Biotechnological
Communication
Biosci. Biotech. Res. Comm. 9(4): 743-749 (2016)
Comparative study of bioethanol production from acid
and enzymatically hydrolyzed cotton stalk using co
culture of
Saccharomyces cerevisiae
and
Pachysolen
tannophilus
Mirza Zaheer Baig* and Dharmadhikari Smita M.
Department of Microbiology, Government Institute of Science, Aurangabad
ABSTRACT
Cotton stalk is one of the abundant feedstock and has been selected for producing ethanol at economically feasible
manner. In the present investigation a comparative account of ethanol production has been developed from acid
and enzymatically hydrolyzed cotton stalks. For this cotton stalk was subjected to series of treatment including acid
hydrolysis followed by detoxi cation in one set; and alkaline pretreatment followed by enzyme hydrolysis in second
set. The sugars released during acid and enzyme hydrolysis was obtained as 11g/L and 24.5 g/L respectively. Both the
sets were separately fermented for ethanol production. During fermentation, test organisms in association utilized
93.84% and 97.81% of total available sugars and produced an ethanol concentration of 4.96 g/L and 9.56 g/L with
corresponding yield of 0.179 g/g and 0.191 g/g of biomass (native cotton stalk) respectively.
KEY WORDS: FERMENTATION, BIOETHANOL, COTTON STALK
, SACCHAROMYCES CEREVISIAE, PACHYSOLEN TANNOPHILUS
743
ARTICLE INFORMATION:
*Corresponding Author: drmzbaig@gmail.com
Received 9
th
Nov, 2016
Accepted after revision 21
st
Dec, 2016
BBRC Print ISSN: 0974-6455
Online ISSN: 2321-4007
Thomson Reuters ISI ESC and Crossref Indexed Journal
NAAS Journal Score 2015: 3.48 Cosmos IF : 4.006
© A Society of Science and Nature Publication, 2016. All rights
reserved.
Online Contents Available at: http//www.bbrc.in/
INTRODUCTION
The increasing need for ethanol as energy source has
stimulated worldwide investigations in search of cheaper
substrate for bulk ethanol production. As a substrate,
conventional crop such as corn and sugarcane are una-
ble to meet the global demand of bioethanol production
due to their primary value of food and feed therefore,
lignocellulosic substance such as agricultural wastes are
attractive feedstock for bioethanol production (Behera
et al., 2010). In the present investigation cotton stalk was
used as substrate. According to United State Department
of Agriculture (USDA), India is expected to emerge as
largest cotton producer in the world, estimated cotton

744 COMPARATIVE STUDY OF BIOETHANOL PRODUCTION BIOSCIENCE BIOTECHNOLOGY RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS
Mirza Zaheer Baig and Dharmadhikari Smita
area in country in 2015-16 is 11.26 million hectors and
cotton production is estimated as 6.3 million metric tons.
The lignocellulosic nature and potential availability of
cotton stalk open its way as renewable raw material for
various commercial applications including ethanol pro-
duction (Kaur et al., 2012). Prior to ethanol fermenta-
tion by organisms, the feedstock needs to be process by
scari cation technology in order to retain fermentable
sugars. Acid hydrolysis is simple and easy method to
perform and is prominently used for depolymerization
of biomass into fermentable sugar. Acid hydrolysis was
carried out in two stages including concentrated acid
decrystallization followed by dilute acid hydrolysis with
steam and heat treatment (Liao et al., 2006). It is the
most widely used method for sacchari cation of ligno-
cellulosic material, due to its relatively low cost, ease of
use and high ef ciency. The important drawback of this
treatment is the formation of toxic compound (furfural
and hydroxymethyl furfural) released during hydroly-
sis. These inhibitors decrease the fermentation yield by
retarding microbial activity, which must be removed by
applying proper detoxi cation process (Chandel et al.,
2007).
Another method is alkaline pretreatment and enzy-
matic hydrolysis of lignocellulosic biomass. The major
effect of alkali pretreatment is the saponi cation of
intermolecular ester bonds which crosslink lignin and
carbohydrates, thus increasing porosity and internal
surface of the biomass matrix as well as decreasing the
degree of crystallinity of cellulose, resulting in improved
susceptibility of remaining polysaccharides to enzyme
attach during hydrolysis (Sun and Cheng, 2002). Alka-
line pretreatment process utilizes lower temperature and
pressure compare to other pretreatment technologies
(Balat et al., 2008). However, unlike acid pretreatment,
it is much more time consuming and some of the alkali
is converted to irrecoverable salt or incorporated as salt
into the biomass by the pretreatment reaction (Mosier
et al., 2005).
