
Biotechnological
Communication
Biosci. Biotech. Res. Comm. 10(2): 173-181 (2017)
Effect of rat cartilage essence on omentum cells
cultured through micromass method
Zahra Goudarzi
1
, Kazem Parivar
2
, Susan Kiaei
3*
and Roudabeh Razaz
4
1,3,4
Master of Biology, Department of Biology, Science and Research Branch, Islamic Azad University,
Tehran, Iran
2
Department of Biology, Science and Research Branch, Islamic Azad University, Tehran, Iran
ABSTRACT
Omentum`s tissue MSCs have recently been recognized as multipotent cells. In this study inducing effects of cartilage
essence obtained from the NMRI bred rat on omentum cells cultured through Micromass method have been evaluated.
12 days NMRI rats were used as cell sample. Omentum tissue lacking fast was removed from the intestines. To culture
in cellular compressed mass through micromass, cells numbers were added in level unit. Before culturing, cells were
precipitated at the bottom of the tube like a compressed mass by centrifuge and then DMEMculturing environment
containing glutamine, glucose and sodium pyruvate, without sodium B carbon was added to the resulted cellular
mass. Furthermore, FBS serum amount was reduced to 2% in culturing environment gradually. Thereafter, stem cells
were exposed to various doses of cartilage essence. Investigations showed that density rate of cartilage essence 50
Landa were able to ease the process of turning to cartilage for these cells in 21 days. Cartilage essence`s other densi-
ties have led to the elimination of stem cells. To prove the differentiation of mesenchymal cells chondroblast turn,
Alison blue and Toluidine blue which are the speci c colors of outer cellular matrix was used.
KEY WORDS: MESENCHYMAL CELLS, OMENTUM TISSUE, STEM CELLS, CARTILAGE ESSENCE, CHONDROBLAST, DIFFERENTIATION
173
ARTICLE INFORMATION:
*Corresponding Author:
Received 12
th
April, 2017
Accepted after revision 28
th
June, 2017
BBRC Print ISSN: 0974-6455
Online ISSN: 2321-4007 CODEN: USA BBRCBA
Thomson Reuters ISI ESC and Crossref Indexed Journal
NAAS Journal Score 2017: 4.31 Cosmos IF : 4.006
© A Society of Science and Nature Publication, 2017. All rights
reserved.
Online Contents Available at: http//www.bbrc.in/

174 EFFECT OF RAT CARTILAGE ESSENCE ON OMENTUM CELLS CULTURED BIOSCIENCE BIOTECHNOLOGY RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS
Zahra Goudarzi et al.
INTRODUCTION
Stem cells are a kind of an undifferentiated somatic cell
which have two unique characteristics: Self-renewal:
which they can continuously replicate themselves in
culturing environment and maintain their restoration
for an in nite period. Differentiation: which they can
under certain conditions turn into speci ed cells and
differentiate other constructing cell type’s pf a living
body. These cells exist in blood, bone marrow, skeletal
muscle, retinal, retina, teeth pulp, brain, nerve cord,
liver, skin, intestine, pancreas and venous blood (Kadi-
var, M., 2009). Regarding replication and differentiation
potential, stem cells with different sources are different
in a way that this potential decreases from embryonic
stem cells to adult’s stem cells (Baksh, 2004).
Despite embryonic stem cells high potential, their use
due to problems related transplant rejection of the cells,
ethical problems and tumorigenicity of these cells after
transplant is highly limited (Romanov, 2003). Unlike
embryonic stem cells, MSCs are not replicated perma-
nently whereas after some time face senescence. Studies
showed that cell replication in lab environment leads to
the decrease of their differentiating replication ability
process (Baqb an et al. 2008). Till today stem cells func-
tions included genomics studies, biological processes
studies and development of cell treatment. Currently
scientists use stem cells for screening of new medicines
in labs. (Toyooka, 2003). Methods of identifying primary
MSCs are diverse. Flowcytometry is based on the MSCs
reaction to a number of antibodies (Alagumuthu, 2006,
Chapel, 2003, Liu,2010).
