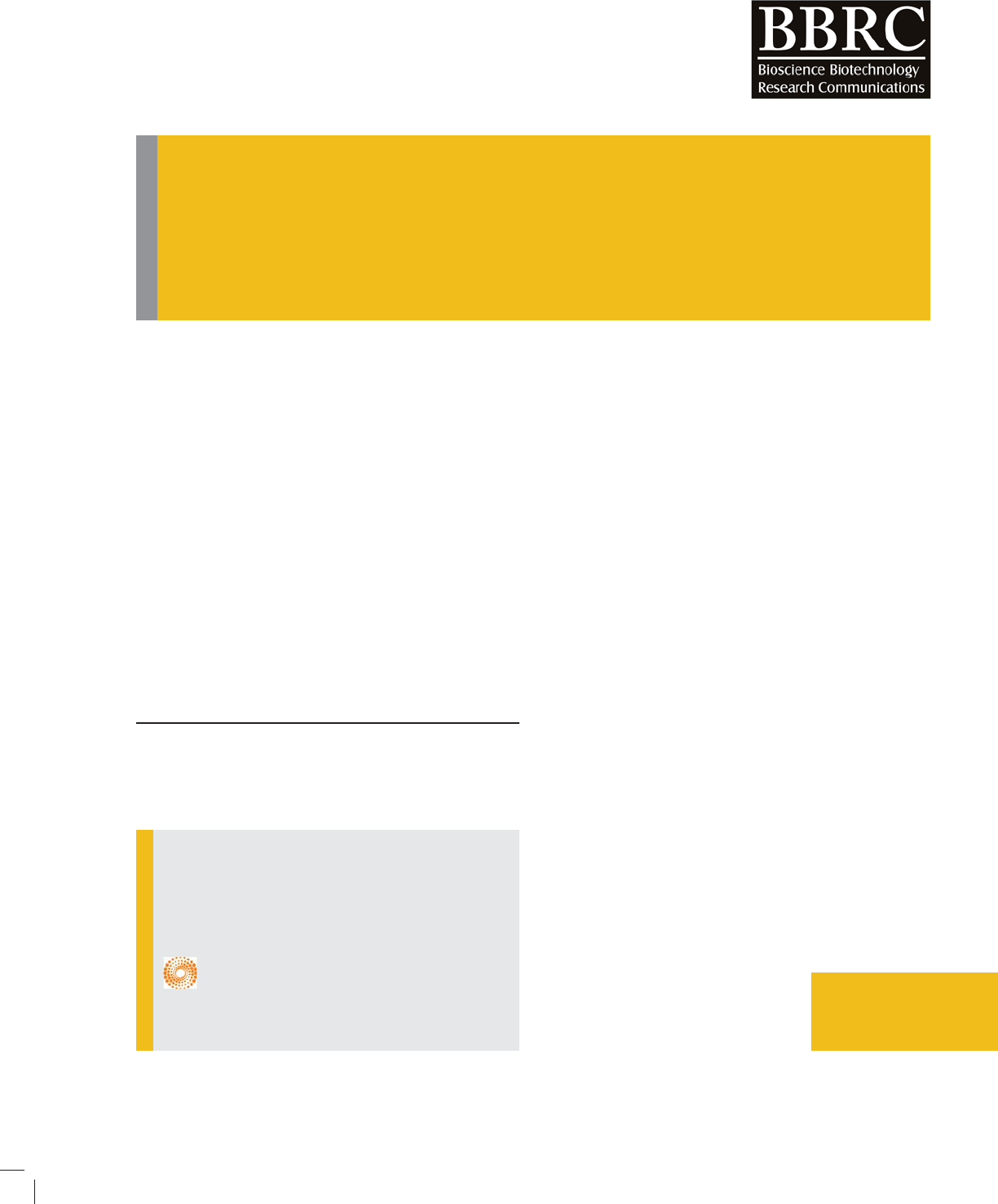
Biotechnological
Communication
Biosci. Biotech. Res. Comm. 9(4): 625-632 (2016)
Biokinetic modeling for aerobic treatment of aqueous
phase of oil-water emulsion
Alireza Nazari Alavi
1
*, Mohammad Mirzai
1
, Ali Akbar Sajadi
1
and Hamed Hasanian
2
1
Institute of Water and Energy, Sharif University of Technology, P.O. Box 11155-8639, Tehran, I.R. Iran
2
Faculty of Environment, University of Tehran, P.O. Box 14155-6135, Tehran, I.R. Iran
ABSTRACT
Discharge of used cutting oil (oil-water emulsion) to the environment is not allowed without proper treatment.
Usually, more than 90% of oil-water emulsion used in machine shop wastes is water. After separation of oil from
water, further treatment of aqueous phase could be carried out by biological methods. In this paper, an experimental
method is developed in a batch reactor. The ratio of initial substrate to the initial biomass concentration is adjusted to
be between 0.9< S0/X0 <10. Biomass concentration, COD, nutrient (nitrogen & phosphor) and suspended solid were
determined for different ratio of S0/X0. The achieved data were applied to determination of kinetic model parameters.
These parameters can be used in designing treatment plants of oil-water emulsions. In this paper, mathematical model
based on live biomass is used for simulation of experimental data from biological treatment of oil-water emulsion in
aqueous phase. Newton numerical method is selected for determination of model’s parameters. Results show adjust-
ment of presented model with experimental data. According to the results, constant parameters of speci c growth
rate and conversion rate of substrate to biomass are determined. Achieved results are in a good accordance with the
Monod model and it strongly supports that aqueous phase of oil-water emulsion has a suitable capability of biologi-
cal treatment.
KEY WORDS: BIOLOGICAL TREATMENT; OIL-WATER EMULSION; AQUEOUS PHASE; MODELING
625
ARTICLE INFORMATION:
*Corresponding Author: alavi@sharif.edu
Received 1
st
Nov, 2016
Accepted after revision 25
th
Dec, 2016
BBRC Print ISSN: 0974-6455
Online ISSN: 2321-4007
Thomson Reuters ISI ESC and Crossref Indexed Journal
NAAS Journal Score 2015: 3.48 Cosmos IF : 4.006
© A Society of Science and Nature Publication, 2016. All rights
reserved.
