
Microbiological
Communication
Biosci. Biotech. Res. Comm. 10(2): 225-232 (2017)
Evaluation of antibacterial effect of
Eucalyptus
and
ginger on dentinal tubules
Enterococcus faecalis
in the
presence of smear layer
Samira Shahsiah,
1
* Eskandar Moghimipour,
2
Nooshin Shamsizadeh
3
and Azardokht Khosravi
4
1
Department of Endodontics, Faculty of Dentistry, Ahvaz Jundishapur University of Medical Sciences,
Ahvaz, Iran
2
Medicinal Plant Research Center, Faculty of Pharmacy, Ahvaz Jundishapur University of Medical Sciences,
Ahvaz, Iran
3
Dentist
4
Professor of Clinical Microbiology, Ahvaz Jundishapur Univesity of Medical Sciences, Ahvaz, Iran
ABSTRACT
Enterococcus faecalis is a resistant microorganism and plays an important role in root canal treatment failure. One of
the most critical steps in root canal treatment is chemical cleaning of the root canal with endodontic irrigation solu-
tions. The most commonly used solution is Sodium hypochlorite which in spite of its broad antimicrobial activity, has
many disadvantages. Therefore, this study was designed to evaluate the antibacterial effect of eucalyptus and ginger
on dentinal tubules Enterococcus faecalis in the presence of smear layer. In this study dentin cylinders from 80 single
rooted human teeth were prepared and contaminated with Enterococcus faecalis with smear layer created in each
dentin disk. Experimental groups were as follows: Group 1: Sodium hypochlorite 5.25%, Group 2: ginger extract,
Group 3: eucalyptus extract, Group 4: Normal saline (positive control), Group 5: sterile cylinders. Then dentin chips
were collected from three different depths of dentin including 0.1,0.2 and 0.3 millimeters. Optical density comparison
of different experimental groups showed that there is a signi cant difference between groups in 0.1 and 0.2 millim-
eters depth (p<0.01), however no signi cant difference in 0.3 millimeters depth was obtained. Antimicrobial ef cacy
of eucalyptus and Sodium hypochlorite in the presence of smear layer showed no signi cant differences, while this
effect was weaker with ginger compared to Sodium hypochlorite.
KEY WORDS:
ENTEROCOCCUS FAECALIS
, SMEAR LAYER, EUCALYPTUS, GINGER
225
ARTICLE INFORMATION:
*Corresponding Author: shahsiahs@gmail.com
Received 31
st
March, 2017
Accepted after revision 29
th
June, 2017
BBRC Print ISSN: 0974-6455
Online ISSN: 2321-4007 CODEN: USA BBRCBA
Thomson Reuters ISI ESC and Crossref Indexed Journal
NAAS Journal Score 2017: 4.31 Cosmos IF : 4.006
© A Society of Science and Nature Publication, 2017. All rights
reserved.
Online Contents Available at: http//www.bbrc.in/
226 EVALUATION OF ANTIBACTERIAL EFFECT OF
EUCALYPTUS
AND GINGER BIOSCIENCE BIOTECHNOLOGY RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS
Samira Shahsiah et al.
INTRODUCTION
Today different in canal detergents are used. The most
popular one is sodiumhypochlorite (homemade bleach).
Main advantage of this material is solving necrotic tis-
sue and its anti-microbial properties against wide range
of micro-organisms such as Enterococcus faecalis. This
material has some disadvantages too which include
unpleasant smell and taste, toxicity during contact with
pre radicular tissues, removing cloth’s color, and capacity
of metal corrosion (Torabinejad and Walton 2003; Gulve
and Gulve 2010). Studies indicated that sodiumhypochlo-
rite has very less ability for removing smear layer. In addi-
tion, overusing this material causes reduction of dentinal
elasticity strength (Hargreaves 2011).
We selected herbals for this research because of fol-
lowing reasons: Eucalyptus (which out of them Euca-
lyptus camaldulensis is most popular in Iran) and ginger
are found in Iran region, there is no need to import this
medicine from other countries, providing their effective
concentrate has less price than chemical medicine, in
compare to chemical medicine, these are more adap-
tive to natural environment of the body and has less
unfavorable effect. No research has so far made about
investigating this material as a detergent in canal at the
presence of dentine and smear layer so there is need
to research in this case. Historically, numerous combi-
nations of aqueous solution are recommended as root
canal detergents; including ineffective sodium chloride
(saline) and so toxic and allergist biocids such as formal-
dehyde (Zehnder 2006).