Previous researches have proved the exibility of
stem cells differentiated from nerve cell, skin cover, lung,
liver, intestine, kidney, and spleen. (Evans, 2002, Mar-
tin 2003). Studies showed that MSCs, when cultured in
a 22 monolayer fashion, show lesser Chondrogenic dif-
ferentiation compared to 3d culturing. We believe that
cell when culturing in 3D fashion (cellular mass) experi-
ences a similar environment to precartilage environment
in embryonic genesis period (Johnstone,1998). Under
these condition chondrocytes maintain their cartilage
phenotype. It seems that the main reason of cartilage
phenotype maintenance in micromass culturing is the
cellular reaction due to direct cell to cell contact in cel-
lular mass. Omentum is a big peritoneal wrinkle. From
omentum`s special features we can refer to its rich source
of angiogenic factor, having a strong lymphatic system,
having the ability to produce security specialized cells
and a big source of various growth factors such as neu-
rotransmitters, neurotrophic factors and in ammatory
mediators. Furthermore, it includes multipotent stem
cells which can differentiate between various types of
cells (Carlos 1992, Khaluqi, 2011).
Various ways can be considered for creating directed
differentiation in lab environment which can include
adding growth factor(s) or chemical morphogens (Li,
wg; 2005), co-culturing of stem cells with inducing
cells, stem cells transplant to certain regions or organs
and etc. In this research project cartilage essence effect
on omentum MSCs differentiation toward cartilage cells
in micromass culturing with gradual reduction of the
serum is investigated.
MATERIAL AND METHODS
In this research 12 days NMRI bred rat, ranging between
18-22 gms, were used as test animals.All the dilutions
used in this article wereprovided though commerce and
were used without further puri cation. Purchased cul-
turing environment was DMEM (Dulbeccos Modi ed
Eagles Medium-high glucose), containing glutamine,
glucose sodium pyruvate, without sodium bicarbonate
from Royan Stem Cells technology Co. FBS dilution
which contains required proteins and factors for cell
growth, was produced from cow serum. PBS without
calcium and magnesium ions was provided with its PH
domain within the range of 7.2 to 7.4. All the dilutions
used in culturing such as PBS, DMEM, and FBS were
sterile before use by passing through syringe head lter
with 0.22 micrometer penetrative diameter.
First under the laminar hood wish disinfected using
UV and alcohol 10ml PBS dilution was poured into 10cm
Petri dishes. Then, a couple of pen strep drops (penicillin
and streptomycin dilution) were added. In animal room
a rat was made unconscious and was transferred to the
surgery bed. Using 70 & alcohol all of its body especially
its stomach surface was disinfected and stomach`s wall
and peritoneum were exposed using scissors and stretch-
ing stomach to the sides. Then,using forceps and scissors
omentum tissue lacking fat was removedfrom intestines.
Omentum tissues placed on ice were washed using cool
PBS dilution containing 1% penstrep three times so that
it became blood cell free, cellular wastes and any other
possible pollution free. Thereafter, omentum tissues were
gathered in a new Petri dish containing sterile DMEM,
using scissors fragmented and then centrifuged.
Common technique for chondrogenic differentiation
of MSCs in lab environment through micromass method
was derived from Johnstone et al., method (Johnstone
et al.,1998). In this technique, to simulate differentia-
tion environment in a natural way in embryo, a greater
number of cells were exposed to the essence in falcon in
a compressed fashion in a way that 250000 to 300000
in 500 landa of culturing environment were added using
centrifuge with 1200 rpm for 5 minutes in a compressed
fashion slowly at the bottom of the falcon. Also, FBS

BIOSCIENCE BIOTECHNOLOGY RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS EFFECT OF RAT CARTILAGE ESSENCE ON OMENTUM CELLS CULTURED 175
Zahra Goudarzi et al.
serums amount in culturing environment was reduced
gradually. Meaning when changing culturing environ-
ment, each time a lesser amount of FBS were added to
DMEM. Therefore, cells were cultured with 2% FBS
Almost 24 hours after the birth of rat, their stemum
cartilage tissue was removed and were homogenized and
centrifuged. We discard the above dilution and a speci c
amount of nitrogen was added tp cartilage parts depos-
ited, inside a rocky pounder. Due to sudden reduction of
cartilage parts temperature, in its matrix of mid-cellular
tissue crystals are formed which leads to easy fragmen-
tation by the pounder. We added 4ml DMEM containing
FBS15% to the easily fragmented cartilage parts. Now
we homogenize them with high rmp to obtain a suspen-
sion of cartilage. It will take 5 to 7 minutes. Then we
transfer to centrifuge and centrifuge it with 700rpm. We
remove the above dilution and lter it with 0.45 microm-
eter syringe head lter. Dilution withdrawn is cartilage
essence. Five groups were studied. Respectively, observer
which only contained culturing environment with 10%
serum, free group or without serum and falcons with
various doses, with doses of 20, 40, and 50 landa which
serum amount in each of the gradually was reduced to
2% and placed in incubator for 21 days.