Online Contents Available at: http//www.bbrc.in/
INTRODUCTION
Water is used in almost all industries and is converted
to waste water. Usually it should be treated to the stand-
ard level before discharging to the environment or reus-
ing. Emulsion system is generated in widespread type
of industries such as cosmetics, pharmaceutics, biologi-
cal systems, petroleum plants, food industries. Cutting
oil waste water is generated in machine shop wastes
consists of an emulsion of oil and water (O/W). Main

626 TREATMENT OF OIL-WATER EMULSION BIOSCIENCE BIOTECHNOLOGY RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS
Alireza Nazari Alavi et al.
functions of this cutting oil are lubrication, friction
reduction and cooling of mechanical parts. This waste
water is classi ed as a toxic waste due to existence of
some additive material used for corrosion prevention as
well as bacterial growth. Treatment of this waste water
is a special problem for industries located inside cit-
ies and towns. Importance of treatment of such oil and
wastewater increases due to sewage collection network
de ciencies especially in developing countries, (Arif n
et al 2016).
Rheological behavior investigation of O/W emulsions
has been carried and it was found that viscosities of
emulsion and also the stability of emulsions are strongly
affected by shear rate, temperature, water contents,
interfacial tensions and particles nature O/W emulsions
are thermodynamically unstable and breaking down the
emulsion (separation of water and oil) which normally
consist 1-10% oil and the rest water, enables the biologi-
cal treatment of aqueous phase. The biological treatment
of aqueous phase in machine shop wastes could be car-
ried out similar to the procedure reported for treatment
of agro-industries wastes, such as ef uent from olive
mills which constitutes a serious environmental prob-
lem especially in the Mediterranean Sea region (Mant-
zavinos & Kalogerakis 2005, Berton-Carabin et al. 2014,
Ahmadi-Dastgerdi et al. 2015, and Arif n et al. 2016).
Importance of cutting oil wastewater treatment is
reported in many recent studies. Prediction the rate of
pollutants removal from aqueous solutions is neces-
sary in order to design a treatment plant (Souza et al.
2016). Biodegradability of oil-water emulsion is under
the question due to high pollution (COD=60g/l) and also
presence of undesirable material such as antibacterial
material in the emulsion and it has led the research-
ers to use physicochemical processes such as membrane
separation (reverse osmosis\ultra ltration) (Portela et al.
2001, Hadj et al. 2004), electro coagulation hydrother-
mal oxidation (Deepak et al., 1994, Sanchez et al. 2007)
and using nanoparticles. Other researchers have also
reported biological treatment application for solving this
environmental concern (Krstic et al., 2007, Hesampour
et al. 2008, Kobya et al. 2008, Rios et al. 1998, Rella et
al. 2003, Bensadok et al. 2007, Abdel-Aziz et al. 2016),
Kalliola et al. 2016).
Biodegradability of wastewater in a batch reactor
were evaluated to show its ef ciency, i.e., for investi-
gation of biodegradable material such as nitrate (Kris-
tensen et al. 1992), soluble organic carbon (Servais et al.
1987) and bacterial counting (Munch & Pollard 1997).
Quality and progress rate in a batch reactor is con-
trolled by ratio of initial substrate (S
o
) according to COD
or BOD to initial biomass concentration (X
0
) according
to MLVSS or MLSS (Chudoba et al., 1992, Spanjers &
Vanrolleghem 1995, Kappeler & Gujer 2005).
Low quantity of S
0
/X
0
usually makes microorganism’s
growth investigation impossible, on the other hand at
higher quantities of (S
0
/X
0
>1) microorganism’s growth
will be measurable and it can be used in explanation
of experimental results and modeling of reaction rate
(Wentzel et al. 1995).Veri cation of biological treat-
ment in this region develops results to the conventional
systems similar to SBR with so many advantages have
reported about its function (Irvine et al. 1983). One of
the major advantages of SBR systems is the ability to
treat wastewaters with varying organic loadings with
different ratios of S
0
/X
0
(Jamrah & Abu-Ghunmi 2005).
Since having a sedimentation tank is not required in this
process, therefore, it is suitable for use in small scale
industries located inside of towns.
Concentrations of substrate in in uent and in out-
ow as well as retention time are important keys in per-
formance of activated sludge process. These data often
are suf cient to produce simple models like Monod.
However for models with complicated concepts, it is
necessary to study more about other factors like as inhi-
bition effect. It is known that Inhibition can affect mass
transfer and concentration of substance during start up
time which affects microorganism growth. Therefore it
is obvious that accommodation of experimental data
with the complicated models and determination of their
parameters is a dif cult process. Due to the fact that
mathematical models are complex and it is too hard to
solve them with analytical methods, researchers prefer
to solve them by advanced regulated and numerical
methods. As a matter of fact, application of numerical
method is a procedure to solve occurred problems during
the process of experimental data.
Mathematical models such as the Monod kinetic
model, rst-order substrate removal model, Grau sec-
ond-order model, and Stover-Kincannon model have
been used to design speci c unit operations, optimize
and control treatment processes, understand the under-
lying biotechnology, and transport mechanisms within
the reactor (Fu et al. 2013). Monod model is based on the
results of batch reactor system for pure culture which fed
by simple nutrient. While the Monod model has some
success in describing steady state growth rates, it has
been found to be inadequate to predict where the ini-
tial data does not correspond to the globally attracting
steady state (Meng et al. 2010). Effect of concentration
of contaminant in in uent of a reactor on concentra-
tion of that contaminant in output of reactor, variation
of semi saturation constant (K
s
) and effect of inhibi-
tive substance in medium are reported de ciencies of
this model (Orhon & Tunay 1979). Constant logarith-
mic growth rate is basic thesis of this model whereas
this concept is a challenging subject. Researchers have
proved that there is not a speci c constant growth rate
BIOSCIENCE BIOTECHNOLOGY RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS TREATMENT OF OIL-WATER EMULSION 627
Alireza Nazari Alavi et al.
for mixed bulk of bacteria (Grady & Williams 1975).