There are different factors including numbers and
diameter of dentinal tubules, scleroticdentin, and also
smear layer can affect dentine permeability and can
avoid penetration of anti-microbial materials to dentinal
tubules. During preparation of canal walls, some parts of
dentinal wall which has contact with tools are covered
by one smear layer (Hargreaves and et al, 2011; McCom-
bEand et al, 1976). Smear layer is amorf, granular and
disordered that is made from minerals such as dentianls
and organic materials including pulp remnants, odonto-
blastic excrescence, suliva, and blood cells (Kakehashi
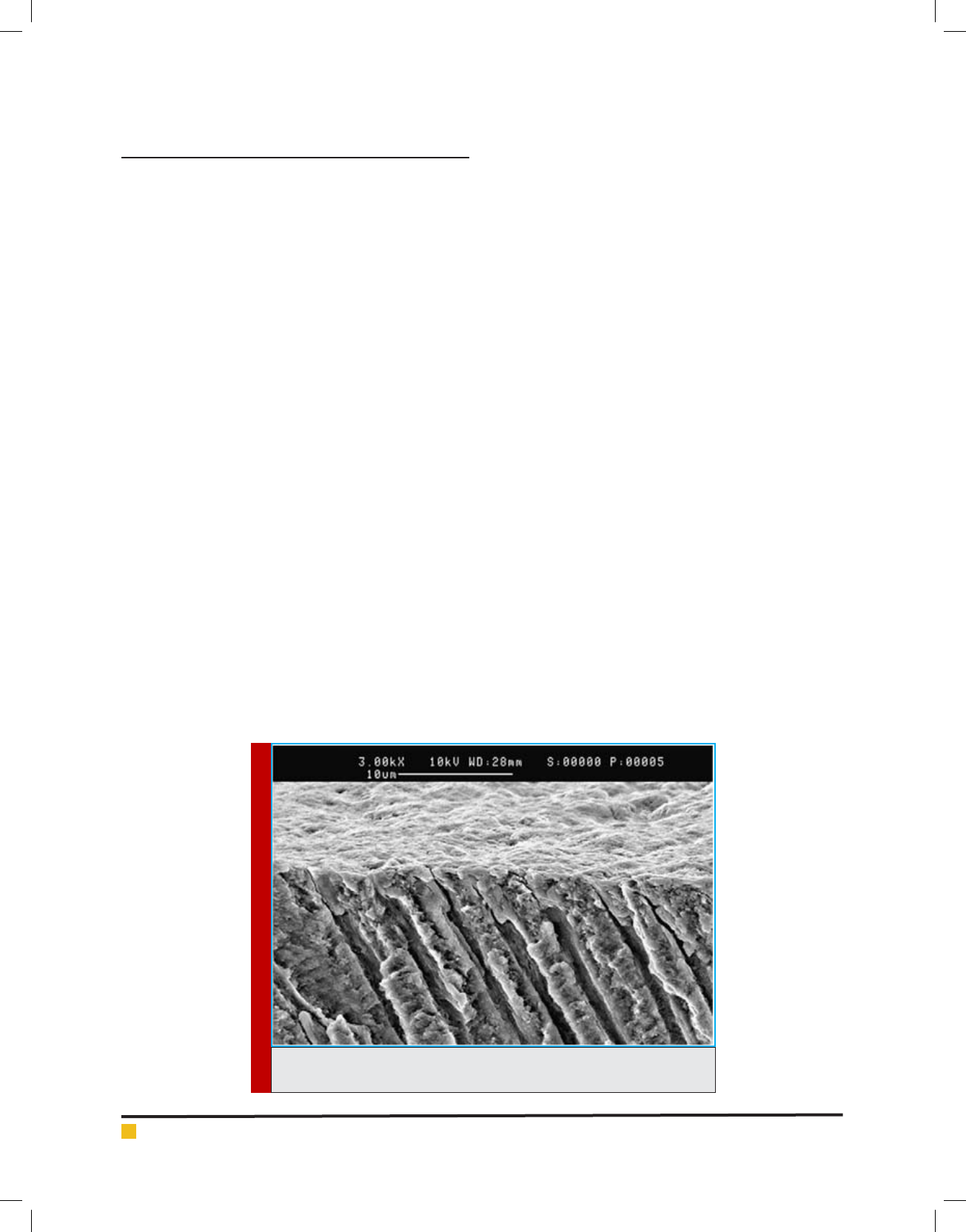
and et al, 1965; Gwinnett 1984). (Figure 1).
Maekawa et al performed a research in 2013 in Brazil.
They investigated effect of ginger and propolis1 concen-
trate on some microorganisms in canal and endotoxin.