Enzyme hydrolysis is another method of degrading
pretreated cellulose to mono sugars with the help of
complex of enzyme known as cellulases. Cellulasee is
described in terms of three major classes. The endoglu-
canases (EC 3.2.1.4, EG) act randomly on soluble and
insoluble cellulose chain. The exoglucanases, which
include cellobiohydrolases (EC 3.2.1.91, CBHs), acts pro-
cessively to preferentially liberate cellobiose (and glu-
cose in some cases) from the reducing and non-reduc-
ing ends of the cellulose chain. The -glucosidase (EC
3.2.1.21) liberates D-glucose from cellobiose and exo-
glucosidases. Among the studied microorganism, fungi
are most active against natural polymers, being capable
of producing different amounts of each type of cellu-
lases, which act synergistically. Almost all commercial
cellulases obtained by submerged fermentation are pro-
duced by the fungi Trichoderma, Humicola, Aspergillus
and Penicillium (Sohail et al., 2009; Tolan and Foody,
1999).
The present study is the extension of our previous
work carried out to produce ethanol from acid and
enzymatically hydrolyzed cotton stalk using co culture
of Saccharomyces cerevisiae (hexose fermenting yeast)
and Pachysolen tannophilus (pentose fermenting yeast).
In this study a comparison has been made to focus on
pros and cons of each sacchari cation and fermentation
process based on sugar and ethanol yield respectively.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
BIOMASS
The cotton stalks was collected from the farmers eld
and were shredded, sundried, debarked, bailed and
ground to 1mm particle size. It contains approximately
42.40% glucan and 23.20% xylan (carbohydrate content
was determined by the method of Laboratory Analytical
Procedure (LAP # 002) of National Renewable Energy
Laboratory (NREL) using HPLC, Zodiac. Ltd). Klason
lignin was found to be 24.18%, determined by method
adopted by Teramoto et al., (2008).
YEAST CULTURES
The cultures of Saccharomyces cerevisiae MTCC 36 and
Pachysolen tannophilus MTCC 1077 were procured from
Microbial Type Culture Collection, IMTECH-Chandigarh,
India.
SACCHARIFICATION PROCESS
In this process two separate sets of biomass were prepared
for hydrolysis, one set was hydrolyzed by using acid and
another set was hydrolyzed by using the enzyme.
ACID HYDROLYSIS
Cotton stalk was subjected to dual stage sulfuric acid
treatment. During its rst stage 75% H
2
SO
4
was used
to decrystallize the biomass under speci c sample acid
ratio of 1:2 (by weight) followed by diluting this decrys-
tallized biomass to make it 1N in second stage, then
employing steam under pressure at 121
o
C in an autoclave
for 30 minutes and four hour heat treatment at 90
o
C in
water bath respectively (Baig, 2014). The obtained acid
hydrolysate was detoxi ed by addition of dried lime up
to pH 10 for an hour and then ltered and readjusted of
pH up to 6 with acid. The obtained over limed hydro-

BIOSCIENCE BIOTECHNOLOGY RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS COMPARATIVE STUDY OF BIOETHANOL PRODUCTION 745
Mirza Zaheer Baig and Dharmadhikari Smita
lysate was treated with 4% (w/v) charcoal treatment for
half an hour with stirring and then ltered (Baig and
Dharmadhikari, 2014). The obtained ltrate solution was
used as sole carbon source for fermentation.
ENZYME HYDROLYSIS
Alkaline pretreatment and enzymatic hydrolysis was
carried out in second set of experiment. In this regard,
2.0 % (w/v) concentration of alkaline solution has been
prepared from NaOH pellets (Qualigens. Ltd) in aque-
ous medium. 5 gram of cotton stalk powder was treated
with alkaline solution at a substrate loading of 10%
(w/v). The ask was steam treated at 121
o
C for 60 min-
utes. After steam treatment, the biomass has been sepa-
rated from ligni ed liquor by centrifugation at 10000
rpm for 10 minutes and supernatant (black liquor) was
separately collected for quantitative detection of lignin
content. The deligni ed biomass was repeatedly washed
with distilled water till to become neutral pH and dried
in hot air oven at 60
o
C till constant weight. Enzymatic
hydrolysis of pretreated biomass was carried out using
commercial cellulases purchased from Sisco Research
Laboratories Pvt. Ltd. Mumbai, India. Pre-treated cot-
ton stalk was incubated with 5% solid loading in 50mM
acetate buffer (pH 4.8) with 100 CMC (carboxymethyl
cellulose) unit of enzyme per gram of biomass and was
incubated at 50
o
C with 150 rpm for 72 hours (Baig and
Dharmadhikari, 2012). After incubation, the sample was
centrifuged in chilled condition at 5000 rpm for 10 min-
utes and supernatant was collected as sugar solution for
fermentation process.
FERMENTATION STUDIES
The sugar solutions obtained from both the hydrolysate
were separately fermented for analyzing the potential
of bioethanol production and develop a comparative
account in between them. The reliability of results was
checked statistically by passing through ANOVA (analy-
sis of variance).
