Medical
Communication
Biosci. Biotech. Res. Comm. 9(4): 737-742 (2016)
A sociological study of self-medication
among 18-50 year-old people in Ahvaz
Ali Hossein Hosseinzadeh
1
, Abdoreza Navah
1
, Mehrnaz Mohammaedzadeh
2
, Fereidoon
Naja Shabankareh
2
and Maryam Ghanavati
1
1
Department of Social Sciences of Shahid Chamran University, Ahvaz, Iran
2
Research Attaris Expert, Ahvaz Jundishapur University of Medical Sciences, Ahvaz, Iran
ABSTRACT
Self-medication is one of the problems encountered in treatment cycles. Unfortunately, given the prevailing social
perception of medicine as a safe and healing substance, the problem of self-medication not only seems inevita-
ble, but it should also be considered a social pathology. Thus, the present study was aimed at identifying the fac-
tors associated with indiscriminate use of drugs among 18-50 year-old citizens in Ahvaz. The present research
is a descriptive cross-sectional study conducted as a survey in 2013. Cluster random sampling was used to select
229 citizens of Ahvaz aged between 18 and 50 years as the sample. The required data were collected through a
questionnaire accompanied by an interview. Research ndings showed that diazepam pills and cold tablets had
the highest frequency of consumption among the statistical population. Acetaminophens and antihistamines were
ranked next. The ndings also indicated that awareness of the consequences of drug use, awareness of drug use
practices, public health level, and age had signi cant relationships with self-medication. Society’s unawareness and
common misconceptions and false beliefs among the public (drug use culture) are the most important reasons for
irrational and indiscriminate use of drugs in Iran, as compared to the global standards. Correcting wrong drug use
practices, especially self-medication, requires comprehensive public education and culture-building at the societal
level.
KEY WORDS: SELF-MEDICATION, SELF-TREATMENT, DRUG
737
ARTICLE INFORMATION:
*Corresponding Author: Naja -f@ajums.ac.ir
Received 13
th
Sep, 2016
Accepted after revision 25
th
Nov, 2016
BBRC Print ISSN: 0974-6455
Online ISSN: 2321-4007
Thomson Reuters ISI ESC and Crossref Indexed Journal
NAAS Journal Score 2015: 3.48 Cosmos IF : 4.006
© A Society of Science and Nature Publication, 2016. All rights
reserved.
Online Contents Available at: http//www.bbrc.in/

738 A SOCIOLOGICAL STUDY OF SELF-MEDICATION AMONG 18-50 YEAR-OLD PEOPLE IN AHVAZ BIOSCIENCE BIOTECHNOLOGY RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS
Ali Hossein Hosseinzadeh et al.
INTRODUCTION
Medicine and its various branches are aimed at main-
taining and improving public health level and help-
ing patients regain their health. These goals are realized
through a series of factors. Provision, distribution and
consumption of drugs are among the keys to achieving
this goal(Afkar, 2006). In fact, drug use, as one of the
links of the treatment chain, is inevitable. Medical experts
believe that accurate and systematic use of drugs can lead
to patient recovery in many cases. Today, scienti c and
industrial advancements in medical and pharmaceuti-
cal elds have provided access to a wide range of drugs.
Unsystematic access to drugs can cause many problems
such as indiscriminate and improper use of drugs(Arab
et al., 2014; Dejman et al., 2015). As deduced from the
discussions, drug use is linked to all cultural, social and
ideological aspects of society. Unfortunately, society only
perceives drugs as safe and healing substances, while the
medical literature considers any drug as a double-edged
sword. One edge of the sword ghts with the causes of
disease and the other one can put human health at risk
due to the lack of awareness regarding the correct use of
the drug(Moghadam Nia and Ghadimi, 2000).
