
Pathological
Communication
Biosci. Biotech. Res. Comm. 10(2): 68-75 (2017)
Identi cation of
Plasmodium
species from outdated
blood samples by nested-PCR compared with
microscopy diagnosis in Jazan region, Saudi Arabia
O. M. Dafalla
1
, A. A. Alsheikh
1
, Abakar A. D.
2
, W. S. Mohammed
1
, Bakri Y. M.Nour
3
,
Shrwani K. J
1
and E. M. Noureldin*
1
1
National Center for Vector-Borne Diseases, MoH-Jazan, Saudi Arabia
2
Department of Medical Parasitology, Faculty of Medical Laboratory Sciences, University of Gezira, Sudan
3
Department of Parasitology, Blue Nile National Institute for Communicable Diseases, University of Gezira, Sudan
ABSTRACT
Precise diagnosis of plasmodium species is essential for accurate and prompt malaria control and elimination. The
present study was conducted to assess the ef ciency of malaria parasites’ diagnosis by microscopy and nested-PCR
techniques in Jazan region. Eight hundred eighty four samples were collected from hospitals and malaria control
centers of the eleven Governates of Jazan region to con rm their microscopy diagnosis for Plasmodium species. One
hundred thirty eight (15.6%) samples were randomly selected from the saved positive microscopy con rmed samples.
The samples were re-diagnosed by microscopy for plasmodium species and found positive for two plasmodium spe-
cies (128 for P. falciparum [92.8%] and 10 for P. vivax [7.2%]). But no other plasmodium species or mixed-infections
were detected. On other hand, the diagnosis by nested-PCR indicated 119 (86.23%) and 6 (4.35%) mono infection by
P. falciparum and P. vivax, respectively. In addition, the method detected also 13 (9.42%) mixed-infections with both
P. falciparum and P. vivax. Considerable numbers of species mismatch and under-reporting of mixed infections had
been noticed in the diagnosis of malaria by microscopy alone in Jazan region. The nested-PCR is valuable technique
as a con rmatory test and should be considered by reference laboratories in the region and other malaria endemic
regions of the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia.
KEY WORDS: MALARIA,JAZAN, SAUDI ARABIA,
PLASMODIUM
SPECIES,MICROSCOPY, NESTED-PCR
68
ARTICLE INFORMATION:
*Corresponding Author:
Received 1
st
April, 2017
Accepted after revision 30
th
June, 2017
BBRC Print ISSN: 0974-6455
Online ISSN: 2321-4007 CODEN: USA BBRCBA
Thomson Reuters ISI ESC and Crossref Indexed Journal
NAAS Journal Score 2017: 4.31 Cosmos IF : 4.006
© A Society of Science and Nature Publication, 2017. All rights
reserved.
Online Contents Available at: http//www.bbrc.in/

Dafalla et al.
INTRODUCTION
Malaria is considered one of the most life-threatening
pathogens capable of infecting human communities.
Malaria infection is caused by parasites belonging to the
genus Plasmodium.
More than 100 species of Plasmo-
dium have been identi ed and ve species are capable of
infecting humans; these species are Plasmodium vivax
(the most widely spread parasite in the world), Plas-
modium falciparum (a fatal malaria parasite causing a
high mortality rate, ~90%), Plasmodium malariae, Plas-
modium ovale and Plasmodium knowlesi (a newly dis-
covered malaria-causing parasite). Transmission of the
infectious agent is caused by the bite of female Anophe-
les mosquitoes, which is the vector of this parasite (Cow-
man and Crabb, 2006). Around fteen Anopheles species
are found in Saudi Arabia and four species are recog-
nized as malaria vectors; these vectors are Anopheles
gambiae (arabiensis), Anopheles Superpictus, Anopheles
stephensi, and Anopheles sergentii (Sebai, 1988; Zahar,
1985 and CDC, 2016).
Recent gures suggest that approximately 3.2 bil-
lion people are at risk of malaria transmission due to
several reasons, including immigration, international
travel, poverty, lack of health system infrastructure,
wars and emergence of multi-drug resistance. (Cow-
man and Crabb, 2006; Sebai, 1988; WHO, 2014; Askling
et al., 2005). Because of proactive international health
programs for combating malaria, the mortality rates
have gradually decreased to around 438,000 deaths in
2015 (WHO, 2016).
According to the WHO, Saudi Arabia is known as a
malaria epidemic country with around 5% of the pop-
ulation at risk of transmission malaria (about 2.4 mil-
lion people), particularly in its South Western regions
of Tihama area, where more than 50% of all malaria
cases in the country are reported. This is mostly related
to travel and immigration with reports suggesting that
from 2000 to 2014, more than 5500 of diagnosed malaria
cases were local compared to over 9900 imported cases.
Plasmodium falciparum causes over 90% of the malaria
cases in the coastal plains along the Red Sea in southern
and southwestern parts of the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia
(Tihama) .Plasmodium vivax is the predominant species in
the northwest regions; whereas Plasmodium malariae is
scarce. There is still transmission in all the southwestern
regions of the country, except for the high altitude regions
along the Yemen border in the Assir region. The main
transmission season of malaria occurs between October
and April and coincides with the rainy season (Al-Sheik,
2011, El-Hassan et al., 2015, Moke et al., 2015).