According to the results, researchers recommended that
propolis and ginger concentrate in combination with
calciumhydroxide can be used as a medicine in alterna-
tive canal although there is need more studies on bio-
compatibility, chemical interactions of these materials
and their clinical effects to be made so their use in endo-
dontic treatment is approved. In another study of Martos
et al in 2012 in Brazil, they considered anti-microbial
activities of chloroform solution, eucalyptus oil essence,
and orange oil essence lonely and also with Cetrimide
in 0.05%, 0.1%, 0.2%, 0.3% densities. These research-
ers observed that bio lm reduction in orange oil and
eucalyptus oil in 2 minutes indicated no signi cant dif-
ference; however, bio lm removal percent by orange oil
in 5 minutes was more than eucalyptus oil.
Shari an et al (2011) in Tehran performed a research
in order to investigating anti-microbial properties of lime
on Enterococcus faecalis in dentinal tubules in presence
of smear layer on 140 dentinal cylinderprovided from
central incisor of cow. These researchers concluded that
FIGURE 1. Root dentine section which is covered with smear layer resulted
from canal working tools

BIOSCIENCE BIOTECHNOLOGY RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS EVALUATION OF ANTIBACTERIAL EFFECT OF
EUCALYPTUS
AND GINGER 227
Samira Shahsiah et al.
at the presence of smear layer, anti-microbial properties
of lime was less than NaOCl while there was no differ-
ence between anti-microbial properties of lime skin and
NaOCl. Abdul Rahman et al in 2010 studied anti-micro-
bial and bio chemical properties of food avors in meat
products. In this experiment, Disk diffusion method was
used and it was indicated that cinnamon is the most
effective avor against all under studied micro-organ-
isms except micrococcusluteus. In addition, ginger had
anti-microbial activity against Enterococcus faecalis.
Gulve et al.,( 2010 )from India, managed study for
comparing invitro anti-microbial properties of ginger
concentrate 2% sodiumhypochlorite against Enterococ-
cus faecalis on 18 growth medium by Agar diffusion.
These two researchers observed that ginger concentrate
signi cantly avoid bacteria’s growth in compare to
sodiumhypochlorite. This study aimed at nding better
alternative for sodium hypochlorite as a relative ideal
root canal detergent. Thus, by aim of determining anti-
microbial properties of eucalyptus concentrate - ginger
concentrate- sodiumhypochlorite, and 5.25%– normal
saline against Enterococcus faecalis at presence of smear
layer in 0.1, 0.2 and 0.3 millimeter depth of dentine
and comparing anti-microbial properties of eucalyptus
concentrate – ginger concentrate- sodiumhypochlorite
and 5.25% –normal saline in 0.1, 0.2 and 0.3 millimeter
depth of dentine at presence of smear layer.At the fol-
lowing we will discuss materials and methods of col-
lecting data, and collecting samples. Then in section 3
we will explain research results and statistical tests, in
addition to results of the test and nally we explained
the conclusion.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
In this study, in order to determining of eucalyptus con-
centrate – ginger concentrate - 5.25% sodium hypochlo-
rite- normal saline against enterococcus faecalis in 0.1,
0.2 and 0.3 milliliter depth from dentine at the presence
of smear layer.We selected 80 human teeth which were
withdrawn due to different diseases including periodon-
tal, orthodontia, dental corruption were selected from
therapeutical centers in Ahvaz. These single root teeth
have maxilar anseizure and mandible premolars. After
withdrawn of these teeth, tissues connected to outer
surface of root were separated with one court. Then in
order to disinfection of teeth surface, they put in 2.5%
sodium hypochlorite, and they were kept in steal normal
saline at the room temperature. Eucalyptus leaves, 70%
ethanol, dried rhizome of ginger, stilled water, stand-
ard strain of Enterococcus faecalis , growth medium BHI
Broth (Merck-Germany), growth medium of BHI Agar
(Merck-Germany), laboratory tube, microbial cultivation
plate, cotton, gloves, 15 milliliter falcon tube (Maxell-
China), sampler (Trasnferpette-Germany), head sampler,
5.25% sodium hypochlorite (Golrang-Iran), laboratory
Handpiece (NSK-Japan), coal disk, medin broach (Mani-
Japan), number 4Gates-Gliddendrills(Mani- Japan), nail
polish, aluminum foil, self-cure acryl (Acro Pars-Iran),
EDTA17% (Cerkamed-Poland), needlegauge 23.
