
Pathological
Communication
Biosci. Biotech. Res. Comm. 10(3): 391-397 (2017)
Comparison of multiplex ligation-dependent probe
ampli cation and qPCR for screening PAX5 gene
detection in acute lymphoblastic leukemia
Sahar Mehranfar
1, 2
, Sirous Zeniali
3,4
, Nasser Samadi
5
, Nazanin Maleki Sadeghi
6
and
Abbasali Hosein Pour Feizi
7
*
1,7
Hematology & Oncology Research Center, Tabriz University of Medical Sciences, Tabriz, Iran
2
Department of Molecular Medicine, School of Advanced Medical Science, Tabriz University of Medical
Science, Tabriz, Iran
3
Department of Molecular Medicine, Biotechnology Research Center, Pasteur Institute of Iran, Tehran, Iran
4
Kawsar Human Genetics Research Center, Kawsar Genomics Center, Tehran, Iran
5
Department of Biochemistry, Faculty of Medicine, Tabriz University of Medical Sciences, Tabriz, Iran
6
Lorestan University of Medical Sciences, Khorramabad, Iran
ABSTRACT
Despite the advances in diagnosis of leukemia, still we need a rapid and cost-bene t screening method in patients
with acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL). The aim of the present study is to evaluate the ability of Multiplex Ligation-
dependent Probe Ampli cation (MLPA) method in screening patients with ALL. 45 patients with ALL were selected. DNA
were extracted, then PAX5 gene copy number abnormalities (CNAs) were studied by adopting MLPA and QPCR methods.
To prove the results of two methods, PCR product from three samples were sent for sequencing. From 45 patients with
B-ALL, 11 (24%) patients, showed CNAs after applying MLPA method. From among all mutations, 22 samples (29%)
were seen in PAX5 gene. We used Sanger sequencing as a gold standard method to compare the two methods. After
sequencing, we were submitted 2 genes in Gene Bank by accession numbers (ID) KX608846 and KX707789 in exon 10
of PAX5. MLPA is a rapid and valid method for screening of genes mutation and can be used in these laboratories as
routine method especially in low-income countries.
KEY WORDS: ACUTE LYMPHOBLASTIC LEUKEMIA, COPY NUMBER ABNORMALITY, MLPA, QPCR
391
ARTICLE INFORMATION:
*Corresponding Author: pourfeizi@yahoo.com
Received 2
nd
July, 2017
Accepted after revision 22
nd
Sep, 2017
BBRC Print ISSN: 0974-6455
Online ISSN: 2321-4007 CODEN: USA BBRCBA
Thomson Reuters ISI ESC and Crossref Indexed Journal
NAAS Journal Score 2017: 4.31 Cosmos IF: 4.006
© A Society of Science and Nature Publication, 2017. All rights
reserved.
Online Contents Available at: http//www.bbrc.in/
DOI: 10.21786/bbrc/10.3/9

Sahar Mehranfar et al.
INTRODUCTION
Today, B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (B-ALL) is the
most common childhood malignancy, especially in chil-
dren below ve years of age. Today, we have extensive
knowledge about leukemia like other cancers. In the last
two decades, molecular methods have provided the physi-
cians and researchers with a new vision towards the role
of molecular factors in pathogenesis of diseases. Alterna-
tive expression leads to the abnormal proliferation and
differentiation of lymphoid ancestors (Fazio, Biondi, &
Cazzaniga, 2011; O’neil & Look, 2007 Seiter etal., 2014).
Paired Box5 (PAX5) is an important transcription
factor located on chromosome 9p13 and includes 10
exons. PAX5 is essential factor for the development
of pro-B cell to mature B-cell(Fazio etal., 2011). Up to
now, nine PAX transcription factors have been demon-
strated, although, PAX5 is the only PAX protein which is
expressed in the hematopoietic system (Busslinger, 2004;
Cobaleda, Schebesta, Delogu, & Busslinger, 2007; Mat-
thias & Rolink, 2005). The improvement of diagnostic
and treatment protocols by using risk-adapted methods
have enhanced cure rate up to 80%(Carter etal., 2001).
Therefore, the identi cation of biomarkers can be a
great help for the patients and the health-care system to
reduce the health-care costs and side effects of chemo-
therapy. Screening is highly pivotal in the developing
countries where the nancial resources and drugs are
limited. Childhood cancer rates has been rising slightly
in the past few decades (Fathi etal., 2015).
In Iran, leukemia has an increasing trend and leaves
a heavy burden on the whole society,(Fazeli etal., 2013).
Thus, more attention needs to be paid to screening, early
diagnosis, and effective treatment in order to increase the
survival rate for children’s cancer (Mousavi etal., 2008).
