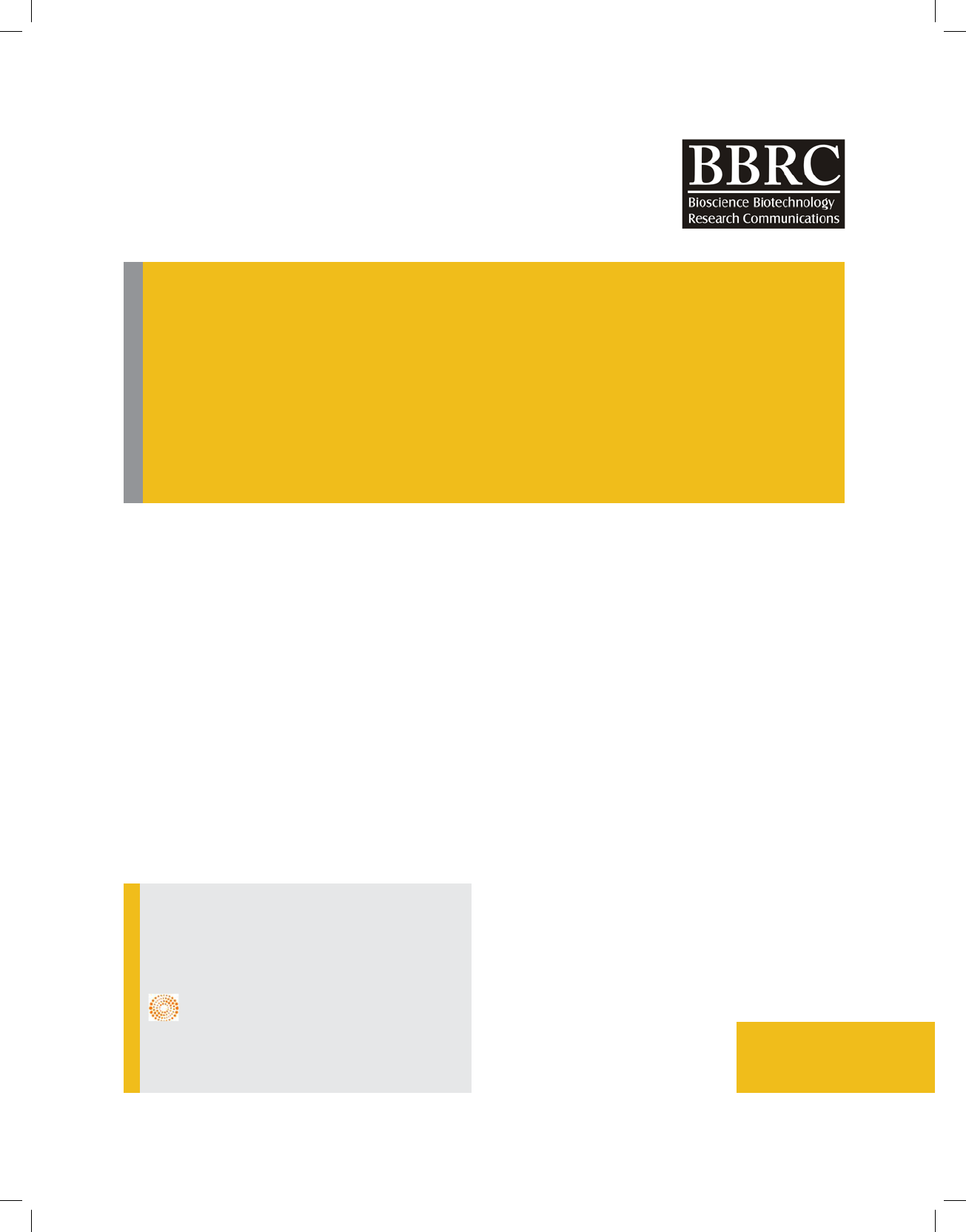
Biomedical
Communication
Biosci. Biotech. Res. Comm. 10(3): 445-454 (2017)
Fe3+-EDTA-zinc oxide nano-diagnostics: Synthesis and
in vitro cellular evaluation
Kimia Roshani
1
, Mazyar Etemadzade
2
, Ramin Farhoudi
3
, Seyed Esmaeil Sadat Ebrahimi
4
,
Morteza Pirali Hamedani
4
, Artin Assadi
5
and Mehdi Sha ee Ardestani
5
*
1
Faculty of Pharmacy, International Campus, Tehran University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran
2
Natioanl Institute for Genetic Engineering and Biotechnology (NIGEB)
3
Department of Laboratory Animal Science, Pasteur Institute of Iran, Karaj, Iran
4
Department of Medicinal Chemistry, Faculty of Pharmacy, Tehran University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran
5
Department of Radiopharmacy, Faculty of Pharmacy, Tehran University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran
ABSTRACT
Resulting from many efforts in opportune recognizing and correct treating brie y molecular imaging and therapy,
some methods or molecules have been developed by now to overcome any unwanted defaults in imaging and
therapy, speci cally nanoparticles. Generally, synthesis new compounds, for example Zinc Oxide-Iron nano-complex
consisting non-toxic paramagnetic ion [Fe3+] and its cellular uptake vehicle [zinc oxide] as a lowering risk of toxicity
and increase in cellular uptake liability, could be useful and noticeable in molecular imaging purposes. The isolated
nano-contrast was structurally analyzed by variety of techniques such as EDAX, AFM, Zeta and size measuring, SEM,
FTIR and UV spectrums. Finally for monitoring the nano-complex toxicity and cellular uptake on human embryonic
kidney cells named as HEK 293 was assessed respectively. The analytical result showed a very good promising size
at nanoscale and zeta potential as well as iron content for the suggested ferric containing nano-complex as well as
paramagnetic properties. Also outcome of cell study were resulted in no signi cant cellular toxicity comparing to
62% toxicity of control drug Magnevist and higher cellular uptake of 56% comparing to 9% for that of Magnevist
as well. In summary, it seems that the proposed ZnO-Fe nano-complex may be useful as a novel low risk contrast
agent to increase resolution in molecular Imaging like MRI and improve the current situation with the minimum cost.