There is a straight relation between constant growth rate
and initial concentration of contaminant. If the concen-
tration of contaminant increases, the constant of growth
rate will decrease. It means contaminant with high con-
centration operates as an inhibitor.
Variation trend of X/X
0
to S/S
0
should be increasing
otherwise it is probable that there is an inhibitor fac-
tor in the environment which affects on the microor-
ganism’s growth and activity. Research have presented
that aforementioned trend inclines to an asymptote, it
reveals that there is a factor that affect the live biomass
production. Goal of this study is to investigate biologi-
cal treatment of liquid phase of oil-water emulsion in a
batch reactor and to presents a model which consists of
effective factors by numerical methods
MATERIAL AND METHODS
EXPERIMENTAL SETUP
Cutting oil from a local supplier was used in this study.
Oil-water emulsions were made arti cially in this labora-
tory and then it was broken by adding Calcium Chloride
to separate two phases and obtain the aqueous phase.
Sewage (oil-water) consists of 2% oil and 98% water. To
ful ll this task, 1 g of CaCl
2
was added to emulsion for
each percent of oil and after complete mixing it was left
for one day in decanter ampoule to separate the aque-
ous phase.
Gradual increasing of oily water concentration was
used to study compatibility of activated sludge with sew-
age. For this purpose 3 lit sludge (MLSS=1.8g/l) mixed
with 3 lit sewage (30% oily water plus 70% water) and
aerated for one day. After aeration period and 2 hours
for settlement, 3 lit of reactor replaced by sewage with
40% oily water. This process continued up to reaching
sewage with 100% oily water. This compatible and aer-
ated sludge was used in experiments. Schematic drawing
of experimental set up is shown in Figure 1.
All experiments were performed in ambient tempera-
ture at about 21˚C. The pH for aqueous phase was neu-
tral and almost constant (6.9-7) therefore, it didn’t need
further adjustment. Dissolved oxygen during the experi-
ment was measured between 6.5-7.2mg/l. Required
parameters such as COD, nutrient (nitrogen & phosphor)
and suspended solid were measured according to the
Standard Methods and were controlled before each test
(APHA 1999). During the experiment, ratios of initial
substrate concentration to initial biomass concentration
were 0.9, 1.3, 2.2, 5.86, 10 and samplings were done by
an ampoule at the one third heights from the surface.
NEWTON’S METHOD TO SOLVE EQUATION
Newton iterative numerical method is used to determine
parameters of presented model. In Newton method, for
a continues and differentiable function on the interval
(a,b), function f is approximated by its tangent line in an
arbitrary initial value x0, initial guess could be reason-
ably close to the true root to better convergence.
By computing x-interception of tangent line, a better
approximation to the function’s root obtained in each
step and iteration can be continued to reaching a rea-
sonable approximation of root as X
n+1
:
(1)
DEVELOPING MONOD MODEL
Explanation of some basic concept is necessary before
presentation of the model which based on the obtained
experimental data. The most current available model is
the Monod model which stated in equations 2 and 3
(Tchobanoglous & Burton 1991):
(2)
(3)
µ: speci c growth rate (time inverse)
µ
max
: maximum speci c growth rate (time inverse)
FIGURE 1. Experimental setup.

628 TREATMENT OF OIL-WATER EMULSION BIOSCIENCE BIOTECHNOLOGY RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS
Alireza Nazari Alavi et al.
K
s
: semi saturation constant (mg/l )
X: biomass concentration (mg/l )
S: substrate concentration (mg/l )
Concentration of biomass in reactor is usually meas-
ured by MLSS. This parameter comprises all live, just
active, microorganisms and remained cells; therefore it
is not a representative parameter for reactions (Weddle
& Jenkins 1971). Thus researchers tried to give a more
precise de nition of existence biomass as follows:
(4)
Where X
v
is biomass concentration which can repro-
duce, X
nv
is just active biomass (organic oxidation),
X
d
is dead or inactive biomass and P is remained cells
and biopolymers. X
v
and X
d
can be realized by painting
method (Jones 1987). Measurement of X
nv
is so dif cult
and its quantity is not considerable and usually consid-
ered negligible or may be merged by X
d
. If P in compari-
son with X
v
+X
d
is small, live biomass growth rate can
be de ned as:
(5)
Biomass variation rate in a reactor depends on the repro-
duction rate (r
xv
) and death rate (r
xd
) as follow:
(6)
From a practical point of view, determination of biomass
growth rate is very dif cult; therefore a relationship is
described between MLSS and live biomass. For this pur-
pose primary live biomass rate is de ned as:
(7)
According to classic law of cell reproduction, real rate
of live biomass growth can be considered zero-order to
substrate and rst-order to X
v
:
(8)
On the other point of view, velocity of losing produc-
tion power depends on cell concentration and inhibitor
substance as follow:
(9)
Where is kinetic coef cient of missing reproducibil-
ity and I is concentration of produced inhibitor sub-
stances which are produced by microbial production as
follow:
(10)
Therefore equation 6 is rewritten as follow:
(11)
At the steady state and live biomass concentration
(X
v
) is the maximum, therefore:
(12)
By replacing in equation 11, live biomass growth rate
can be written as:
(13)
This equation has been used by most of researchers
for evaluation of biomass consensus rate (Tulear &
Eharaclis 1982, Vavilin & Vsiliev 1983).
By de ning
max maxvo
XXX
and
vo
XXX
, equa-
tion 13 is rewritten as:
(14)
By integration from equation 14, real concentration of
biomass during the time is obtained as:
(15)
By using this equation and experimental results,
parameters
v
and K
1
can be calculated by adjusting
numerical methods and veri ed by substrate removal
rate model. To achieve this goal, mathematical equa-
tion for substrate removal model should be determined.
