
Medical
Communication
Biosci. Biotech. Res. Comm. 10(2): 102-107 (2017)
Comparison of two transconjunctival and
transcutaneous approaches in the incidence of scleral
show during lower eyelid blepharoplasty
Hooman Hooshangi
1
, Mehdi Sezavar
2
*, Behnam Bohluli
3
, Farzin Sarkarat
3
, Fatemeh
Nasrollahi
1
and Sina Seyedabbaszadeh
1
1
Resident of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Islamic Azad University, Dental Branch, Tehran, Iran
2
Assistant Professor, Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Islamic Azad University, Dental Branch,
Tehran, Iran
3
Associated Professor, Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Islamic Azad University, Dental
Branch, Tehran, Iran
ABSTRACT
Despite its effectiveness for the facial rejuvenation, blepharoplasty has been associated with several adverse effects.
One of the most common side effects of this surgery is eyelid malposition and scleral show which is not suitable from
esthetic point of view. Although some techniques have been used for the blepharoplasty of the lower eyelid, the effect
of these techniques has not been de nitely identi ed in the incidence of scleral show. The present study compared
the effects of lower eyelid blepharoplasty with transconjunctival and transcutaneous approaches in the incidence of
scleral show in patients. 22 candidates of the lower eyelid blepharoplasty were studied. The patients had no history
of systemic disease, previous lower eyelid blepharoplasty, trauma or dry eye syndrome. The patients were randomly
assigned in 2 methods of transconjunctival and transcutaneous approaches. The surgeries were perform on 2 eyelids
of the left and right sides and in total, 44 eyelids were subjected to blepharoplasty surgery in both sides of the patients
in 2 approaches. The incidence of scleral show in both modalities was studied 2, 4 and 6 months post-surgery. In this
study, 22 patients were included for eyelid blepharoplasty (44 eyelids). In the transconjuctival approach, 4 males and
7 females with average age of the 57.09 years old were included. For transcutaneous approach, 5 males and 5 females
average age of the 56.18 years old were included. According to the results, no scleral was showed using transconjucti-
val approach after 2 months. Two months after transcutaneous approach only 2 (9%) scleral was observed (P<0.8). No
102
ARTICLE INFORMATION:
*Corresponding Author: sina.seyedabbaszadeh.omfs@gmail.com
Received 11
th
March, 2017
Accepted after revision 2
nd
June, 2017
BBRC Print ISSN: 0974-6455
Online ISSN: 2321-4007 CODEN: USA BBRCBA
Thomson Reuters ISI ESC and Crossref Indexed Journal
NAAS Journal Score 2017: 4.31 Cosmos IF : 4.006
© A Society of Science and Nature Publication, 2017. All rights
reserved.
Online Contents Available at: http//www.bbrc.in/
Hooman Hooshangi et al.
signi cant difference detected in scleral using transconjuctival or transcutaneous operations after 4 months, however
only 2 (9%) scleral was observed using transcutaneous approach (P<0.8). The same results observed after 6 months
follow-up period (P<0.8).Despite insigni cant differences between 2 lower eyelid blepharoplasty approaches regard-
ing the scleral show incidence, using transconjunctival technique was recommended for the lower eyelid blepharo-
plasty in order to decrease the incidence of the scleral show.
KEY WORDS: LOWER EYELID BLEPHAROPLASTY, TRANSCUTANEOUS, TRANSCONJUNCTIVAL, SCLERAL SHOW
INTRODUCTION
Blepharoplasty remains one of the most common con-
temporary facial surgical procedures performed. While
in oculo-facial plastic surgery functional upper eye-
lid blepharoplasty still encompasses the majority of
the specialties procedures, cosmetic upper and lower
blepharoplasty are rapidly increasing in number.The
skin-muscle ap approach to lower blepharoplasty was
popularized in the 1970s. It remained the most gener-
ally used method because of e fast, effective and widely
applicable (Hidalgo, 2011; Massry and Hartstein, 2012).
Post blepharoplasty treatment of lower eyelid retraction
is challenging (Yoo et al. 2013). Several methods intro-
duced to improve lower eyelid blepharoplasty outcome
(Schwarcz et al. 2016, Kossler et al. 2017).