KEY WORDS: SYNTHESIS, CONTRAST AGENT, MOLECULAR IMAGING, ZNO-FE3+ NANOCOMPLEX, HUMAN EMBRYONIC KIDNEY CELL
445
ARTICLE INFORMATION:
*Corresponding Author: sha eeardestani@gmail.com
Received 10
th
July, 2017
Accepted after revision 28
th
Sep, 2017
BBRC Print ISSN: 0974-6455
Online ISSN: 2321-4007 CODEN: USA BBRCBA
Thomson Reuters ISI ESC and Crossref Indexed Journal
NAAS Journal Score 2017: 4.31 Cosmos IF: 4.006
© A Society of Science and Nature Publication, 2017. All rights
reserved.
Online Contents Available at:
http//www.bbrc.in/
DOI: 10.21786/bbrc/10.3/18

446 CELLULAR EVALUATION OF ZINC OXIDE NANOPARTICLE CONTAINING IRON BIOSCIENCE BIOTECHNOLOGY RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS
Kimia Roshani et al.
INTRODUCTION
As per numerous endeavors in perfect perceiving and
right treating [early conclusion and treatment], expan-
sive quantities of creating strategies have been utilized
as of recently. One of the imperative one in this eld
is sub-atomic imaging, an advanced innovation which
gives legitimate component to the early recognition and
portrayal of the ailments, checking of natural process in
body, assessment of treatment and observing reaction,
almost assessing drug pharmacokinetics. Atomic imag-
ing as shows is the molecularly focused on, constant,
and noninvasive imaging of wonders and procedures
at cell and subcellular levels, (Meade et al. 2009). For
upgraded determination execution imaging specialist as
little particles, built protein nanoparticles has been per-
formed, (James etal. 2012 Rameshwar etal. 2015 Langer
etal. 2015).
At present there are a few imaging modalities usually
utilized for atomic imaging like Magnetic Resonance
which bene ts balance operators with paramagnetic
owing to properties and the others incorporate positron
emission tomography (PET), single-photon emission
computed tomography (SPECT), computerized tomogra-
phy (CT), optical imaging [ uorescence and biolumines-
cence], photo acoustic imaging. Contrasted with other
imaging modalities, the principle points of interest of
attractive reverberation imaging is its great determina-
tion which can enhance by upgrading contrast special-
ist. The rst kind of clinically applied radio-opaque usu-
ally known as contrast agents were salts of chemically
designed complexes by paramagnetic diagnostics, such
as Ferric (Fe III), gadolinium (III) and manganese (II)
which their mechanisms show that such complexes of
mentionedparamagnetic radio-metalsdecrease the longi-
tudinal (T1) and transverse (T2) relaxation parameters of
surrounded water molecules, (Lauffer etal.1987), (Toth
etal. 2002) (Schwert etal. 2002).
Indeed it is notifying about paramagnetic compounds
as chemically designed agents ready to go about as dif-
ferentiation operators in the locales where they disperse
in body and improve differentiate amid imaging. Among
the difference operator the greater part of them are low
sub-atomic weight metal edi ces. Also the utilization of
paramagnetic metal for this propose, nanomedicine for-
mulation by employing different types of nanoparticles
such as polymeric or metal based such as zinc oxide
nanoparticles have been vastly used for imaging appli-
cations beside for therapeutic goals. Little size of nano-
particles encourage the auspicious identi cation of little
different changes furthermore give a high surface range
to stacking different atoms. Attractive nanoparticles
have additionally been utilized to convey medications
to a sick range, (Barakat, 2009).
It is another test utilizing nanoparticle as a part
of both indicative and restorative objectives. In such
framework the name as theranostic has been more rec-
ognizable in scientist’s mentality, nanoparticles assume
an essential part as growing high ag force and limit
with regards to various application, (Jain et al. 2008).
The fundamental advantages of utilizing nanoparticle
as a part of symptomatic and imaging are low lethal-
ity, site-particular collection and hours of course time
next to their wellbeing and biocompatibility, (Jesse etal.
2011). In spite of broadly utilization of difference oper-
ator up to now, many looks into are progressing due
symptoms and lethality of complexity specialist espe-
cially in crucial organs, for example, kidney and here
and there low determination that are the primary issues
as dependably uncommonly in the individuals who uti-
lize this strategy to catch up the treatment procedure
forever. Even so, synthesis new compounds with all the
ideal index have still been restricted and have no com-
plete in vitro or in vivo data. Herein, we synthesis a
new Compound including Zink Oxide nanoparticle in
chelation with Fe
3+
-EDTA in optimal condition with the
aim of creating low risk contrast agent and improving
the current situation along with minimum cost. Brie y
in current experimental observations, stable complex of
iron with a chelator was formed and then such complex
loaded into zinc oxide nanoparticle for increase in cel-
lular uptake liability of tumors.
MATERIAL AND METHODS
Zincsulfate hepta hydrate [ZnSO
4
.7H
2
O, Merck], Sodium
Hydroxide [Merck], Deionized Water, EthyleneDiamin
Tetra Acetic acid [99.5 %, Merck], Ferric-Cholorid
hexa hydrate [FeCl
2
.6H
2
O, Merck] were used for the
synthesis of the materials. In the following, scanning
electron microscope [SEM] with EDAX analysis was
provided by Phenom-Prox model made in Holland
Atomic-force microscopy[AFM] image was obtained
by CP-RESEARCH[CP-R] model, VEECO Manufacturer
Company made in America. Zeta potential and size on
nanoparticle in water as a solvent and ultimate nano-
complex in DMSO as a solvent were performed by Mal-
vern Nano-Zetasizer from Pasteur Institute in Tehran.