Conversion rate (Y
obs
) is de ned by observed substrate
removal rate and biomass growth rate as follows (sub-
strate removal rate usually is measured by COD or BOD).
(16)
(17)
Y
obs
remains constant during the experiments and is
equal to:
(18)
By replacing in equation 14 and integration, function of
substrate removal during the time can be determined as:
(19)
BIOSCIENCE BIOTECHNOLOGY RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS TREATMENT OF OIL-WATER EMULSION 629
Alireza Nazari Alavi et al.
Where is the indicator of primary amount of
substrate which can produce primary live biomass (X
vo
)
by digestion. Applying Newton method as a numerical
method to equation 15 and 19 facilitates nding kinetic
parameters of reaction such as biomass growth rate and
substrate removal rate.
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
EXPERIMENTAL RESULTS
As it was stated before, ratios of during experiments
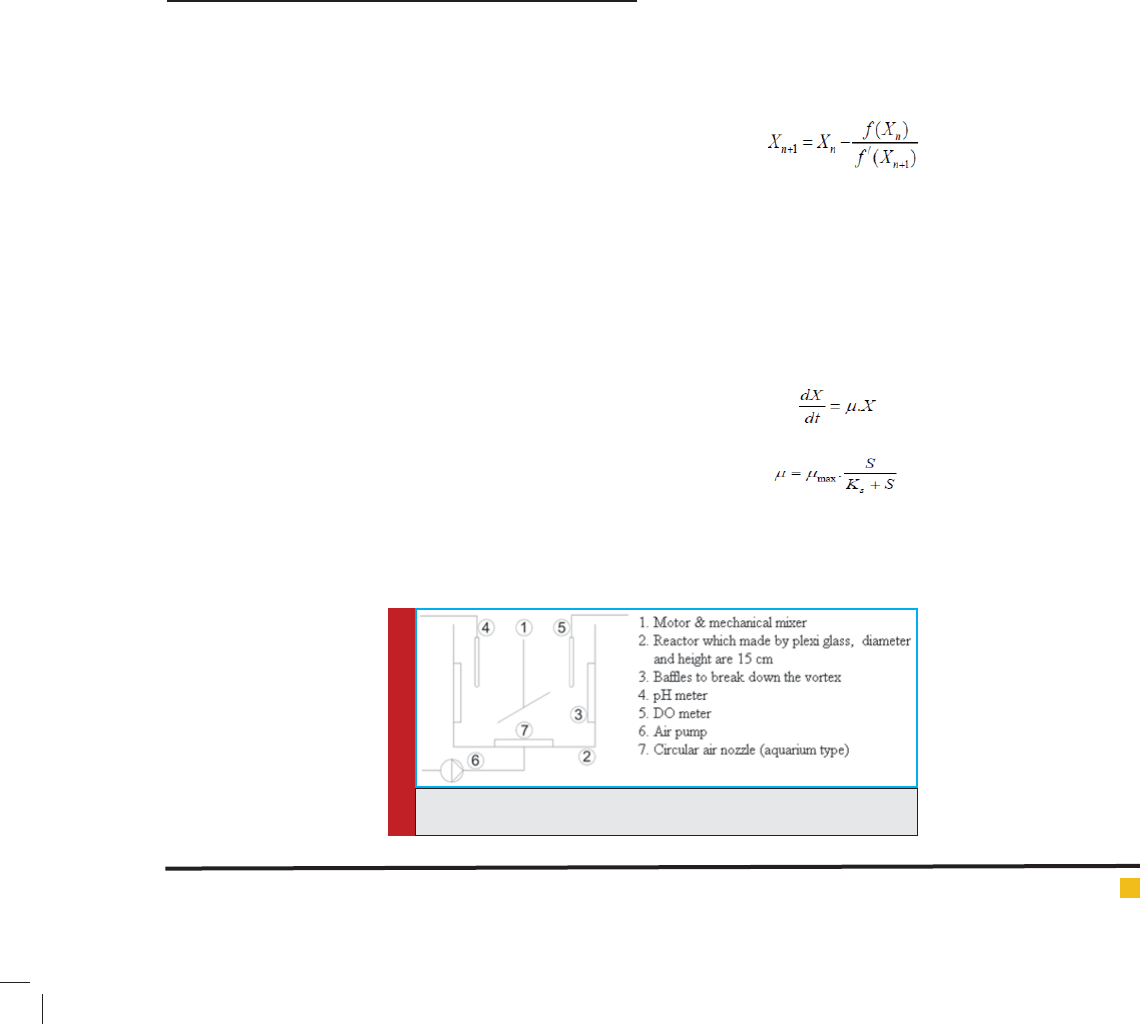
were 0.9, 1.3, 2.2, 5.86 and 10. For instance, variation of
biomass concentration (MLSS) and substrate concentra-
tion (COD) versus time for =1.3 which are the basis of
kinetic modeling of reaction are shown in Figure 2.