Accurate and sensitive laboratory diagnosis of
malaria is essential for assessing disease severity and
prescribing adequate therapy. For the last 100 years,
microscopic examination and identi cation of Plas-
modium species in thin and thick blood smears using
Giemsa-stain have been considered the gold standard
for malaria detection (Perandin et al., 2004). However,
several drawbacks were documented in using micro-
scopic examination, including time-consuming sample
preparation, misdiagnosis of Plasmodium species due
to lack of experience by operators, the complexity of
examining mixed infection samples and poor sensitiv-
ity, especially with low infectious agent numbers (John-
ston et al., 2006; Mangold et al., 2005; McNamara et
al., 2004).
Additionally, immunoassays based on antigen
detection also suffer from several disadvantages leading
to false results in cases of antigemia and malaria para-
siteima (Mangold et al., 2005).
Polymerase chain reactions (PCR) based molecular
detection can be used for the diagnosis of Plasmodium
species. This technique has several advantages compared
to microscopic examination or immune-assay detection,
including speed, high sensitivity, excellent speci city,
and very ef cient species discrimination (Mangold et
al., 2005; Hanscheid, 2003; Jerrard et al., 2002; Moras-
sin et al., 2002; Patsoula et al., 2003).
Conventional PCR
and real-time PCR methods have the ability to differen-
tiate the mixed infections of Plasmodium species and
to detect low levels of parasite copies (Mangold et al.,
2005; Lee et al., 2002). A nested-PCR technique based
on S18 small subunit ribosomal DNA (rDNA) can detect
levels as low as ve parasite units per micro-liter of
blood (Van Hong et al., 2013). Consequently, PCR is a
reliable method of detection and can at least be used as a
valuable con rmatory technique (Johnston et al., 2006).
In Jazan region, very few studies have been pub-
lished to demonstrate the incidence of malaria with
mixed- plasmodium species infections using nested-
PCR and compare it with microscopically con rmed
cases of malaria. However, Bin Dajem (2015) reported
1.9% malaria mixed infection cases in the region using
nested-PCR. The aim of this study is to con rm the
sensitivity of nested-PCR in diagnosis of Plasmodium
species in outdated blood samples inappropriate for
microscopy diagnosis, and to indicate the geographical
distribution of Plasmodium species and comparing the
nding of nested PCR with the previous result of golden
standard microscopic examination, in addition to, prov-
ing the existence of mixed infection in Jazan region.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
STUDY SITE
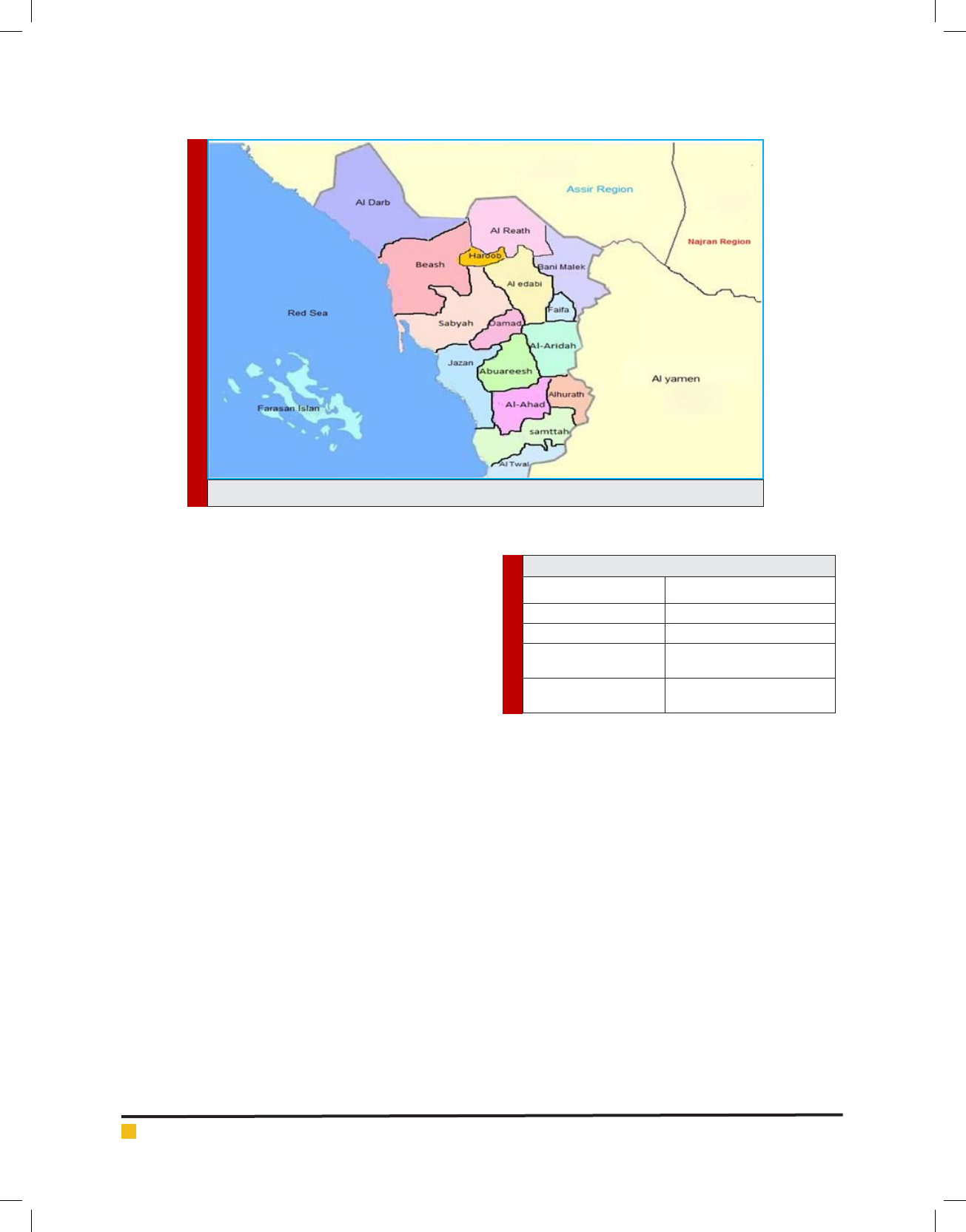
This study carried out at eleven Governates (Al-Ari-
dah, Damad, Twal, Al-Ahad, Jazan Al-Khobah, Samt-
BIOSCIENCE BIOTECHNOLOGY RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS IDENTIFICATION OF
PLASMODIUM
SPECIES FROM OUTDATED BLOOD SAMPLES 69
Dafalla et al.
FIGURE 1. The map of Jazan region showing the distribution of different Governates.