Densities for obtaining 1000l or 1cc culturing envi-
ronment are as follows in thistest. (For 1cc differentiat-
ing material prepared, 0.1ml, pen/strep is added to the
environment).
• Observer (10%FBS + 90%DMEM)1000µl
• Environment without serum (100%DMEM) 1000 µl
• 20 landa dose 20µl (cartilage essence) +(2%
FBS + 98%DMEM)980µl
• 40 landa dose 40µl (cartilage essence) +(2%
FBS + 98%DMEM)960µl
• 50 landa dose 50µl (cartilage essence) +(2%
FBS + 98%DMEM)950µl
To prove chondroblast differentiation of mesenchymal
cells we use Alison Blue and Toluidine Blue coloring
which are the speci c colors of outer cellular matrix. To
color differentiated cells with Alison blue and Toluidine
bluw, rst cells were xed with formaldehyde xator. To
color with toluidine blue, after consolidation, watering
with alcohol and clari cation with xylene, are molded
by paraf n and 5 micrometer cuts are taken from them.
Toluidine blue is treated to cellular plates for 30 seconds
in room temperature with 50 landa cartilage essence and
in the end extra color is washed off with distilled water.
To color with Alison blue, 0.1 Alison blue color is
diluted in 10ml PBS with the help of PHmeter and add-
ing normal hydrochloric acid 0.01 its PH is determined
in the range of 6 to 6/5. Thereafter it was added to the
cellular plated treated with 50 landa cartilage essence
and were incubated for an approximately one hour.
In the end we discarded the dilution on the cells and
washed them with PBS dilution and scanned them. To
prove the existence of chondroblast cells with immu-
nohistochemistry test after tissue consolidation and
preparation, molding with paraf n was performed. After
providing levels, clari cation and watering, levels con-
solidation was performed by sten. To neutralize peroxide
activity of inner tissue hydrogen, samples were placed in
3 percent hydrogen peroxide for 30 minutes. To reveals
antigens, pepsin enzyme with the amount of 1mg in 1ml
acetic acid 0.5m for 40 minutes in 37cc degree was used.
Thereafter samples were incubated in primary antibodies
against collagen molecules of rat type II for 24 hours in
4cc degree. In the next stage, secondary antibody con-
nected to polymer containing horseRadish peroxidase,
were added to the samples and after washing them with
PBS buffer, di-amino benzidie chromogen was added to
the samples. To color the background, hematoxylin was
used. After washing the samples with buffer, study was
conducted by microscope.
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
One of the ways of identi cation and assertion of mes-
enchymal nature of cells is using cell surface markers.
Flowcytometry analysis of CD45 is negative and for
CD44 and CD90 is positive. Therefore, mesenchymal
nature of created cells from omentum is con rmed.
PERCENT OF MARKERS
Omentum: A) CD90 Antibody in 84.5 percent of the
analyzed cells is expressed. B) CD45 antibody which
only in approximately 1.92 percent of analyzed cells is
expressed. C) CD44 in 88.22 percent of the cells were
expressed.
FIGURE 1. Flow cytometry gure for omentum cul-
tured cells.