INOCULUM DEVELOPMENT
The culture maintained on Yeast and Malt Extract Agar
(YM medium: 0.3% yeast extract, 0.3% malt extract, 0.5%
peptone and 1% glucose, pH 6.5). Cell mass required for
inoculum development was obtained by growing each
culture separately on YM medium in Erlenmeyer ask
aerobically at 30
ºC
on rotary shaker incubator with 150
rpm for 48 h. After incubation, completely activated
yeast cells were harvested by centrifugation at 4000
rpm at 4ºC for 10 min, repeatedly washed with distilled
water and used as cell mass for inoculum development.
Inoculum was prepared in cotton stalk hydrolysate, sup-
plemented with 0.5 % yeast extract, 1% peptone and
pH was adjusted to 5.5 %. The yeast cells, harvested by
centrifugation were added in inoculum and incubated
on rotary shaker incubator with 150 rpm at 30 ºC for 24
h and grown aerobically to promote healthy growth of
yeast cells in hydrolysate and used as inoculum for fer-
mentation studies. Quanti cation of cell mass was per-
form by spread-plated method to ensure that each time
the inoculation stayed at approximately 6.0 × 10
7
cfu/mL
corresponding to 10 g dry w/L (Yadav et al., 2011).
FERMENTATION
The obtained hydrolysate was supplemented with 0.1%
yeast extract, peptone, NH
4
Cl, KH
2
PO
4
and 0.05% of
MgSO
4
.7H
2
O, MnSO
4
, CaCl
2
.2H
2
O, FeCl
3
.2H
2
O and ZnSO
4
in 250 mL asks, adjusting the pH 5.5 and autoclaved
at 110 ºC for 20 min (Pasha et al., 2007). Fermenta-
tion performed in semi aerobic mode of aeration (250
mL Erlenmeyer ask containing 150 mL of fermentation
medium), and was initiated by transferring separately
developed 10 % (v/v) co culture inoculum. Proportion of
Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Pachysolen tannophilus in
each inoculum was in the ratio of 60:40 respectively.
Flasks were sealed with aluminum foil and were allowed
to agitate with 120 rpm for rst 24 hours and then kept
in static mode at 30
o
C for 72 hours. Samples were with-
drawn at every 12 hours interval from separate ask for
the estimation of product formation, substrate utiliza-
tion and growth of cell mass (Baig, 2014).
ANALYTICAL METHODS
Sample obtained during fermentation was transferred
to pre weighted centrifuged tube and was centrifuged
at 10000 rpm for 10 min at 4
ºC. The supernatant was
collected and analyzed for concentration of ethanol
and residual sugars in broth while pellet was repeatedly
washed with distilled water and dried in hot air oven at
60
ºC till constant weight. The difference between ini-
tial and nal weight was recorded as cell biomass and
expressed in g/L (Oberoi et al., 2010). The DNSA method
of Miller, (1959) was adopted to quantify the amount
of reducing sugars. Glucose oxidase method was used
for glucose estimation (Bergmeyer et al., 1974). Total
content of phenolic was determined by Folin-Ciocalteus
(FC) method (Singleton and Rossi, 1965). Furans were
estimated by Martinez et al., (2000). Ethanol estima-
tion was carried out by Gas Chromatography (Shimadzu
Japan). GC was carried out according to NREL procedure
LAP # 011, using ZB-Wax column (30mm × 0.25mm)
with Flame Ionization Detector (FID). Cell density was
measured turbidometrically at 600 nm by using UV-VIS
spectrophotometer.