Table 1. Governates area groups
Group No Governorate
Group 1 (Jazan City) Jazan
Group 2 (North Jazan) Sabyah, Beash and AL-Darb
Group 3 (South Jazan) Samttah, AL-Ahad, Twal and
Khobah
Group 4 (East Jazan) Abuareesh, Damad and
AL-Aridah
tah, Abuareesh, Sabyah, Beash and Al-Darb) in Jazan
Region in Southwest Saudi Arabia, lies between 16°-12,
and 18°-25, latitude north. The total area of the region is
about 22,000 km
2
, with 1.3 million populations (Census
2011). Thirty percent of the population concentrated in
six major cities, and the remainders living in over 3500
villages (Al-Sheik, 2011). Jazan region is situated in the
subtropical zone and has average monthly tempera-
tures ranging from 25.8°C in January to 33.4°C in July.
The average relative humidity ranges between 55% and
72.5%. The rainy season is started at August through
October with a monthly average of 77 and 56.7 mm,
respectively (Al-Sheik, 2011).
These eleven locations (Fig.1) although with different
altitudes and geographical Characteristics, they almost
share the same demographical, agricultural, educational,
cultural, housing, health system, and environmental
characteristics.
SAMPLES SIZE AND COLLECTION
During 2011-2012 the National Center for Vector Borne
Diseases received about 884 samples from the hospitals
and malaria control centers of the eleven Governates
to con rm their microscopy diagnosis for Plasmodium.
This research was carried out at the beginning of 2016.
One hundred thirty eight (15.6%) samples were ran-
domly selected from the saved positive microscopy con-
rmed samples. These samples were divided into four
groups based on the geographical locations as shown in
Table (1) bellow:
DNA EXTRACTION
DNA was extracted from the stored microscopy con-
rmed plasmodium human blood using Wizard genomic
DNA Extraction kit (Promega, U.S.A) following the
manufacture´s recommendations: 300 μl of human
blood added to 900μl of cell lysis solution in 1.5 tubes
and incubate the mixture for ten minutes at room tem-
perature (invert 2-3 times once during the incubation).
Then centrifuged at 13000 rpm for 20 seconds at room
temperature then the supernatant discarded and the pel-
let was resuspended by vortex for 15 seconds and 300
μl of Nuclei Lysis Solution added to resuspended cells,
then 100 μl of Protein Precipitation was added. The mix-
ture was puri ed by centrifugation at 13000 rpm for 3
minutes and the supernatant transferred to a clean 1.5ml
tube containing 300 μl of isopropanol and mixed gently.
The DNA was pelleted at 13000 rpm for 1minute and
washed by ethanol twice and dried for 5-10 minutes at
room temperature. DNA Rehydration solution used to
70 IDENTIFICATION OF
PLASMODIUM
SPECIES FROM OUTDATED BLOOD SAMPLES BIOSCIENCE BIOTECHNOLOGY RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS

Dafalla et al.
BIOSCIENCE BIOTECHNOLOGY RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS IDENTIFICATION OF
PLASMODIUM
SPECIES FROM OUTDATED BLOOD SAMPLES 71
re-suspend the DNA at 65°C for 1 hour. The extracted
DNA stored at -86°C till further investigations.