In this study, we carried out Multiplex Ligation-depend-
ent Probe Ampli cation (MLPA) analysis on 45 ALL patients’
samples to determine the copy number abnormality (CNA)
of PAX5 gene. MLPA is a technique capable of showing
variations in the copy number of several human genes.Due
to this capability, MLPA is mostly used in the molecular
diagnosis of several genetic diseases whose pathogenesis
is related to the presence of deletions or duplications of
speci c genes,(Schouten etal., 2002; Stuppia, Antonucci,
Palka, & Gatta, 2012). Also, we adopted the real-time PCR
method for comparing the results of two methods.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
58 Bone marrow(BM) or/and peripheral blood (PB) sam-
ples were taken at the time of diagnosis of patients with
B-ALL, who were presented to the Children’s Hospital
of Tabriz University of Medical Sciences, between 2014
and 2016. The selection criteria included having at least
20% blast cells, and being between 1-14 years of age
at the time of diagnosis. The exclusion criteria were the
samples from foreign patients and DNA with insuf -
cient quality. Six samples were excluded due to failure
of MLPA, Five samples due to bad quality of DNA and
two of them were withdrawn. Additionally, 4 bone mar-
row and 7 peripheral blood samples from healthy donors
were analyzed as control samples. Graphical abstract of
diagnosis process in this study are shown in (Figure 1).
The written informed consent was obtained from all
the parents and the study protocol was approved by Eth-
ics and Human Rights Committee of Tabriz University of
Medical Sciences.
The DNA was extracted from BM or PB samples,
using the QIAamp DNA minikit (Qiagen, Hilden, Ger-
many) according to the manufacturer’s
instructions. In
order to verify the delity of DNA concentration and to
evaluate its quality, a spectrophotometer,(NanoDrop,Wi
lmingtonDE,,USA) and 1.5% agarose electrophoresis gel
were used respectively.
Two pairs of primer for exone10 of PAX5 gene were
designed using the online program oligo7. The primer
sequences are shown in (Table 1). SYBR Green Real-time
PCR (BIO-RAD iQ5, Bio-Rad, Hercules, California, USA)
was done using a serial dilution of DNA samples includ-
ing 100, 50, 25, 12.5 and 6.25ng in triplicate repeats.
Then, according to the standard curves and by compar-
ing the slope and ef ciency of each reaction (Schmitt-
gen, Lee, & Jiang, 2008), 50 ng of DNA were preferable
as the best concentration. The analysis was performed
in a total volume of 20 l including 50 ng of DNA, 0.2
mM speci c primers and 10 l of SYBR Green Master
mix (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, California, United
States) according to the manufacturer’s instructions,
then (2
−∆∆Ct
) was calculated by normalizing samples and
the relative gene copy numbers were calculated. The
FIGURE 1. Graphical
abstract of diagnostic
process.
392 COMPARISON OF MULTIPLEX LIGATION-DEPENDENT PROBE AMPLIFICATION AND QPCR BIOSCIENCE BIOTECHNOLOGY RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS
BIOSCIENCE BIOTECHNOLOGY RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS COMPARISON OF MULTIPLEX LIGATION-DEPENDENT PROBE AMPLIFICATION AND QPCR 393
Sahar Mehranfar et al.
copy numbers compared to the reference gene were
determined. Following values were considered for result
analysis: 1 for normal samples, 0.5 for heterozygous
deletions, and 1.5 for heterozygous duplications. Results
were analyzed using Microsoft Excel.
The MLPA probe sizes, chromosomal position and
sequences and other complete details are available on the
Website (www.MRC-Holland.com). The sensitivity of the
MLPA kit P335-B2 was assessed previously by Kuiperetal
(Kuiper etal., 2007) . In each run of MLPA, appropriate
numbers of the samples, and three to six control samples
were used in same run. All control samples were taken
from the children with no acute leukemia or other types
of malignancy. In this study, 50 ng of genomic DNA in
nal volume of 5 µl were used to determine copy number
of PAX5 gene by using the SALSA MLPA kit P335-B2
(MRC Holland, The Netherlands). Capillary electropho-
resis were run on 3130XL Genetic Analyzer (Life Tech-
nologies, Carlsbad, CA, USA) and ampli ed PCR products
were analyzed by Gene Marker version 1.95 (Soft Genet-
ics State College, Pennsylvania, USA). Values over < 0.75
and > 1.35 were considered to be abnormal and values
below 0.25 indicated biallelic deletion. Schematic MLPA
analysis is shown in (Figure 2).
Normality of data was calculated by Kolmogorov-
Smirnov test and was presented by Mean and Stand-
ard Deviation. Non-normal variables were incidental as
Median (Max & Min). The gene CNAs difference between
the ALL and control samples were calculated by inde-
pendent sample T-test and regression tree for accuracy
of MLPA method. P-values less than 0.05 were consid-
ered statistically signi cant. All statistical analyses were
done using the Statistical package for the Social Sci-
ences (SPSS), version 16.0 (SPSS Inc, Chicago, IL, USA).
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
45 patients with ALL, including 27 (60%) boys with
mean age of 5.8±3.4 and 18 (40%) girl with mean age
of 6.0 ±2.7 years were studied (p>0.05). Statistically, no
signi cant differences were seen between the mean ages
of genders. Demographic data of the participants have
been summarized in (Table 2).