VERIFYING MONOD MODEL WITH
EXPERIMENTAL RESULTS
Conversion rate of substrate to biomass usually is used
to solve differential equation of Monod equation accord-
ing to variable X. This equation is simpli ed as follow in
exponential growth phase:
(20)
If is determined, calculating the biomass concentration
during the time by equation 21 will be possible
can be
determined as gradient of following equation:
(21)
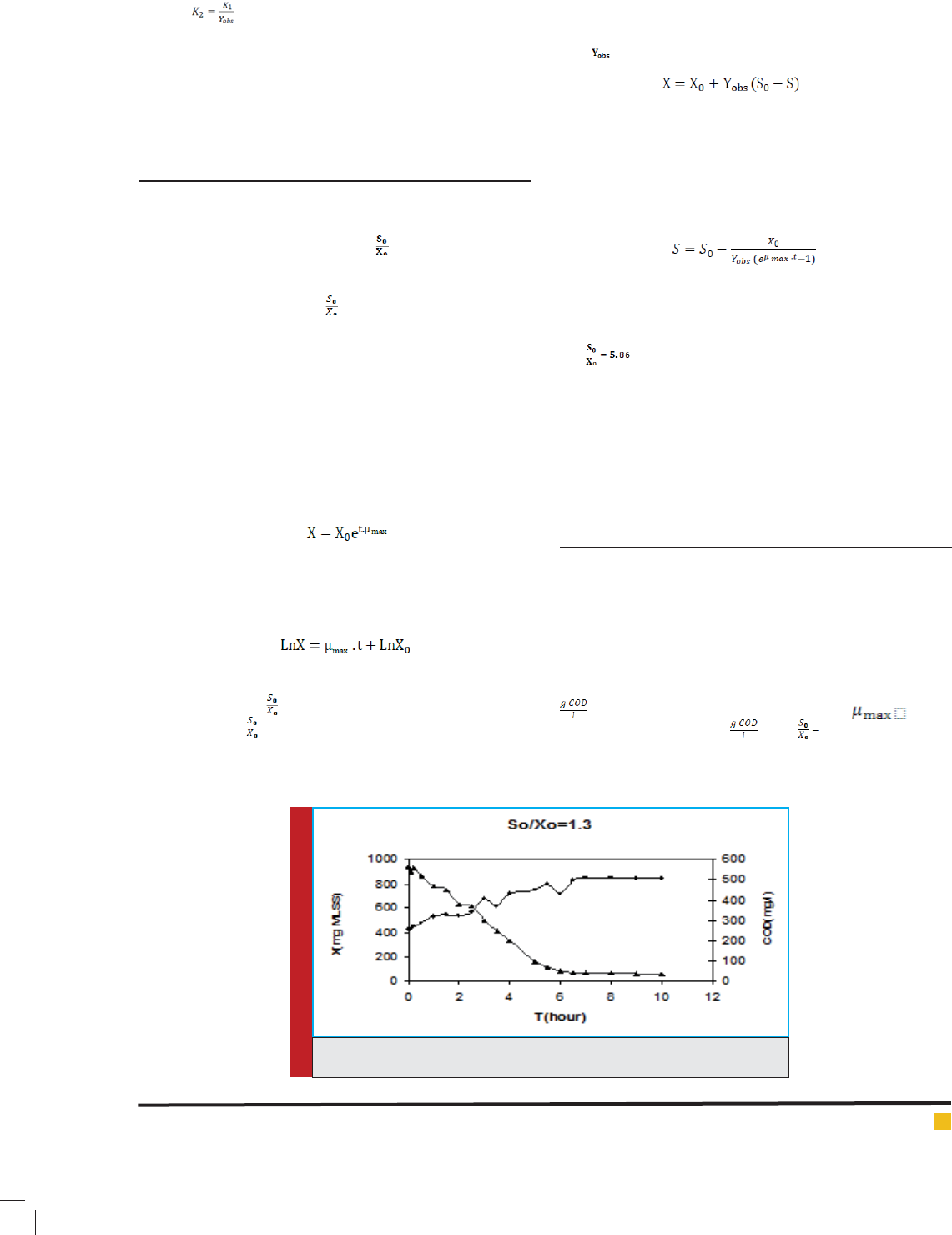
Figure 3 shows aforementioned function in exponential
growth phase for
= 5.86 and Table 1 lists µ
max
for dif-
ferent value of .
Calculation was based on presumption that conver-
sion rate of substrate to biomass (Y
obs
) during the experi-
ment is constant, con rming this presumption is neces-
sary. Y
obs
can be calculated from equation 22. Table 1
lists for different value of
Parameters of model must be veri ed, so parameters
resulted from experiments must be usable in model for
calculating other variables in order to accept the model.
Equation 23 is used in exponential growth phase in
Monod model for forecasting substrate concentration
during the time.
Comparison between calculated and measured substrate
during the time is necessary for veri cation of model
and experimental results. This comparison presented
for = 5.86 in Table 2. Differences in exponential
growth phase are about 5.8%.
Certainty of Monod model is under discussion from
the past as it was stated in introduction. Main idea of
Monod model is based on that exponential speci c
growth rate (µ) remains constant. In the present experi-
ments µ
can be considered near constant.
DISCUSSION ABOUT THE PRESENTED MODEL
Analysis of biomass growth rate according to pre-
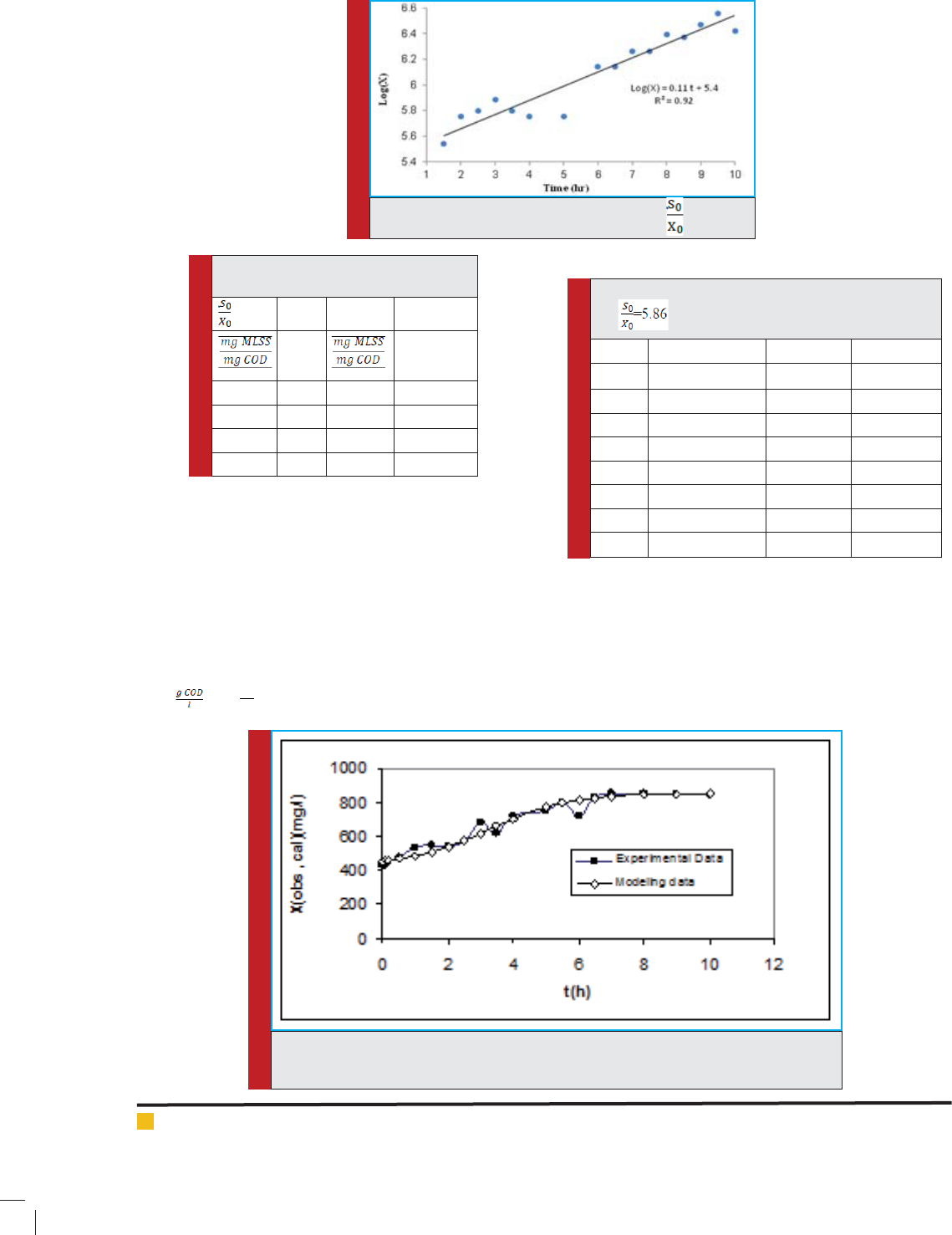
sented model should be discussed. Figure 4 illustrates
both experimental data and results which derived from
numerical analysis of presented model.
As it is shown, the presented model is well compatible
with experimental data. Numerical analysis outcome is
optimum value for kinetic parameters namely K
1
=27
and h
-1
. Sanchez (2007) determined equal
to 0.01 h
-1
and K
S
= 16 for =1 for an ef uent
derived from the anaerobic digestion of two-phase olive
mill solid residue (Sanchez et al. 2007). Bajaj (2009)
FIGURE 2. Biomass and substrate variation during time for .
(22)
(23)
Alireza Nazari Alavi et al.
630 TREATMENT OF OIL-WATER EMULSION BIOSCIENCE BIOTECHNOLOGY RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS