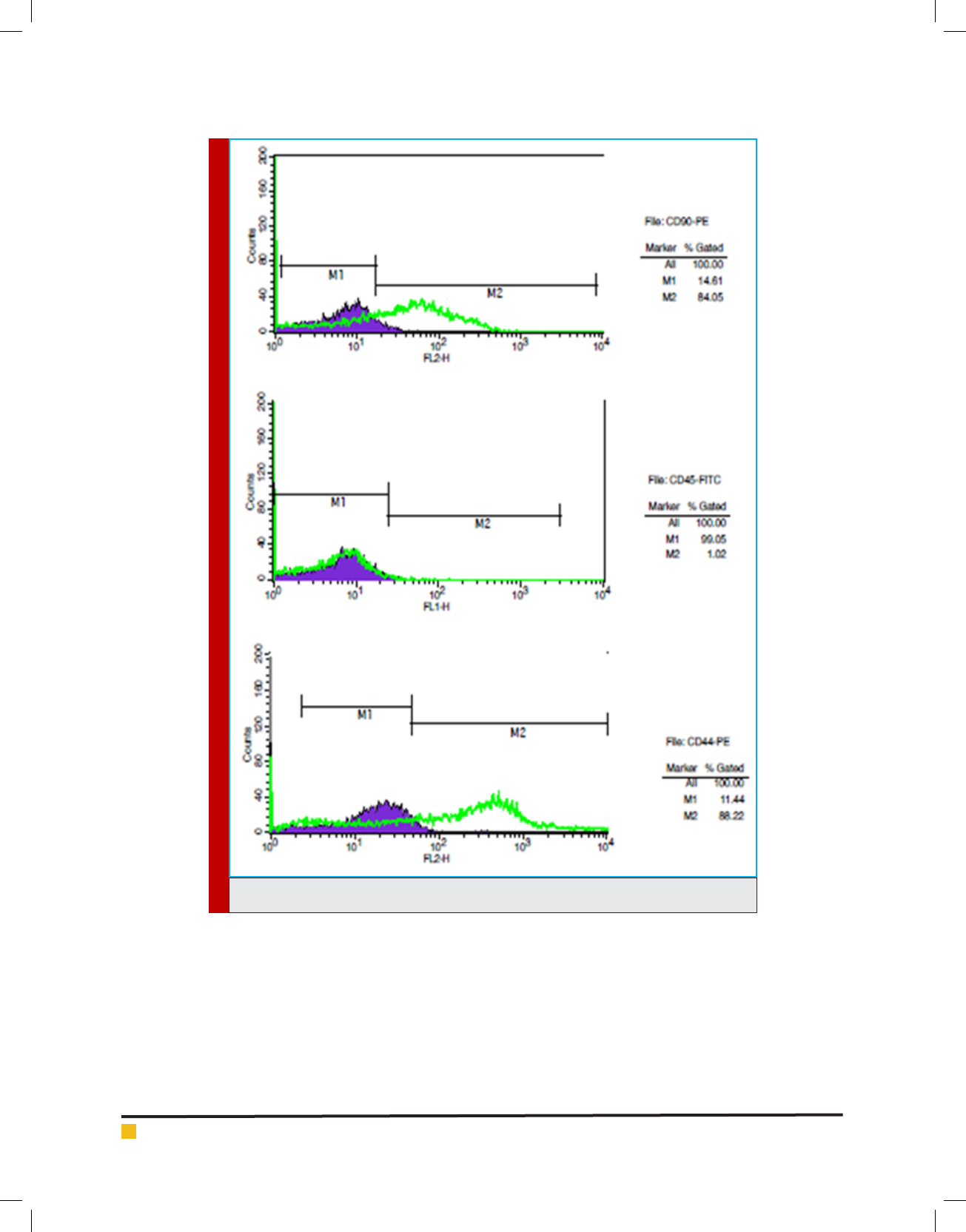
176 EFFECT OF RAT CARTILAGE ESSENCE ON OMENTUM CELLS CULTURED BIOSCIENCE BIOTECHNOLOGY RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS
Zahra Goudarzi et al.
FIGURE 2. Flow cytometry analysis for cultured cells.
In the current study RNA samples were extracted
from omentum cultured cells and inverted transcription
reaction was performed using designed starters. In this
test, we used WT-1 gene as the marker of mature stem
cells and Oct-4 as the marker of embryonic powerful
cells, and ACTB gene as the house keeper (this gene is
always expressed, if not it is an indication of incorrect
use of PCR). Observations showed that in this test both
WT-1 and Oct-4 genes are expressed, however, RT-PCR
band related to MRNA with WT-1 gene was brighter and
clearer than RT-PCR band related to mRNA with Oct-4
gene. Therefore, WT-1 and Oct-4 gene expressions are
proof of stem cells existence in omentum.
Cellular mass enlargement shows that cells discharge
matrix among themselves and created cartilage tissue.
To prove this claim, after the end of 21 days of differen-
tiation, we performed sectioning on the samples. Inves-
tigations was carries out by microscope and colored by

BIOSCIENCE BIOTECHNOLOGY RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS EFFECT OF RAT CARTILAGE ESSENCE ON OMENTUM CELLS CULTURED 177
Zahra Goudarzi et al.
Image 1. RT-PCR test results for speci c genes expression of omentum stem cells. Cellular plates were
measured every two days which are as follows:
1. Observer: cellular plate decomposed and disappeared after one week.
2. Environment without serum: cellular plate shrink and decomposed and disappeared after
one week.