746 COMPARATIVE STUDY OF BIOETHANOL PRODUCTION BIOSCIENCE BIOTECHNOLOGY RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS
Mirza Zaheer Baig and Dharmadhikari Smita
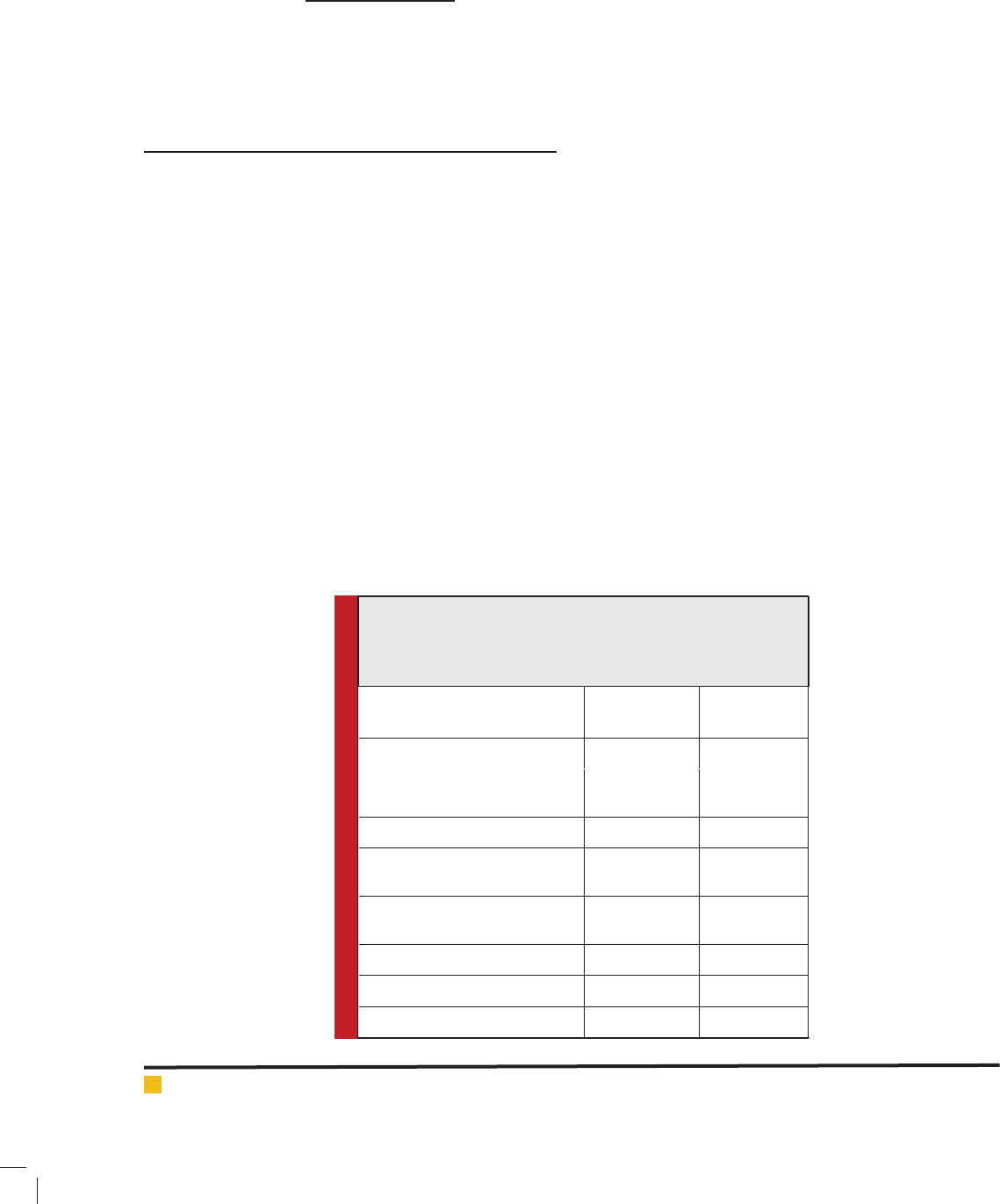
Table 1: Comparative performance of sugar yield and ethanol
fermentation obtained from acid and enzymatically hydrolyzed
cotton stalk by co-culture of Saccharomyces cerevisiae and
Pachysolen tannophilus
Comparative account Acid
hydrolysate
Enzyme
hydrolysate
Initial sugar conc. (g/L) 11.00 24.50
Initial sugar yield (g/g of biomass)
Ethanol concentration (g/L)
0.396
04.96
0.490
09.56
Ethanol yield (g/g of biomass) 0.179 0.191
Ethanol yield (g/g of
holocelluloses)
0.278 0.298
Ethanol yield (g/g of fermentable
sugar)
0.446 0.392
Fermentation ef ciency (%) 87.52 76.85
Sugar consumed (%) 93.84 97.81
Cell mass concentration (g/L) 08.06 12.20
FERMENTATION EFFICIENCY
Fermentation ef ciency was calculated as
Practical yield of ethanol
Fermentation ef ciency = x 100
Theoretical yield of ethanol
Theoretical yield is 0.511 gram per gram of sugar con-
sumed.
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
ACID HYDROLYSIS
The hydrolysis process yielded maximum fermentable
sugar and speci cally D-glucose of 0.49 g/g and 0.36
g/g of biomass (native cotton stalk) respectively (Baig,
2014). The obtained results were in agreement with
those of Liao et al., (2006). Byproducts of hydrolysis
such as furans and phenolics were also formed with a
concentration of 1.971 mg/L and 4.909 g/L respectively.
To overcome these inhibitors, detoxi cation with over
liming followed by charcoal treatment was applied on
hydrolysate. It gives maximum reduction in inhibitors
including 92.69% furans and 88.89% phenolics while
19.84% sugar losses were also reported during process
(Baig and Dharmadhikari, 2014). The detoxi ed hydro-
lysate achieved having sugar concentration of 11 g/L,
corresponds to a yield of 0.396 g/g of biomass was then
exposed to fermentation for ethanol production.