FIGURE 3. Biomass variation versus time for = 5.86.
Table 1: Y
obs
and removal ef ciency
for different values of S
0
/X
0
.
μ
max
Y
obs
Difference
hr
-1
%
0.9 0.099 0.61 90
2.2 0.12 0.83 83
5.86 0.11 0.39 85
10 0.14 0.41 90
Table 2: Calculated and measured S during the time
for
Time S (Experiment) S (model) Difference
Hr mg/lit mg/lit %
2 1256 1304 4
4 1067 1224 13
5 956 1080 11
6 832 968 14
7 694 732 5
8 539 580 7
10 174 320 46
FIGURE 4. Comparison between experimental data and results from presented model for
biomass growth.
determined
max
=0.3095 h
-1
for biodegradation of phenol
with a mixed bacterial consortium in batch conditions
(Bajaj et al. 2009).
If the parameters of biomass growth rate which derived
from presented model are correct, they should be veri ed
in the substrate removal modeling. Therefore according
to equation 18, Y
obs
(tangent of function S=f(X)) should
remain constant; Figure 5 shows this function.
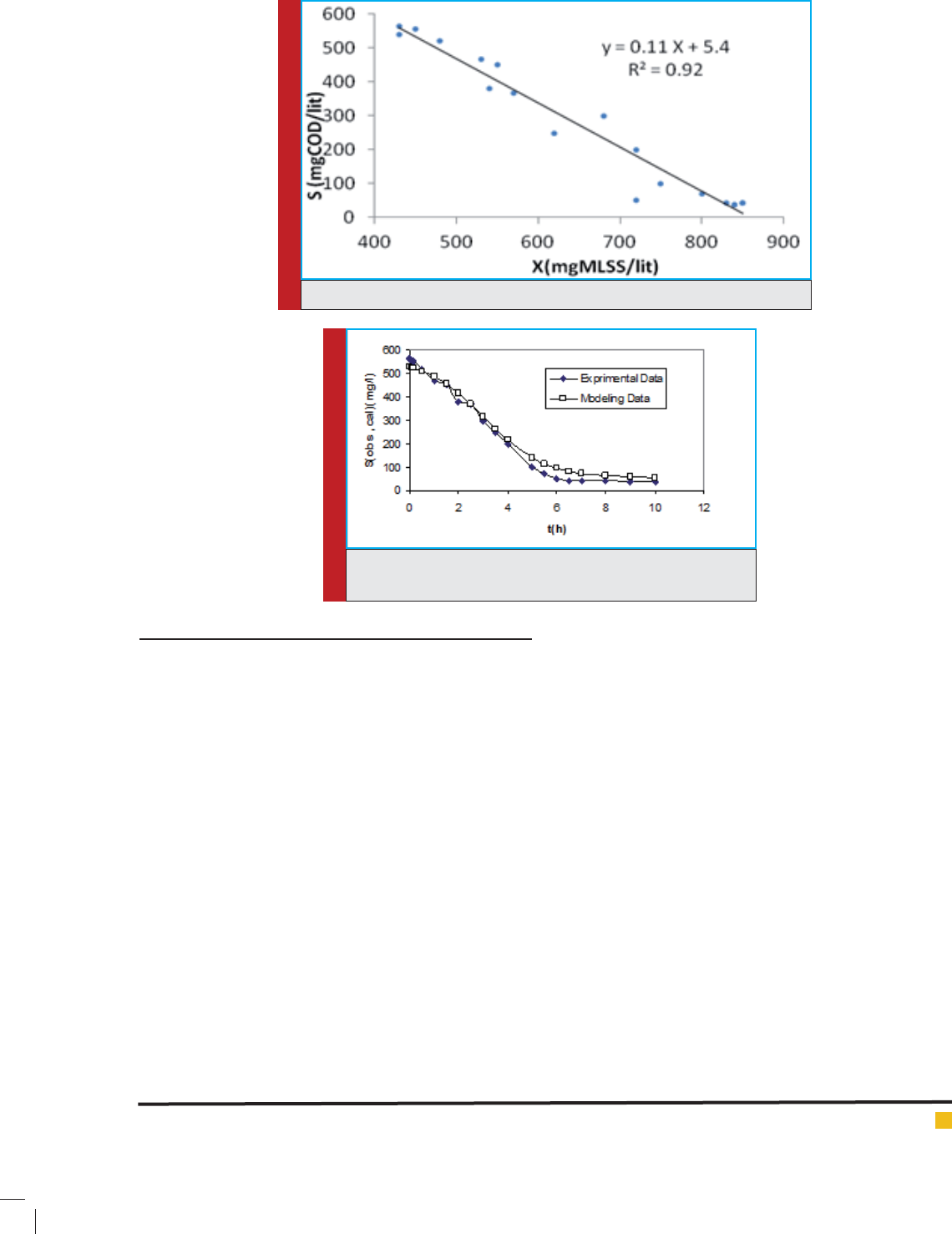
As it is indicated above, Y
obs
is equal to 0.728 and as it
is supposed to be constant, K
2
can be calculated as equal
to 37
for
o
o
X
S
1.3.
Afterward, substrate removal can be calculated by
equation 22 during the time and can be compared with
experimental data.
As it is indicated in Figure 6, experimental results are
in accordance with calculated parameters for substrate
concentration. It follows that model and is completely
veri ed with experimental results.
Alireza Nazari Alavi et al.
BIOSCIENCE BIOTECHNOLOGY RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS TREATMENT OF OIL-WATER EMULSION 631
CONCLUSION
The research shows that aqueous phase of oil-water
emulsion has a suitable capability of biological treat-
ment. Kinetic parameters of biological treatment, which
are the basis of modeling, are determined. These param-
eters can be utilized to increase the ef ciency of design-
ing units of treatment plants of O/W emulsions. Compat-
ibility of the process with the Monod model shows that
this model is an acceptable descriptor for O/W emul-
sion and can be used in designing process.In the future
studies about biological treatment of aqueous phase of
oil-water emulsion, to increase the accuracy and com-
patibility of the model, kinetic of live biomass which are
able to reproduce should be considered with real growth
rate of . Also it should be noticed that dead biomass acts
as an inhibiting factor.
REFERENCES
Abdel-Aziz, M. H., El-Ashtoukhy, E. S., Zoromba, M. Sh. and
