech. Res. Comm. 10(1): 103-108 (2017)
Preparation of nanoliposomes containing
Rosmarinus
of cinalis
L essential oil: A comparative study
Mohammad Hossein Arabi
1
, Hora Chabok
1
, Azam Mirzapour
1
, Mehdi Sha ee
Ardestani
2
and Mostafa Saffari
3,4
*
1
Biochemistry Department, School of Medicine, Kashan University of Medical Sciences, Kashan, Iran
2
Radiopharmacy Department, School of Pharmacy, Tehran University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran
3
Department of Pharmaceutics & Medical Nanotechnology, School of Pharmacy, Pharmaceutical Branch of
Azad University, Tehran, Iran
4
Herbal medicine research center (HMRC) and Department of Pharmaceutics. Branch of Pharmaceutical
Sciences. Islamic Azad University, Tehran, Iran
ABSTRACT
According to progressive trend of herbal application in modern medicine, various studies has been shown several
properties for Rosemary essential oil (EO) such as antioxidant, anti-bacterial, anti-cancer and anti-in ammatory
effect. Owing to liposomal bene ts such as increased solubility, enhanced performance and increased stability of its
content, the main objective of this study was to design nanoliposomes containing rosemary essential oils to achieve
more ef cacy. Nano-liposomes containing EO was prepared by three different methods including thin lm hydration,
sonication and extrusion methods. The physical properties of nanoliposomes such as particle size, poly dispersity
index, zeta potential, encapsulation ef ciency and release pro le of EO were studied. The mean size of liposomes
containing essential oils of rosemary prepared by sonication method was 162 nm which, is greater than extruder
method (470 nm) and liposomes were prepared by thin lm hydration were about one µm. Encapsulation ef ciency
was higher in sonication method rather that extrusion method. Both methods lead to spherical particles. Release of EO
from liposomes in aqueous media was negligible (P value > 0.05). It was found that the method of liposomes prepa-
ration, cholesterol concentration and essential oil concentration is effective on the size and encapsulation ef ciency
of nanoliposome.
KEY WORDS: NANOLIPOSOME, ROSEMARY ESSENTIAL OIL, THIN FILM HYDRATION, EXTRUSION, SONICATION
103
ARTICLE INFORMATION:
*Corresponding Author: mostafa.saffary@gmail.com
Received 10
th
Jan, 2017
Accepted after revision 21
st
March, 2017
BBRC Print ISSN: 0974-6455
Online ISSN: 2321-4007 CODEN: USA BBRCBA
Thomson Reuters ISI ESC and Crossref Indexed Journal
NAAS Journal Score 2017: 4.31 Cosmos IF : 4.006
© A Society of Science and Nature Publication, 2017. All rights
reserved.
Online Contents Available at: http//www.bbrc.in/

104 PREPARATION OF NANOLIPOSOMES CONTAINING
ESSENTIAL OIL OF ROSMARY
BIOSCIENCE BIOTECHNOLOGY RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS
Mohammad Hossein Arabi et al.
INTRODUCTION
Plants have been the basis for medical treatments through
much of human history, and such traditional medicine is
still widely practiced today. Modern medicine make use
of many plant-derived compounds as the basis for evi-
dence-tested pharmaceutical drugs, and phytotherapy
works to apply modern standards of effectiveness test-
ing to herbs and medicines that are derived from natural
sources. There are many forms in which herbs can be
administered, in many cases essential oils are used as
medicine. An essential oil is a concentrated hydropho-
bic liquid containing volatile aroma compounds from
plants. An oil is “essential” in the sense that it contains
the characteristic fragrance of the plant that it is taken
from (Oxford dictionary, 2014). Essential oils are com-
plex blends of a variety of volatile molecules such as
terpenoids, phenol-derived aromatic components, and
aliphatic components have been great interest in vari-
ous industries such as food and medicine (Bilia et al.,
2014).