MOLECULAR DETECTION
Nested PCR was carried out for detection and identi -
cation of Plasmodium species as described by Snounou
et al. (1993). DNA samples were ampli ed by oligonu-
cleotide primers obtained from Integrated DNA Technol-
ogy (Belgium). These primers targeting the Plasmodium
small subunit ribosomal RNA (ssRNA) genes. Primer
pairs rPLU5 and rPLU6 used to detect Plasmodium genus
in Primary ampli cation and species-speci c primers
rFAL1/rFAL2 (P. falciparum), rVIV1/rVIV2 (P. vivax),
rOVAL1/rOVAL2 (P. ovale) and rMAL1/rMAL2 (P. malar-
iae) for nested PCR in 2 separated reaction.
In brief, primary and nested PCR were carried out
in total 25 μl reaction volume, each containing 12.5 μl
GoTag®G2 green master mix ready to use from Promega
and25μM of each primer. Five μl of extracted DNA was
used as a sample for the primary ampli cation and two
μl of the PCR product for the nested PCR. In each run,
negative and positive controls were included. Thermal
cycling was done in T100 thermal cycler (Bio-Rad, USA),
PCR conditions are shown in Table (2). The PCR products
of nested ampli cation were analyzed by gel electropho-
resis (1.5 agaroses in Tris-Acetate-EDTA buffer) staining
with ethidium bromide. The visualization was carried
out using Gel Doc XR Imaging System (Bio-Rad).
RESULTS
A total of 138 samples re-diagnosed for Plasmodium
species were Plasmodium positive by microscopy dur-
ing 2011-2012, 92.8% (128/138) of the samples diag-
nosed as P. falciparum and, 7.2% (10/138) as P. vivax, no
mixed infections were detected by the golden standard
microscopic examination done by the best microscopists
(details are shown in Table 3). Based on the nested PCR
assay, P. falciparum (mono infection) has been detected
in 86.23% (119/138) of the samples, 4.35% (6/138) were
found P.vivax (mono infection) and 9.42% (13/138) of
the samples were positive to both P. falciparum and P.
vivax (mixed infection) (Table 4 and Fig.2). No other
Plasmodium species were detected by the microscopy
and nested PCR.
DISSCUTION
Malaria transmission in Saudi Arabia occurs mainly
in the southwest region in Asir and Jazan where the
Table 2. Primers used and PCR conditions
PCR CONDITION
PCR
PRODUCT
SIZE (bp)
SEQUENCE (5-3)
PRIMER
NAME
SPECIES
Initial denaturation at 94°C for 3 min, 35
cycles of denaturation at 94°C for 60 seconds,
annealing at 60°C(45°C for P.ovale) for 90
second, extension at 72°C for 90 second and
nal extension for 5 minutes
110 0
CCTGTTGTTGCCTTAAACTTC
TTAAAATTGTTGCAGTTAAAACG
rPLU5
rPLU6Plasmodium sp.
Initial denaturation at 94°C for 3 min, 35
cycles of denaturation at 94°C for 60 seconds,
annealing at 55°C for 90 second, extension at
72°C for 90 second and nal extension for 5
minutes
205
TTAAACTGGTTTGGGAAAACC
AAATATATT
ACACAATGAACTCAATCATGA
CTACCCGTC
rFAL1
rFAL2
P. falciparum
Initial denaturation at 94°C for 3 min, 35
cycles of denaturation at 94°C for 60 seconds,
annealing at 55°C for 90 second, extension at
72°C for 90 second and nal extension for 5
minutes
120
CGCTTCTAGCTTAATCCACAT
AACTGATAC
ACTTCCAAGCCGAAGCAAAGA
AAGTCCTTA
rVIV1
rVIV2
P. vivax
Initial denaturation at 94°C for 3 min, 35
cycles of denaturation at 94°C for 60 seconds,
annealing at 45°C for 90 seconds, extension
at 72°C for 90 second and nal extension for
5 minutes
800
ATCTCTTTTGCTATTTTTTAG
TATTGGAGA
GGAAAAGGACACATTAATTGT
ATCCTAGTG
rOVA1
rOVAL2
P.ovale
Initial denaturation at 94°C for 3 min, 35
cycles of denaturation at 94°C for 60 seconds,
annealing at 55°C for 90 second, extension at
72°C for 90 second and nal extension for 5
minutes
144
ATAACATAGTTGTACGTTAAG
AATAACCGC
AAAATTCCCATGCATAAAAAA
TTATACAAA
rMAL1
rMAL2
P. malariae
Dafalla et al.
72 IDENTIFICATION OF
PLASMODIUM
SPECIES FROM OUTDATED BLOOD SAMPLES BIOSCIENCE BIOTECHNOLOGY RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS
disease is endemic. Transmission of malaria is seasonal
during winter where rain falls from September to Febru-
ary (Jamjoom et al., 2006). Introducing infection to non-
endemic areas by pilgrims during Hajj and Umrah or
through expatriate is a major threat to health authorities
(Al-Taw g and Memish, 2014). The quality of malaria
diagnostic services would remain the main challenge in
elimination and control in the region. Therefore, accu-
rate and rapid diagnosis of Plasmodium infections is
critical for proper malaria treatment. Giemsa-stained
thick and thin lms for malaria diagnosis remain the
main conventional and classic method of microscopic
examination for malaria in the region (Jamjoom et al.,
2006). The method is highly subjective and laborious
with low sensitivity for chronic and asymptomatic car-
riers (WHO, 2013).