Fourier Transform Infrared spectroscopy [FTIR] result
was measured by Perkin Elmer, Spectrum Two FT-IR and
at the end ultraviolet-visible spectrum was measured on
VARIAN, CARY 100 Bio UV-VIS. Cells and related medi-
ums were provided from Pasteur Institute of Iran.
SYNTHESIS OF ZINC OXIDE NANOPARTICLE
In order to synthesize ZnO nanoparticle water based
solution [0.2 M] of zinc nitrate as well as a prepared

BIOSCIENCE BIOTECHNOLOGY RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS CELLULAR EVALUATION OF ZINC OXIDE NANOPARTICLE CONTAINING IRON 447
Kimia Roshani et al.
[0.4 M] of NaOH was prepared by using deionized water,
respectively. The accessible NaOH solution was dropped
into zinc nitrate medium at room temperature[rt] with
accurate stirring, which advanced in the accumulation
of abeyance with a white color. Resulting white nished
compound was elaborately centrifuged at 5000 rpm for
at least 20 min and then washed three times with eluting
solution of distilled water as well as washing with abso-
lute alcohol nally. The acquired artefact was nally
calci ed at 500 °C in air atmosphere for 3 hrs to achieve
zinc oxide NP respectively.
SYNTHESIS FE
3+
-EDTA COMPLEX
1 mol EDTA equivalent 0.25g [M=292.2 g/mol] was
mixed with 20ml distilled water and after 5 minutes of
stirring, 1 mol Ferric Choloride hexa hydrate equivalent
0.27g [M=270 g/mol] was added to the container. The
mixture was heated to 90
0
C for 10 minutes with stirring.
Then after wrapping the foil placed 7-10 days without
moving in laboratory condition to form the intended
complex. Eventually puri ed by sephadex G25 column
or Dialysis bags [cut off 1000Da] as well.
SYNTHESIS ZNO-FE-EDTA NANOCOMPLEX
To synthesis the ultimate complex, half of the amount of
Fe-EDTA complex was added to the double amount of
Zinc Oxide nanoparticle with 5-7ml distilled water and
were stirred for 20 minutes to obtaine light brick color
transparent solution and placed 7-10 days without mov-
ing in 25
0
C, covering with aluminum foil. Henceforth
puri cation by sephadex G25 was performed as previ-
ous step.
In order to con rm the nal structure, nanocomplex
was structurally analyzed by variety of techniques. To
characterize size, morphology, elements Scanning Elec-
tron Microscopy[SEM] withEDAX analysis was used,
andcalculation of the roughness parameters meas-
ured by means of the Atomic Force Microscopy[AFM],
Zeta and size measuring ,also Fourier transform infra-
red spectroscopy[FTIR] is an established tool for the
structural characterization of the new complex and in
additionUltraviolet[UV] spectrum was used to identify
the active site in nanocomplex, measuring zeta potential
and size of nanoparticle was done eventually.
IN VITRO CELLULAR TOXICITY [XTT]
In order to nd and assesse the possible toxic param-
eters of synthesized zinc oxide nanoparticles contain-
ing trivalent iron-EDTA, XTT method was employed
as described in detail in the literature. Furthermore, as
stated in literature one of the possible route of discretion
of nanoparticle from the body as well as major affected
body part of human by the contrast agents is kidney,
HEK-293 was elected for XTT experimental analysis and
observations based on the effects of different dosages of
zinc oxide nanoparticles containing trivalent iron-EDTA,
Fe
3+
-EDTA and Magnevist [as a FDA approved MR con-
trast agent] as controls. XTT data were performed for 72
h period of time.
IN VITRO CELLULAR UPTAKE
To evaluate the cancerous cellular permeability of zinc
oxide nanoparticles containing trivalent iron-EDTA,
MCF-7 was chosen and different dosages of zinc oxide
nanoparticles containing trivalent iron-EDTA, Fe
3+
-EDTA
and Magnevist [as a FDA approved MR contrast agent]
as controls were assessed at an obvious time of 6 hours
after exposure. After a subjected times cells treated by
the agents were eluted by cell culture medium and the
cells were centrifuged and lysed by acidic medium. The
resultant solution was transferred to detect amunts of
Gd
3+
and Fe
3+
by ICP-Mass spectroscopy as well. Inter-
cellular concentration of metals were considered as per-
centage of cellular uptake.
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
In Figure 1 SEM with EDAX analysis for ZnO nanopar-
ticle is presented, in addition the image of the sample in
various dimension, the result of SEM also be displayed as
spectrums. The EDAX pattern exhibited different peaks
that each of them shows a speci c element percentage.
The higher peak represents greater concentration. In
this way, each element has a special atomic structure
containing series of peaks. We have followed the same
procedure after preparation of Fe-EDTA complex and
ultimate nanocomplex and prominent additional peaks
for new elements are obvious whereas those peaks are
completely absent in the case of EDAX spectra of the
ZnO nanoparticle.