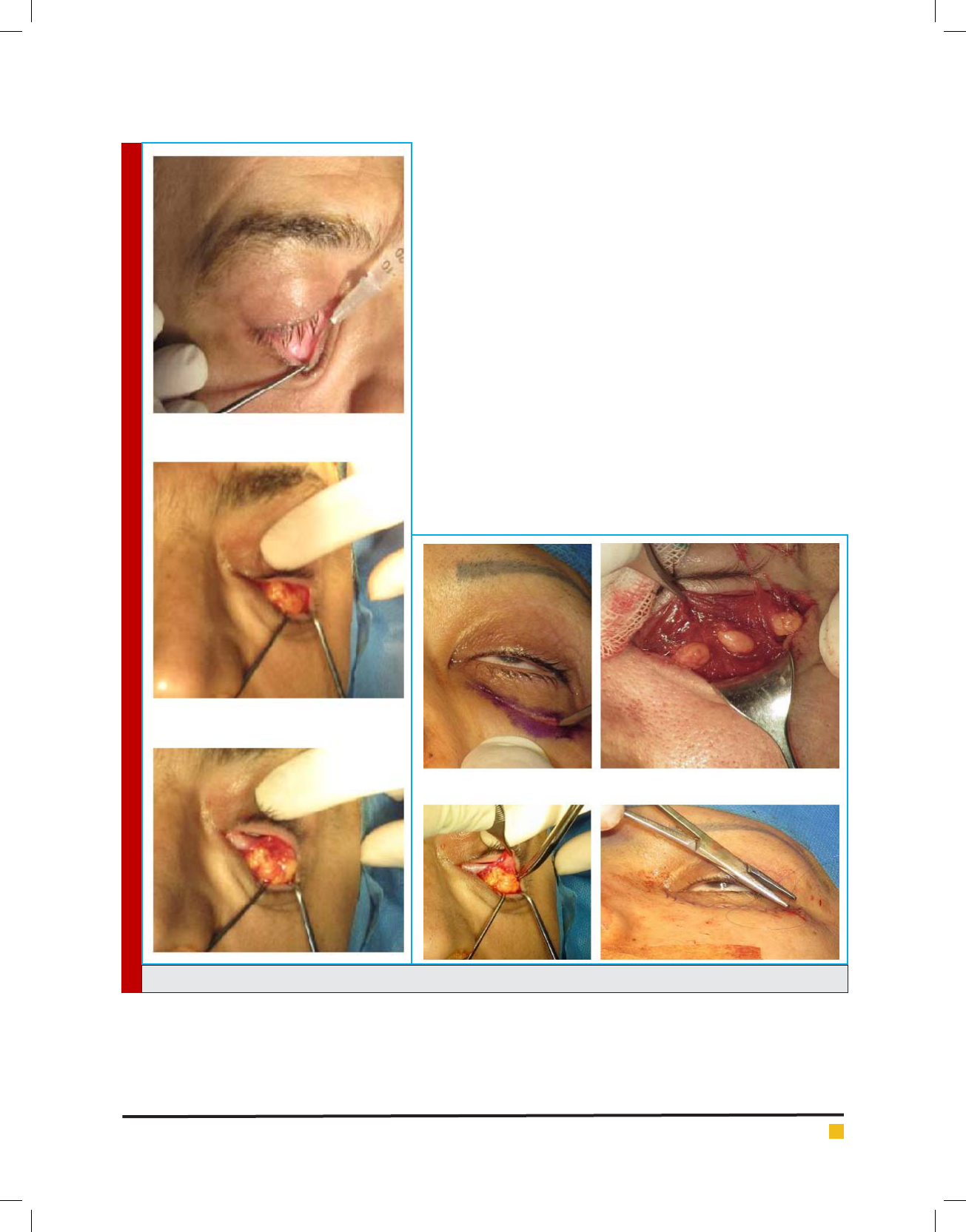
Transcutaneous lower eyelid blepharoplasty with fat
excision has been the paradigm for addressing the un-
desirable sequelae of the aging eye (Grif n et al. 2014).