Currently, self-medication and improper use of drugs
is considered as one of the major healthcare problems in
many countries, especially Iran(Bennadi, 2014; Mogh-
adam Nia and Ghadimi, 2000). The ndings of studies
conducted in various countries, including Iran, are indic-
ative of a high prevalence of self-medication and irra-
tional use of drugs. According t o the statistics provided
by the U.S. National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA), the
prevalence rate of self-medication has increased from
22.1% in 2002 to 32.71% in 2003 (Awad et al., 2008).
Furthermore, the prevalence rates of self-medication in
Bangladesh, Tanzania, Nigeria, and Nepal were reported
81%, 56%, 63%, and 75%, respectively (Mortazavi and
Hajebi, 2003)|.
Given Iran’s consumption culture, the country’s sit-
uation regarding irrational use of drugs is more criti-
cal. According to the latest statistics, Iran’s prevalence
rate of self-medication is almost three times the global
average rate. Thus, Iran is ranked the twelfth country
with the highest prevalence rate of self-medication in
the world. In Asia, It is ranked number two only after
China(Moghadam Nia and Ghadimi, 2000; Mortazavi
and Hajebi, 2003; Persell, 2011). The attempts made to
adjust Iran’s pattern of drug use have failed to bring
success and the country’s pharmaceutical system is still
faced with the problem of improper and indiscriminate
use of drugs and self-medication. This has caused bac-
terial resistance, failure of optimal treatment, uninten-
tional poisoning, unintended side effects and compli-
cations, pharmaceutical market disruption, nancial
loss, and an increase in pharmaceutical expenditure per
capita in Iran(Sattari et al., 2012). Adjusting Iran’s pat-
tern of drug use and developing appropriate healthcare
policies aimed at preventing the increasing prevalence
of self-medication requires, in the rst place, a detailed
understanding of the factors in uencing the consump-
tion behavior of individuals and scienti c explanation
of the phenomenon.
METHODS
This research was a descriptive-survey study. The statis-
tical population consisted of all 18-50 year-old citizens
who had visited 24-hour pharmacies in Ahvaz. The indi-
viduals would be considered in the study if they were
older than 18 years, at least literate and willing to par-
ticipate. The data collection tool was a researcher-made
questionnaire. The questionnaire consisted of two parts.
The rst part dealt with demographic characteristics,
including gender, marital status, age, education, and job.
The second part covered research. The variables were
evaluated based on 40 items and a ve-point Likert scale
(very high, high, medium, low, very low).
The questionnaire’s face and content validities were
measured. Accordingly, the questionnaire was prepared
based on the credible sources and books on the sub-
ject and presented to two experienced scholars in the
elds of social and cultural studies for approval. Upon
approval, 40 questionnaires were distributed among the
population. Next, faculty members (from different uni-
versities) with adequate experience and expertise reeval-
uated the results obtained through completed question-
naires. Their comments and corrections were applied to
the questionnaire. Ultimately, the questionnaire’s valid-
ity was con rmed. Cronbach’s alpha coef cient was
used to measure the questionnaire’s reliability. The value
of alpha was 0.814. Therefore, the questionnaire had an
appropriate degree of reliability. Frequency, percentage
and mean values (descriptive statistics), Pearson’s cor-
relation coef cient, Spearman’s correlation coef cient,
and analysis of variance (ANOVA) (inferential statistics)
were used to analyze the collected data.
RESULTS
According to the descriptive statistics, the sample con-
sisted of 94 females (41%) and 135 males (59%). Of the
229 residents, 109 individuals were married (47.59%),
86 were single (37.55%), and 34 were divorced (14.88%).
Frequency distributions of other demographic variables
are shown in the demographic variables table (Table 1).
The ndings showed that more than 92% of respond-
ents had practiced self-medication at least once last year.
BIOSCIENCE BIOTECHNOLOGY RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS A SOCIOLOGICAL STUDY OF SELF-MEDICATION AMONG 18-50 YEAR-OLD PEOPLE IN AHVAZ 739
Ali Hossein Hosseinzadeh et al.