ENZYME HYDROLYSIS
The second set comprised of alkaline pretreatment and
enzymatic hydrolysis. Upon alkaline pretreatment,
lignin extraction from debarked cotton stalk was sig-
ni cantly achieved up to 80% (0.201 gram of lignin
per gram of biomass). Following pretreatment of cot-
ton stalk, the deligni ed solid residue was enzymatically
hydrolyzed via 100 CMC units of enzyme at substrate
loading of 10% (w/v); yielded total sugar of 0.49 g/g of
biomass, corresponds to a concentration of 24.5 g/L; as
was optimized in previous studies (Baig and Dharma-
dhikari, 2012). Similar ndings were also reported from
Silverstein et al., (2007).
COMPARATIVE ACCOUNT OF ETHANOL
PRODUCTION FROM ACID AND ENZYME
HYDROLYSATE
The sugar concentration obtained after acid and enzyme
hydrolysis of cotton stalk was 11 g/L and 24.5 g/L
respectively, which were kept constant in fermentation
broth and fermented separately. As the fermentation
started, during rst 6 hours of inoculum addition no
ethanol production could be detected in both the sets,
while it commenced from 12 hours onwards and steadily
increased up to 48 hours. It was found maximum at this
stage, where co-culture of Saccharomyces cerevisiae and
Pachysolen tannophilus in association utilized 93.84%
from acid hydrolysate and 97.81% from enzyme hydro-
lysate of total available sugars and produced ethanol of
BIOSCIENCE BIOTECHNOLOGY RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS COMPARATIVE STUDY OF BIOETHANOL PRODUCTION 747
Mirza Zaheer Baig and Dharmadhikari Smita
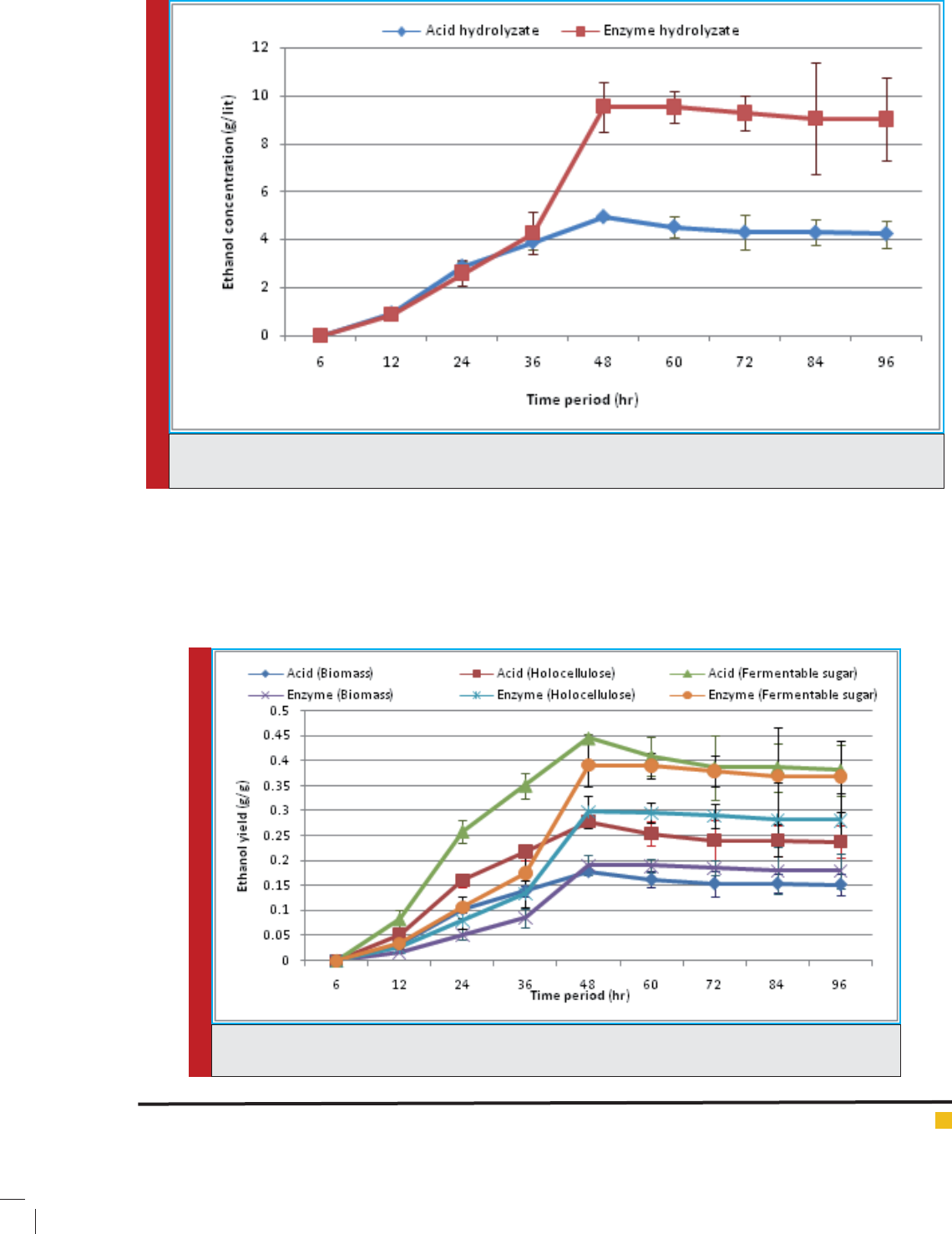
FIGURE 2. Comparative analysis of ethanol yield calculated from total biomass, holocelluloses and ferment-
able sugar available for fermentation respectively.