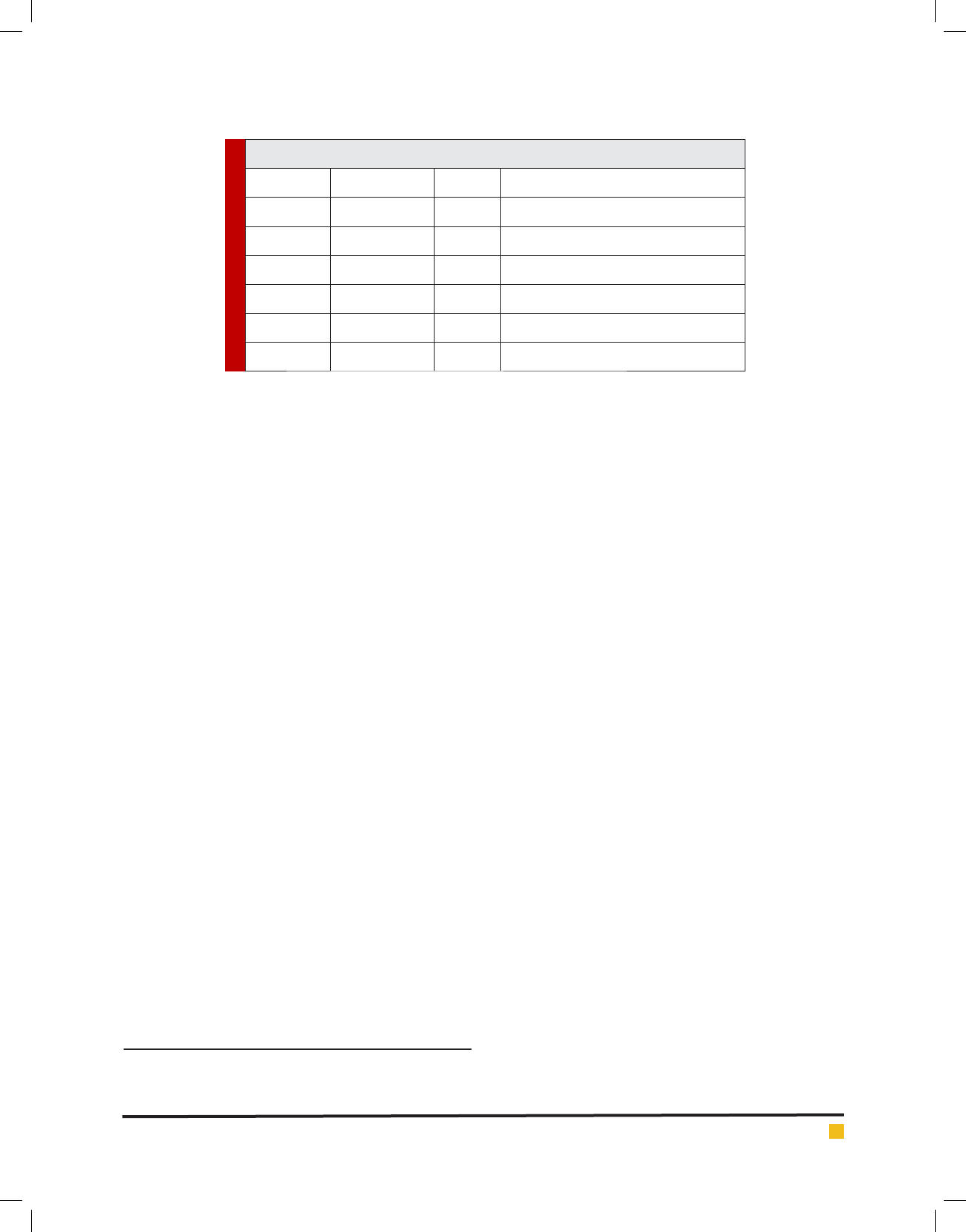
We found a wide range of alterations in the PAX5
gene in this study; deletion or duplication in one or
more exons. In 2 cases, deletion and duplication were
seen in different exons simultaneously. From among all
patients, 11 (24%) patients showed 76 CNAs, from which,
22 (29%) were seen in PAX5 gene. The more frequent
exons were 6, 7, and 8 (55%); the least one was exon
1 (4%). No signi cant difference was observed between
CNAs and sex, age, National Cancer Institute (NCI) risk
group or source of samples (p<0.05). Schematic detected
CNAs are shown in (Figure 3).