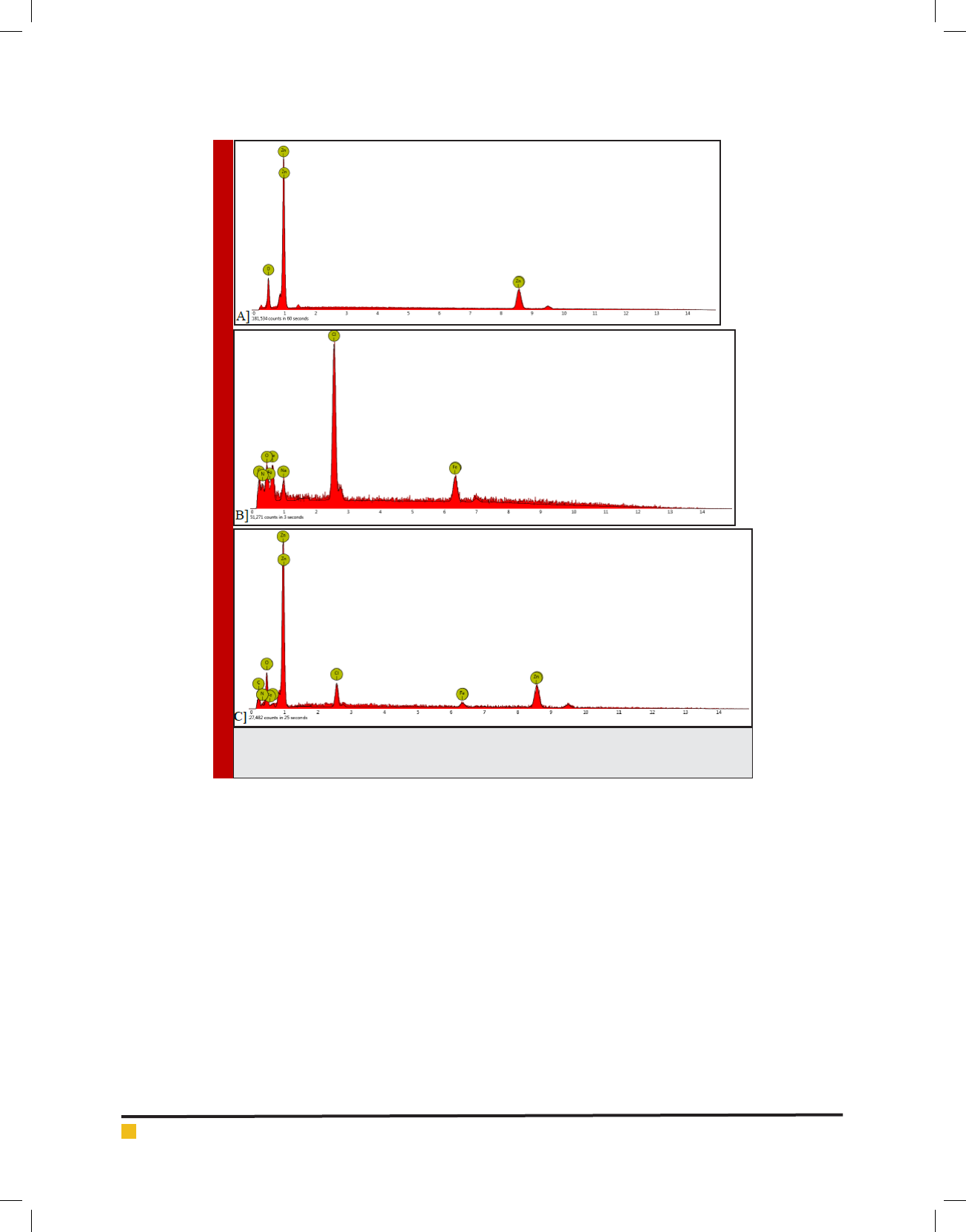
In Figure 2 AFM topography of the as prepared ZnO
nanoparticle and the ultimate nanocomplex are pre-
sented. The diagram and two-dimensional images of the
initial nanoparticle and conclusive nanocomplex are
shown in Figure 2a-b which shows the approximate the
height of the sample. Three-dimensional images of ZnO
nanoparticle and nal complex are displayed in Figure
2c-d that shows peak-valley more concretely. The Fe-
EDTA complex is inside ZnO nanoparticle pores ran-
domly resulting in the formation and size of nanocom-
plex. As the load increases, the values of area roughness,
line roughness, and also peak−valley height increases
obviously. Thus surface morphology veri cation of
nanoparticle and terminal nanocomplex was deter-
mined by AFM technique. The changes are explicated by
448 CELLULAR EVALUATION OF ZINC OXIDE NANOPARTICLE CONTAINING IRON BIOSCIENCE BIOTECHNOLOGY RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS
Kimia Roshani et al.
FIGURE 1. SEM with EDAX analysis, [A] EDAX of ZnO nanoparticle, [B] EDAX of Fe-EDTA
complex, [C] EDAX of ZnO nanoparticle with Fe-EDTA as a nanocomplex.
comparing the graphs. Another physicochemical param-
eter which has been investigated by Zetasizer is particle
size and zeta potential. The average diameter, particle
size distribution index, intercept of ZnO nanoparticle
and nal nanocomplex is shown in Figure 3 and in
addition the nanoparticles charge surface before and
after reactionsare-7.31mv and -5.63mv respectively.