In order to provide plant concentrate, maceration
method was used (Martos j, et al, 2013). For providing
detergent, dried concentrate obtained from freezer drier
were solve into stilled water slowly until a homogenous
solution. Mass concentration for ginger solution was
calculated equaled to gr/ml0.51and for eucalyptus con-
centrate solution equled to gr/ml0.57. then these deter-
gents were transferred to sanitary-therapeutic center in
Golestan Hospital of Ahvaz and then they were sterile ed
with X-ray (Shalaby E. A, 2011). Standard ndard strain
of 29212 ATCC
1
Enterococcus faecalis bacteria was pro-
vided from Pastor Institute of Iran in Tehran. Brain heart
infusion broth steal Growth medium (Merck-Germany)
was prepared and added into Lyophilizated in order to
solve it completely. Then it was cultivating on BHI Agar
growth medium (Merck-Germany) and they were incu-
bated in aerobiccondition in C°37 for 24 hours. Then
by biochemical tests for bacteria identi cation (smear
provision, PYR test, Bile esculin, Catalaz) we assured
from its purity. So 24 hours colonies provided fro,m
pure enterococcus faecalis. For providing bacteria sus-
pension, bacteria clonies were taken from solid growth
medium and solved in a tube with sterile BHI Broth and
then we obtained a suspension with turbidityMc farland
(cfu/ml 3×
Samples withdrawn from autoclave were opened
under laminar air ow hood and they were all inoculated
by 20-10 micro litter bacteria suspension of enterococcus
faecalis with strain 1 of Mc Farland (cfu/ml 3× except
negative control group. Then cylinders were covered
with a lid made from sterile aluminum paper and growth
medium with bacteria were added into each cylinder
every two days by sample (Trasnferpette-Germany) and
trough sterile head sampler. In negative control group,
sterile BHI Broth growth medium were added into teeth.
This was repeated 4 weeks for providing maximum pen-
etration of bacteria into dentinal tubules (Shabahang S
and Torabinejad M, 2003; Ahangari Z, et al, 2008) and
the samples were incubated in aerobiccondition and in
37
0
C.
When inoculation ended, I order to make sure of
micro-organisms penetration into dentinal tubules, 10
samples were randomly selected out of samples. Then
acrylic layer were removed from lumenof these sam-
ples and patterned by low speed and Gates Gilden
(Mani-Japan) number 5 (o.1 milliliter depth), Gates
1
American type culture collection
228 EVALUATION OF ANTIBACTERIAL EFFECT OF
EUCALYPTUS
AND GINGER BIOSCIENCE BIOTECHNOLOGY RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS
Samira Shahsiah et al.
Gilden (Mani-Japan) number 6 (0.2 milliliter depth) and
pisormer (Mani-Japan) number 6 (0.3 milliliter depth)
from dentine.
Provided dentine chips from different dentinal sec-
tions were placed separately in 15 milliliter falcon tubes
(Maxell-China) with 3 milliliter sterile BHI Broth and
were incubated 48 hours in 37 C° temperature. Then, out
of 30 mentioned tube some samples were cultivated on
plates with BHI Agar and were incubated in aerobic con-
dition and in 37
0
C temperature. After incubation end,
micro-organisms identi cation test in order to be sure
about that bacteria are single strain and its penetration
in 3 depths.
In other samples, smear layer was created by sterile
hedstroms number 50 (Mani-Japan). In a way that hed-
strom number 50 were withdrawn three times and by
push and pull movement on canal wall. In order to avoid
pollution of environment implying to Luman cylinders
each hedstrom were changed after one time use.
In next step, samples in group 1,2,3 and 4 were
washed separately by 5 milliliter sterile syringe (Homa-
Sorang-Iran) and 23 needles with gauge and from neg-
ative control group, patterning was made in 3 depth.
Washing syringe were changed for each sample after
using them once in order to minimize environmental
pollution. Group washing was made as follow:
Group 1: 2 milliliter Naocl 5.25% in each sample
for 20 minutes.
Group 2: 2 milliliter ginger concentrate with mg/
ml127.5 density in each sample for 20 minutes.
Group 3: 2 milliliter eucalyptus concentrate with
mg/ml17.8 density in each sample for 20 minutes.
Group 4 (positive control): 2 milliliter sterile nor-
mal saline in each sample for 20 minutes.
Group 5 (negative control): washing was not made
in this group. In order to be con dant about lack
of cylinder pollution penetration into another
bacteria and test correction was patterned except
Enterococcus faecalis.
When acryliclayer washing, cylinders were remove
from lumen of then dentine sampling was performed
by low speed and Gates Gilden (Mani-Japan) number 5
drills (o.1 milliliter depth ), Gates Gilden (Mani-Japan)
number 6 drills (0.2 milliliter depth) and pisormer (Mani-
Japan) number 6 (0.3 milliliter depth) from dentine. In a
way that 15 milliliter falcon tubes (Maxell-China) with
3 milliliter sterile BHI Broth was prepared and dentine
chips obtained from shaving were transferred into these
tubes in each step from dentine cylinders.