This is eyelid contour and no changes in eyelid position
when performed in a conservative fashion. Transcutane-
ous is a time-tested method that achieves satisfactory
cosmetic results (Garcia and McCollough, 2006). The lat-
est evolution of the transcutaneous lower eyelid blepha-
roplasty is a skin ap or skin muscle ap method in
which the incision is placed inferiorly to the tarsal mar-
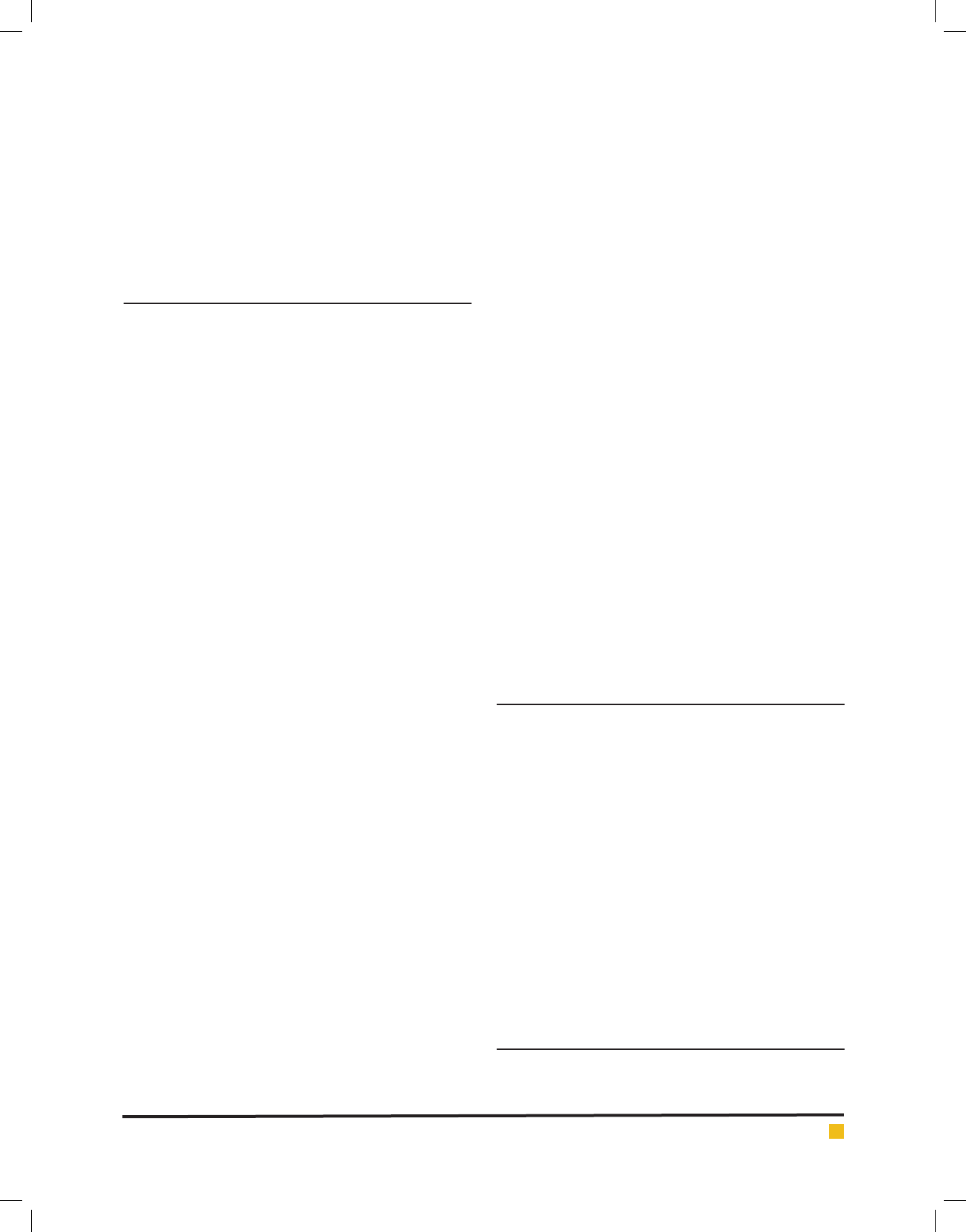
gin (Freeman, 2000). The transconjunctival approach
was primary described in 1924 to the lower orbital fat
and the inferior orbital surface (Korchia et al. 2003).
Transconjunctival lower eyelid blepharoplasty is most
acceptable as a safe and effective method to eliminate
herniated orbital fat from the lower eyelid and avoid-
ing the complications of a cutaneous incision (Belinsky
et al. 2015).
The transconjunctival approach avoids numer-
ous complications of the classic transcutaneous lower
blepharoplasty (Kossler et al. 2017). It is reported
the limitations of the transcutaneous approach was
improved by the transconjunctival approach (LoPiccolo
et al. 2013). The transconjunctival approach has gained
popularity over the transcutaneous approaches because
of its inconspicuous scar and decreased risk of postop-
erative ectropion and scleral show (Salhi and Cordoba,
2015).