Rosmarinus of cinalis L that belongs to the family
Lamiaceae (Lamiaceae) and have at least 1% (volume
/ weight) volatile oil Rosemary commonly used in the
food industry as spice and avors. Rosemary of cinalis’s
essential oil possess a verity of properties include anti-
oxidant, antimicrobial, antitumor anti-HIV, anti-in a-
mation, analgestic effect and etc Peng et al., 2007). The
most important constituents of the Iranian Rosemary
are 1,8-cineole (23.47%), -pinene (21.74%), berbonone
(7.57%), camphor (7.21%) and eucalyptol (4.49%) (Alti-
nier et al., 2007, Honorio et al., 2015).
Rosemary essential oil used in various commercial
products on the market, Including bath additive for sup-
port the function of the skin and auxiliary treatment in
conditions of exhaustion, ointment for the symptomatic
treatment of muscle and joint pain, solutions for stimu-
lation of circulation (Jalali-Heravi et al., 2011).
Studies have shown that a new drug delivery meth-
ods such as encapsulation can reduce volatility, increase
solubility in water, increase dilution for use in the end
product and the ef cacy of essential oils (Sherry et al.,
2013). Nanocarriers can be structured by a great vari-
ety of material and designs (Saraf, 2010).
Liposomes are
bilayer vesicles that obtained from association of amphi-
philic lipids that can carry up hydrophilic, hydrophobic
and amphiphilic compounds. Nanoliposomes accord-
ing to the method and ingredients can have different
shapes and sizes (Moghimipour et al., 2012; Mozafari
et al., 2010). The aim of this study was encapsulation of
Rosemary EO oil in nanoliposome that done by three dif-
ferent methods including thin lm hydration, extruder
and sonication. Then prepared liposomes, will compared
for their physicochemical properties.
MATERIAL AND METHODS
Soybean lecithin, cholesterol and DOTAP taken from
Sigma–Aldrich (Steinheim, Germany), Merck KGaA
(Darmstadt, Germany) and Lipoid GmbH (Ludwigshafen,
Germany), Rosemary essential oil (taken from Barij
Essence Kashan, Iran), PBS were purchased from Sigma–
Aldrich (Steinheim, Germany).
Cholesterol, phosphatidyl choline and rosemary
essential oil in several ratios of essential oil to total
lipids, and several molar ratio of cholesterol: lecithin
and lipid composition(DOTAP), were solved in chloro-
form/ ethanol (2: 1, v/v) inside the 500 ml round-bottom
ask then by using rotary evaporator in constant tem-
perature above the lipid phase transition temperature
(Tc), under negative pressure and high vacuum for 2
hour organic solvent was removed and a thin layer was
formed in bottom ask. Then the obtained lipid lm was
hydrated by Phosphate buffered saline (PBS pH: 7.4) for
1.5 hour at temperatures above Tc and in 120 rpm of
speed.
Initial ratio of essential oils/total lipid was 1/3, 1/4
and 1/5. Molar ratio of Cholesterol: Phosphatidyl Cho-
line was 1: 1, 1: 2 and 1: 3 in 100 mM total lipid con-
centration.
In the preparation of Cationic liposomes containing
essential oil, phosphatidyl choline (E80), 1,2-dioleoyl-
3-trimethylammonium-propane (DOTAP), and choles-
terol (Chol) at a molar ratio of E80:DOTAP:Chol = 1:1:1
Formulation was used (Table1).
Liposomes obtained from thin lm hydration method
was passed through Nucleopore polycarbonate lters
(0.2 and 0.1 m in series, Whatman, UK) under strong
pressure at above the lipid transition temperature in
three stages by using the extruder device.
Table 1: Composition of cationic liposomes
formulation
Formulation
name
Chol: PC:
DOTAP
Rosemary essential
oil/total lipid
H1
1:1:0 1/3
H2 1:1:0 1/4
H3 1:1:0 1/5
H4 1:2:0 1/3
H5 1:3:0 1/3
H6 1:1:1 1/3
BIOSCIENCE BIOTECHNOLOGY RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS PREPARATION OF NANOLIPOSOMES CONTAINING
ESSENTIAL OIL OF ROSMARY
105
Mohammad Hossein Arabi et al.