It should be mentioned that tubes were incubated 48
hours in 37 C° temperature. Then, out of 30 mentioned
tube some samples were cultivated on plates with BHI
Agar and were incubated in aerobic condition and in
37
0
C temperature. After incubation end, micro-organ-
isms identi cation test in order to be sure about that
bacteria are single strain and its penetration in 3 depths.
In order to measure strain from microbial growth, 2.5
milliliter was extracted from BHI Broth in tubes with
dentinal chips removed from incubator and its optical
density was studied by Spectrophotometer (WPA-bio-
wave2-USA) 540 nano-meter in wave length. Optical
density of groups under experiment and positive control
groups were compared together.
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Optical density related to experimental groups in three
depths (0.1, 0.2, 0.3) milliliter from dentine was meas-
ured by Spectrophotometer (Biochrom WPA - USA).
Mean and standard deviation of OD were mustered for
different depths in table 1.
Comparing experimental groups considering OD rate
in 3 measured dentinal depths was performed based on
statistical analysis of One-way ANOVA and SPSS soft-
ware.
According to table 2, and One-way ANOVA in 0.1
millimeter of dentine there was signi cant difference
between under studied groups (p<0.01). in addition, in
0.2 millimeter of dentine there was signi cant differ-
ence between under studied groups (p<0.01). But in 0.3
millimeter of dentine there was no signi cant difference
between under studied groups.
Shortly, comparing different groups with consider-
ing OD in each depth by one-way ANOVA analysis indi-
cated that there is signi cant difference between groups
Table 1. Mean ±standards deviation of optical density of provided lings from three dentinal depth under study
Mean (±standards deviation)
0.3 millimeter depth
Mean (±standards deviation)
0.2 millimeter depth
Mean (±standards deviation)
0.1 millimeter depth
Detergent solutions
(0.08±)0.23 (0.11±)0.22 (0.04±)0.016 Sodium hypochlorite 1- Sodium hypochlorite
(0.25±)0.34 (0.21±)0.34 (0.07±)0.24 2- ginger concentrate
(0.21±)0.26 (0.04±)0.21 (0.04±)0.18 3- eucalyptus concentrate
(0.08±)0.40 (0.07±)0.46 (0.07±)0.41
4- Normal saline
(positive control)

BIOSCIENCE BIOTECHNOLOGY RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS EVALUATION OF ANTIBACTERIAL EFFECT OF
EUCALYPTUS
AND GINGER 229
Samira Shahsiah et al.
DIAGRAM 1. Mean of optical density of provided lings from three dentinal depth under
study
Table 2. comparing OD between groups under study in 0.1 millimeter depth from dentine
Depth Sum of Squares df Mean Square F Sig.
0.1 Between Groups .308 4 .077 28.084 .000
Within Groups .178 65 .003
Total .486 69
0.2 Between Groups .376 4 .094 5.005 .001
Within Groups 1.220 65 .019
Total 1.596 69
0.3 Between Groups .219 4 .055 1.606 .183
Within Groups 2.214 65 .034
Total 2.433 69
Table 3. comparing pairwise OD of under study groups in 0.1 milliliter depth from dentine
Depth
(I)
group
(J)
group
Mean Difference
(I-J)
Std. Error Sig.
95% Con dence Interval
Lower Bound Upper Bound
0.1 1
2 -.085650* .016549 .000 -.11870 -.05260
3 -.018150 .016549 .277 -.05120 .01490
4 -.251650* .026166 .000 -.30391 -.19939
2
1 .085650* .016549 .000 .05260 .11870
3 .067500* .016549 .000 .03445 .10055
4 -.166000* .026166 .000 -.21826 -.11374
3
1 .018150 .016549 .277 -.01490 .05120
2 -.067500* .016549 .000 -.10055 -.03445
4 -.233500* .026166 .000 -.28576 -.18124
4
1 .251650* .026166 .000 .19939 .30391
2 .166000* .026166 .000 .11374 .21826
3 .233500* .026166 .000 .18124 .28576

Samira Shahsiah et al.