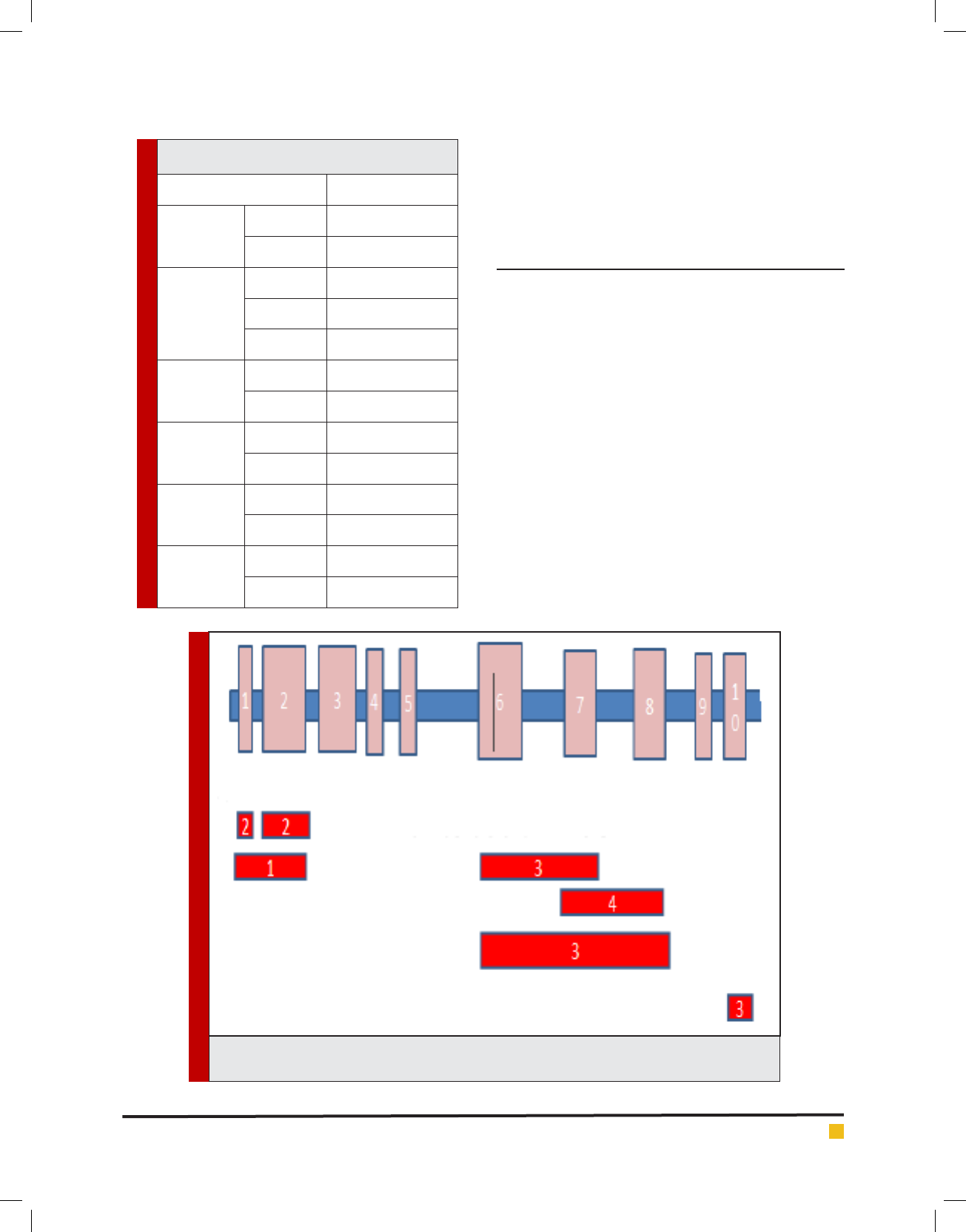
From among all samples, three samples showed
changes in exon 10 by MLPA. All of these samples (3)
were validated by real-time PCR. The standard melting
curve of real-time PCR is shown in (Figure 1).
The accuracy obtained for MLPA method for detec-
tion of CNAs comparisons of real-time PCR was 86%.