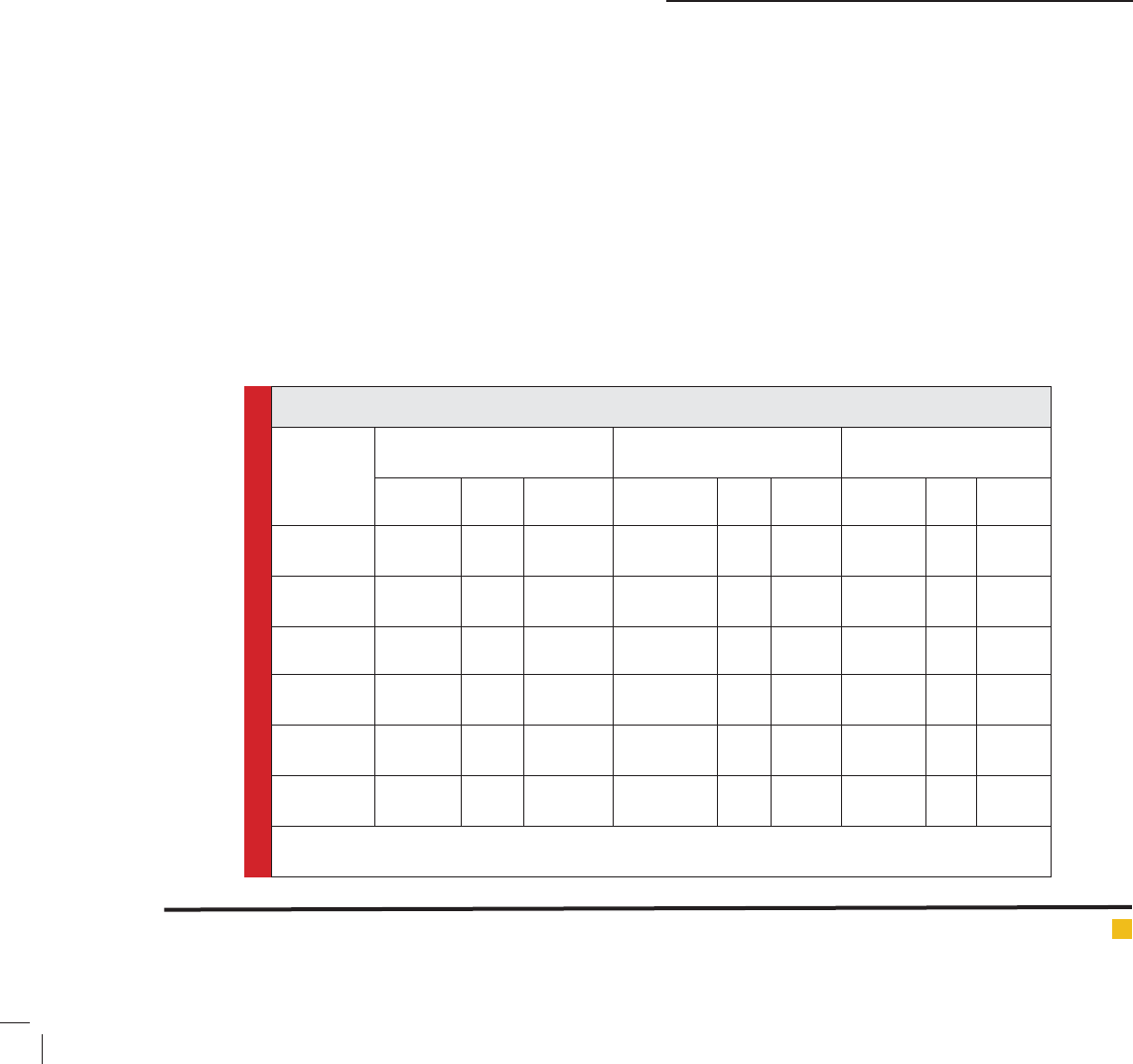
Table 2: Characterization of Rosemary EO containing nanoliposomes
Formulation
Extrusion method Sonication method
Thin lm hydration
method
MD(nm) PDI) EE (%) MD(nm) PDI EE (%) MD(nm) PDI EE (%)
H1
358.6±
1.3
0.46 83 ± 6.3 122 ±
3.2
0.35 98.9 1833.5 ±
926.5
0.51 100
H2
346.9 ±
9.3
0.3 67.4 ± 6.9 104.33 ± 3.4 0.22 99.03 2747.5 ±
1632.5
0.50 100
H3
230.9±
8
0.26 41.9 ± 4.3 92.36 ± 4.5 0.24 99.3 2453.9 ±
2186.1
0.65 100
H4
366.9 ± 9 0.19 64.7 ± 3.3 154 ± 3.2 0.15 95.3 1757.5 ±
332.5
0.77 100
H5
469.7 ±
2.5
0.19 47.7 ± 6.3 162 ± 4.3 0.12 96.3 1053
37
0.64 100
H6
871.3 ±
14
0.29 97.5 ± 2.5 133 ±
1.0
0.23 95.3 2720 ±
11
0.71 100
MD: Mean diameter; PDI: Poly dispersity index; EE: encapsulation ef cacy;
Mean ± standard error of mean (SEM)
Liposomes obtained from thin lm hydration method
were sonicated by probe sonicator (Hielscher UP400S,
Germany) at 70 Watt amplitude for 30 minutes.