230 EVALUATION OF ANTIBACTERIAL EFFECT OF
EUCALYPTUS
AND GINGER BIOSCIENCE BIOTECHNOLOGY RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS
under study in 0.1 and 0.2 milliliter depth from dentine
(p<0.01). but this difference in 0.3 depth is not signi -
cant. According to post hoc test of Fisher’s least signi -
cant differences
(LSD) with 95% con dence we performed comparing
groups as pairwise in each depth. Group numbering is
as follow:
Group number 1: 5.25% sodiumhypochlorite
Group number 2: ginger concentrate
Group number 3: eucalyptus concentrate
Group number 4: normal saline (positive control)
According to post hoc test and table 3 in 0.1 mil-
liliter depth of dentine, anti-microbial effect of 5.25%
sodium hypochlorite was signi cantly better that ginger
concentrate and eucalyptus concentrate (p<0.01). While
there was no signi cant difference between 5.25%
sodium hypochlorite and eucalyptus concentrate.
In addition comparing ginger concentrate and euca-
lyptus concentrate indicated that in 0.1 milliliter depth
of dentine, there is no signi cant difference between
these two concentrate anti- microbial effect (p<0.01).
and eucalyptus concentrate had better anti- microbial
effect on enterococcus faecalis in dentinal tubules at the
presence of smear layer.
In 0.1 milliliter depth of dentine, anti- microbial
effect of5.25% sodium hypochlorite, ginger concentrate
and eucalyptus concentrate was signi cantly better than
normal saline (p<0.01).
According to post hoc test and table 4 in in 0.2 mil-
liliter depth of dentine, 5.25% sodium hypochlorite was
signi cantly better that ginger concentrate and normal
saline (p<0.02). While there was no signi cant differ-
ence between 5.25% sodium hypochlorite and eucalyp-
tus concentrate.
In addition comparing ginger concentrate and euca-
lyptus concentrate indicated that in 0.2 milliliter depth
of anti- microbial effect dentine there is no signi cant
difference (p<0.01). and eucalyptus concentrate has bet-
ter anti- microbial effect on enterococcus faecalis in
dentinal tubules at the presence of smear layer.
In 02 milliliter depth of dentine, anti- microbial effect
of 5.25% sodium hypochlorite and eucalyptus concen-
trate was signi cantly better that normal saline (p<0.01)
while there was no signi cant difference between anti-
microbial effect of ginger concentrate and normal saline.
According to post hoc test and table 5 in 0.3 milliliter
depth of dentine, there is no signi cant difference in
anti-microbial effect of 5.25% sodium hypochlorite, gin-
ger concentrate , eucalyptus concentrate , and normal
saline was signi cantly better that ginger concentrate
and normal saline (p<0.02). While there was no signi -
cant difference between 5.25% sodium hypochlorite and
eucalyptus concentrate.
3-1 results of growth and lack of growth after applying
canal detergents
In this study, in addition to measure optical density of
all environments under experiment, some samples were
cultivated as what is described in methodology. Growth
and lack of growth of bacteria on growth medium was
reported in each dentinal cylinder. Results of samples
cultivation was reported in table 8.
Table 8 indicates that:
In group 1(5.25% sodiumhypochlorite) 30% canals
had alive batteries.
In group 2( ginger concentrate ) 45% canals had
alive batteries.
In group 3( eucalyptus concentrate ) 20% canals
had alive batteries.
Table 4. comparing pairwise OD of under study groups in 0.2 milliliter depth from dentine
Depth
(I)
group
(J)
group
Mean Difference
(I-J)
Std. Error Sig.
95% Con dence Interval
Lower Bound Upper Bound
0.2 1
2 -.111750* .043327 .012 -.19828 -.02522
3 .013000 .043327 .765 -.07353 .09953
4 -.234400* .068507 .001 -.37122 -.09758
2
1 .111750* .043327 .012 .02522 .19828
3 .124750* .043327 .005 .03822 .21128
4 -.122650 .068507 .078 -.25947 .01417
3
1 -.013000 .043327 .765 -.09953 .07353
2 -.124750* .043327 .005 -.21128 -.03822
4 -.247400* .068507 .001 -.38422 -.11058
4
1 .234400* .068507 .001 .09758 .37122
2 .122650 .068507 .078 -.01417 .25947
3 .247400* .068507 .001 .11058 .38422
Samira Shahsiah et al.
BIOSCIENCE BIOTECHNOLOGY RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS EVALUATION OF ANTIBACTERIAL EFFECT OF
EUCALYPTUS
AND GINGER 231
In group 4( normal saline (positive control ) 100%
canals had alive batteries.
In group 5( negative control ) no canals had alive
batteries.