In addition, 34% of respondents had visited pharmacies
to buy drugs without a prescription. The prevalence of
self-medication was highest (35.4%) in the 30-49 age
group. The lowest prevalence of self-medication (7.2%)
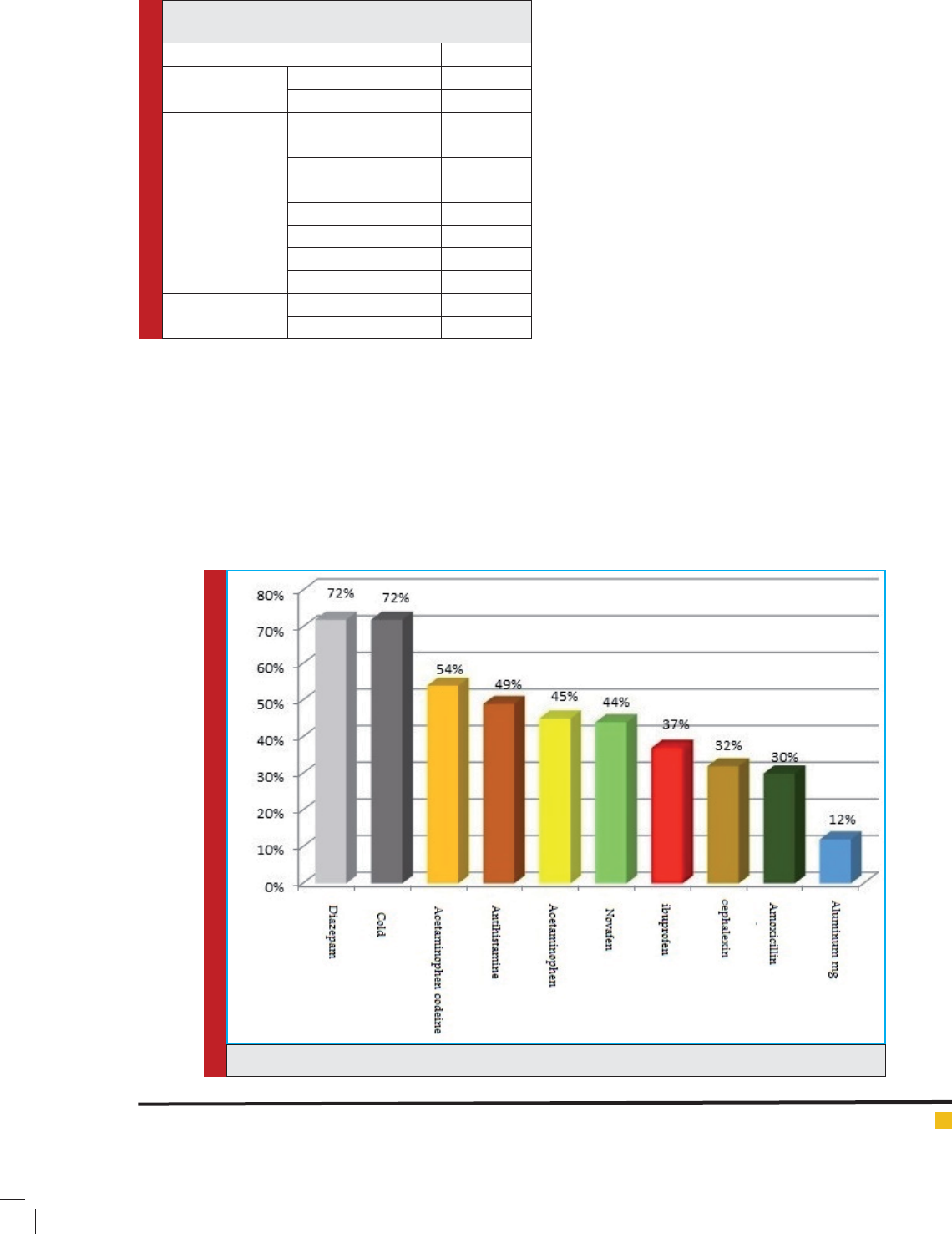
was seen among teenagers (18-20 age group). Diaz-
epam pills and cold tablets had the highest frequency
of consumption among the statistical population. Aceta-
minophens and antihistamines were ranked next and
Magaldtrate suspension had the lowest frequency of
consumption (Figure 1).