The size and polydispersity (PDI) of formed liposome
was measured by Dynamic light scattering in a Zeta-
sizer Nano ZS (Malvern ZEN 3600). The samples were
diluted with phosphate buffer saline and measurement
was triplicate.
Charge on loaded vesicles surface and average zeta
potential is measured by zeta potential analyzers Zeta-
sizer instrument (Malvern ZEN 3600) (Kraft et al., 2014).
Encapsulation Ef ciency was determined by centrifu-
gation techniques (Bhatia et al., 2014).
In brief, liposomes
containing essential oil was isolated from unencap-
sulated materials by using centrifuge at 10000rpm for
10 minutes (laboratory centrifuge Hettich Universal
320 R). The liposomes were destroyed in ethanol 90%
(Merck,Germany) and encapsulated essential oil content
was measured by using UV/VIS spectrophotometer at
270 nm of wavelength.
The morphology of liposomal formulation were Stud-
ied by Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) using an
AIS2100 (Seron Technology, South Korea).The release
study was performed by using dialysis membranes
method. In summary, the 1000 L of the 14.20 mg/mL
essential oil encapsulated liposomal samples were inside
the dialysis bag (MWCO 12kDa, Thermo Fisher Scienti c).
The dialysis system was suspended in a release volume
of 100 mL PBS at 37°C and rotated at 100 rpm (1:100
dilution between donor and acceptor compartments). At
scheduled intervals, 1 ml of the release medium was col-
lected for the UV spectrophotometric assay. The same
volume of fresh PBS buffer at the same temperature was
added immediately to maintain constant release volume.
The length of the dialysis tubing was kept consistent
for all methods to ensure that the surface area available
for dialysis remained constant. To ensure that dilution
between the donor and acceptor compartments provided
sink conditions, a 1:100 dilution study was conducted
and release volume was set at 100 mL PBS.
Results are presented as mean ± SEM. Statistical
analysis was performed using SPSS Software (version
22). The mean values were compared by one-way analy-
sis of variance (ANOVA) followed by the post-hoc test.
The differences of P < 0.05 were considered as statisti-
cally signi cant.
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
The results showed that nanoliposomes contain-
ing essential oils obtained from sonicator method are
smaller than extruder method. The average size of
nanoliposomes containing essential oil of three methods
were as follows: Thin Film> Extruder>sonicator. It was
also found that the concentration of essential oils affect
the size of the liposomes and nanoliposomes with low-
est essential oils have smaller size. On the other hand, it
was found that the ratio of cholesterol to total lipid in
the same concentration of Essential oil also affects the
particle size and in higher ratio of cholesterol to total
lipid, smaller nanoliposome can be achieved (Table 2).
The results showed that there was not signi cant
change on the PDI concentrations by changing the

Mohammad Hossein Arabi et al.
106 PREPARATION OF NANOLIPOSOMES CONTAINING
ESSENTIAL OIL OF ROSMARY
BIOSCIENCE BIOTECHNOLOGY RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS
effective in loading of essential oil and increasing the
percentage of cholesterol lead to increase the loading of
the essential oil (Table 2).
THE MORPHOLOGY OF NANOLIPOSOMES
SEM Images of nanoliposome shown in Figure1. As can
be seen all containing particles are spherical shape and
a coherent. They are homogeneous in size and shape.