Scleral show is one of the main complications of
lower blepharoplasty which may result to manifest as
lack of de nition of the lateral part of the eyes and eye-
lid retraction (Pascali et al. 2015). Lower eyelid retraction
is known for the existence of scleral show (which each
patient stated (Grif n et al. 2014). Scleral show is one of
the most feared complications of lower blepharoplasty
surgery. The attendant scleral show and rounding of the
eye are poorly tolerated by patients from a cosmetic and
often functional stand-point (Grif n et al. 2014). The
surgical correction of postsurgical eyelid retraction can
be challenging as well as frustrating (Yoo et al. 2014).
Despite its effectiveness for the facial rejuvenation,
blepharoplasty has been associated with several adverse
effects. One of the most common side effects of this sur-
gery is eyelid malposition and scleral show which is not
suitable from esthetic point of view. Although some tech-
niques have been used for the blepharoplasty of the lower
eyelid, the effect of these techniques has not been de -
nitely identi ed in the incidence of scleral show. So, the
current study was compared the effects of lower eyelid
blepharoplasty with transconjunctival and transcutaneous
approaches in the incidence of scleral show in patients.
MATERIAL AND METHODS
In a prospective randomized clinical trial, 22 candidates
of the lower eyelid blepharoplasty in patients referred
to two private clinics and Bu Ali hospital at 2015. The
patients had no history of systemic disease, previous
lower eyelid blepharoplasty, trauma or dry eye syn-
drome. The patients were randomly assigned in 2 meth-
ods of transconjunctival and transcutaneous approaches.
The surgeries were perform on 2 eyelids of the left and
right sides and in total, 44 eyelids were subjected to
blepharoplasty surgery in both sides of the patients in
2 approaches. The incidence of scleral show in both
modalities was studied using standard photographs of
patients taken before the surgery and 2, 4 and 6 months
post-surgery. The frequency of the scleral show was sta-
tistically analyzed by exact sher test in two approaches
in different time intervals.
RESULTS
In this study, 22 patients were included for eyelid blepha-
roplasty (44 eyelids). In the transconjuctival approach, 4
BIOSCIENCE BIOTECHNOLOGY RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS COMPARISON OF TWO TRANSCONJUNCTIVAL AND TRANSCUTANEOUS APPROACHES 103

Hooman Hooshangi et al.
Table 1. the demographic information of the patients based on the surgery operation
Sex Location age Following period (month)
Male Female Left Right
Transconjuctival 4 7 11 11 57.09 6
Transcutaneous 5 6 11 11 56.18 6
Table 2. the results of the scleral show at 2-6 months post Transconjuctival or Transcutaneous operation
Follow (2 months) Follow (4 months) Follow (6 months)
scleral show
No Yes No Yes No Yes
Transconjuctival 22 (100%) 0 (0%) 22 (100%) 0 (0%) 22 (100%) 0 (0%)
Transcutaneous 20 (91%) 2 (9%) 20 (91%) 2 (9%) 20 (91%) 2 (9%)
Fisher’s P value <0. 8 <0. 8 <0. 8
males and 7 females with average age of the 57.09 years
old were included. For transcutaneous approach, 5 males
and 5 females average age of the 56.18 years old were
included. Then all patients were followed-up 6 months
for possible scleral show (table 1).
The results of the scleral show at 2-6 months post
transconjuctival or transcutaneous operations are pre-
sented in table 2. According to the results, no scleral was
showed using transconjuctival approach after 2 months.
Two months after transcutaneous approach only 2 (9%)
scleral was observed (P<0.8). No signi cant difference
detected in scleral using transconjuctival or transcuta-
neous operations after 4 months, however only 2 (9%)
scleral was observed using transcutaneous approach
(P<0.8). The same results observed after 6 months fol-
low-up period (P<0.8).
DISCUSSION
Eyelid tone, position and scleral show have been the
most common limiting aspects of lower blepharoplasty.