3. 20 landa dose: till the rst week it was observer sized, however gradually after one week
decomposed and disappeared.
4. 40 landa dose: It gew in the rst week and became bigger than the observer. However, in
the second week cellular mass shrink and decomposed and disappeared.
5. 50 landa dose: cellular plate became bigger compared the previous in the rst week and
reached more than 1
ab
IMAGE 2. Images are related to omentum mesenchymal cells cultured through 3D culturing
method after cartilage effect with the amount oof 2% FBS serum. a) 20 landa dose of cartilage
essence after one week. b) 40 landa dose of cartilage essence after one week.
Alison blue and Toluidine blue and Collagen 2 expres-
sion was investigated by immunohistochemistry.
Microscopic investigations showed that with serum
reduction better differentiation occurs and chondrocytes
affected by the cartilage essence with 50 landa dose
showed better morphology. Following images con rm
these claims.
Colored sections with toluidine blue show metachro-
matic characteristic and background material turns into
purple.

178 EFFECT OF RAT CARTILAGE ESSENCE ON OMENTUM CELLS CULTURED BIOSCIENCE BIOTECHNOLOGY RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS
Zahra Goudarzi et al.
ab
IMAGE 3. Images related to cultured omentum mesenchymal cells through 3D culturing method
after the cartilage essence effect with 50 landa dose and amount of 2% FBS. a) After one day
which as big as observer group. b) After one week which is slightly bigger.
IMAGE 4. Images related omentum cultured msenchymal cells with 3D culturing method after
cartilage essence effect with 50 landa dose and 2% FBS amount. a) After two weeks. b) After
three weeks.
a
b
ab
IMAGE 5. Image is related to omentum mesenchymal cells 21 days after the cartilage essence effect with 50
landa dose and 2% FBS. a) Dual and ternary cells are completely visible in clear lacuna halo. b) Cells differentia-
tion are completely obvious.
BIOSCIENCE BIOTECHNOLOGY RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS EFFECT OF RAT CARTILAGE ESSENCE ON OMENTUM CELLS CULTURED 179
Zahra Goudarzi et al.
a
IMAGE 6. Image is related to 3D culturing section 21 days after cartilage essence effect with 50 landa dose
and 2% FBS serum. After coloring with toluidine blue, cells round morphology and their dark core is visible
in image b.
b
c
d
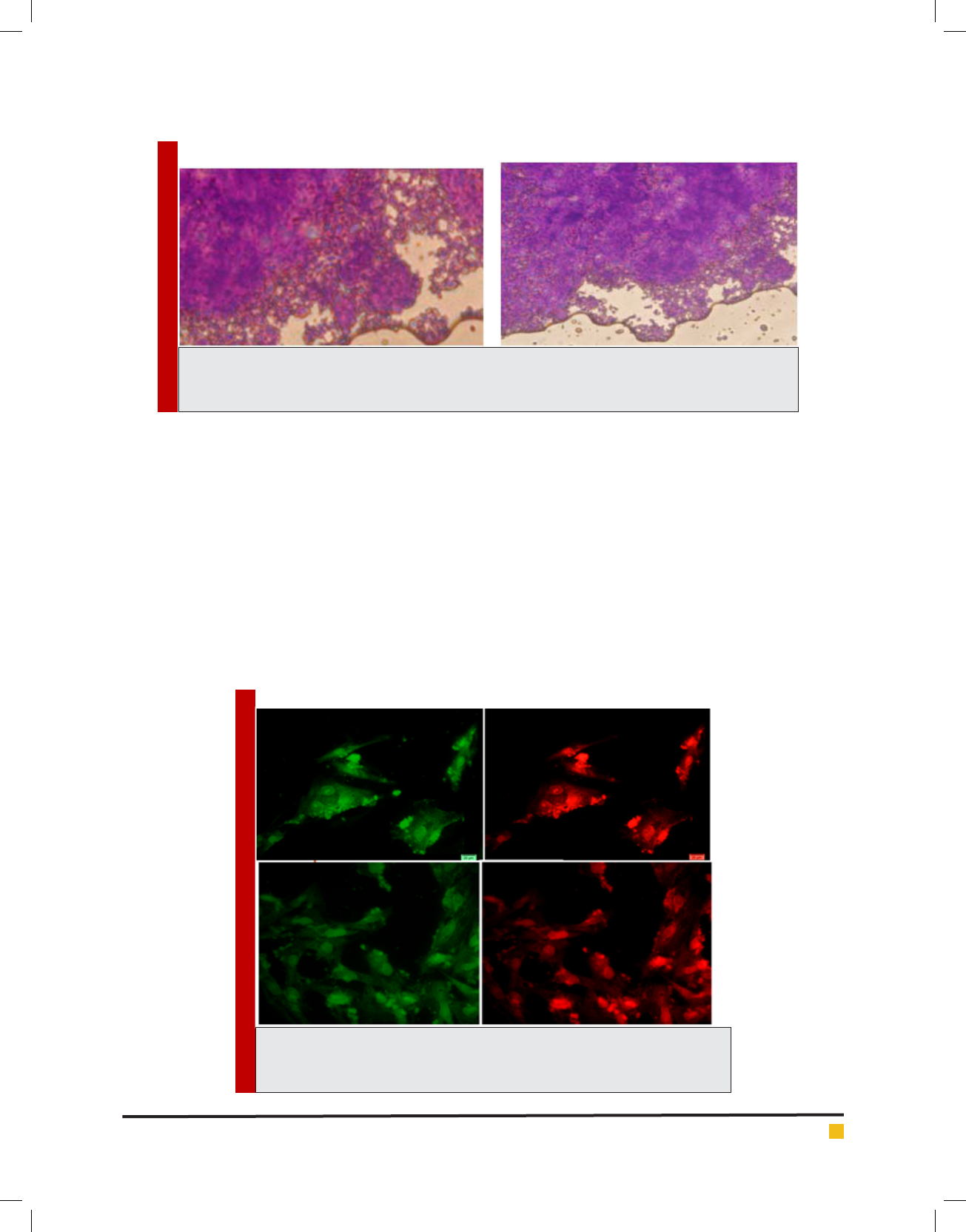
IMAGE 7. Images are related to omentum mesenchymal cells 21 days after the
cartilage essence effect. Green colors (a,b) are collagen 2 molecules indicator and
green (c,d) are related to cores coloring by IP.
ab