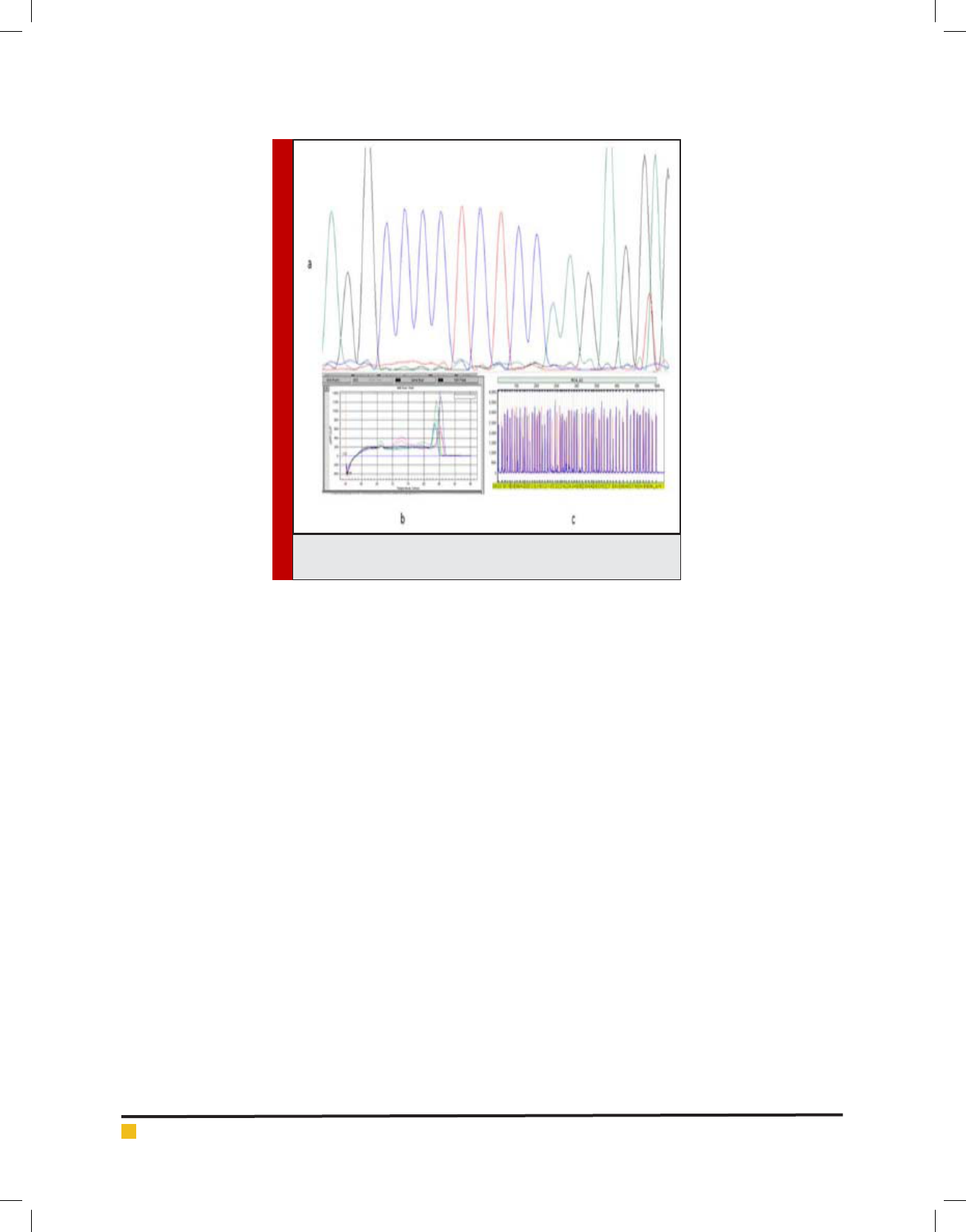
To prove the results of two methods, PCR product from
these patients was sent to Bioneer for sequencing. The
sequencing analyses were done by Chromas software,
and the results were compared with the reported gene
sequences. We submitted 2 genes in GenBank by acces-
sion numbers (ID) KX608846 and KX707789 in exon 10
of PAX5. Schematic representation of each method is
shown in (Figure 4).
ALL is a heterogeneous disease with differing in
response to chemotherapy. The results of some studies
demonstrated that the identi cation of molecular mark-
ers may improve the treatment approaches (Yang etal.,
2011). Today, the determination of gene dosage is impor-
tant for both clinical and research medicine and it is also
required for therapeutic, prognostic, or diagnostic goals
(Ginsburg & Willard, 2009; Vogelstein & Kinzler, 2004).
Due to the growing need for molecular studies, a lot of
new molecular markers have been discovered (Mrózek,
Table 1. The primer sequencing used in QPCR for PAX5 copy number abnormalities.
Gene name Product length Tm(Cº) Primer sequence
PAX5 F1 170 64 5-ATCTTAACCTAGGCAGAGCATC-3
PAX5 R1 170 61 5-CAAGAGACACACCATTTGGG-3
PAX5 F2 164 62 5-CTCCTTCTTAGTATCTACGAG-3
PAX5 R2 164 60 5-GAACTCAAAGAAACTGTCTGG-3
GAPDH F 120 60 5 -CGGTGGATCCCTTTAATTG-3-3
GAPDH R 120 58 5 –CAATAAAGGGGATCCACCG-3

Sahar Mehranfar et al.
Döhner, & Bloom eld, 2007; Thiede et al., 2006). It
seems that in the future, patients could be divided into
two groups in terms of presence or absence of these bio-
markers (Mi etal., 2012).
PAX5 translocations do not in uence the progno-
sis or outcome by themselves but it is in association
with other molecular aberrancies in theirs pathway
that they in uence the prognosis or outcome (Sellner &
Taylor, 2004). Similar to our ndings, the incidence of
PAX5rearrangements was seen about 30% in the B-cell
precursor ALL, in a previous study (Barbosa etal., 2015;
Hunger & Mullighan, 2015; C. Schwab etal., 2010; C. J.
Schwab etal., 2013). Array-based approaches can pro-
vide high resolution data on CNAs, but these methods
are restricted by low throughput, high cost, and time
consumption. Therefore, the need for a simple, fast and
cost-ef cient method to screen molecular changes has
remained hitherto. (Vermeesch etal., 2007).