As showed in the Figure 2, Essential oil concentra-
tions within solvent is relatively stable. It indicates lack
of EO leakage from liposomes over time. After initial
release of less than 1 % of total EO no more release
could be seen. This behavior is very desirable in stor-
age stability of nanoliposomes. It is important that
liposomes can protect and keep inside their cargo before
reach target site.
DISCUSSION
Essential oils and their components are volatile and sen-
sitive to environmental factors such as light, heat, pH
and oxidation. Encapsulation of essential oils reduced
degradation and increased its stability before arriving
target site.
Compare liposomes with different ratio of essential
oil/ total lipid showed that the essential oils in uence
the size of nanoliposomes and increasing in Rosemary
essential oil concentrations, increased the size of the
liposomes. Probably due to the arrangement of essential
oil into the lipid bilayer of liposomes fusion of bilayer
fragment increase and larger liposomes would formed.
Also, results revealed that by increasing the concen-
tration of essential oils, encapsulation ef ciency is
increased (Stimac et al., 2017).
The results of this study
as well as previous studies conclude that the method
FIGURE 1. The SEM image of nanoliposomes contain-
ingrosemary essential oils; prepared by sonication
method (A) and extrusion method(B).
concentration of essential oil. But as the concentration
of cholesterol increased in both sonication and extrusion
methods, PDI was increased. EO containing liposomes
prepared by thin lms have the highest PDI (0.9), but in
comparison the sonication and extrusion showed no sig-
ni cant difference (0.2; P value > 0.05). Add DOTAP to
the lipid composition of liposomes in comparison with
the same concentration of essential oils and cholesterol
showed not-signi cant difference, as shown in Table 2.
ZETA POTENTIAL
Nano-liposomes containing DOTAP have a zeta poten-
tial of +17 mV. Other liposomes due to the lack of charg-
ing ingredients, showed neutral charge.
Results showed that the preparation method of
nanoliposomes is effective on encapsulation of essential
oil. Nanoliposome prepared by sonicator and extrusion
have the maximum and Minimum of Essential oil load
respectively. Also increasing concentration of essential
oils is increasing its load into liposomes. On the other
hand, it was found that the percentage of cholesterol is
FIGURE 2. release curve for Rosemary Essential
Oil from H3 nanoliposomes containing Rose-
mary essential oils in hours

Mohammad Hossein Arabi et al.
BIOSCIENCE BIOTECHNOLOGY RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS PREPARATION OF NANOLIPOSOMES CONTAINING
ESSENTIAL OIL OF ROSMARY
107
of preparation of liposomes is effective on the size and
encapsulation ef ciency (Stimac et al., 2017; Saffari
et al., 2013).
In comparison with the three methods of
nanoliposome preparation: thin lm hydration, sonica-
tion and extrusion, the lowest and largest size of the
liposomes was related to sonication and thin lm hydra-
tion method but the Essential loaded into the liposomes
is more in the sonication method compare to extrusion
method one.
Against studies that showed use of sonication method
reduces the encapsulation ef ciency in nanoliposomes
production and may also lead to damage liposomes
phospholipid and loaded compounds (Stimac et al., 2017;
Khatibi et al., 2015)
this study doesn’t show a signi cant
reduction in encapsulation ef ciency in preparation of
liposome by sonication method.
Poly dispersity index is an index of particle size dis-
tribution in a system, which low level of that, re ects
the uniformity of particle diameter distribution. PDI less
than 0.1, indicating homogeneous particle diameter and
the value of that greater than 0.3 indicates heterogene-
ous distribution of particle diameter (Sinico et al., 2005).
In previous studies it has been reported that essential oil
containing liposome have wider size distribution than
liposomes without essential oils (Ruozi et al., 2005).
Comparisons between different concentrations of essen-
tial oil in the preparation of liposomes showed that
change in oil concentration had not a signi cant effect
on the liposome size distribution. (P value: 0.178) in
preparation of rosemary containing liposomes.
Also in the comparison between three methods of lipo-
some preparation, Method of preparation of liposomes
did not have signi cant effect on PDI, However, thin
lm hydration method was highest PDI.