In coloring with Alison bluematerial nds a bluish
green background. Image 6: Image is related to the DC
culturing section 21 days after cartilage essence effect
with 50 landa dose and 2% FBS serum. After color-
ing with Alison blue, a community of cells which that
have turned into a colony and discharged matrix among
themselves is seen. To investigate the expression of Col-
lagen type 2, primary and secondary antibodies which
are anti- collagen type 2 are used in the cartilage dif-
ferentiated cells, which the results are visible in the fol-
lowing images.
Stem cells are a kind of undifferentiated somatic cells
that are found in the majority of the multicellular liv-
ings. Some of their characteristics are self-renewal abil-
ity, high mitotic distribution and differentiation power
toward different types of speci ed cells (Becker, 1963,
Siminovitch, 1963). We can refer to MSCs as one of the
most important mature stem cells that have attracted
researcher’s attention. Omentum mesenchymal cells play
a role in treating damages and it was identi ed in 1948
by Cannaday for the rst time (Kadivar, 2009). These
cells are utilized as supporting cells for inner growing
organs in vivo conditions (Iwashima, 2011). Recently
extracting MSCs from omentum tissue is carried out
successfully (Alagumuthu, 2006, Singh, 2008). In this
study too, rst omentum mesenchymal cells of 12 days

180 EFFECT OF RAT CARTILAGE ESSENCE ON OMENTUM CELLS CULTURED BIOSCIENCE BIOTECHNOLOGY RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS
Zahra Goudarzi et al.
NMRI ratis extracted and summarized. Some lab stud-
ies have shown that if mature chondrocytes are cultured
in simple dishes, lose their differentiation rapidly and
their physiological activities decrease (Ng 2005). One
of the important conditions for creating culturing is
using micromass (Johnstone,1998). Weused this method
for creating suitable cellular mass, which is increasing
number of cells in level unit.
Thereafter, cells phenotype and genotype was con-
rmed with various evaluations such as ow cytometry.
Accordingly, in human and other rodents such as rat, sur-
face antigens related to these cells were investigated by
ow cytometry and using monoclonal antibodies. What
today is important in identi cation of MSCs, is if they
have broblast morphology and are negative in terms
of hematopoietic stem cells, they can be presented as
MSCs (Barry, 2004). Expressing speci c markers of MSCs
includes CD90 and CD44 and lack of expressing special
marker of hematopoietic cells is con rmed as CD45 in
separated cells from the omentum, which is aligned with
Pancholi et.al results (Pancholi et al 2010 Li, 2005).
