Ecological
Communication
Biosci. Biotech. Res. Comm. 9(4): 872-877 (2016)
On the sh diversity, conservational management and
rehabilitation aspects of Wular Lake, Kashmir India
Rumysa K.
1
, Sharique A. Ali
2
, Bilal A.
3
, Tariq Z.
4
and Farooq M.
5
1
Goverment Degree College for Boys Sopore, Kashmir.
2
Department of Biotechnology Sai a Science College, Bhopal.
3
Division of Veterinary Microbiology Shuhama Alustang, SKUAST-K.
4
Bhoj (Open) University, Bhopal.
5
Department of Zoology and Head Hydrobiology Research Laboratory, Government Sri Pratap College,
Srinagar, Kashmir, India
ABSTRACT
Biodiversity and conservation are regarded as one of the major issues of enabling sustainable use of natural resources.
This contribution focuses on sh population and their conservation aspects in the freshwater Wular Lake in Kashmir.
It was a valuable shery resource of the region but due to anthropogenic pressures such as encroachment over open
water area and entry of sewage and disturbance in the catchment area have affected water quality and consequently
its shery potential adversely. The sh fauna of Kashmir is appreciably different from rest of the country and is
mainly represented by the cold water Schizothoracine group of shes. It is observed that some of the Schizothorax
species have almost disappeared from the scenario. The study revealed the occurrence of sixteen sh species belong-
ing to three orders namely Cypriniformes (81%), Siluriformes (12.5%) and Cyprinodontiformes (6.25%) and 5 families
includes Cyprinidae (62.5%), Balitoridae (12.5%), Sisoridae (12.5%), Cobitidae (6.25%) and Poeciliidae (6.2%).
KEY WORDS: DIVERSITY, ECOSYSTEM, EXOTIC, INDIGENOUS, KASHMIR AND WULAR
872
ARTICLE INFORMATION:
*Corresponding Author: rumysaaqua@gmail.com
Received 21
st
Nov, 2016
Accepted after revision 24
th
Dec, 2016
BBRC Print ISSN: 0974-6455
Online ISSN: 2321-4007
Thomson Reuters ISI ESC and Crossref Indexed Journal
NAAS Journal Score 2015: 3.48 Cosmos IF : 4.006
© A Society of Science and Nature Publication, 2016. All rights
reserved.
Online Contents Available at: http//www.bbrc.in/
INTRODUCTION
Freshwater sh are one of the most threatened taxo-
nomic groups (Darwall and Vie, 2005) because of their
high sensitivity to the quantitative and qualitative alter-
ation of aquatic habits (Laffaille et al., 2005; Sarkar
et al., 2008; Kang et al., 2009). Fish is sensitive to
changes in water chemistry due to different anthropo-
genic activities from their catchment. Fish responses to
environmental disturbances, including hydro-morpho-
logical factors are different in time and space in compar-
ison to simpler organisms, as they tend to be integrated

Rumysa et al.
over larger intervals. Fish have been identi ed as suit-
able for biological assessment due to its easy identi ca-
tion and economic value (Silas 1951; Smith et al., 1999,
Siligato and Bohmer 2001, and Vibhute 2016).
Fish have been regarded as an effective biological indi-
cator of environmental quality and anthropogenic stress in
aquatic ecosystems (Simon and Lyons, 1995; Bhat, 2003;
Jayalekshmy and Sanalkumar, 2012) not only because of
their iconic value, but also because of sensitivity to sub-
tle environmental changes. They represent a wide range
of tolerance at community level. Today the sh diversity
and associated habitats management is a great challenge
(Dudgeon et al., 2006). Conservation measures to mitigate
the impact of the pressures have largely been slow and
inadequate and as a result many of the species are declin-
ing rapidly (Venkateshwarlu 2014).
MATERIAL AND METHODS
Wular Lake, a rural lake in the north-west of Kashmir
about 55 km from Srinagar city, is lying in the ood
plains of River Jhelum. Its recognition of its biological,
hydrological and socio-economic values, the lake was
included in 1986 as a wetland on national importance
under the wetlands programme of the Ministry of Envi-
ronment and Forests, Government of India for intensive
conservation management purposes. Subsequently in
1990, it was designated as a wetland of International
importance under the Ramsar convention.