Distinction between malaria parasite species is crucial
in the clinical management of patients since the treat-
ment depends mainly on the type of species that cause
the infection (Mangold et al., 2005).In the present study,
138 samples were re-diagnosed by microscopy for Plas-
modium species and found positive for two Plasmodium
species (128 for P. falciparum [92.8%] and 10 for P.
vivax [7.2%]). But no other plasmodium species or mixed
infections were detected. The miss-diagnosing of the
mixed infections with P. falciparum and P. vivax using
microscopy may be attributed to cross-species immunity
or competition at the level of host red blood cells (RBC)
(Gupta et al., 2010). On other hand, the diagnosis by
nested-PCR indicated 119 (86.23%) and 6 (4.35%) mono
infection by P. falciparum and P. vivax, respectively. In
addition, the method detected 13 (9.42%) mixed infec-
tions with both P. falciparum and P. vivax.
These results suggest that where only microscopy-
based diagnostic methods are used, many cases of mixed
Plasmodium species infections may be misdiagnosed.
The ndings of the present study contradict many stud-
ies in Saudi Arabia that revealed the dominancy of
P. falciparum over other plasmodium species and the
absence of mixed infections (e.g. Dawoud et al., 2008).
The discrepancies between the results of the two meth-
ods are due to the fact that microscopists tend to misdi-
agnose mixed infections and identi ed them as either P.
falciparum or P. vivax mono infections. Interestingly, the
percentage of the mixed infections in the present inves-
tigation (9.42%) is higher than previous reported from
Sudan (4.2%, Talha et al., 2014), Saudi Arabia (1.9%, in
Jazan region, Bin Dajem, 2015; and 2.4%, Bashrawi et
Table 3. Distribution of Plasmodium species to the Governorates based on the microscopic diagnosis.
+Ve
P. malariae
+Ve P. ovale
+Ve Mixed
(P. vivax + P.
falciparum)
+Ve P.vivax+Ve P.falciparumSamples noGovernorates
zerozerozero7 (31.8%)15 (68.2%)22Jazan
zerozerozero1 (2.38%)41 (97.62%)42
Sabyah, Beash and
AL-Darb
zerozerozero1 (2.22%)44 (97.8%)45
Samttah, AL-Ahad,
Towal and Khobah
zerozerozero1 (3.5%)28 (96.6%)29
Abuareesh, Damad
and AL-Aridah
zerozerozero10 (7.2%)128 (92.8%)138Total
Table 4. Distribution of Plasmodium species to the Governorates based on the nested-PCR.
+Ve
P. malariae
+Ve
P. ovale
+Ve Mixed
(P. vivax and P.
falciparum)
+Ve P.vivax
+Ve
P. falciparum
Number of
samples
Governorates
zero
zero3 (13.64)
5 (22.73%)14 (63.64%)22Jazan
zerozero4 (9.5)1 (2.4%)37 (88.1%)42
Sabyah, Beash and
AL-Darb
zerozero5 (11.1%)Zero (0%)40 (88.9%)45
Samttah, AL-Ahad,
Towal and Khobah
zerozero1 (3.4%)Zero (0%)28 (96.6%)29
Abuareesh, Damad
and AL-Aridah
zerozero13 (9.42%)6 (4.35%)119 (86.23%)138Total

Dafalla et al.
BIOSCIENCE BIOTECHNOLOGY RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS IDENTIFICATION OF
PLASMODIUM
SPECIES FROM OUTDATED BLOOD SAMPLES 73
al., 2002), Ethiopia (2.3%, Mekonnen et al., 2014) and
Afghanistan (6.5%, Zakeri et al., 2010). However, it was
less than reported from Bangladesh (27.5%, Fuehrer et
al., 2010), Brazil Amazon Regions (26.9%, Lorenzetti
et al., 2008), Pakistan (23.5%, Zakeri et al., 2010), Iran
(22%, Zakeri et al., 2010) and Yemen (11.6%, AlMekhla
et al., 2010).
In mixed malaria infections, it is generally accepted
that an antagonism exists between the Plasmodium
species, where each species tends to dominate through
the period of infection (Knowles et al., 1930; Coatney,
1968). This phenomenon could explain why mixed
infections are dif cult for microscopists to detect, par-
ticularly when the patient is sampled once (Snounou et
al., 1993). It could be explained also by the reason that
under microscopy and at early stage the size of P. vivax
parasite resembles the size of P. falciparum. Addition-
ally, fever induced by low parasiteima caused by P. vivax
might hinder the pathogenic potential of P. falciparum
(Yewhalaw et al., 2010). Therefore, the microscopists
may frequently miss to differentiate between species
especially when morphologic characteristics overlaps or
in cases that parasite morphology has been altered by
drug treatment, or in case of bad storage of the blood
lms and the sample processes (Talha et al., 2014).