Group number 1: 5.25% sodiumhypochlorite
Group number 2: ginger concentrate
Group number 3: eucalyptus concentrate
Group number 4: normal saline (positive control)
Many studies have been made so far on anti-micro-
bial properties of plant (Karlovic´ et al, 2000; Hammer
et al, 1999; Rahman et al, 2010; Adeniyi et al, 2006;
Shalaby et al, 2011; Dulger and Gonaz 2004) and there
are many studies that considered anti-microbial prop-
erties of plant as detergents (Gulve and Gulve 2010;
Shari an et al, 2011; Maekawa et al 1013). It is clear
that this topic is very important. Consequently, in many
researches, no groups under study were able to remove
bacteria of canal at the presence of smear layer. Nor-
mal saline groups indicated 100% growth. This material
has no inhibition properties against Enterococcus faeca-
lisand its effect on existing micro-organisms in canal
happens through mechanical act. In sterile dentinal cyl-
inder (negative control), no growth was observed which
indicates that there is no pollution in environment and
applied tools so accuracy of performance was approved.
Anti- microbial effect of Eucalyptus camaldulensis con-
centrate on enterococcus faecalis (ATCC29212) in cylin-
ders provided from human teeth at the presence of smear
layer, with 5.25% sodium hypochlorite has no signi cant
difference. In addition, anti- microbial effect of Zingiber
of cinale on Enterococcus faecalis (ATCC29212) in cyl-
inders provided from human teeth at the presence of
smear layer is weaker than 5.25% sodium hypochlorite.
Table 5. comparing pairwise OD of under study groups in 0.3 milliliter depth from dentine
Depth
(I)
group
(J)
group
Mean Difference
(I-J)
Std. Error Sig.
95% Con dence Interval
Lower Bound Upper Bound
0.3 1
2 -.114500 .058369 .054 -.23107 .00207
3 -.036700 .058369 .532 -.15327 .07987
4 -.176650 .092289 .060 -.36096 .00766
5 -.017050 .092289 .854 -.20136 .16726
2
1 .114500 .058369 .054 -.00207 .23107
3 .077800 .058369 .187 -.03877 .19437
4 -.062150 .092289 .503 -.24646 .12216
5 .097450 .092289 .295 -.08686 .28176
3
1 .036700 .058369 .532 -.07987 .15327
2 -.077800 .058369 .187 -.19437 .03877
4 -.139950 .092289 .134 -.32426 .04436
5 .019650 .092289 .832 -.16466 .20396
4
1 .176650 .092289 .060 -.00766 .36096
2 .062150 .092289 .503 -.12216 .24646
3 .139950 .092289 .134 -.04436 .32426
5 .159600 .116737 .176 -.07354 .39274
Table 6. numbers of samples with bacterial growth
Lack of growth growth numbers of samples Group
14 6 20 5.25% sodium hypochlorite
11 9 20 Gin
16 4 20 eucalyptus concentrate
0 5 5 Normal saline (positive control)
505
Dentinal cylinder (negative
control)

Samira Shahsiah et al.
232 EVALUATION OF ANTIBACTERIAL EFFECT OF
EUCALYPTUS
AND GINGER BIOSCIENCE BIOTECHNOLOGY RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS
REFERENCES
Abubakar EMM. (2010). Antibacterial potential of crude leaf
extract of Eucalyptus camaldulensis against some pathogenic
bacteria. Afr J Plant Sci; 4(6):202-209.
Adeniyi BA, Odufowoke RO, Olaleye SB. (2006). Antibacterial
and gastroprotective properties of Eucalyptus torelliana (myrt-
aceae) crude extract. Int J Pharmacol; 2:362-365.
Ahangari Z. (2008). Antimicrobial activity of three root canal
irrigants on Enterococcus faecalis: An in vitro study. Iran
Endod J; 3(2):33-37.
Ali BH, Blunden G, Tanira MO, Nemmar A. (2008). Some phy-
tochemical, pharmacological and toxicological properties of
Ginger (Zingiber of cinale roscoe): a review of recent research.
Food Chem Toxicol; 46(2):409-420.
Chanadarana H, Baluja S, Chanda SV. (2005). Comparison of
antimicrobial activities of selected spices of Zingiberaceae
family and some synthetic compounds. Turk J Biol. 29:83-97.
Dulger B, Gonaz A. (2004). Antimicrobial activity of certain
plants used in Turkish traditional medicine. Asian journal of
plant sciences. 3(1):104-107.
Forbes BA, Sahm DF, Weissfeld AS. (2007). Bailey and Scott’s
diagnostic microbiology. 12th ed. St.Louis:Mosby.
Foschi F, Cavrini F. (2005). Detection of bacteria in endodontic
samples by polymerase chain reaction assay and association
with de ned clinical signs in Italian patients. Oral Microbiol
Immunol; 20(5):289-295.
Fux CA., Shirtliff M. (2005). Can laboratory reference strains
mirror “real-world” pathogenesis. Trends MIcrobiol. 13:58-63.