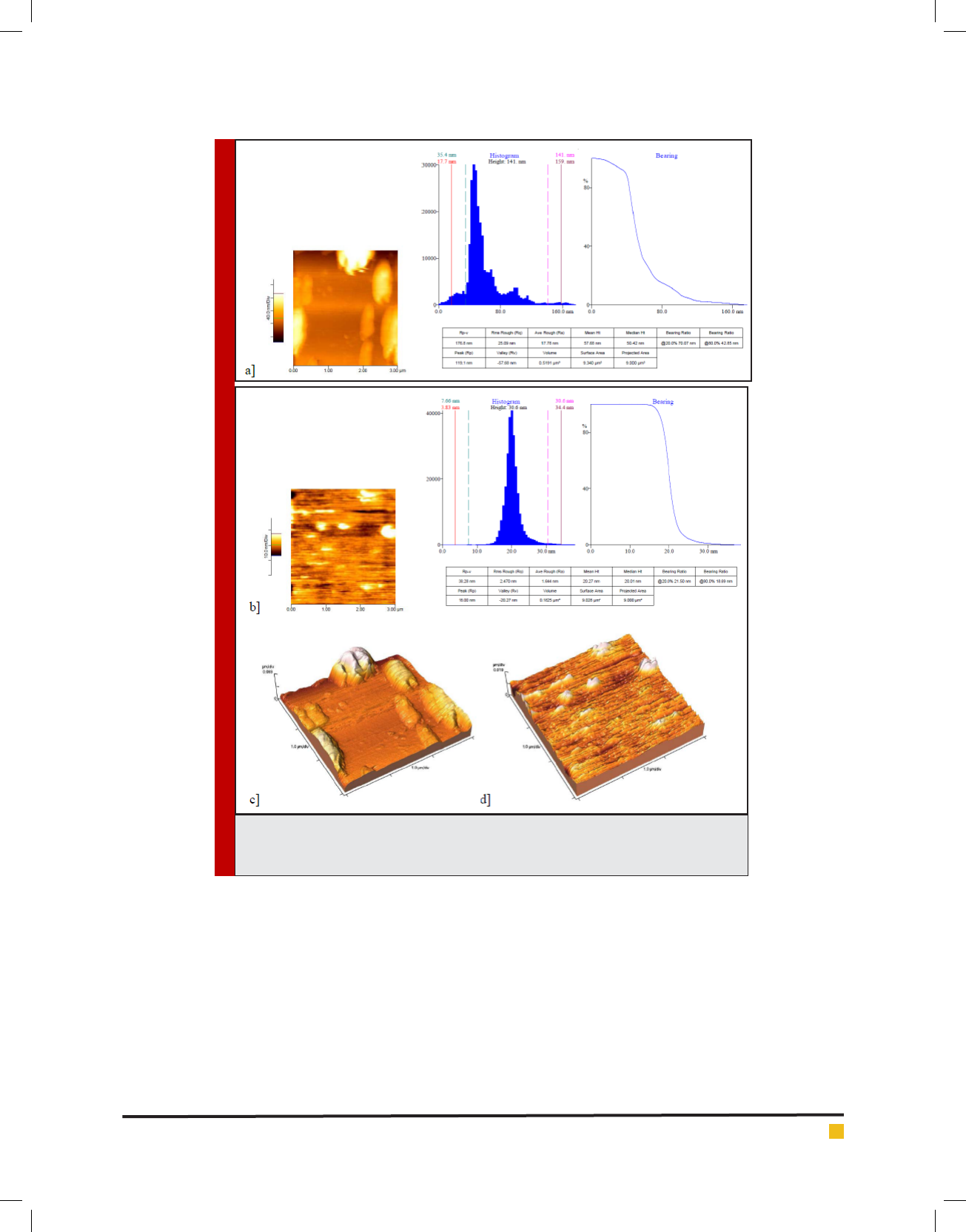
The FTIR spectrum support the result obtained from
SEM, AFM, Zetasizer. After each reaction new peaks
appear that proverecent atoms and links as an example
a FTIR absorption band is observed at 3436 cm
-1
which
represents NH link related an amino group of EDTA or
the peak in ngerprint zone, about 440 cm
-1
reveals
presence of halogen of FeCl
3
in nal nanocomplex and
background spectrum of ZnO nanoparticle including a
peak at 2926 cm
-1
con rms the presence of zinc oxide
nanoparticle.Figure.4 give more explanation about spec-
trums.
At the end UV-VIS spectra absorption is recorded
between 200-800nm wavelengths. In Figure 5 there is
a clear indication of Fe-EDTA complex in the absorp-
tion spectrum after loading. The absorption spectrum
of the Fe-EDTA complex shows two peaks with absorp-
tion between 1.5-2.5 which the rst one is related to
Carboxylic Acid group of EDTA and the second one
demonstrates Ferric Choloride that because of its orbital
properties is tended to long wavelengths or visible light.
Also the nal nanocomplex dissolved in DMSO shows
a sharp and narrow peak between 0.2-1nm comparably
the previous one.
Moreover, as stated in Figure. 6 zinc oxide nanoparti-
cles containing trivalent iron-EDTA, Fe
3+
-EDTA at all the
BIOSCIENCE BIOTECHNOLOGY RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS CELLULAR EVALUATION OF ZINC OXIDE NANOPARTICLE CONTAINING IRON 449
Kimia Roshani et al.
FIGURE 2. [a] 2D image and diagram of ZnO nanoparticle, [b] 2D image and diagram of
ultimate nanocomplex, [c] 3D image of ZnO nanoparticle at the previous zone, [d] 3D
image of ultimate nanocomplex at the previous zone.