In this research cartilage essence was used for cre-
ating differentiation induction instead of using com-
mon growth factors, since using growth factors such as
TGF can have unknown effects on other cells and have
tumorigenic effects. However, using natural essences in
addition tolacking the above mentioned shortcomings
can have the advantage of lesser transplant rejection due
to tissue similarities and cells differentiate with more
similar conditions with their natural den. Treatment
with cellular essence, is a new strategy for cells differ-
entiation which is able to transform a type of somatic
cell into another. MSCs affected by cartilage essence
induction can nd chondrocyte cells morphology. For
instance cells took an oval shape which is a characteris-
tic of chondrocyte cells (Shamblott, 1998). Then matrix
construction begins to separate chondroblasts. Differen-
tiation occurs from the center toward exterior. There-
fore, more central cells have chondrocytes characteris-
tics, however, ambient cells typically are chondroblasts
(Liu, 2010).
Various dilutions of cartilage essence were used, after
mesenchymal cells were treated by cartilage essence
with 50 landar dose, signi cant changesoccurred from
the fourth day onward. In some regions cellular colonies
were created. With an increase in number of cells, they
absorb cellular extras. And cells move toward oval and
round formation, which means they are chondroblasts
which later use of speci c Alison blue and Toludine blue
coloring con rmed this notion. These cells seem com-
pletely alive and active and replication process still con-
tinues in them. These change occur while in other groups
under study, their cells still remain between chondro-
cytes morphology phase and spindly and lengthy mor-
phology which is speci c tp broblasts and with passage
of time face senescence and apoptosis.
Collagen type 2 is the most abundant existing col-
lagen in cartilage. Collagen type 2 contains speci c
sequences to connect to the cell and as a result has
a high interaction with the cell. It can be suitable for
maintaining cartilage cells phenotype and activities (Li,
2005, Zambrano, et al, 1982). In this experience we were
able to con rm production of collagen type 2 through
immunohistochemistry in cartilage cells derived from
omentum MSCs of NMRI breed rat after 21 days from
the start of differentiation induction. Therefore, consid-
ering cellular mass and morphological changes in the
cultured stem cells it seems that we succeeded in pro-
ducing chondroblasts.
CONCLUSION
This research is carried out to investigate inducing
effects of cartilage essence obtained from rat on cul-
turing omentum cells through micromass with reducing
serum amount and understanding and interpreting the
results. Results are the indication of the cartilage essence
effect on omentum`s MSCs in the absence of growth fac-
tors, common induction and their differentiation with
chondrocytes. It seems that our method of separating
omentum`s mesenchymal cells and producing cellular
lnie was completely successful and powerful and have
appropriate and acceptable progress toward differentia-
tion, specially creating a compression and production of
chondroblasts. Considering the results that Dubler et.al
have obtained from culturing on collagen and results
that Tuli and Okafor obtained regarding culturing with
tissue engineering using collagen type 2, we can con-
clude that the cartilage essence used in this research as
an induction factor can intensify differentiation process
in cells due to existence if collagen in itself with the help
of creating and maintain cellular connections.
REFERENCES
Alagumuthu, M., Das, BB., Pattanayak, SP., Rasananda, M.,
2006, The omentum: A unique organ of exceptional versatility,
Indian J Surg; 68:136-41.
Baksh, D., Song, L., Tuan, R.S, 2004, Adult mesenchymal stem
cells: Characterization, differentiation and application in cell
and gene therapy, J. cell. mol. Med, vol l8, No 3, 301-316
Baqban Eslami Nejad, M, Talkhabi, M, Zeynali, B, Eftekhari
Yazdi, P, 2008. Investigating Lithium chloride on replication
rate of MSCs derived from rat`s bone marrow. Year 6. Issue 23.
Pages 363-372
Barack Johnstone, T.M. Hering, A.I. Caplan etal.,1998 Invitro
chondrogenesis of bone marrow-derived mesenchymol pro-
genitor cells, Exp Cell Res, Vol. 238, no.1, PP. 265-272,

BIOSCIENCE BIOTECHNOLOGY RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS EFFECT OF RAT CARTILAGE ESSENCE ON OMENTUM CELLS CULTURED 181
Zahra Goudarzi et al.