FIGURE 1 Comparative analysis of ethanol concentration obtained from acid and enzymatically hydrolyzed cotton stalk
using co culture of Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Pachysolen tannophilus.
4.96 g/L and 9.56 g/L in acid and enzyme hydrolysate
respectively.
The obtained yield from the fermentation contain-
ing acid hydrolysate was recorded as 0.179 g/g of bio-
mass (native cotton stalk), 0.278 g/g of holocelluloses
and 0.446 g/g of sugar available for fermentation. While
using enzyme hydrolysate; it was recorded as 0.191 g/g
of biomass (native cotton stalk), 0.298 g/g of holocellu-
loses and 0.392 g/g of sugar available for fermentation.
The ef ciency of fermentation containing acid hydro-
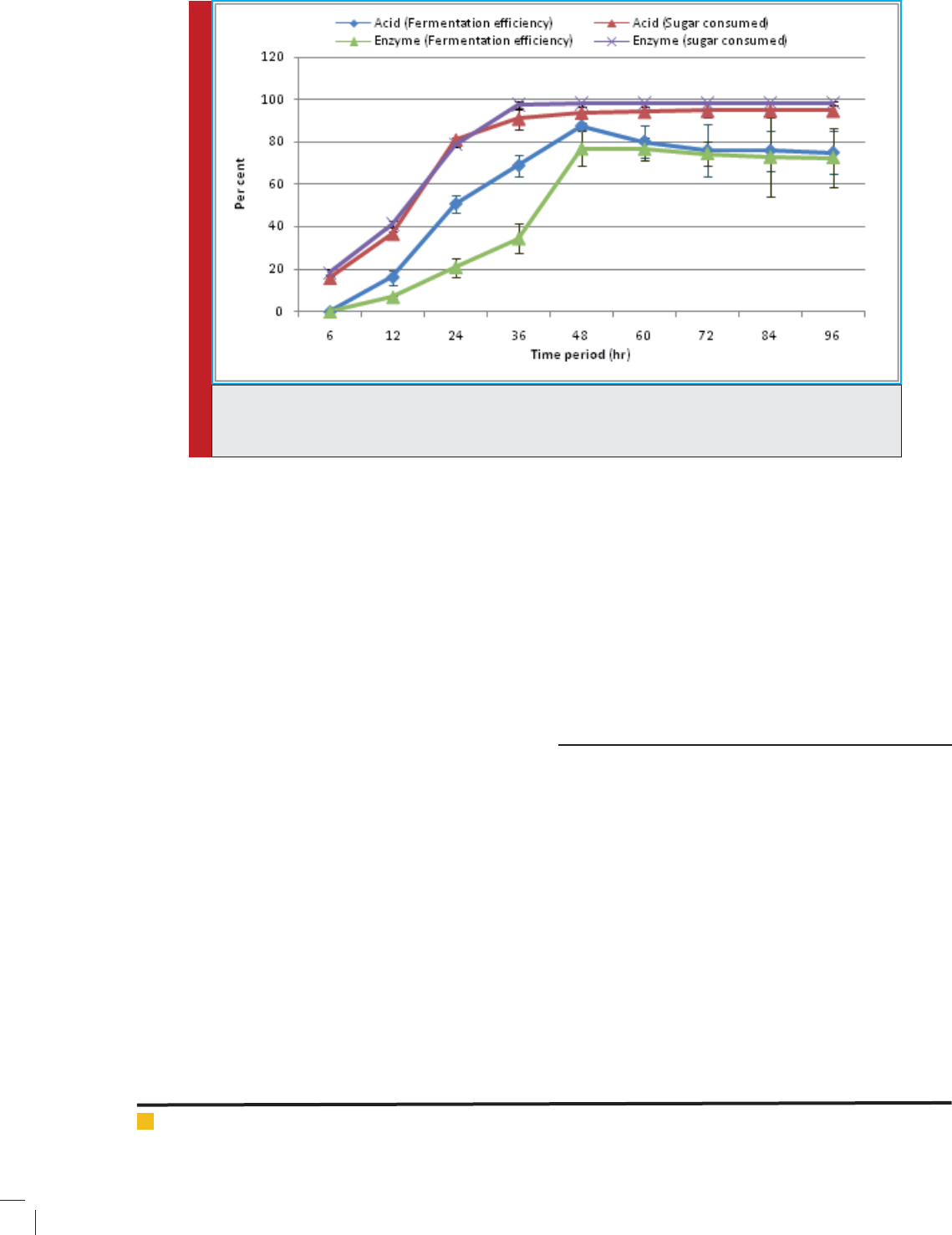
Mirza Zaheer Baig and Dharmadhikari Smita
748 COMPARATIVE STUDY OF BIOETHANOL PRODUCTION BIOSCIENCE BIOTECHNOLOGY RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS
lysate as carbon source was recorded as 87.52% while
with enzyme hydrolysate it shows 76.85%.