The detection of mixed infections is highly important
for both ascertaining the exact incidence of each spe-
cies and its consequent transmission potential, and the
successful clinical treatment. Moreover, the reduction
of parasiteima in mixed infections due to suppression
of one the species, changes the resulting morbidity and
mortality (Snounou et al., 1993).In this study, we found
that the nested-PCR techniques were able to detect the
mixed infections of malaria, a result that leads to correct
treatment and prompt diagnosis.
CONCLUSION
Considerable numbers of species mismatch and under-
reporting of mixed infections had been noticed in the
diagnosis of malaria by microscopy alone in Jazan
region. The nested-PCR used in the present study is reli-
able to detect precisely the type of Plasmodium species
and any Plasmodium mixed-infections. It is valuable as a
con rmatory test and should be considered by reference
laboratories in the region and other malaria endemic
regions of the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. False diagno-
sis of plasmodium species along with under reporting
of mixed infections need special attention and should
be improved for accurate and reliable malaria diagno-
sis and malaria control and/or elimination efforts. The
molecular techniques are thought to be not practical in
rural areas for examination of P. falciparum and/or P.
vivax, yet they could be used in epidemiological surveil-
lance and control or/and elimination programs.
REFERENCES
Al-Mekhla , A. MQ, Mohammed AK Mahdy, Ahmed Azazy A,
Mun Yik Fong (2010). Molecular epidemiology of Plasmodium
species prevalent in Yemen based on 18 s rRNA Parasites and
Vectors. 2010; 3:110.
Al-Sheik, A. A. (2011). Larval habitat, ecology, seasonal abun-
dance and vectorial role in malaria transmission of Anopheles
arabiensis in Jazan Region of Saudi Arabia. Journal of the
Egyptian Society of Parasitology,41 (3): pp. 615-634.
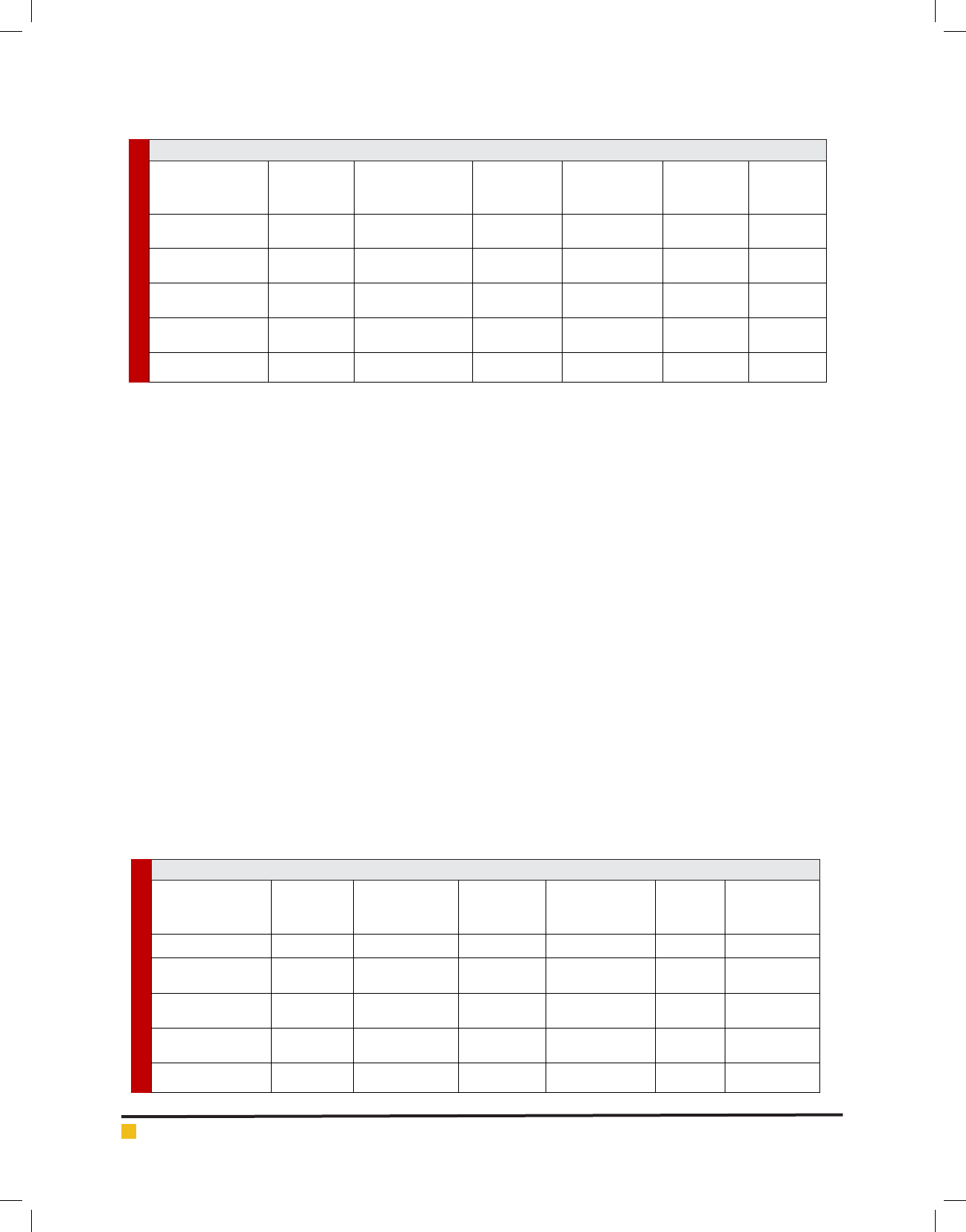
FIGURE 2. Agarose gel electrophoresis of nested-PCR by the Plasmodiumspecies-speci c prim-
ers. Lane (1) 100bp DNA marker, lane (2) negative control, lane (3) positive P. falciparum
control, lane (4,5) positive P. falciparum samples (205bp), lane (6) positive P. vivax control and
lane (7,8) positive P. vivax samples (120bp).