The average maximum depth of the lake is reported
5.8m (Pandit, 2002). The lake is situated at an altitude
of 1,580 m (AMSL) lying between 34°16´- 34°20´N lati-
tudes and 74°33´-74°44´E longitudes. The lake is becom-
ing steadily shallower as a result of continuous depo-
sition of silt brought from its catchment area through
its main tributaries (Erin, Madhumati, Ashtung, Hartal,
etc.), and the River Jhelum. River Jhelum is the main
feeding channel entering the lake basin at Gurur, it is
further drained at Ningli (Sopore) in the north-east by
the only single outlet in the form of River Jhelum. The
lake is situated between Bandipore and Sopore. Ban-
dipore is situated in its eastern bank and is popularly
known as port of Wular, the Madhimati and Erin Nallas
ow into the lake on its eastern side
For studying the sh biodiversity, various data and
information where collected by physical veri cation
and interview with the local sherman of the study
area. The sampling was carried out on monthly basis,
10 attempts were made by sherman/day. The collected
samples where immediately dipped into 10% formalin in
a large container that allowed proper separating of their
ns. Then the specimens were examined and classi ed
into families, which were carried in separate container
each container was labeled properly against the physi-
cal data sheet of sampling and brought to the labora-
tory for further examine exercise. Identi cation of shes
was done with the help of standard taxonomic works
of Day (1878), Hora (1936), Mukerji (1936), Talwar and
Jhingran (1991), Kullander et al., (1999). In the present
study, diversity has been measured by number of species
and by using indicies. They are given below:
1. Simpson’s diversity index (D)
Diversity within the benthic macro invertebrate commu-
nity was described using the Simpson’s diversity index
(“D”), which was calculated as:
Where, “pi” is the proportion of individuals in the “ith”
taxon of the community and “s” is the total number of
taxa in the community (Simpson, 1949).
2. Shannon-Weiner diversity index (H
/
)
Species diversity was determined after Shannon-Weiner
(1949) as:
Where: H
/
= Index of species diversity
n
i
= Density of one species
N = Density of all the species
e = Base of natural logarithm of = 2.303
S = Addition of the expression for values of i from i
= 1 to i
3. Evenness Index
Evenness Index an important component of the diversity
indices. Evenness index expresses how evenly the indi-
viduals are distributed among the different species for a
particular area.
4. Margalef Index
It isa measure ofspecies diversity, calculatedfrom the
total number of species present and the abundance or
total number of individuals. The higher the index the
greater the diversity.
Margalef’s richness index:(S-1)/ln (n), whereSis the
number of taxa, andnis the number of individuals.
5. Berger-Parker diversity index
It is simple measure of the numerical importance of the
most abundant species. Berger-Parker diversity indices
were determined by PAST software.
BIOSCIENCE BIOTECHNOLOGY RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS FISH DIVERSITY OF WULAR LAKE KASHMIR INDIA 873
Rumysa et al.
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Present study standardizes the shing status along the
different sites of Wular Lake, which yielded sixteen sh
species viz, Cyprinus carpio specularis, Cyprinus carpio
communis, Carassius carassius, Schizothorax niger, Schi-
zothorax esocinus, Schizothorax curvifrons, Schizotho-
rax labiatus, Schizothorax plagiostomus, Crossocheilus
diplochilus, Puntius conchonius, Botia birdi, Triplophysa
kashmirensis, Triplophysa marmorata, Gambusia af nis,
Glyptothorax kashmirensis, Glyptothorax pectinoptrus
belonging to three orders namely Cypriniformes (81%),
Siluriformes (12.5%) and Cyprinodontiformes (6.25%)
and 5 families includes Cyprinidae (62.5%), Balitoridae
(12.5%), Sisoridae (12.5%), Cobitidae (6.25%) and Poe-
ciliidae (6.2%).