In the inferential statistics section, Pearson’s corre-
lation coef cient was used to test research hypotheses.
As shown in Table 2, awareness of the consequences of
drug use, awareness of drug use practices, public health
level, and age had signi cant relationships with self-
medication. The relationship between self-medication
and awareness of the consequences of drug use is nega-
tive. In other words, an increase in awareness of the
consequences of drug use leads to a decrease in self-
medication. The relationship between age and self-med-
ication is positive, meaning self-medication increases
with age (Table 2).
As education is an ordinal variable, Spearman’s cor-
relation coef cient was used to test the related hypoth-
esis. The results showed that there was a signi cant
relationship between education and self-medication.
The relationship was very strong and negative, i.e., self-
medication decreased with education level (Table 3). In
addition, the results showed that no signi cant relation-
ship was found between gender, marital status, and job
of the respondents and self-medication.
Table 1: Distribution of demographic variables of
population
Variable Number Percent
Gender
Female 94 41%
Male 135 59%
Marital status
Married 109 47.60%
Single 86 37.56 %
Divorced 34 14.84
Education level elementary 39 17.03%
Junior 44 19.21%
Diploma 105 45.85%
Bachelor 22 9.61%
Graduate 19 8.30%
Employment status Practitioner 58 25.33%
Jobless 171 74.67%
FIGURE 1. Diagram of used drugs
740 A SOCIOLOGICAL STUDY OF SELF-MEDICATION AMONG 18-50 YEAR-OLD PEOPLE IN AHVAZ BIOSCIENCE BIOTECHNOLOGY RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS
Ali Hossein Hosseinzadeh et al.