Dafalla et al.
74 IDENTIFICATION OF
PLASMODIUM
SPECIES FROM OUTDATED BLOOD SAMPLES BIOSCIENCE BIOTECHNOLOGY RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS
Al-Taw q, JA and Memish, JA, 2014: Mass gathering medi-
cine: 2014 Hajj and Umra preparation as a leading example.
Int J Infect Dis. 2014; 27: 26–31.
Askling, H. H., Nilsson, J., Tegnell, A., Janzon, R., and Ekdahl,
K. (2005). Malaria risk in travelers.Emerg Infect Dis, 11 (3):
pp. 436-41.
Bashawri, L. AM, Ahmed A Mandil, Ahmed A Bahnassy, Mir-
ghani A Ahmed (2002). Malaria: Hematological Aspects Annals
of Saudi Medicine. 2002; 22:5-6.
Bin Dajem, S. M. (2015) Molecular investigation of mixed
malaria infections in Southwest Saudi Arabia. Saudi Medical
Journal, Vol. 36, No 2 (2015).
CDC (2016). Malaria parasites [Online]. Available from: https://
www.cdc.gov/malaria/about/biology/parasites.html (Accessed
4/2/2017).
Coatney, G.R. (1968) Simian malaria in man: facts, implica-
tions and predictions. Am. J. Trop. Mcd. l-lyg. 17. 147 155.
Cowman, A. F., and Crabb, B. S. (2006). Invasion of red blood
cells by malaria parasites.Cell,124 (4):
pp. 755-766.
Dawoud HA, Ageely HM, Heiba AA. (2008). Evaluation of a
real-time polymerase chain reaction assay for the diagnosis of
malaria in patients from Jazan area, Saudi Arabia.J Egypt Soc
Parasitol2008; 38: 339-350.
El Hassan, I. M., Sahly, A., Alzahrani, M. H., Alhakeem, R. F.,
Alhelal, M., Alhogail, A.and Atas, M. (2015). Progress toward
malaria elimination in Jazan Province, Kingdom of Saudi Ara-
bia: 2000–2014.Malaria Journal,14 (1): pp. 1-10.
Fuehrer H, Fuehrer H, Peter Starzengruber , Paul Swoboda,
Wasif Ali Khan , Julia Matt, Benedikt Ley, et al (2010). Indig-
enous Plasmodium ovale Malaria in Bangladesh. Am J Trop
Med. Hyg. 2010; 83(1):75–78.
Gupta B, Gupta P, Sharma A, Singh V, Dash AP, Das A
(2010). High proportion of mixed-species Plasmodium infec-
tions in India revealed by PCR diagnostic assay.Trop Med Int
Health2010; 15: 819-824.
Hänscheid, T. (2003). Current strategies to avoid misdiagnosis
of malaria.Clinical Microbiology and Infection,9 (6): pp. 497-
504.
Jamjoom MB,Azhar EA,Tonkol AK,Al-Harthi SA,Ashankyty
IM (2006). Detection of malaria in Saudi Arabia by real-time
PCR. J Egypt Soc Parasitol.2006 Dec; 36(3):737-48.
Jerrard, D. A., Broder, J. S., Hanna, J. R., Colletti, J. E., Grund-
mann, K. A., Geroff, A. J., and Mattu, A. (2002). Malaria: a ris-
ing incidence in the United States.The Journal of emergency
medicine,23 (1): pp. 23-33.
Johnston, S. P., Pieniazek, N. J., Xayavong, M. V., Slemenda, S.
B., Wilkins, P. P., and da Silva, A. J. (2006). PCR as a con rma-
tory technique for laboratory diagnosis of malaria.Journal of
clinical microbiology,44 (3): pp. 1087-1089.
Knowles, R., White, R.S. and Das Gupta. B.M. (1930) Studies in
the parasitology of malaria. Indian Medical Research \1cmoirs
18, I 4)6.
Lee, M. A., Tan, C. H., Aw, L. T., Tang, C. S., Singh, M., Lee, S.H.,
and Yap, E. P. (2002). Real-time uorescence-based PCR for
detection of malaria parasites. Journal of clinical microbiol-
ogy,40 (11): pp. 4343-4345.