Dysfunction of the lateral canthal tendon can be caused
by aging, iatrogenic damage, and so on (Sacchidan-
and et al. 2012). Lower eyelid retraction might occur
by dynamic imbalance in the lateral suspension system
of the lower eyelid, lack of elasticity of mid facial soft
tissue and etc. (Oestreicher and Mehta, 2012). Base on
the results of the current study, no scleral was showed
using transconjuctival approach after 2 months. Two
months after transcutaneous approach only 2 (9%) scle-
ral was observed. No signi cant difference detected in
scleral using transconjuctival or transcutaneous opera-
tions after 4 months, however only 2 (9%) scleral was
observed using transcutaneous approach. The same
results observed after 6 months follow-up period. In
this regard, Bernardino et al. (2016) reported there was
improvement in all 16 female and 2 male patients in the
appearance of increased the lower eyelid and reduction
in skin and lateral ligament laxity. Also, eyelid retrac-
tion, ectropion, unaesthetic scars, diplopia and remnant
fat bags were not observed (Bernardino et al. 2016).
During the 1998–2008 in 2400 patients underwent
lower blepharoplasty Transconjunctival blepharoplasty
was the rst choice for primary eyelid bags. Transcu-
taneous lower blepharoplasty (skin ap or skin-muscle
ap procedures) is indicated for the senile eyelid with
excess skin and muscles (Guo et al. 2010).Both transcon-
junctical and transcutaneous approaches is applied for
upper and lower lid blepharoplasty. Even though trans-
cutaneous upper and lower eyelid surgery and transcon-
junctival lower lid procedures are popular with facial
plastic surgeons, transconjunctival upper blepharoplasty
is new technique with limited indications (Jacono et al.
2001). These researchers suggested the transconjunctival
lower lid blepharoplasty as it circumvents the risk of
lower eyelid retraction associated with the transcutane-
ous approach (Jacono et al. 2001). A lower rate of com-
plications reported via the transconjunctival approach,
with greater patient satisfaction (Rancati et al. 2015).
The transconjunctival and approaches were preferred
in 42 and 58 % (Rancati et al. 2015). In transconjunc-
tival versus transcutaneous lower eyelid blepharoplasty
(Netscher et al. 1995) in 6 months follow-up reported 10
consecutive patients presented for blepharoplasty, and
in all patients the transcutaneous subciliary musculocu-
taneous ap approach was used on the left lower eyelid
and the transconjunctival preseptal approach was used
on the right. No signi cant variance on the 2 sides (0.60
on the left and 0.68 on the right) (Netscher et al. 1995).
No signi cant difference reported in lower eyelid posi-
tion change between the transconjunctival lower blepha-
roplasty with versus without a skin pinch groups. Using
the transcutaneous approach, the presented infection
104 COMPARISON OF TWO TRANSCONJUNCTIVAL AND TRANSCUTANEOUS APPROACHES BIOSCIENCE BIOTECHNOLOGY RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS
Hooman Hooshangi et al.
BIOSCIENCE BIOTECHNOLOGY RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS COMPARISON OF TWO TRANSCONJUNCTIVAL AND TRANSCUTANEOUS APPROACHES 105
FIGURE 1. Results of the transconjunctival apporeach (left) and transcutaneous (right)

Hooman Hooshangi et al.
106 COMPARISON OF TWO TRANSCONJUNCTIVAL AND TRANSCUTANEOUS APPROACHES BIOSCIENCE BIOTECHNOLOGY RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS
FIGURE 2. Results of the transconjunctival apporeach before and after the surgery
FIGURE 3. Results of the transcutaneous apporeach before and after the surgery
(2%), scleral show (2%) and insuf cient skin resection
(1%) was reported (Hidalgo, 2011). The transconjunctival
approach is an ideal procedure due to its simplicity and
less traumatic effect, except in the lower eyelid weakness
and surgical resolution (Collar et al. 2013). In conclu-
sion, despite insigni cant differences between 2 lower
eyelid blepharoplasty approaches regarding the scleral
show incidence, using transconjunctival technique was
recommended for the lower eyelid blepharoplasty in
order to decrease the incidence of the scleral show.

Hooman Hooshangi et al.
BIOSCIENCE BIOTECHNOLOGY RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS COMPARISON OF TWO TRANSCONJUNCTIVAL AND TRANSCUTANEOUS APPROACHES 107
REFERENCES
Belinsky I, Patel P, Charles NC, Lisman RD. 2015. Ointment
granulomas following sutureless transconjunctival blepha-
roplasty: diagnosis and management. Ophthal Plast Reconstr
Surg;31:282–286
Bernardino IP. 2016. Transconjunctival lower blepharoplasty
with skin resection and preservation of the orbicularis muscl.