M. Bassyouni (2016). Oil-in-water Emulsion Breaking by Elec-
trocoagulation in a Modi ed Electrochemical Cell. Interna-
tional Journal of Electrochemical Science, 11, pp. 9634-9643
Ahmadi-Dastgerdi, A., Nasirpour, A., Rahimi, E. (2015). Phys-
ical and Rheological Properties of Oil in Water Heat Stable
Emulsions Made from Different Stabilizers. Journal of Food
Biosciences and Technology,5(1), pp. 45-62
APHA (1999). Standard Methods for the examination of water
and wastewater. 20th Edn.
Arif n, Tajnor S. T., Yahya, Effah and Husin, Hazlina (2016).
The Rheology of Light Crude Oil and Water-In-Oil-Emulsion.
Procedia Engineering, 148, pp. 1149-1155
Bajaj, M., Gallert, C and Winter, J.(2009). Phenol degrada-
tion kinetics of an aerobic mixed culture. Bioch. Eng. J.2(46),
pp. 205-209
Bensadok, K., Belkacem, M. & Nezzal, G. (2007). Treat-
ment of cutting oil/water emulsion by coupling coagulation
and dissolved air otation. Desalination, 206(1), pp. 440-
448
Berton-Carabin, Claire C. C., Ropers, Marie Helene & Genot,
Claude (2014). Lipid Oxidation in Oil-in-Water Emulsions:
Involvement of the Interfacial Layer. Comprehensive Reviews
in Food Science and Food Safety 13, pp. 945-977
Chudoba, P., Capdeville B. and Chudoba J. (1992).Explanation
of biological meaning of the S0/X0 ratio in batch cultivation.
Wat. Sci. and Tech., 26(3-4), pp. 743-751
FIGURE 5. Substrate concentration versus biomass growth for S
0
/X
0
= 5.86.
FIGURE 6. Comparison between experimental data and results
from presented model for substrate removal.

Alireza Nazari Alavi et al.
632 TREATMENT OF OIL-WATER EMULSION BIOSCIENCE BIOTECHNOLOGY RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS
Deepak, D., Anand, V. and Bhargava, R. (1994). Biodegradation
kinetics of metal cutting oil: evaluation of kinetic parameters.
The Chem. Eng. J.,56, pp. 91-96
Fu, X., Zhenxing, H. and Hengfeng, M. (2013) Identical full-
scale biogas-lift reactors (BLRs) with anaerobic granular
sludge and residual activated sludge for brewery wastewater
treatment and kinetic modeling, J. of Env. Sci. 25(10), pp.
2031-2040
Grady, P. and Williams, D. (1975) Effects of in uent substrate
concentration on the kinetics of naturel microbial population
in continuous culture, Wat. Res., 9 (2), pp. 171-180
Hadj, Z., Amel, Z. and Moulay, S. (2004). Microemulsion
breakdown using the pervaporation technique:application to
cutting oil models, Desalination, 170(1), pp. 91-97.