Out of sixteen species of shes Cyprinus carpio com-
minus was dominant. Cyprinus carpio comminus seems
to be well established and may pose a threat to the
endemic lake dwelling species in competing for space
and food. Das (1978) and Mir and Shahnawaz (2006)
reported introduction of exotic shes like common carp
decline the catch as well as the diversity of indigenous
shes of Kashmir lakes. Khan et al., (2016) also reported
that introduction of exotic sh species in freshwater
ecosystems of Punjab and Pakistan is in great risk of
decline due to their vigorous reproductive potential and
feeding competitions with the native sh fauna.
The introduction of exotic species is the sec-
ond leading cause, after habitat degradation, of species
extinction in freshwater systems (Hill et al., 1997). A
survey of 31 studies of sh introductions in Europe,
North America, Australia, and New Zealand found that
in 77% of cases native sh populations were reduced
or eliminated following the introduction of exotic sh.
Fotedar and Qadri (1974) considered Cyprinus carpio to
present serious competition to local origins like Schizo-
thorax niger, Schizothorax esocinus, Schizothorax curvi-
frons, Sxhizothorax labiatus andCrosschelius diplochilus,
whose number would be dwindling for this reason. The
species which were rare are Schizothorax plagiostomus,
Puntius conchonius, Botia birdi, Triplophysa kashmi-
rensis, Triplophysa marmorata, Gambusia af nis, Glyp-
tothorax kashmirensis and Glyptothorax pectinoptrus.
The population of Schizothracine shes in Wular Lake
has considerably decreased over the years particularly
after the introduction of common carp in 1956 (Fotedar
and Qadri 1974; Vass et al., 1984). The sh species like
Schizothorax richardsonii and Bangana diplostoma once
abundant and even caught in commercial quantities,
which has now disappeared. Similarly, the indigenous
shes of Lake Sone of Assam are being fast replaced
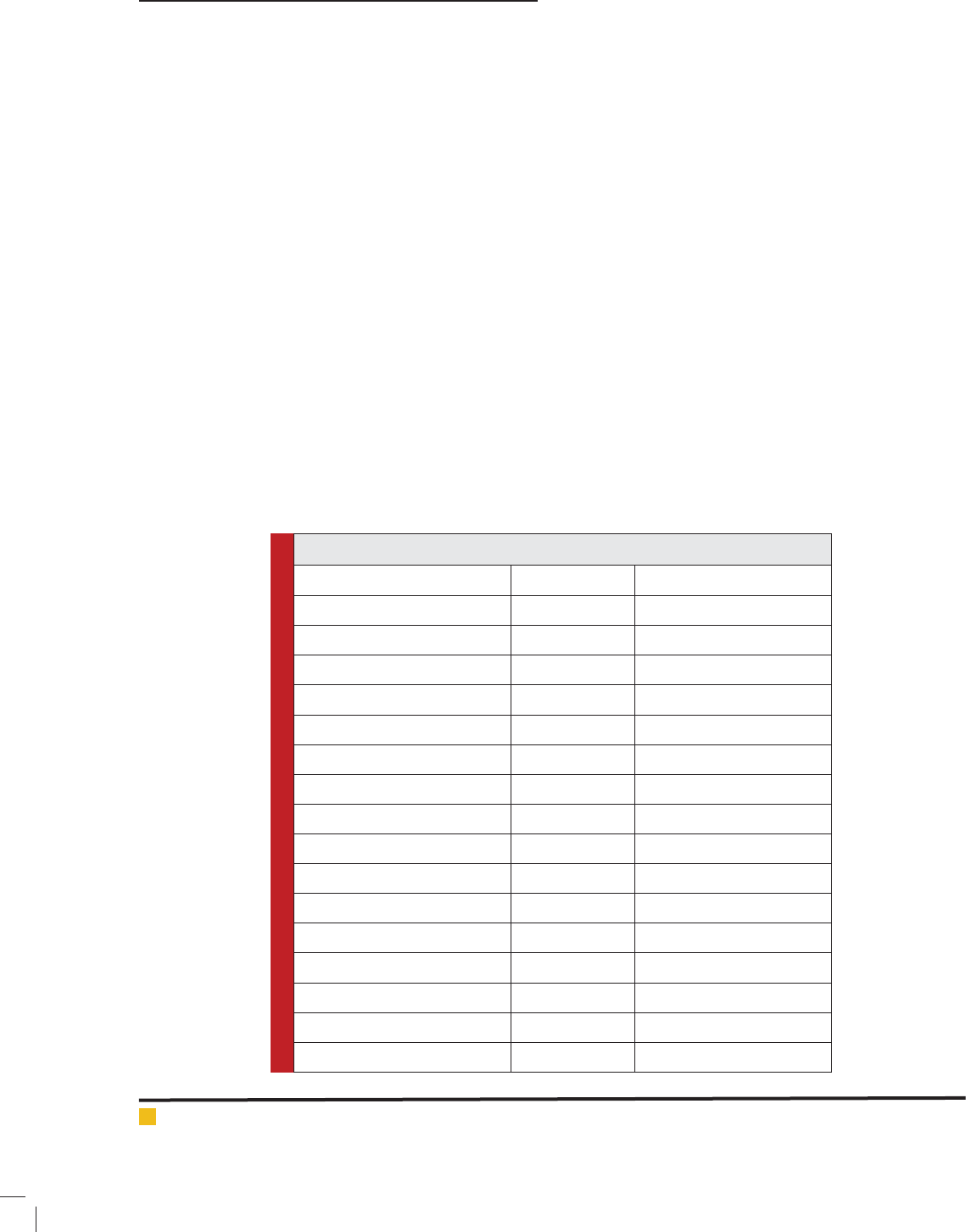
Table 1: Fish diversity in Wular Lake of Kashmir
Scienti c name of sh Local name Occurance
Cyprinus carpio specularis Gang gad Abundant