Barry, F-P-, Murphy, J.M., 2004, Mesenchymal stem cells:
clinical application and biological characterization, The
international journal of biochemistry & cell Biology 36:568-
584
Becker, A.J., Mcculloch, E.A., Till, J.E., 1963, Cytological dem-
onstration of the clonal nature of spleen colonies derived from
transplanted rat marrow cells, Nature; 197:452-4
Carlos Junquera, L, jose carneiro, Robert. O.K: (1992), Basic
histology
Chapel, A., Bertho, JM., Bensidhoum, M., Fouillard, L.,Young,
R.G., 2003, Mesenchymal stem cells home to injured tissues
when co-infused with hematopoietic cells to treat a radiation–
induced multi-organ failure syndrome, J Gene Med; 5(12):
1028-38
Evans, MG., Kaufman, MH., Establishment in culture of Pluari
potential Cell from rat embryos. Nature (2002) 2, 2 : 154-156
Gomez, I., 2012, Omentum in the Repair of Injured Tissue:
Evidence for Omental Stem Cells,stem Cells and Cancer Stem
Cells, Volume 2
Iwashima, M., Love, R., Braun, R., Sethupathi, P., Knight, K.L.,
2011, Omentum as a source of stromal/ stem cells and medical
treatments using stroma) stem cells, Patent Application pub-
lication
Jones, EA S.E. Kinsey, A. English et al., Isolation and Charac-
terization of bone marrow multipotential mesenchymol pro-
genitor cells, Arthritis Rheum, Vol. 46, no.12, PP. 3349-3360,
2002
Kadivar, M. Piryiayi F and Ramezani, M. 2009. Separation,
culturing and MSCs differentiation of chickens bone marrow.
Journal of Armaqan Danesh. Round 14. Issue 4
Khaluqi, K. Shahbazi, A. Sojoudi, M. Vosouq, M. 2011. Stem
cells in simple language. Tehran. House of Biology. First Vol-
ume
Li, WG Tuli, R; Okafor, C A three –dimensional nano brous
scaffold for cartilage tissue engineering using human mesen-
chymal steem cells Biomaterials, (2005)
Liu, Y., Yue, W., Ji, L., Nan, X., Pei, X., 2010, Production of
erythriod cells from human embryonic stem cells by fetal liver
cell extract treatment, BMC Developmental Biology; 10:85
Martin GR. 2003 Isolation of a Pluripotent Cell line From early
rat embryos cultured in medium conditioned by teratocarci-
noma Stem cells . Proc . Natl . Acad . Sci, 78: 7634-7638
Ng, S., Wua, Y.N., Zhou, Y., Tohb, Y.E., Ho, Z.Z., Chia, S.M.,
2005, Optimization of 3D hepatocyte culture by controlling the
physical and chemical properties of the extra- cellular matri-
ces, Biomaterials; 26(16) :3153-3163
Pancholi, N., Patel, J., Gudehitblu, K., Kraus, M., Dunea, G.,
Arruda, J., Singh, AK., 2010, Culture of omentum-induced
regenerating liver yielded hepatocyte-committed stem cells,
Tranalation Research, Voiume l56, Number 6; 156(6):358-68
Pournasr, B. Baharvand, H. 2010. Stem cells and human`s msen-
chymal: biological characteristics, treatment functions and sep-
aration methods. Tehran. House of Biology. Volume 2. 28-67
Romanov, YA., Swvintsitskaya, VA., Smirnov, VN., Searching
for alternative Sources of postnatal humar mesenchymal Stem
cells: candidate MSC like cells from umbilical cord . Stem Cells
(2003) 21 : 105-110
Shamblott, MJ., Axelmanj, J., 1998 Derivation of pluripotent
stem cells from Cultured human primordial germ cells. Proc
Natl Acad Sci, (1998).
Siminovitch, L., Mcculloch, E.A., Till, J.E., 1963, The distribu-
tion of colony-forming cells among spleen colonies. Journal of
cellular and comparative physiology; 62:327-36
Singh, A.K., Patel, G., Litbarg, N.O., Gudehithlu, H.P.,
Sethupathi, P., Arruda, G.A . and Dunea, G., 2008, Stromal
cells cultured from omentum express pluripotent markers, pro-
duce high amount of VEGF and engraft to injured sites. Cell
and Tissue Research, 332:81-88
Toyooka, Y; Tsunekawa, N; Akasu, R; 2003 Embryonic stem
cells can from germcells in vitro.
Zambrano, NZ; et al. collagen arrangement in cartilages Acta
Anat (1982). 113:26