Lorenzetti A, Patrıcia Aparecida Fornazari, Ana Carolina B,
Roberta de Souza Rodrigues Penhalbel, Erika Fugikaha, Clau-
dia RB, et al (2008). Mixed Plasmodium falciparum infections
and its clinical implications in four areas of the Brazilian Ama-
zon region. Acta Trop. 2008;107(1):8-12.
Mangold, K. A., Manson, R. U., Koay, E. S., Stephens, L., Reg-
ner, M., Thomson, R. B., and Kaul,
K. L. (2005). Real-time PCR for detection and identi cation of
Plasmodium spp.Journal of clinical microbiology,43 (5): pp.
2435-2440.
McNamara, D. T., Thomson, J. M., Kasehagen, L. J., and Zim-
merman, P. A.(2004). Development of a multiplex PCR-ligase
detection reaction assay for diagnosis of infection by the four
parasite species causing malaria in humans. Journal of clinical
microbiology,42 (6): pp. 2403-2410.
Mekonnen, S.K., Abraham Aseffa, Girmay Medhin, Nega
Berhe and Thirumalaisamy P Velavan (2014). Re-evaluation
of microscopy con rmed Plasmodium falciparum and Plas-
modium vivax malaria by nested PCR detection in southern
Ethiopia. Malaria Journal. 2014; 13:48.
Mok, S., Ashley, E. A., Ferreira, P. E., Zhu, L., Lin, Z., Yeo, T.,
and Nguon, C. (2015). Population transcriptomics of human
malaria parasites reveals the mechanism of artemisinin resist-
ance.Science,347 (6220): pp. 431-435.
Morassin, B., Fabre, R., Berry, A., and Magnaval, J. F. (2002).
One year’s experience with the polymerase chain reaction as
a routine method for the diagnosis of imported malaria.The
American journal of tropical medicine and hygiene,66 (5): pp.
503-508.
Patsoula, E., Spanakos, G., So anatou, D., Parara, M., and Vakalis,
N. C. (2003). A single-step, PCR-based method for the detection
and differentiation of Plasmodium vivax and P. falciparum.Annals
of Tropical Medicine & Parasitology,97 (1): pp. 15-21.
Perandin, F., Manca, N., Calderaro, A., Piccolo, G., Galati, L.,
Ricci, L., and Chezzi, C. (2004)
Development of a real-time PCR assay for detection Plasmo-
dium falciparum, Plasmodium vivax, and Plasmodium ovale
for routine clinical diagnosis. Journal of clinical microbiol-
ogy,42 (3): pp. 1214-1219.
Sebai, Z. (1988). Malaria in Saudi Arabia. Trop. Doctor (18):
pp. 183-88.
Snounou, G. S., S. Viriyakosol, X. P. Zhu, W. Jarra, L. Pinheiro,
V. E. do Rosario, S. Thaithong, and K. N. Brown. 1993. High
sensitivity of detection of human malaria parasites by the use
of nested polymerase chain reaction.
Talha A, Pirahmadi S, Elgaily EM et al. (2014). Low preva-
lence of Plasmodium vivax - Plasmodium falciparum mixed-
infection in patients from central and eastern part of Sudan:
Implication for case management in Sudan. Int J of Trop Dis
Health 2014:4; 887–95.

Dafalla et al.
BIOSCIENCE BIOTECHNOLOGY RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS IDENTIFICATION OF
PLASMODIUM
SPECIES FROM OUTDATED BLOOD SAMPLES 75
Van Hong, N., van den Eede, P., Van Overmeir, C., Vythiling-
ham, I., Rosanas-Urgell, A., Thanh, P. V., and Erhart, A. (2013).
A modi ed semi-nested multiplex malaria PCR (SnM-PCR)
for the identi cation of the ve human Plasmodium species
occurring in Southeast Asia.The American journal of tropical
medicine and hygiene,89 (4): pp. 721-723.
WHO, 2013: World Malaria Report 2013. Geneva: WHO Press.
WHO. (2014). World malaria report 2013. Geneva: World Health
Organization; 2014. http://www.who.int/malaria/publications/
world_malaria_report_2013/en/.
World Health Organization (2016). Fact Sheet: World malaria
report 2015. http://www.who.int/malaria/media/world-malaria-
report-2015/en. /
Yewhalaw D, Kassahun W, Woldemichael K, Tushune K,
Sudaker M, Kaba D, Duchateau L, Van Bortel W, Speybroeck
N (2010).The in uence of the Gilgel-Gibe hydroelectric dam
in Ethiopia on caregivers’ knowledge, perceptions and health-
seeking behaviour towards childhood malaria. Malar J. 2010,
9: 47-10.1186/1475-2875-9-47.
Zahar, A. (1985). Vector Bionomics in Epidemiology and Con-
trol of Malaria Part I, WHO Geneva.
Zakeri S, Qutbuddin Kakar, Faezeh Ghasemi, Ahmad Raeisi,
Waqar Butt, Navid Dinparast Djadid et al (2010). Detection
of mixed infection of P. falciparum and P. vivax infection by
nested PCR in Pakistan, Iran and Afaganistan, Indian J of Med
Res 132. 2010;31:35