The PCR-based multiplex ligation-dependent probe
ampli cation (MLPA) technique is a relative quanti-
cation method for gene dosage determination and
deletions/duplications mutations in unknown samples
which are recognized by comparison to the normal and
standard control (Al Zaabi, Fernandez, Sadek, Riddell,
& Greer, 2010). Buijs etal. performed genomic pro ling
using MLPA in 45 cases with (ALL), showing that MLPA
is able to detect anomalies similar to PCR method (Buijs,
Krijtenburg, & Meijer, 2006).
A similar study was done by Coll-Mulet etal., who car-
ried out MLPA in 50 chronic leukemia patients. Their results
illustrated that only cases with a low percentage (<25%) of
cells, were not detected by MLPA (CollMulet etal., 2008).
Many other studies on different types of leukemia revealed
excellent accuracy and speci city of MLPA as compared to
QPCR and showed clinical capability of these techniques
with different disease(Abdool, Donahue, Wohlgemuth, &
Yeh, 2010; Donahue, Abdool, Gaur, Wohlgemuth, & Yeh,
2011; Fabris etal., 2011; Mullighan etal., 2008; C. Schwab
etal., 2010; Schwartz & Dunø, 2004).
However, there are still some limitations such as being
unable to detect balanced rearrangements, mosaicism,
heterogeneity or contamination with normal cells. Like
PCR, MLPA reactions are also more sensitive to contami-
nants (Stuppia etal., 2012; Tavtigian & Le Calvez-Kelm,
2007). According to the manufacturer’s instructions of
MLPA, it works with only 20 ng of DNA. Besides, the
results don’t depend on the amount of used sample DNA
but, our study showed that 50 ng are required for reli-
able results.
Moreover, it is recommended to compare differ-
ent MLPA analyses only by using one DNA extraction
method from different sources of samples from each
patient, to compare specify the sensitivity of this method
for different sources of samples. Real-time PCR method
is highly sensitive and speci c as reported in many stud-
ies all over the world, though, it is a time-consuming
method and can survey only one target sequence in per
run (Ponchel etal., 2003; Ramalingam etal., 2009).
But Compared to QPCR, MLPA is a low cost, fast, and
technically uncomplicated method for the analysis of
FIGURE 2. MLPA analysis sheet; a: compares peaks between
standard and patients probes; b: peaks ratio; c: demonstrated
probes ratio in cut-off range (Red peak: mean of whole sam-
ples peak, Blue peaks: samples peak, Black peak: reference
peak).
394 COMPARISON OF MULTIPLEX LIGATION-DEPENDENT PROBE AMPLIFICATION AND QPCR BIOSCIENCE BIOTECHNOLOGY RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS
BIOSCIENCE BIOTECHNOLOGY RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS COMPARISON OF MULTIPLEX LIGATION-DEPENDENT PROBE AMPLIFICATION AND QPCR 395
Sahar Mehranfar et al.
Table 2. Demographic data of acute lymphoblastic
leukemia patients
Variable Frequency (Percent)
Sex
Female 18(40%)
Male 27(60%)
Age
1-4 22(48%)
5-10 17(37%)
10-14 6(13%)
Mean of age
Female 6.0 ±2.7
Male 5.8±3.4
NCI risk group
Standard risk 28(62%)
High risk 17(37%)
Source of
samples
BM samples 19(42%)
PB samples 26(57%)
WBC count
>50,000 11
<50,000 34
FIGURE 3. Schematic representation of the CNAs found in this study. PAX5 exons (1-10) are shown
above. Numbers in the red shapes show the occurrence times for each rearrangement.
results. Moreover, in the future, MLPA could be applied
to large CNAs screening. PCR and sequencing can be
used for con rming mutation only in selected gene seg-
ments, but MLPA can be considered for screening a large
area of genes, simultaneously.
CONCLUSION
Molecular screening is an essential test for comprehen-
sive survey of disease, and provides complementary
information for better diagnosis, treatment and follow-
up of patients with acute leukemia. This approach may
be useful as a criterion for measuring the effectiveness
of new molecular tools such as genetic profiling. Con-
sidering differences between two methods, more clini-
cal studies are required to nd out the best one for our
objectives. Our data clearly indicated that MLPA can
be an attractive alternative method to other molecular
and cytogenetic techniques that are now routinely used.
Screening of critical genes in pathobiology of all cancers
such as acute lymphoblastic leukemia could help early
diagnosis in the early stages. It is especially useful when
the inexpensive and available techniques are used eve-
rywhere. It has been established that early diagnosis has
a positive impact on the prognosis.
Sahar Mehranfar et al.
REFERENCES
Abdool, A ., Donahue, A. C., Wohlgemuth, J. G., & Yeh, C.-H.
(2010). Detection, analysis and clinical validation of chro-
mosomal aberrations by multiplex ligation-dependent probe
ampli cation in chronic leukemia. PLoS One, 5(10), e15407.
Al Zaabi, E. A., Fernandez, L. A., Sadek, I. A., Riddell, D. C., &
Greer, W. L. (2010). Multiplex ligation-dependent probe ampli-
cation versus multiprobe uorescence in situ hybridization to
detect genomic aberrations in chronic lymphocytic leukemia: a
tertiary center experience. The Journal of molecular diagnos-
tics, 12(2), 197-203.