Contrary to Ortan et al. reports, the results of this study
showed that cholesterol help to entrapment of essential
oil into nanoliposome structure, (Ortan et al., 2009) Unlike
previous studies that had been done on MLV liposome,
this study showed that in both methods of extrusion and
sonication, in the presence of essential oil, increasing the
concentration of cholesterol reduces the size of nanoli-
posomes (Arriaga et al., 2009; Detoni et al., 2009).
In analyze of SEM image of Nanoliposome contain-
ing Rosemary Essential Oil, particles had monodisper-
sity and spherical structure. This can reveal that critical
packing parameter of our composition is suitable for EO
containing liposomes.
The release study showed that essential oil release
from nanoliposome was very low during 24 hours
incubation time, which is probably due to lipophilic
properties of essential oil. Results showed impression
of multiple factor must be considered in this regard as
mentioned by different works (Fathi Moghaddam et al.,
2008; Rezaee et al., 2015)
.
EO can be trapped well inside
the liposomes. Adding DOTAP to the lipid composition
of liposomes enhances the encapsulation Ef ciency of
essential oil and on the other hand, increase the size of
the liposomes.
In brief, this study showed that the method of prepa-
ration of nanoliposomes containing Rosemary essential
oil has been effective on the particle size, dispersity and
encapsulation of essential oil. The study also found that
changes in formulation, percentage of cholesterol, addi-
tion of ionic lipid and using different ratio of essential oil
can cause changes in the physicochemical properties of EO
containing nanoliposomes. Present study also, revealed
that due to lipophilic and connection with nanoliposomes
rosemary EO have fewer tendency to release in physiolog-
ical environments. To determine the ef ciency and effec-
tiveness of drug delivery of liposomes, in-vivo studies on
animal models and MIC studies are useful.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The authors would like to thank Ms. Zahra Abbasian
& Ms. Astaraki for their valuable technical assistance.
This research was performed with support from research
Center of Kashan University of Medical Sciences.
Con ict of interest
There is no con ict of interest.
ABBREVIATIONS
EO: Essential Oil Tc: Transition temperature,PBS: Phos-
phate Buffered Saline, DOTAP: 1, 2-dioleoyl-3-trimeth-
ylammonium-propane, PC: Phosphatidyl Choline , Chol:
Cholesterol, PDI: Polydispersity Index, EE: Encapsula-
tion Ef ciency SEM: Scanning Electron Microscopy
REFERENCES
Altinier G, Sosa S, Aquino RP, Mencherini T, Della Loggia R,
Tubaro A.(2007) Characterization of topical antiin ammatory
compounds in Rosmarinus of cinalis L. J Agric Food Chem
55-1718-23.
Arriaga LR, López-Montero I, Monroy F, Orts-Gil G, Farago B,
Hellweg T. (2009) Stiffening effect of cholesterol on disordered
lipid phases: a combined neutron spin echo+ dynamic light
scattering analysis of the bending elasticity of large unilamel-
lar vesicles. Biophysical journal. 96(9):3629-37.
Bhatia A, Kumar R, Katare OP. (2004)Tamoxifen in topical
liposomes: development, characterization and in-vitro evalua-
tion. J Pharm Pharm Sci..7(2):252-9.
Bilia AR, Guccione C, Isacchi B, Righeschi C, Firenzuoli F,
Bergonzi MC.(2014) Essential Oils Loaded in Nanosystems: A
Developing Strategy for a Successful Therapeutic Approach.
Evid Based Complement Alternat Med,

Mohammad Hossein Arabi et al.
108 PREPARATION OF NANOLIPOSOMES CONTAINING
ESSENTIAL OIL OF ROSMARY
BIOSCIENCE BIOTECHNOLOGY RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS
Detoni C, Cabral-Albuquerque E, Hohlemweger S, Sam-
paio C, Barros T, Velozo E.(2009) Essential oil from Zanth-
oxylum tingoassuiba loaded into multilamellar liposomes use-
ful as antimicrobial agents. Journal of microencapsulation.
2009;26(8):684-91.