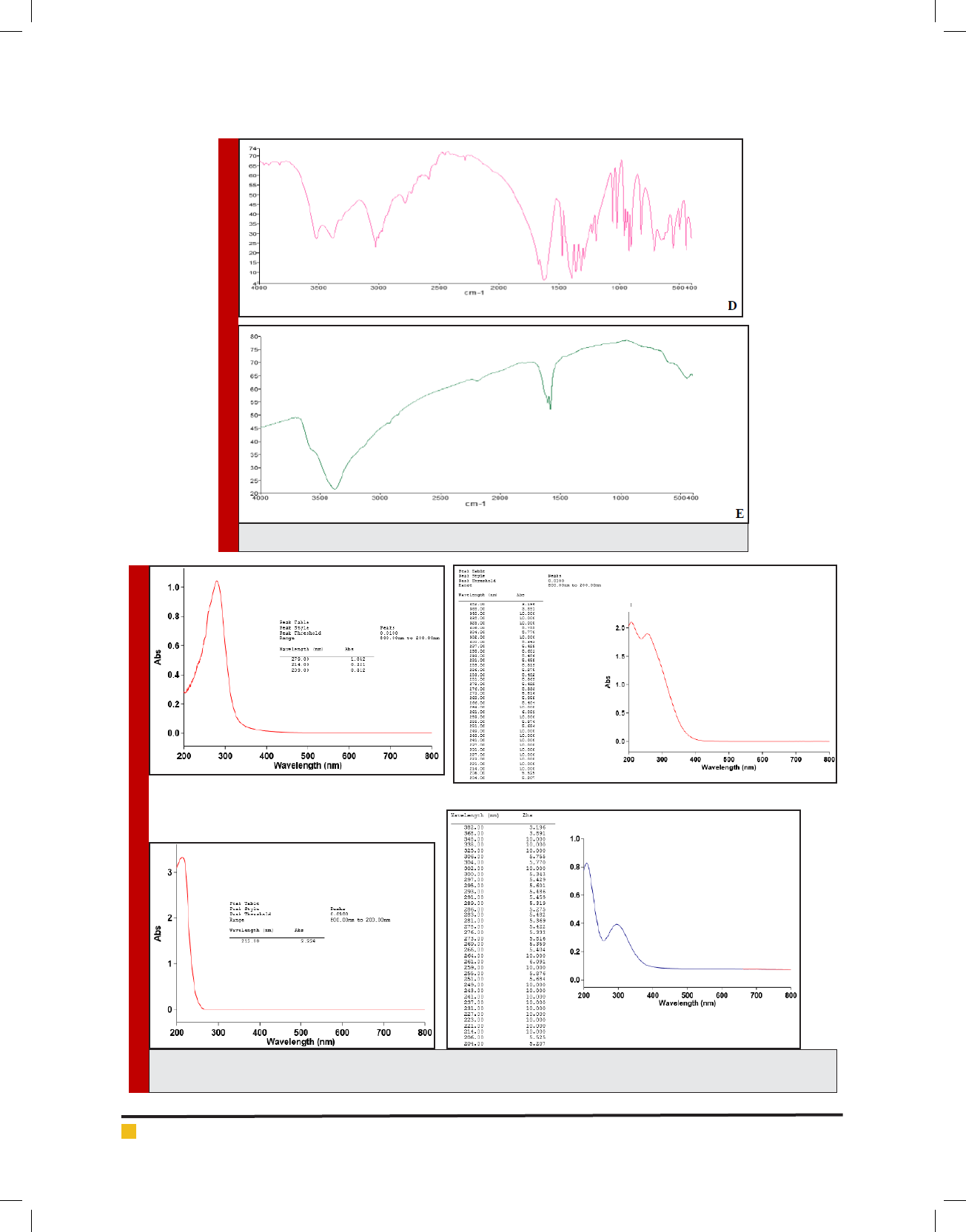
used dosages did not rise any signi cant toxic effects on
human kidney cells otherwise a signi cant toxic effects
was shown by Magnevist 100 μM [as a FDA approved
MR contrast agent] as control caused 62% cellular mor-
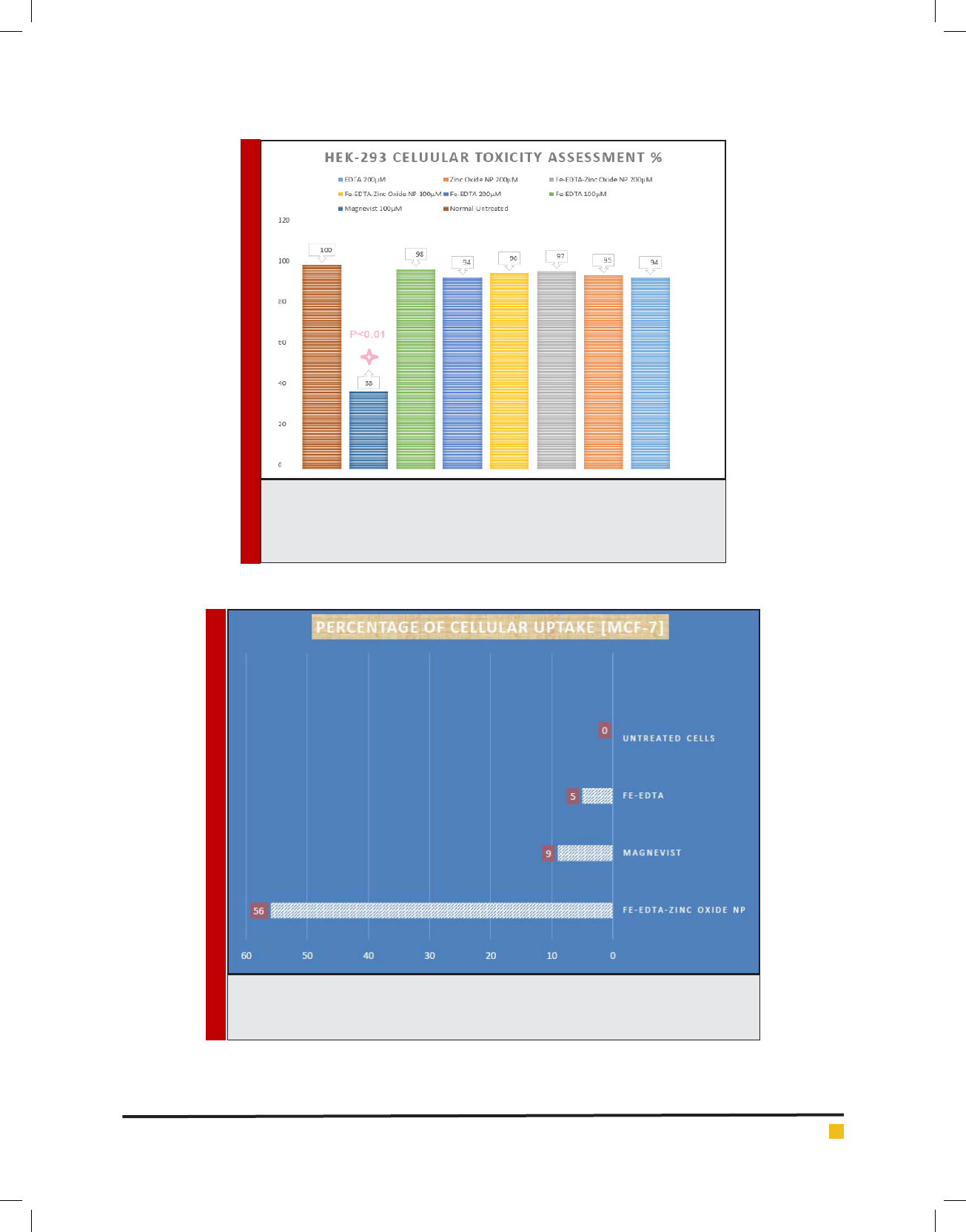
tality respectively. Additionally a very good promising
cancer cell uptake was recorded for zinc oxide nanopar-
ticles containing trivalent iron-EDTA 56% comparing to
9% for that of Magnevist and 5% for Fe-EDTA as well
[more details Figure 7].