Comparative analysis showed that yield calculated
from total biomass (native cotton stalk) and holocellu-
loses found higher in fermentation of enzyme hydro-
lysate as compare to acid hydrolysate. In contrast to that,
Fermentation ef ciency and ethanol yield obtained from
available sugar for fermentation is signi cantly higher
in acid hydrolysate as compare to enzyme hydrolysate.
This might be due to high sugar concentration of enzy-
matically treated biomass compare to acid hydrolysate,
and traces of inhibitors (i.e. furans and phenolics) still
present in acid hydrolysate (even after detoxi cation),
which favors respiration mode (increased in cell mass
concentration) in enzyme hydrolysate over fermentation
(ethanol production).
In both the cases, sugars were effectively consumed by
yeast cultures but consumption rate was slightly higher
in enzyme hydrolysate as compared to acid hydrolysate,
the possible reason might be the presence of traces of
inhibitors even after detoxi cation. Such inhibitors were
not observed in enzyme hydrolysis; as it separately del-
igni ed by alkaline treatment and no harsh condition
developed during hydrolysis as was in acid hydrolysis,
as discussed earlier. As for sugar consumption pattern is
concern, no diauxy was observed in both the cases, as
both contained same types of sugar molecules. Simulta-
neously cell mass concentration was also increased up
to 36 hours of incubation and after that no signi cant
change was observed. It was found greater in enzyme
hydrolysate (12.20 g/L) compare to acid hydrolysate
(8.06 g/L), as sugar concentration was found to be
higher in fermentation of enzyme treated cotton stalk.
Our results are harmony with results reported earlier by
Gupta et al., (2009), who reported that fermentation of
both acid and enzymatic hydrolysates of prosopis juli-
ora, containing 18.24 g/L and 37.47 g/L sugars, with
Pichia stipitis and Saccharomyces cerevisiae produced
7.13 g/L and 18.52 g/L of ethanol with corresponding
yield of 0.39 g/g and 0.49 g/g, respectively.
CONCLUSION
This study could establish a successful comparison in
between acid and enzyme hydrolysis of cotton stalk in
order to achieve maximum sugar and ethanol yield. Fer-
mentation of enzyme hydrolysate was found to domi-
nate over acid hydrolysate. The difference in the ethanol
yield is due to initial sugar concentration, which in u-
enced the fermentation ef ciency. The fermentation pro-
cess gave maximum theoretical yield, but pretreatment
and sacchari cation process needs scienti c efforts to
make it more feasible and cost effective.
REFERENCES
Baig, M.Z., (2014). Studies on production of bioethanol from
cotton stalk (Ph.D. thesis), Dr. Babasaheb Ambedkar Marath-
wada University, Aurangabad, India.
FIGURE 3. Comparative analysis of ethanol concentration obtained from acid and enzymatically hydro-
lyzed cotton stalk using co culture of Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Pachysolen tannophilus Standard
deviation (SD) are presented in the form of error bars.

Mirza Zaheer Baig and Dharmadhikari Smita
BIOSCIENCE BIOTECHNOLOGY RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS COMPARATIVE STUDY OF BIOETHANOL PRODUCTION 749
Baig, M.Z., Dharmadhikari S. M., (2012). Optimization of pre-
treatment and enzymatic hydrolysis of cotton stalk. J of Pure
Appl Microbiol. 6(03): 1437-1441.
Baig, M.Z., Dharmadhikari, S.M., (2014). Optimization of
detoxi cation with over liming and charcoal treatment for
increasing the fermentability of cotton stalk hydrolysate. Ind J
of Appl Res. 4(07): 08-10.
Balat, M., Balat, H., Oz, C., (2008). Progress in bioethanol pro-
cessing. Prog Energ Combust. 34: 551-573.
Baptista, C.M.S.G., Colas, J.M.A., Oliveira, A.C.M., Oliveira, N.M.C.,
Roche, J.M.C., Dempsey, M.J., Lannigan, K.C., Benson, P.S., (2006).
Natural immobilization of microorganism for continuous ethanol
production. Enzyme Microb Technol. 40: 127-131.