Rev. Bras. Cir. Plást. 31(1):74-81.
Collar, R.M., Lyford-Pike, S. and Byrne P. (2013) Algorithmic
Approach to Lower Lid Blepharoplasty. Facial Plastic Surgery,
29, 32-39.
Freeman MS.2000.Transconjunctival sub-orbicularis oculi
fat (SOOF) pad lift blepharoplasty.Arch Facial Plast Surg. 2:
16-21.
Garcia RE, McCollough E. G.2006. Transcutaneous lower eye-
lid blepharoplasty with fat excision. Arch Facial Plast Surg.
8:374-380.
Grif n G, Azizzadeh B, Massry GG.2014. New Insights Into
Physical Findings Associated With Postblepharoplasty Lower
Eyelid Retraction. Aesthetic Surgery Journal. 34: 995
Guo L, Bi H, Xue C, Li J, Yan C, Song J, Zhang M, Xing X.
2010. Comprehensive considerations in blepharoplasty in an
Asian population: a 10-year experience. Aesth Plast Surg
34:466–474.
Hidalgo DA. 2011. An integrated approach to lower blepharo-
plasty. Plast. Reconstr. Surg.127: 386.
Jacono AA, Moscowitz B.2001. Transconjuctival versus Trans-
cutaneous approach in upper and lower blepharoplasty. Facial
Plast Surg 17(1):21-28.
Korchia D Braccini, F, Paris J Thomassin, JM. 2003. Transcon-
junctival approach in lower eyelid blepharoplasty. Can J Plast
Surg 11(3):166-170.
Kossler AL, Peng GL, Yoo DB, Azizzadeh B, Massry GG. 2017.
Current trends in upper and lower eyelid blepharoplasty among
american society of ophthalmic plastic and reconstructive sur-
gery members. Ophthal Plast Reconstr Surg;XX:00–00
LoPiccolo MC, Mahmoud BH, Liu A, et al.2013. Evaluation of
orbi-cularis oculi muscle stripping on the cosmetic outcome
of upper lid blepharoplasty: a randomized, controlled study.
Dermatol Surg 39:739–43.
Massry GG, Hartstein ME. 2012.The lift and ll lower blepha-
roplasty. Ophthal Plast Reconstr Surg 28:213–8.
Netscher DT,Patrinely JR,Peltier M,Polsen C,Thornby J. 1995.
Transconjunctivalversustranscutaneouslower eyelid blepha-
roplasty: a prospective study. Plast Reconstr Surg; 96(5):1053-
1060.
Oestreicher J, Mehta S. 2012 Complications of blepharoplasty:
prevention and management.Plast Surg Int. 2012: 252368.
Pascali M, Avantaggiato A, Brinci L, Cervelli V, Carinci F. 2015.
Tarsal sling: an essential stitch to prevent scleral show in lower
blepharoplasty. Aesthetic Surgery Journal 35(1) 11–19.
Rancati A, Jacovella P, Edoardo Zampieri A, Dorr J, Daniele
M, Liedtke S, Rancati A. 2015. Lower blepharoplasty review:
transconjunctival vs. transcutaneous approach. Modern Plast
Surg 5:1-8.
Sacchidanand SA, Deepak HS, Vishal C, Revathy TN.2012
Transcutaneous blepharoplasty in blepharochalasis. J Cutan
Aesthet Surg. 5:284-286.
Salhi S, Cordoba C. 2015. Distichiasis following transconjunc-
tival approach to the inferior orbital rim and orbital oor.
JPRAS Open 5 29-33.
Schwarcz R, Fezza JP, Jacono A, et al. 2016. Stop blaming the
septum. Ophthal Plast Reconstr Surg 32:49–52.
Taban M, Taban M, Perry JD. 2008. Lower eyelid position after
trans-conjunctival lower blepharoplasty with versus without a
skin pinch.Ophthal Plast Reconstr Surg 24(1):7-9.
Yoo D, Grif n GG, Azizzadeh BA.2014. The minimally invasive
orbicularis sparing lower eyelid recession. JAMA Arch Facial
Plast Surg. 16:140-146.
Yoo DB, Peng GL, Massry GG.2013. Effacing the orbitogla-
bellar groove with transposed upper eyelid fat. Ophthal Plast
Reconstr Surg 29:220–4.