Cyprinus carpio communis Gang gad Less Abundant
Carassius carassius Gung gad Abundant
Schizothorax niger Ale gad Less Abundant
Schizothorax esocinus Churun Moderately Abundant
Schizothorax curvifrons Satter gad Less Abundant
Schizothorax labiatus Chush Moderately Abundant
Schizothorax plagiostomus Khont Moderately Abundant
Crossochelius diplochilus Zub Less Abundant
Puntius conchonius Gang gad Moderately Abundant
Botia birdi Rama gurun Very Rare
Triplophysa kashmirensis Ara gurun Very Rare
Triplophysa marmorata Ara gurun Very Rare
Gambusia af nis Mahi gad Less Abundant
Glyptothorax kashmirensis Nayid gad Rare
Glyptothorax pectinoptrus Nayid gad Rare
874 FISH DIVERSITY OF WULAR LAKE KASHMIR INDIA BIOSCIENCE BIOTECHNOLOGY RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS

Rumysa et al.
by the introduction of exotic carp, Cyprinus carpio (Kar
et al., 2006).
The Cyprinus carpio has not only ourished well in
the aquatic habitats of the Wular Lake but also provides
the maximum sh catch.Another factor responsible for
decline in indigenous shes is the encroachment of the
shallow areas of the lake for agricultural activities which
became the most dangerous practice which causes harm
to some species of indigenous shes, used to breed in
shallow areas of the lake. Use of arti cial fertilizers,
pesticides and herbicides in apple orchards and paddy
elds from nearby areas have also effected the indig-
enous shes due to increase of nutrients in water which
in turn increases growth of algal blooms and other mac-
rophytes in the lake. The excess nutrients may originate
from fertilizers that are applied to land for agricultural
or recreational purposes. These nutrients can then enter
watersheds through water runoff (Lathrop et al. 1998).
When phosphates are introduced into water systems,
higher concentrations cause increased growth of algae
and plants. Algae tend to grow very quickly under high
nutrient availability, but each algae is short-lived, and
the result is a high concentration of dead organic matter
that starts to decay. The decay process consumes dissolved
oxygen in the water, resulting in low oxygen conditions.