Gulve MM, Gulve ND. (2010). Comparison of antimicrobial
ef cacy of ginger extract and 2% Sodium hypochlorite against
Enterococcuc faecalis using Agar diffusion method. Int Dent
Assoc; 4(10):347-349.
Gwinnett AJ. (1984). smear layer: morphological considera-
tions. Oper Dent Suppl 3:2-12.
Hammer K.A. (1999). Antimicrobial activity of essential oils
and other plant extracts. J appl microbial. 86:985-990.
Hargreaves KM, Cohen S, Berman LH. (2011). Pathways of the
pulp. 10th ed.St Louis:Catherine Jackson.
Kakehashi S. Stanley HR, Fitzgerald RJ. (1965). The effects of
surgical exposures of dental pulp in germ free and conven-
tional laboratory rats. Oral Surg; 26:340-349.
Karlovi
c´ Z. (2000). Antimicrobial activity of Halothane, Euca-
lyptol and Orange oil. Acta stomatol Croat; 34(3):307.
Keskin D, Toroglu S. (2011). Studies on antimicrobial activities of
solvent extracts of different spices.J Environ Biol; 32:251-256.
Maekawa LE. (2013). Effect of Zingiber of cinale and Propolis
on microorganisms and endotoxins in root canals. J Appl Oral
Sci. Jan-Feb; 21(1):25-31.
Martos j, Luque CMF. (2013). Antimicrobial activity of essen-
tial oils and Chloroform alone and combined with Cetrimide
against Enterococcus faecalis bio lm. Eur J Microbiol Immu-
nol. 3(1):44-48.
McComb D, Smith DC, Beagrie GS. (1976). The results of in
vivo endodontic chemomechanical instrumentation-a scan-
ning electron microscopic study. J Br Endod Soc; 9:11-18.
Murad CF. (2012). Antimicrobial activity of Sodium hypochlo-
rite, Chlorhexidine and MTAD against Enterococcus faecalis
bio lm on human dentin matrix in vitro. RSBO 9(2):143-
150.
Onçag˘ O, Hosgör M, Hilmiog˘lu S, Zekiog˘ lu O, Eronat C, Burh-
anog˘lu D. (2003). Comparison of antibacterial and toxic effects
of various root canal irrigants. Int Endod J. 36(6):423-32.
Peciuliene V, Reynaud AH, Balciuniene I, Haapasalo M.
(2001). Isolation of yeast and enteric bacteria in root- lled
teeth with chronic apical periodontitis. Int Endod J. 34(6):
429-34.
Rahman MSA, Thangaraj S, Salique SM, Khan KF, Natheer
SE. (2010). Antimicrobial and biochemical analysis of some
spices extract against food spoilage pathogens. Int J Food Safe.
12:71-75.
Retamozo B, Shabahang S, Johnson N, Aprecio RM, Torabi-
nejad M. (2010). Minimum contact time and concentration OD
Sodium hypochlorite required to eliminate Enterococcus faeca-
lis. J Endod. 36(3):520-3.
Shabahang S, Torabinejad M. (2003). Effect of MTAD on
Enterococcus faecalis–contaminated root canals of extracted
human teeth. J Endod; 29(9):576-579.
Shalaby EA, Nasr NF, El Sherief SM. (2011). An in vitro study
of the antimicrobial and antioxidant ef cacy of some nature
essential oils. Planta Med; 5(6):922-931.
Shari an MR. (2011). Antimicrobial effect of Citrus auran-
tifolia extract on Enterococcus faecalis within the dentinal
tubules in the presence of smear layer. J Dent Med; 24(3):148-
155.
Sheykhrezaei MS, Aligholi M, Biglar KH. (2004). An in-vitro
evaluation of the ability of 5.25% NaOCl in the elimination
OD Enterococcus faecalis from root canal. Journal of dentistry,
TUMS. 1(2):45-48.
Torabinejad M, Handysides R, Khademi AA, Bakland LK.
(2002). Clinical implications of the smear layer in endodontics:
a review, oral surg oral med oral pathol oral radiol Endod.
94(6): p 658.
Torabinejad M, Walton RE. (2008). Endodontics: principles and
practice. 4th ed. St. Louis: Saunders.
Yiu CK, García-Godoy F. (2002). A nanoleakage perspective on
bonding to oxidized dentin. J Dent Res; 81:628-632.
Zehnder M. (2006). Root canal irrigants. J Endod; 32(5):389-
398.
Zoletti GO, Siqueira JF Jr, Santos KR. (2006). Identi cation
of Enterococcus faecalis in root- lled teeth with or without
periradicular lesions by culture dependent and independent
approaches. J Endod; 32(8):722-726.