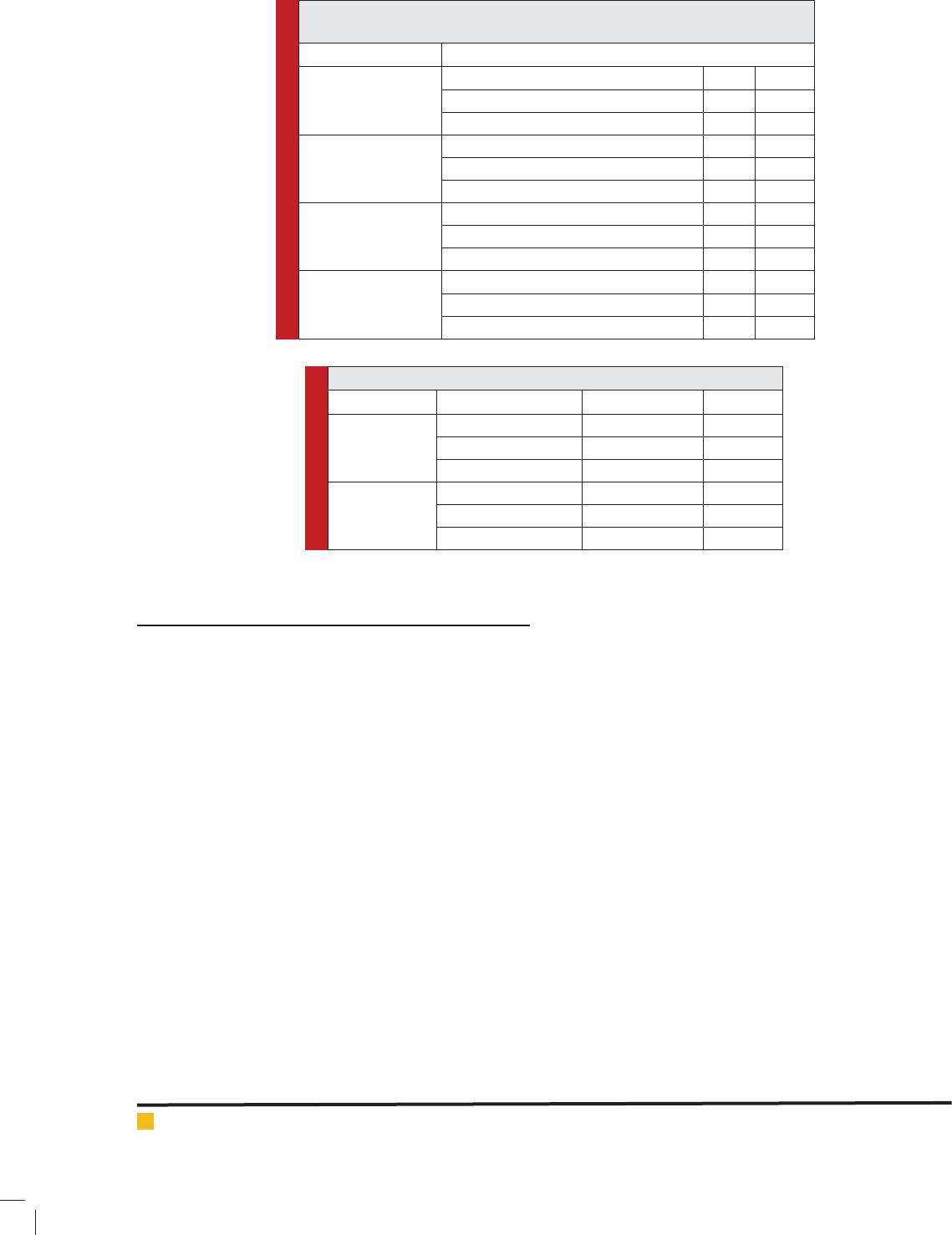
Table 2: The relationship between awareness of the consequences of drug use,
awareness of drug use practices, Public health level and age
Variable Data interpretation
awareness of the
consequences of drug
use
The pearson correlation coef cient 1 -0.206
Signi cant level 0 0.002
Number 229 229
awareness of drug use
practices
The pearson correlation coef cient 1 -0.147
Signi cant level 0 0.026
Number 229 229
Public health level
The pearson correlation coef cient 1 -0.152
Signi cant level 0 0.021
Number 229 229
Age
The pearson correlation coef cient 1 -0.170
Signi cant level 0 0.010
Number 229 229
Table 3: The relationship between Education level and Drug use
Data interpretation Education level Drug use
Education level
correlation coef cient 1000 -0.189**
Signi cant level 0 0.004
Number 229 229
Drug use
correlation coef cient -0.189** 1000
Signi cant level 0.004 0
Number 229 229
DISCUSSION
According to the ndings of the present study, the fol-
lowing drugs had respectively the highest percentage
of consumption among the respondents: diazepam,
cold tablets, acetaminophen-codeine, antihistamines,
Novafen, ibuprofen, cephalexin, and amoxicillin. Drugs
such as diazepam and lorazepam depress the central
nervous system. Although rational prescription of such
drugs by a physician has the desired effects on the
recovery of patients, indiscriminate and irrational use
of them can be very destructive(Buusman et al., 2007).
Given the pain-relieving properties and hypnotic effects
of these drugs, individuals will be more inclined to use
them over time and eventually become physically and
mentally dependent on them(Gunja, 2013).