Without suf cient dissolved oxygen in the water, animals,
and plants die off in large numbers. Over the past decades,
excessive nutrient loading has emerged as an important
direct driver of freshwater ecosystem change. World con-
sumption of nitrogenous fertilizers grew nearly eightfold
between 1960 and 2003, from 10.8 million tons to 85.1
million tons (Millennium Ecosystem Assessment 2005).
Leveque (2008) also reported overexploitation, ow
modi cation, destruction of habitats, and invasion by
exotic species, pollution and eutrophication as major
threats to sh biodiversity. Wular lake waters have achieved
a high trophic status on account of nutrient enrichment
from its catchment .Wular Lake is under eutrophic state as
a result of human stress in the catchment area.
Shannon-Weaver index functions as a sensitive indi-
cator for pollution. It is a combination of the number of
species and the evenness of distribution of individuals
among taxa (Klemm et al., 1990). Shannon index was
very low indicating that sh diversity in Wular Lake is
very poor due to pollution and other unfavorable envi-
ronmental conditions. Simpson index and Evenness indi-
cate that sh diversity of Wular is degrading day by day;
same is true for Margalef index and Berger-Parker index.
CONSERVATIONAL MANAGEMENT AND
REHABILITATION SUGGESTIONS
Freshwater biodiversity and freshwater ecosystems are
seriously jeopardized by human activities in world. This
is undoubtedly a consequence of growing human pop-
ulations and economic development above everything
else (Wu et al., 1999). Human activity can alter physical,
chemical and biological processes and, thereby change
the character of the lakes. The ecology and biodiversity
of Wular Lake is under the impact of: (i) direct discharge
of untreated sewage coming from highly populated vil-
lages and agriculture activities (ii) catchment runoff (iii)
tourist pressure (iv) sand mining; channelization and
impoundment; (v) illegal shing. Combinations of these
threat factors affect the biodiversity and puts freshwater
biodiversity uniquely at risk as also stated by Hynes,
(1960) in his study.
SUGGESTIONS
• Master plan should be developed for the treatment
of all point source of pollution entering into the
Wular Lake, especially for the sewage coming from
the residential area of the Wular Lake which other-
wise will affect the water quality and will deterio-
rate over all ecosystem health.
• Watershed management plan should be imple-
mented along the catchment area of Wular Lake
and construction and human habitation should be
prohibited
• Deforestation and overgrazing should be properly
controlled in order to prevent soil erosion and loss
of biodiversity.
• Indiscriminate mining of sand should be restricted
or minimized as this practice destroys the breeding
grounds and dwelling place of Lake Fauna.
• Sustainable sheries development to maintain/
restore sh diversity and yield.
• Control of invasive species and enhancing biodi-
versity.
• In order to protect the lake from silt problem
brought in through main feeding channel-river
Jhelum and other small streams like Madumati,
Erin and Ningli settling basins need to construct
near their points into the lake.
• Large areas of the lake have been illegally
encroached and converted into paddy elds and
vegetables gardens. The further encroachment in
the lake must be stopped.
• Continuous deposition and pouring of domestic
wastes, garbage and dead animals into the River
Jhelum which ends at Wular be stopped under
strict orders.
• We have done enough harm to our natural resources.
In such situation eco-restoration is the way by which
we can ameliorate the situation. There is need to cre-
ate small decentralized decision making groups like
Lake study groups, cooperative societies.
BIOSCIENCE BIOTECHNOLOGY RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS FISH DIVERSITY OF WULAR LAKE KASHMIR INDIA 875

Rumysa et al.
• Carry out environmental impact assessment peri-
odically to ensure lake conservation and sustain-
able use of lake resources.
• Since the Lake is owned by various state gov-
ernment departments such as wildlife, shery,
urban environment engineering department, lakes
and waterways development authority etc., there
should be common consensus amongst these
departments so that if the project is to be under-
taken in the lake it should be with the consent of
all the departments involved and not to disturb the
ecology of lake.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The authors are thankful to Maulana Azad National
Fellowship of University Grants Commission, Bahadur
Shah Zafar Marg New Delhi – 110002, for the nancial
assistance. The authors gratefully acknowledge the help
and assistance provided by the Hydrobiology Research
Laboratory, Govt. Sri Pratap College, Srinagar, Kashmir.