Barbosa, T. C., Terra-Granado, E., Magalhães, I. M. Q., Neves,
G. R., Gadelha, A., Guedes Filho, G. E., . . . Pombo-de-Oliveira,
M. S. (2015). Frequency of copy number abnormalities in com-
mon genes associated with B-cell precursor acute lymphoblas-
tic leukemia cytogenetic subtypes in Brazilian children. Cancer
genetics, 208(10), 492-501.
Buijs, A., Krijtenburg, P. J., & Meijer, E. (2006). Detection of risk-
identifying chromosomal abnormalities and genomic pro ling
by multiplex ligation-dependent probe ampli cation in chronic
lymphocytic leukemia. Haematologica, 91(10), 1434-1435.
Busslinger, M. (2004). Transcriptional control of early B cell
development 1. Annu. Rev. Immunol., 22, 55-79.
Carter, T. L., Watt, P. M., Kumar, R., Burton, P. R., Reaman, G.
H., Sather, H. N., Kees, U. R. (2001). Hemizygous p16 INK4A
deletion in pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia predicts
independent risk of relapse. Blood, 97(2), 572-574.
FIGURE 4. The comparison of the results of 3 methods; a: sequenc-
ing result, b: QPCR result, c: MLPA result.
Cobaleda, C., Schebesta, A., Delogu, A., & Busslinger, M.
(2007). Pax5: the guardian of B cell identity and function.
Nature immunology, 8(5), 463-470.
CollMulet, L., Santidrián, A. F., Cosialls, A. M., IglesiasSerret,
D., De Frias, M., Grau, J., Domingo, A. (2008). Multiplex liga-
tiondependent probe ampli cation for detection of genomic
alterations in chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. British journal
of haematology, 142(5), 793-801.
Dona hue, A. C., Abdool, A. K., Gaur, R., Wohlgemuth, J. G., &
Yeh, C.-H. (2011). Multiplex ligation-dependent probe ampli -
cation for detection of chromosomal abnormalities in myelo-
dysplastic syndrome and acute myeloid leukemia. Leukemia
research, 35(11), 1477-1483.
Fabr is, S., Scarciolla, O., Morabito, F., Cifarelli, R. A., Dininno,
C., Cutrona, G., . . . Ciceri, G. (2011). Multiplex ligationdepend-
ent probe ampli cation and uorescence in situ hybridization
to detect chromosomal abnormalities in Chronic lymphocytic
leukemia: A comparative study. Genes, Chromosomes and
Cancer, 50(9), 726-734.
Fathi , A., Amani, F., & Bahadoram, M. (2015). Epidemiology of
Childhood Cancer in Northwest Iran. Asian Paci c Journal of
Cancer Prevention, 16(13), 5459-5462.
Fazel i, Z., Pourhoseingholi, M. A., Vahedi, M., Abadi, A.,
Bavand-Pour, F. S. F., & Baghestani, A. R. (2013). Leukemia
cancer mortality trend in Iran, from 1995 to 2004. Iranian
journal of cancer prevention, 6(3), 170.
Fazio , G., Biondi, A., & Cazzaniga, G. (2011). The Role of PAX5
in ALL: Citeseer.
396 COMPARISON OF MULTIPLEX LIGATION-DEPENDENT PROBE AMPLIFICATION AND QPCR BIOSCIENCE BIOTECHNOLOGY RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS

BIOSCIENCE BIOTECHNOLOGY RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS COMPARISON OF MULTIPLEX LIGATION-DEPENDENT PROBE AMPLIFICATION AND QPCR 397
Sahar Mehranfar et al.
Ginsb urg, G. S., & Willard, H. F. (2009). Genomic and person-
alized medicine: foundations and applications. Translational
research, 154(6), 277-287.
Hunge r, S. P., & Mullighan, C. G. (2015). Acute lymphoblas-
tic leukemia in children. New England Journal of Medicine,
373(16), 1541-1552.
Kuipe r, R., Schoenmakers, E., Van Reijmersdal, S., Hehir-Kwa,
J., van Kessel, A. G., Van Leeuwen, F., & Hoogerbrugge, P.
(2007). High-resolution genomic pro ling of childhood ALL
reveals novel recurrent genetic lesions affecting pathways
involved in lymphocyte differentiation and cell cycle progres-
sion. Leukemia, 21(6), 1258-1266.
Matth ias, P., & Rolink, A. G. (2005). Transcriptional networks
in developing and mature B cells. Nature Reviews Immunol-
ogy, 5(6), 497-508.
Mi, J ., Wang, X., Yao, Y., Lu, H., Jiang, X., Zhou, J. Tang,
J. (2012). Newly diagnosed acute lymphoblastic leukemia in
China (II): prognosis related to genetic abnormalities in a series
of 1091 cases. Leukemia, 26(7), 1507-1516.