Cold tablets are one of the drugs that are very widely
used for self-medication in Ahvaz. The results of new
studies published in the Journal of Pediatrics shows that
cold tablets can cause apnea (shortness of breath) in
children. In January 2008, U.S. Food and Drug Asso-
ciation (FDA) strictly prohibited over-the-counter cold
and cough medicines for children who are under age
two(Asta; Food and Administration, 2013)
Acetaminophens are one of the most commonly used
drugs in Iran. Most people take acetaminophens for
the slightest feeling of pain. Despite society’s percep-
tion of acetaminophens as simple and safe substances,
long-term use of these drugs can cause poisoning, which
in turn might lead to liver and kidney failure. In addi-
tion, use of codeine-based drugs and narcotic analge-
sic combinations can cause physical dependence over
time(Noshad et al., 2010).
From the pathological point of view, the results of
the present research indicated that there was a signi -
cant relationship between the awareness of the con-
sequences of drug use and self-medication. It seems
that Iranians’ mental image of drugs as safe and heal-
ing substances plays an important role in their drug
consumption behavior and self-medication practices
because many respondents believed that drugs used
for self-medication do not have signi cant side effects.
Selling of over-the-counter drugs by pharmacies has
also endorsed the aforementioned false belief. These
results are consistent with the results of two studies
conducted by Mohammadi et al. (2010) and Karimy
et al. (2010) (Al-Mohamadi et al., 2013; Karimy et al.,
2011).

BIOSCIENCE BIOTECHNOLOGY RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS A SOCIOLOGICAL STUDY OF SELF-MEDICATION AMONG 18-50 YEAR-OLD PEOPLE IN AHVAZ 741
Ali Hossein Hosseinzadeh et al.
Naturally, drug use increases with age. Unfortu-
nately, self-medication and indiscriminate use of drugs
also tend to increase with age. Financial impotence and
physical disability are among the factors that contribute
to self-medication among the elderly(Azami-Aghdash et
al., 2015). Education was another variable that had a
signi cant relationship with indiscriminate use of drugs
and self-medication. Increase in the level of education
will not affect self-medication and indiscriminate use
of drugs in itself(Machado-Alba et al., 2014). Educa-
tion acts more like a mediator variable. Individuals with
a higher level of education are more aware and adopt
better decisions when faced with problems, diseases,
etc(Azami-Aghdash et al., 2015).
Although ndings showed not signi cant relation-
ships between the respondents’ gender, martial status,
and job and self-medication, the results indicated that
females, married people and employed individuals prac-
tice self-medication more frequently than males, sin-
gle people and unemployed individuals. Unemployed
females show a stronger tendency towards use of tradi-
tional drugs and home remedies.
CONCLUSION
The problem of self-medication and indiscriminate use
of drugs has become a culture in the Iranian society and
is widely prevalent in the country. Unaware of the dire
consequences of self-medication for their health, many
people are very careless in using unprescribed drugs.
Society’s unawareness and common misconceptions and
false beliefs among the public (drug use culture) are the
most important reasons for irrational and indiscriminate
use of drugs in Iran, as compared to the global stand-
ards. Correcting wrong drug use practices, especially
self-medication, requires comprehensive public educa-
tion and culture-building at the societal level. Pharma-
ceutical macro-plans and policies should change direc-
tion so that intervention measures can be taken in order
to minimize the underlying factors of drug abuse and
use of harmful drugs. These measures include: (1) limit-
ing society’s unconditional access to drugs (2) educating
people on the rational use of drugs and restricting the
amount and type of drugs stored at home, (3) improving
the quality of health and medical services and increas-
ing public access to healthcare delivery system, and (4)
instructing people on how to use and store drugs (by
physicians and pharmacists).
AUTHORS CONTRIBUTIONS
All authors had equal role in design, work, statistical
analysis and manuscript writing.
Con ict of interest
The authors declare no con ict of interest.
FUNDING/ SUPPORT
This study was nancially supported by grant U-95071
from the Ahvaz Jundishapur University of Medical Sci-
ences, Ahvaz, IR Iran
REFERENCES
Afkar, A., 2006. System of provision, distribution, maintenance,
control and drug consumption in teaching hospitals of Rasht.