Fathi Moghaddam H, Sha ee Ardestani M, Saffari M, Navid-
pour L, Sha ee A, Rahmim A. (2008) Dopaminergic but not
glutamatergic neurotransmission is increased in the striatum
after selective cyclooxygenase-2 inhibition in normal and
hemiparkinsonian rats. Basic & clinical pharmacology & toxi-
cology 103(4):293-296.
Honorio VG, Bezerra J, Souza GT, Carvalho RJ, Gomes-Neto NJ,
Figueiredo RC. (2015) Inhibition of Staphylococcus aureus cock-
tail using the synergies of oregano and rosemary essential oils
or carvacrol and 1,8-cineole. Frontiers in Microbiology. 6:18-27.
Jalali-Heravi M, Moazeni RS, Sereshti H(2011) Analysis of Ira-
nian rosemary essential oil: application of gas chromatogra-
phy-mass spectrometry combined with chemometrics. J Chro-
matogr A. 1218(18):2569-76.
Khatibi SA, Misaghi A, Moosavy M-H, Amoabediny G, Basti
AA. (2015) Effect of Preparation Methods on the Properties of
Zataria multi ora Boiss. Essential Oil Loaded Nanoliposomes:
Characterization of Size, Encapsulation Ef ciency and Stabil-
ity. Pharmaceutical Sciences. 20:141.
Kraft JC, Freeling JP, Wang Z, Ho RJ. (2014) Emerging research
and clinical development trends of liposome and lipid nano-
particle drug delivery systems. Journal of pharmaceutical sci-
ences. 2014;103(1):29-52.
Moghimipour E, Aghel N, Mahmoudabadi AZ, Ramezani Z, Han-
dali S. (2012) Preparation and characterization of liposomes con-
taining essential oil of Eucalyptus camaldulensis leaf. jundishapur
journal of natural pharmaceutical products. 7(3):117-22.16.
Mozafari M.(2010) Nanoliposomes: preparation and analysis.
Liposomes: Methods and Protocols, Volume 1: Pharmaceutical
Nanocarriers. p. 29-50.
Ortan A, Câmpeanu G, Dinu-Pirvu C, Popescu L. (2009) Studies
concerning the entrapment of Anethum graveolens essential
oil in liposomes. Roum Biotechnol Lett. 14:4411-7.
Oxford English Dictionary, (2014) NEssential oil. (online,
American English ed.) 2014;07-21.
Peng CH, Su JD, Chyau CC, Sung TY, Ho SS, Peng CC.(2007)
Supercritical Fluid Extracts of Rosemary Leaves Exhibit Potent
Anti-In ammation and Anti-Tumor Effects. Bioscience, Bio-
technology, and Biochemistry. 71(9):2223-32.
Rezaee S, Khalaj A, Adibpour N, Saffary M. (2015) Correla-
tion between lipophilicity and antimicrobial activity of some
2-(4-substituted phenyl)-3 (2H)-isothiazolones. DARU Journal
of Pharmaceutical Sciences. 17(4):256-263.
Ruozi B, Tosi G, Forni F, Fresta M, Vandelli MA. (2005) Atomic
force microscopy and photon correlation spectroscopy: two
techniques for rapid characterization of liposomes. European
Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences. 25(1):81-9.
Saffari M, Tamaddon AM, Shirazi FH, Oghabian MA, Moghimi
HR.(2013) Improving cellular uptake and in vivo tumor sup-
pression ef cacy of liposomal oligonucleotides by urea as a
chemical penetration enhancer.; The journal of gene medicine
15(1):12-19.
Saraf S. (2010) Applications of novel drug delivery system for
herbal formulations. Fitoterapia. 81(7):680-9.
Sherry M, Charcosset C, Fessi H, Greige-Gerges H. (2013)
Essential oils encapsulated in liposomes: a review. Journal of
liposome research. 23(4):268-75.
Sinico C, De Logu A, Lai F, Valenti D, Manconi M, Loy G.
(2005) Liposomal incorporation of Artemisia arborescens L.
essential oil and in vitro antiviral activity. European Journal
of Pharmaceutics and Biopharmaceutics. 59(1):161-8.
Stimac A, Sekutor M, Mlinaric
´
-Majerski K, Frkanec L, Frkanec
R.(2017) Adamantane in Drug Delivery Systems and Surface
Recognition. Molecules. 22:297.