REFERENCES
Bhat, A (2003). Diversity and composition of freshwater shes
in river systems ofcentral Western Ghats, India.Env. Biology
of Fishes. 68, 25-38.
Darwall, W. R. T., Vie, J. C (2005). Identifying important sites
for conservation of freshwater biodiversity: Extending the spe-
cies-based approach. Fish Manage Ecol. 12, 287–293.
Das, S. S (1978). Algal weeds and their chemical control. A
review. Indian J. Plant Prot. 4, 201-208.
Day, F (1878). The shes of India: Being a natural his-
tory of the shes known to inhabit seas and freshwaters of
India, Burma and Ceylon. William Dawson & Sons, London.
778 pp.
Dudgeon, D., Arthington, A. H., Gessner, M. O., Kawabata,
Z.-I., Knowler , D. J., Leveque, C. R., Naiman, J., Prieur-Rich-
ard, A.-H., Soto, D., Stiassny, M. L. J and Sullivan, C. A (2006).
Freshwater biodiversity: importance, threats, status and con-
servation challenges. Biological Reviews.81, 163-182.
Fotedar, D. N and Qadri, M. Y. (1974). Fish and sheries of
Kashmir and the impact of carp, Cyprinus carpio, on the
endemic shes. Journal of Science. 2, 79-89.
Hora, S. L (1936). Yale North India Expedition. Article 18.
Report on shes. Part I. Cobitidae. Mem. Conn. Acad. Arts Sci.
10, 299-321.
Hill, G., J. Waage and Phiri, G. (1997). The water hyacinth
problem in tropical Africa, in E.S. Delfosse and N.R. Spencer,
eds., Proceedings of the International Water Hyacinth Consor-
tium. Washington, DC: World Bank.
Hynes, H. B. N. (1960). The biology of polluted waters. Liver-
pool University Press, Liverpool, England, pp. 202.
Jayalekshmy, V and Sanalkumar, M. G (2012). Bi-seasonal var-
iation inthe Piscian diversity in relation to physico-chemical
parametersof Pallickal River-Kerala, India.InternationalJour-
nalofScienti candResearchPublications.2(11),1-5.
Kang, B., He, D., Perrett, L., Wang, H., Hu, W., Deng, W and
Wu, Y (2009). Fish and fisheries in the Upper Mekong: Current
assessment of the fish community, threats and conservation.
Rev Fish Biol Fish.19, 465–480.
Kar, Devashish., Nagarathna, A. V., Ramachandra T. V and
Dey, S. C (2006). Fish diversity and conservation aspects in
an aquatic ecosystem in north eastern India, Zoos’ print Jour-
nal.21(7),2308-2315.
Khan, M.N., Khurram S., Ansar C., Muhammad S., Marina P.,
and Tomislav T. (2016). A review of introduction of common
carp Cyprinus Carpio in Pakistan: Origin, purpose, impact and
management. Croatian Journal of Fisheries, 2016, 74, 71 – 80.
Klemm, D. J, Philip, A. L, Florence and Lozoreckak (1990).
Macro invertebrate eld and laboratory method for evaluating
the biology integrity of surface water. U.S. EPA, EPA/600/4-
90.030 Xii 256pp.
Kullander, S. O. Fang, F., Delling, B and Ehlander, E (1999).
The shes of the Kashmir Valley,pp. 99-168 In: River Jehlum,
Kashmir valley, impacts on the aquatic environment. (Linhart
Nyman eds).
Laffaille, P., Acou, A., Guillouet, J and Legault,A (2005). Tem-
poral changes in European eel,
Anguilla anguilla, stocks in
a small catchment after installation of sh passes.
Fisheries
Management and Ecology.
12, 123-129.
Lathrop, RC., Carpenter, SR., Panuska, JC., Soranno, PA., and
Stow, CA., (1998). Loading reductions needed to control blue-
green algal blooms in lake Mendota. Canadian Journal of
Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences 55:1169-1178.