Journal of Guilan university of medical sciences 15, 81-86.
Al-Mohamadi, A., Badr, A., Mahfouz, L.B., Samargandi, D., Al
Ahdal, A., 2013. Dispensing medications without prescription
at Saudi community pharmacy: Extent and perception. Saudi
Pharmaceutical Journal 21, 13-18.
Arab, M., Torabipour, A., Rahimifrooshani, A., Rashidian, A.,
Fadai, N., Askari, R., 2014. Factors affecting family physicians’
drug prescribing: a cross-sectional study in Khuzestan, Iran.
International journal of health policy and management 3,
377.
Awad, A., Al-Rabiy, S., Abahussain, E., 2008. Self-medication
practices among diabetic patients in Kuwait. Medical Princi-
ples and Practice 17, 315-320.
Azami-Aghdash, S., Mohseni, M., Etemadi, M., Royani, S.,
Moosavi, A., Nakhaee, M., 2015. Prevalence and Cause of Self-
Medication in Iran: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Article. Iranian Journal of Public Health 44, 1580.
Bennadi, D., 2014. Self-medication: A current challenge. Jour-
nal of basic and clinical pharmacy 5, 19.
Buusman, A., Andersen, M., Merrild, C., Elverdam, B., 2007.
Factors in uencing GPs’ choice between drugs in a therapeutic
drug group. A qualitative study. Scandinavian journal of pri-
mary health care 25, 208-213.
Dejman, M., Vameghi, M., Roshanfekr, P., Dejman, F., Ra ey,
H., Forouzan, A.S., Assari, S., Bass, J., Johnson, R.M., 2015.
Drug Use among street children in Tehran, Iran: a Qualitative
study. Frontiers in public health 3.
Food, U., Administration, D. 2013. OTC cough and cold products:
not for infants and children under 2 years of age (Accessed).
Gunja, N., 2013. The clinical and forensic toxicology of
Z-drugs. Journal of Medical Toxicology 9, 155-162.
Karimy, M., Heidarnia, A., Ghofranipour, F., 2011. Factors
in uencing self-medication among elderly urban centers in
Zarandieh based on Health Belief Model.
Machado-Alba, J.E., Echeverri-Cataño, L.F., Londoño-Builes,
M.J., Moreno-Gutiérrez, P.A., Ochoa-Orozco, S.A., Ruiz-Villa,
J.O., 2014. Social, cultural and economic factors associated
with self-medication. Biomédica 34, 580-588.
Moghadam Nia, A., Ghadimi, R., 2000. Self-medication of
patients with common cold among 15-45 year old individuals,
Babol, 1998. J Babol Univ Med Sci 2, 26-32.

Ali Hossein Hosseinzadeh et al.
742 A SOCIOLOGICAL STUDY OF SELF-MEDICATION AMONG 18-50 YEAR-OLD PEOPLE IN AHVAZ BIOSCIENCE BIOTECHNOLOGY RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS
Mortazavi, S., Hajebi, G., 2003. The knowledge of referrers
to Tehran pharmacies of OTC drugs requested. Journal of
Research In Medical Sciences 27, 299-304.
Noshad, H., Sadreddini, S., Etemadi, J., 2010. Acetaminophen
Self-Poisoning: Suicidal and Accidental. Iranian Journal of
Psychiatry and Behavioral Sciences 4, 47-52.
Persell, S.D., 2011. Prevalence of resistant hypertension in the
United States, 2003–2008. Hypertension 57, 1076-1080.
Sattari, M., Dilmaghanizadeh, M., Hamishehkar, H., Mash-
ayekhi, S.O., 2012. Self-reported use and attitudes regarding
herbal medicine safety during pregnancy in Iran. Jundishapur
Journal of Natural Pharmaceutical Products 7, 45.