As it is clear utilizing contrast specialist as a part of
sub-atomic imaging is a discussable subject in atomic
prescription, so pro ted a low dangerous balance opera-
tor with ideal impact has dependably been a worry. Too
Many diverse diagnosis of some targeted human body
sections in molecular imaging methodology including
Magnetic Resonance Imaging MRI showed noticeable
drawbacks that could be considered as dif culties to
remain them also without other con rmation techniques
that mostly would be invasive or even de ned as impos-
sible, (Rameshwar etal. 2015).
Nephrotoxicity and unfavorably susceptible response
of many difference operator are the other test because

Kimia Roshani et al.
450 CELLULAR EVALUATION OF ZINC OXIDE NANOPARTICLE CONTAINING IRON BIOSCIENCE BIOTECHNOLOGY RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS
FIGURE 3. [a] size of ZnO nanparticle is shown at the left side, and the graph on the right
related to nal nanocomplex. [b] ZP of ZnO nanoparticle is on the left and the right one is ZP
of ultimate nanocomplex.
of their structure and phisico-concoction portrayal. In
such cases FDA caution is not immaterial showing the
improving shot of Nephrogenic Systemic Fibosis [NSF]
and or Nephrogenic Fibrosing Dermopathy [NFD] for
the determined patients confounded to have renal dis-
appointment maladies. [Enzo et al. 2010] What’s more
moderate discharge and high lethality of numerous mac-
romolecular complex, for example, Gd III, are because of
the digestion system which can discharge Gd III parti-
cle in body, (Zheng-Rong etal. 2003). Magnetic nano-
bio-materials like fe-EDTA-prepared zinc oxide NP
nanocomplex using in MRI have been well offered for
the next subsequent imaging such viable tumor places
(Langer etal. 2015) then again different techniques which
require keeps imaging amid treatment. However nano-
drugs like nano-complex can defeat natural obstructions
which can impact on conclusion and treatment because
of passing particles. Then again this nano scale give a
fast dissemination amid systemic conveyance further-
more can be cleared up easily (Frank etal. 2008). These
qualities gather least danger and time to get the most
extreme impact and tissue aggregation. Numerous mol-
ecule in view of nanotechnology have been considered
to conform the pharmacokinetic properties furthermore
upgrade the relaxivity which metal-based nanoparticle
can be noted, (Enzo etal. 2010, Na etal. 2008).
In this work we have used FeCl
3
chelating with EDTA,
a six dentate ligand, and react the resulting complex to
ZnO nanoparticle to be placed in its pores and structure
properly. Ferric as main recognized paramagnetic iona-
ble to provide adequate magnetic effects on surrounding
water atoms and causes to reduce in T
2
and or T
1
relaxa-
tion time quantities. Subsequently this decline makes a
brighter picture in light of T1 relaxation time lessening
and darker picture consequently diminishing T2 relaxa-
tion time, (Brown etal. 2003) (Na etal. 2008). Contrast-
ing with present difference operator, Gd buildings are
delegated the specialists that impact on T1 relaxation
time and can’t wide water proton resonance and also
T2 specialist, for example, paramagnetic and superpara-
magnetic specialist containing iron. [(Luca etal. 2012))
(Na etal. 2008)]. So creating new compound by having
both T1 and T2 diminishment can be so useful. There-
for in this paper we synthesized ZnO-Fe nanocomplex
besides EDTA as a safe FDA approved and low cost
effective chelator in optimum condition.
The result of physico-chemical study showed a good
and acceptable data and also low toxicity, at least cost
and availability of the material needed are the other pos-
itive aspects. The small size of nanocomplex and exist-
ing Fe
3+
as a paramagnetic agent in ultimate complex
displayed a stable and appropriate complex in different
Kimia Roshani et al.
BIOSCIENCE BIOTECHNOLOGY RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS CELLULAR EVALUATION OF ZINC OXIDE NANOPARTICLE CONTAINING IRON 451
FIGURE 4. FTIR spectrums regarding prepared nanoparticle containing Fe-EDTA [A],
Zinc Oxide NP [B], Fe-EDTA [C], EDTA [D] as well as FeCl3 [E].
features such as size, surface charge, topography, func-
tional groups and fundamental elements. Ease of entry
and low risk of cytotoxicity make this nanocomplex as
a novel carrier in loading some drugs and having thera-
peutic effects in addition to diagnostic effects especially
in tumor cells with prominent uptake.Consequently,
based on these points and outcomes synthesized ZnO-Fe
nanocomplex can freely play an important and effective
role in the replacement of present contrast agent in MR
molecular imaging erelong.
A novel nanocomplex of ZnO-Fe along with EDTA
has been prepared by a simple chemical approach as a
low toxicMR contrast agent. Thus after chelating iron by
EDTA, composed complex reacts with ZnO nanoparti-
Kimia Roshani et al.