Hesampour, M., Krzyzaniak, A. and Marianne, N. (2008). The
in uence of different factors on the stability and ultra ltration of
emulsi ed oil in water, J. of Membrane Sci., 325(1), pp. 199–208
Irvine, L., Ketchum, H., Breyfogle, R. and Barth, F. (1983).
Municipal application of sequencing batch treatment, J. of
WPCF. 55(5), pp. 484-493
Jamrah, A. and
Abu-Ghunmi, L. (2005). One independent
variable rate equation describing utilization of biodegradable
organic matter in activated sludge processes. Env. Mod. and
Ass., 10, pp. 21–31.
Jones, P. (1987). Measures of Yeast Death and Deactivation
and Theire Meaning , Pro. Bioch.22(4), pp. 118-128
Kalliola, Simo, Repo, Eveliina, Sillanpää, Mika, Arora Jaspreet
Singh, He, Jibao & John T. Vijay (2016). The stability of green
nanoparticles in increased pH and salinity forapplications in
oil spill-treatment. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical
and Engineering Aspects, 493, pp. 99-107.
Kappeler, J. and Gujer, W. (2005). Estimation of kinetic
parameters of heterotrophic biomass under aerobic condition
and characterization of wastewater for activated sludge mod-
elling. Wat. Sci. and Tech., 25(6), pp. 125-139
Kobya, M., Ciftci, C., Bayramoglu, M. and Sensoy, T. (2008)
Study on the treatment of waste metal cutting uids using
electrocoagulation, Sepa. and Pur. Tech., 60(3), pp. 285–291
Kristensen, H., Jourgensen, E. & Henze, M. (1992). Charac-
terization of functional microorganism groups and substrate in
activated sludge and wastewater by AUR, NUR and OUR. Wat.
Sci. and Tech,. 25(6), pp. 43-57(1992).
Krstic, M., Ho inger, W., Koris, K. and Vatai, G. N. (2007).
Energy-saving potential of cross- ow ultra ltration with
inserted static mixer: Application to an oil-in-water emulsion,
Sepa. and Pur. Tech., 57(1), pp. 134–139
Mantzavinos, D. and Kalogerakis, N. (2005).Treatment of olive
mill ef uents: Part I. Organic matter degradation by chemical
and biological processes, An overview. Env. Int., 2 (31), pp.
289- 295
Meng, X.,
Gao, Q. and Li, Z. (2010). The effects of delayed
growth response on the dynamic behaviors of the Monod type
chemostat modelwith impulsive input nutrient concentration,
Nonlinear Analysis: Real World App., 11(5), pp. 4476-4486
Munch, E. and Pollard, C. (1997).Measuring bacterial biomass-
COD in wastewater containing particular matter.
Wat. Res., 10( 31), pp. 2252-2256
Orhon, D. andTunay, O. (1979). Mathematical models of bio-
logical waste treatment processes for the design of aeration
tanks discussion. Wat. Res., 13(6), pp. 127-135
Portela, J. R., Lopez, J., Nebot, E. & Maertinez, O. (2001). Elimi-
nation of cutting oil wastes by promoted hydrothermal
oxidation, J.of Hazardous Mat., 88(1), pp. 95–106
Rella, R., Sturaro, A., Parvoli, G., Ferrara, D. and Doretti, L.
(2003). An unusual and persistent contamination of drinking
water by cutting oil, Wat. Res., 37(3), pp. 656–660
Rios, G., Pazos, C. and Coca, J. (1998). Destabilizationof cut-
ting oil emulsions using inorganic salts as coagulants, Colloids
and Surfaces, A: Physicochemical and Eng. Aspects.Colloids
and Surface 138(2-3), pp. 383–389
Sanchez, E.
, Rincón, B., Borja, R., Travieso, L. and Raposo,
F.
(2007).Aerobic degradation kinetic of the ef uent derived
from the anaerobic digestion of two-phase olive mill solid resi-
due, Int. Biodet. and Biodeg. 60(1), pp. 60-67
Sanchez, E., Rincón, B., Borja, R., Travieso, L. and Raposo, F.
(2007). Hydrothermal oxidation: Application to the treatment
of different cutting uid wastes, J. of Hazardous Mat., 144(3)
pp. 639-644
Servais, P., Gilles, G. and Hascoët, M. (1987).Determination of
biodegradable fraction of dissolved organic matter in waters,
Wat. Res. 21(4), pp. 445-450
Souza, R. S., Porto, P. S., Pintor, A. M., Ruphuy, G., Costa, M.,
Boaventura, R. A. and Vilar, V. J. (2016). New insights on the
removal of mineral oil from oil-in-water emulsions using cork
by-products: Effect of salt and surfactants content, Chemical
Engineering Journal, 285, pp.709–717
Spanjers, H. and Vanrolleghem, P. (1995). Respirometry as a
tool for rapid characterizaton of wastewater and activated
sludge, Wat Sci. and Tech., 31(2), pp. 105-114
Srinivasan, A. and Viraraghavan, T. (2010).Oil removal from
water using biomaterials, Bioresource Tech., 101(17),pp. 6594–
6600
Tchobanoglous, G. and Burton, Franklin L.
(1991). Wastewater
Engineering Treatment, Disposal and Reuse, McGraw-Hill Inc.,
4th Edn.
Tulear, M. and Eharaclis, W. (1982).Dynamics of Bio lm Pro-
cesses, Journal of Water Pollution Control Federation, 9(54),
pp. 1288-300
Vavilin, V. and Vsiliev V. (1983). Dependance of biological
treatment rate an species composition in activated sluge or
bio lm, Biotech. Bioeng.25(6), pp. 1521-1538
Weddle, C. and Jenkins, D. (1971).The viability activity of acti-
vated sluge, Wat. Res. 5, pp. 621-628
Wentzel, C., Mbewe, A., Lakay, T. and Ekama, G.A. (1995).Batch
test for measurement of readily biodegradable COD and active
organism concentration in municipal watewater, Water S.A,
21(2), pp. 117-124