Behera, S., Kar, S., Mohanty, R.C., Ray, R.C., (2010). Compara-
tive study of bioethanol production from mahula (Madhuca
latifolia L.) owers by Saccharomyces cerevisiae cells immo-
bilized in agar agar and Ca-alginate matrices. Appl Energy.
87:96-100.
Bregmeyer, H.U., Gawehn, K., Grassl, M., (1974). Methods of
enzymatic analysis (Bregmeyer, H.U., ed) academic press Inc.,
New York. 1(2): 457-458.
Chandel, A.K., Kapoor, R.K., Singh, A., Kuhad, R.C., (2007).
Detoxi cation of sugarcane bagasse hydrolyzate improves
ethanol production by Candida shehatae NCIM 3501. Bioresour
Technol. 98: 1947-1950.
Gupta, R., Sharma, K.K., Kuhad, R.C., (2009). Separate hydrol-
ysis and fermentation (SHF) of Prosopis juli ora, a woody
substrate, for the production of cellulosic ethanol by Saccha-
romyces cerevisiae and Pichia stipitis-NCIM 3498. Bioresour
Technol. 100: 1214-1220.
Kaur, U., Oberoi, H.S., Bhargav, V.K., Sharma-Shivappa, R.R.,
Dhaliwal, S.S. Ethanol production from alkali and ozone
treated cotton stalk using thermo tolerant Pichia kudriavzevii
HOP-1. Ind. Crop. Prod., 2012; 37: 219-226.
Liao, W., Liu, Y., Liu, C., Wen, Z., Chen, S., (2006). Acid hydrol-
ysis of ber from dairy manure. Bioresour Technol. 97: 1687-
1695.
Martinez, A., Rodriguez, M.E., York, S.W., Preston, J.E., Ingram,
L.O., (2000). Effect of Ca(OH)
2
treatments (“overliming”) on the
composition and toxicity and bagasse of hemicellulose hydro-
lysate. Biotechnol Bioeng. 69: 526-536.
Miller, G.L., (1959). Use of dinitrosalicylic acid reagent for
determination of reducing sugars. Anal chem. 31: 426-428.
Mosier, N., Wyman, C., Dale, B., Elander, R., Lee, Y.Y., Holtzap-
ple, M., Ladish, M., (2005). Features of promising technologies
for pretreatment of lignocellulosic biomass. Bioresour Technol.
96 (6): 673-686.
Oberoi, H.S., Vadlani, P.V., Madl, R.L., Saida, L. Abeykoon.
J.P., (2010). Ethanol production from orange peels: two-stage
hydrolysis and fermentation studies using optimized param-
eters through experimental design. J Agric Food Chem. 58:
3422-3429.
Pasha, C., Kuhad, R.C., Rao, L.V., (2007). Strain improvement of
thermo tolerant Saccharomyces cerevisiae VS3 strain for better
utilization of lignocellulosic substrates. J Appl Micro biol. 103:
1480-1489.
Sharma, N., Kalra, K.L., Oberoi, H.S., Bansal, S., (2007). Opti-
mization of fermentation parameters for production of etha-
nol from kinnow wastes and banana peels by simultaneous
sacchari cation and fermentation. Ind J Microbiol. 47: 310-
316.
Silverstein, R.A., Chen, Y., Sharma-Shivappa, R.R., Boyette,
M.D., Osborn, J.A., (2007). A comparison of chemical pre-treat-
ment methods for improving sacchari cation of cotton stalks.
Bioresour Technol. 98: 3000-3011.
Singleton, V.L., Rossi, J.A., (1965). Colorimetric of total pheno-
lics with phosphomolybdic-phosphotungstic acid reagents. Am
J Enol Viticult. 16: 144-158.
Sun, Y., Cheng, J., (2002). Hydrolysis of lignocellulosic mate-
rial for ethanol production: a review. Bioresour Technol. 83:
1-11.
Sohail, M., Siddiqi, R., Ahmad, A., and Khan, S.A., (2009). Cel-
lulases production from Aspergillus niger MS82: effect of tem-
perature and pH. N Biotechnol. 25: 437-441.
Yadav S., K., Naseeruddin, S., Prashanthi, G.S., Sateesh, S., Rao,
L.V., (2011). Bioethanol fermentation of concentrated rice straw
hydrolyzate using co-culture of Saccharomyces cerevisiae and
Pichia stipites. Bioresour Technol. 102(11): 6473-6478.
Teramoto, Y., Lee, S-H, Endo, T., (2008). Pretreatment of woody
and herbaceous biomass for enzymatic sacchari cation using
sulfuric acid-free ethanol cooking. Bioresour Technol. 99:
8856-8863.
Tolan, J.S., Foody, B., (1999). Cellulases from submerged fer-
mentation. Adv Biochem Eng Biotechnol. 65: 41-67.
USDA. United State Department of Agriculture, World Agricul-
tural Supply and Demand Estimate, October 9, 2015.