452 CELLULAR EVALUATION OF ZINC OXIDE NANOPARTICLE CONTAINING IRON BIOSCIENCE BIOTECHNOLOGY RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS
FIGURE 5. U.V spectroscopy data regarding prepared nanoparticle containing Fe-EDTA [A], Fe-EDTA [B], EDTA [C] as
well as FeCl3 [D].
A
B
D
C
FIGURE 4. (Continued)
Kimia Roshani et al.
BIOSCIENCE BIOTECHNOLOGY RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS CELLULAR EVALUATION OF ZINC OXIDE NANOPARTICLE CONTAINING IRON 453
FIGURE 7. Depiction of competitive MCF-7 cellular uptake regarding Magnevist, Fe-EDTA
and Fe-EDTA-Zinc Oxide NP respectively. Obtained data were recorded from a period of 6hr
at the same concentration of 50 μM.
FIGURE 6. Illustrations of HEK-293 Cellular Toxicity resulting from 72 hrs.
Exposure to different concentration of Magnevist, Fe-EDTA and Fe-EDTA-Zinc
Oxide NP respectively. Potential signi cant toxicity regarding to Magnevist was
observed otherwise no toxic effects were recorded for proposed NP as well.

454 CELLULAR EVALUATION OF ZINC OXIDE NANOPARTICLE CONTAINING IRON BIOSCIENCE BIOTECHNOLOGY RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS
Kimia Roshani et al.
cle and a new stable nanocomplex is formed. Small size
of ZnO in nano scale helped to uptake more by cells.
The presence of Ferric Chlorideas a valuable magnetic
agent makes opportune recognizing easier in molecular
imaging like Magnetic Resonance Imaging. The phys-
icochemical characteristics were monitored by different
analysis resulting in desired achievements that con rm
the nal nanocomplex without any structural damage.
In conclusion, along the development of nanoparticles
for targeted diagnosis and therapy for biomedical appli-
cation, proposed ZnO-Fe nanocomplex may be useful
as a novel low risk contrast agent to increase resolution
in molecular Imaging like MRI and improve the current
situation with the minimum cost. Considering lower
normal human cellular toxicity as well as higher and
promising cancerous human cellular uptake comparing
to Magnevist it could be concluded that such iron con-
taining nanoparticle marked as new target for future in
vivo studies as well as clinical practice.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The authors would to thank Tehran University of Medical
Sciences as well as all laboratories and technicians who
provided supported during within the course of the study.
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
The authors declared no con ict of interest.
REFERENCES
Barakat, N. S. (2009). Magnetically modulated nano systems: a
unique drug-delivery platform. Nanomedicine, 4 [7], 799–812.
Brown, M. A.; Semelka, R. C. (2003).MRI: Basic Principles and
Applications; Wiley-Liss: New York.
Enzo T, Daniela D C, Alessandra V, Silvio A. (2010).Challenges
for Molecular Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Chem. Rev, 110,
3019–3042.
Frank ,Eric P,Linda K. M,Omid C. (
2008).Factors Affecting the
Clearance and Biodistribution of Polymeric Nanoparticles.Mol.
Pharmaceutics,5[4], pp 505–515
Jain, P. K.; Huang, X.; El-Sayed, I. H.; El-Sayed, M. A. (2008)
.Noble metals on the nanoscale: optical and photothermal
properties and some applications in imaging, sensing, biology,
and medicine. Acc. Chem. Res, 41 [12], 1578–1586.
James, M. L., and Gambhir, S. S. (2012) . A molecular imaging
primer: modalities, imaging agents, and applications. Physiol.
Rev. 92, 897−965
Jesse V. J, Sanjiv S. G. (
2011).Molecular Imaging with Ther-
anostic Nanoparticles.
Acc. Chem.Res., 44 [10], pp 1050–
1060
Langer, R. and Weissleder, R. (2015). Nanotechnology. JAMA.
313, 135-136
Lauffer, R. B. [1987]. Paramagnetic metal complexes as water
proton relaxation agents for NMR imaging: theory and design.
Chem. Rev. 87, 901−927.
Luca F, Junqing Z, Changning W, Chunying W, Robert H.
M, Yanming W.
(2012) Myelin Imaging Compound [MIC]
Enhanced Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Myelination. J.
Med. Chem.,55[1], pp 94–105
Meade, T. J., and Aime, S. (2009). Chemistry of molecular
imaging. Acc. Chem. Res. 42, 821−821.
Na, H. B.; Hyeon, T. (2009). Nanostructured T1 MRI contrast
agents. J. Mater. Chem., 19, 6267.
Na, H. B.; Song, I. C.; Hyeon, T. (2009). Inorganic Nanoparticles
for MRI Contrast Agents. Adv. Mater., 21, 2133–2148.
Rameshwar P, Alexander V. L, Pallavi R. G, Hui D, Jose
P.A,Shawn W,Satoshi I,Bindu K,Arthur R,Alexandra C,Janet
L. M,Vladimir A. L,Debiao L,Ravi S. P,Keith L. B,Eggehard
H, andJulia Y. L.
(2015). MRI Virtual Biopsy and Treatment
of Brain Metastatic Tumors with Targeted Nanobioconjugates:
Nanoclinic in the Brain.ACS Nano,9[5], pp 5594–5608
Schwert, D., Davies, J., and Richardson, N. (2002) NonGadolin-
ium-Based MRI Contrast Agents [Krause, W., Ed.] pp 165−199,
Springer, Berlin
Toth, E., Helm, L., and Merbach, A. (2002) Relaxivity of
MRI Contrast Agents [Krause, W., Ed.] pp 61−101, Springer,
Berlin.
Zheng-Rong L, Xinghe W, Dennis L. P, K. Craig G, Henry R. B.
(2003). Poly [L-glutamic acid] Gd[III]-DOTA Conjugate with a
Degradable Spacer for Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Biocon-
jugate Chem, 14, 715−719