Leveque, T., Oberdorff , D., Paugy, M. L. J. Stiassny and P. A.
Tedesco (2008). Global diversity of sh (Pisces) in freshwater,
Hydrobiologia. 595, 545-567.
Milleniun Ecosystem Assessment (2005). Ecosystem and
human wellbeing. Biodiversity synthesis. World Resources
Institute, Washington, D C.
Mir, M. Farooq and Shahnawaz, A. (2006). Vertebrate fauna
of Hokarsar wetland, Kashmir. Science for better tomorrow.
Proceedings of the Second J&K Science Congress. University
of Kashmir.
Mukerji, D. D (1936). Yale North India Expedition. Report on
shes. Part II. Sisoridae and Cyprinidae. Mem. Conn. Acad.
Arts Sci.10, 323-359.
Pandit, A. K (2002). Trophic evolution of lakes in Kashmir Hima-
laya. p. 175-222. In: Natural Resources of Western Himalaya (A.
K. Pandit, ed.). Valley Book House, Srinagar-190006, J&K.
Rogozin, A. G (2000). Speci c structural features of zooplank-
ton in lakes differing in trophic status: species populations.
Russ. J. Ecol.31, 405-410.
Sarkar, U. K, Pathak, A. K and Lakra, W. S (2008). Conservation
of freshwater fish resources of India: New approaches, assess-
ment and challenges. Biodivers Conserv.17, 2495–2511
876 FISH DIVERSITY OF WULAR LAKE KASHMIR INDIA BIOSCIENCE BIOTECHNOLOGY RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS

Rumysa et al.
Tallberg, P., Horppila, J., Väisänen, A and Nurminen, L (1999).
Seasonal succession of phytoplankton and zooplankton along
a trophic gradient in a eutrophic lake – implications for food
web management. Hydrobiologia. 412, 81–94.
Silas, E. G (1951). On a collection of shes from the Anamalai
and Nelliampathy hill ranges Western Ghats with: Notes on its
zoogeographical signi cance.
J. Bombay Nat. Hist. Soc. 49,
670-681.
Siligato, S and Böhmer, J (2001). Using indicators of sh health
at multiple levels of biological organization to assess effects of
stream pollution in southwest Germany. Journal of Aquatic
Ecosystem Stress and Recovery. 8, 371-386.
Simon, T. P and Lyons, J (1995). Application of the index of
biotic integrity to evaluate water resource integrity in freshwa-
ter ecosystems. In Davis, W. S. and T. P. Simon (eds).
Smith, A. K., Ajani, P. A., Roberts, D. E (1999). Spatial and
temporal variation in sh assemblages exposed to sewage and
implications for management. Marine Environmental Research
47, 241-260.
Talwar, P. K and Jhingran, A. G (1991). Inland shes of India
and adjacent countries, Vols, 1-2. Oxford and IBH Publishing
Co., New Delhi.
Vass, K. K., Raina, H. S., Sunder, S., Moza, U and Lanoer, R. K
(1984). Proc. Semn. Management Fish. Resources. Jammu Uni.
31-32.
Venkateshwarlu, M., Arun Kumar Shetty, B., and Kiran, B. R.
(2014). Conservation status of sh diversity of Rivers-Sita,
Swarna and Varahi in Udupi District, Western Ghats, Karna-
taka, India. International journal of advanced scienti c and
technical research. ISSN 2249-9954, Issue 4, volume (1),797-
813.
Vibhute SM. (2016). Ichthyofaunal diversity of Rajewadi Lake,
Tal-Atpadi, Dist-Sangli (MS) India International Journal of
Applied Research 2016; 2(8): 781-783.
Wu, C., Maurer, C., Wang, Y., Xue, S and Davis, D. L (1999).
Water pollution and human health in China. Environmental
Health Perspectives. 107, 251-256.
BIOSCIENCE BIOTECHNOLOGY RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS FISH DIVERSITY OF WULAR LAKE KASHMIR INDIA 877