Mousa vi, S., Alamolhoda, A., Gouya, M., & Lickiss, N. (2008).
Implementation of Comprehensive National Cancer Con-
trol Program in Iran: an experience in a developing country.
Annals of Oncology, 19(2), 398-400.
Mróze k, K., Döhner, H., & Bloom eld, C. D. (2007). In uence of
new molecular prognostic markers in patients with karyotypi-
cally normal acute myeloid leukemia: recent advances. Current
opinion in hematology, 14(2), 106-114.
Mulligh an, C. G., Miller, C. B., Radtke, I., Phillips, L. A., Dal-
ton, J., Ma, J., . . . Pui, C.-H. (2008). BCR–ABL1 lymphoblastic
leukaemia is characterized by the deletion of Ikaros. Nature,
453(7191), 110-114.
O’neil, J., & Look, A. (2007). Mechanisms of transcription fac-
tor deregulation in lymphoid cell transformation. Oncogene,
26(47), 6838-6849.
Ponchel , F., Toomes, C., Brans eld, K., Leong, F. T., Douglas,
S. H., Field, S. L. Mighell, A. J. (2003). Real-time PCR based
on SYBR-Green I uorescence: an alternative to the TaqMan
assay for a relative quanti cation of gene rearrangements,
gene ampli cations and micro gene deletions. BMC biotech-
nology, 3(1), 1.
Ramalin gam, N., Liu, H.-B., Dai, C.-C., Jiang, Y., Wang, H.,
Wang, Q. Gong, H.-Q. (2009). Real-time PCR array chip with
capillary-driven sample loading and reactor sealing for point-
of-care applications. Biomedical microdevices, 11(5), 1007-
1020.
Schmitt gen, T. D., Lee, E. J., & Jiang, J. (2008). High-through-
put real-time PCR. Molecular Beacons: Signalling Nucleic Acid
Probes, Methods, and Protocols, 89-98.
Schoute n, J. P., McElgunn, C. J., Waaijer, R., Zwijnenburg, D.,
Diepvens, F., & Pals, G. (2002). Relative quanti cation of 40
nucleic acid sequences by multiplex ligation-dependent probe
ampli cation. Nucleic acids research, 30(12), e57-e57.
Schwab, C., Jones, L., Morrison, H., Ryan, S., Yigittop, H.,
Schouten, J., & Harrison, C. (2010). Evaluation of multiplex
ligationdependent probe ampli cation as a method for the
detection of copy number abnormalities in Bcell precursor
acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Genes, Chromosomes and Can-
cer, 49(12), 1104-1113.
Schwab, C . J., Chilton, L., Morrison, H., Jones, L., Al-Shehhi,
H., Erhorn, A., . . . Harrison, C. J. (2013). Genes commonly
deleted in childhood B-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic
leukemia: association with cytogenetics and clinical features.
Haematologica, haematol. 2013.085175.
Schwartz, M., & Dunø, M. (2004). Improved molecular diagno-
sis of dystrophin gene mutations using the multiplex ligation-
dependent probe ampli cation method. Genetic testing, 8(4),
361-367.
Seiter, K. , Sarkodee-Adoo, C., Talavera, F., Sacher, R., & Besa,
E. (2014). Acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Sarkodee-Adoo
C, Talavera F, Sacher RA and Besa EC: Medscape Reference.
WebMD. Accessed, 17.
Sellner, L . N., & Taylor, G. R. (2004). MLPA and MAPH: new
techniques for detection of gene deletions. Human mutation,
23(5), 413-419.
Stuppia, L ., Antonucci, I., Palka, G., & Gatta, V. (2012). Use
of the MLPA assay in the molecular diagnosis of gene copy
number alterations in human genetic diseases. International
journal of molecular sciences, 13(3), 3245-3276.
Tavtigian, S. V., & Le Calvez-Kelm, F. (2007). Molecular Diag-
nostics: Methods and Limitations. Hereditary Breast Cancer,
179-205.
Thiede, C. , Koch, S., Creutzig, E., Steudel, C., Illmer, T., Schaich,
M., & Ehninger, G. (2006). Prevalence and prognostic impact
of NPM1 mutations in 1485 adult patients with acute myeloid
leukemia (AML). Blood, 107(10), 4011-4020.
Vermeesch, J. R., Fiegler, H., de Leeuw, N., Szuhai, K., Schou-
mans, J., Ciccone, R. Van Ravenswaaij, C. (2007). Guidelines
for molecular karyotyping in constitutional genetic diagnosis.
European Journal of Human Genetics, 15(11), 1105-1114.
Vogelstein , B., & Kinzler, K. W. (2004). Cancer genes and the
pathways they control. Nature medicine, 10(8), 789-799.
Yang, Y. L ., Hung, C. C., Chen, J. S., Lin, K. H., Jou, S. T., Hsiao,
C. C.Lin, S. R. (2011). IKZF1 deletions predict a poor prognosis
in children with Bcell progenitor acute lymphoblastic leuke-
mia: A multicenter analysis in Taiwan. Cancer science, 102(10),
1874-1881.